Published by: Parazitolog in Helminths March 12, 2021
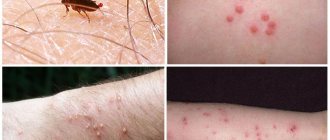
Photo of worms in the human body. People and animals are attacked by these creatures; the infection is easily transmitted to each other through contaminated food, water and dirty hands. Prevention rules and careful personal hygiene will help prevent the appearance of parasites in the body, but even these measures do not guarantee one hundred percent protection. Helminths that inhabit the human body can live in various organs and differ in appearance, size, and the degree of harm caused to humans.
- 1 Parasites in the human body
- 2 How parasites enter the human body
- 3 In which human organs can parasites live?
- 4 Pinworms - what they look like in the human body (Photo of worms)
- 5 Roundworms - what they look like in the human body (Photo of worms)
- 6 Whipworms - what they look like in the human body
- 7 Liver fluke - what it looks like in the human body
- 8 Trichinella - what it looks like in the human body (Photo of worms)
- 9 Wide tapeworm - what it looks like in the human body
- 10 Echinococcus - what it looks like in the human body
- 11 Alveococcus - what it looks like in the human body
- 12 Schistosoma - what it looks like in the human body (Photo of worms)
- 13 Pork tapeworm - what it looks like in the human body (Photo of worms)
- 14 Which doctor to contact if infected with worms
Parasites in the human body
How many situations are there when a person goes to doctors for years and cannot get rid of allergies, treats asthma, takes glucose-lowering drugs and all to no avail? Each of us has such acquaintances who have spent huge sums on the treatment of a variety of diseases, and have not received any results.
Only in rare cases, when the doctor turns out to be either very smart or very responsible, does he refer such a patient for a routine stool analysis and then... Then parasites are discovered in the human body, which are the cause of dozens of diseases, and with which no one can treat these pathologies doesn't fight.
Photo of worms. Contrary to popular belief, worms are not necessarily “prescribed” in the intestines and can be detected by a simple stool test. Many parasites thrive in the lungs, heart, muscles, even in the brain and eyes.
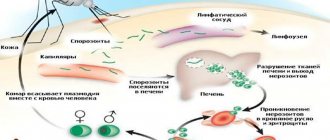
The well-known malaria, which was once defeated on the territory of the USSR, has returned again and this is the most dangerous parasitic disease, according to WHO experts. Malarial plasmodium lives exclusively in the blood and not every doctor will be able to recognize this disease with sufficient confidence.
Earthworm coming out
To lean out of the hole and throw out excrement, the worm extends its tail forward, and if the worm needs to collect leaves, it sticks its head out of the ground. That is, in burrows, earthworms can turn over.
Earthworms do not always throw out soil near the surface; if they find a cavity, for example, in plowed soil or near the roots of trees, then they throw out excrement into this cavity. There are small clumps of earthworm excrement between many rocks and under fallen tree trunks. Sometimes worms fill their old holes with excrement.
How parasites enter the human body
They enter the human body in different ways, most often through the consumption of contaminated water and food.
Pinworm eggs remain viable for up to 6 months and enter the body through toys, carpets, underwear and bedding. Ascaris eggs get inside us through poorly washed vegetables and fruits. Shish kebab or homemade lard is a 95% guarantee of infection with trichinosis.
Parasites penetrate inside us through insect bites, when swimming in freshwater bodies, through the air, and through dust, which carries eggs.
Salted fish, stroganina or caviar are the cause of infection with a tapeworm, the length of which reaches 12 meters and which can live in your body for up to 25 years. Cases of infants becoming infected with parasites in the womb have become more frequent. Dogs and cats, through their moist breath, can disperse parasite eggs at a distance of up to 5 meters.
You can become infected through dirty hands, not only your own, but also sellers, cooks, waiters; parasite eggs travel on money and handrails of public transport. A high concentration of parasite eggs is observed in products such as: bacon, smoked sausage, ham, sausages, pork of any form, beef, chicken, lamb, and even chicken eggs are very often contaminated with them.
Epidemiologists around the world are trying to fight this scourge. In the USA, for example, 1 pig carcass out of every thousand is destroyed to test for helminthiasis. This adds up to multimillion-dollar losses, but there is no other way.
There are no absolutely reliable methods for disinfecting meat, and ordinary cooking does not destroy the larvae. You cannot guarantee the purity of your food by boiling or frying meat; a huge number of parasite larvae still penetrate your body.
Life
Black worms have quite a long history. They played a significant role in soil formation. It is worth noting that it is thanks to these invertebrates that we see the earth as it is today. Worms constantly carry out digging activities, as a result of which the layer of earth is always in motion. Invertebrates have a very good appetite. In just one day, they can eat a volume of food comparable to their weight, in other words, 3-5 grams of food.
As a result of their own activity, black worms promote maximum plant growth, without taking into account the fertilizer they produce. Invertebrates loosen the soil, allowing water and oxygen to enter it much better. Plant roots develop much faster in their burrows.
It should be noted that the result of constant loosening of the soil is that large objects constantly sink deep into the ground. Small particles of foreign origin are gradually ground by the stomachs of invertebrates and turn into sand.
Unfortunately, the number of black worms in our country is decreasing every year. This situation is facilitated by the irrational use of chemicals to fertilize the soil. Currently, eleven varieties of such worms are already listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation. It’s logical: why buy chemicals for fertilizer when there is such a natural miracle as vermicompost?
In which human organs can parasites live?
Photo of worms. Helminthic parasites are divided into two categories, which correspond to the location of activity in the donor’s body:
- cavitary : worms that live in various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. There are about 100 species of intestinal parasites, and for every part of the intestine there are a couple of dozen species. The small intestine is ready to accept roundworms, antelostomas, broad tapeworms and other less common “brethren”. The small intestine will “share living space” with pinworms, dwarf tapeworms and others. The medical literature describes cases where one person was infected simultaneously with several types of parasites;
- tissue: worms localized in organs, tissues and even in the blood. Modern medicine successfully copes with paragonimiasis (lungs), cysticercosis (brain), echinococcosis (liver) and filariasis (lymphatic vessels). Some worm larvae move throughout the body through the circulatory system and randomly attach to any organ. If many eggs are introduced, the entire body can be infected.
Find out more: Ascariasis in children - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Clavelina Lepadiformis
People often call it the “Sea Spray Light Bulb”. Such beauty can be seen off the coast of Norway, Great Britain and Ireland. Occasionally, colonies of Clavelina Lepadiformis are found in the Mediterranean Sea.
These creatures attract attention thanks to their transparent mantle. In the water it gives off a slight glow, making these sea creatures even more spectacular.
Pinworms - what they look like in the human body (Photo of worms)
Pinworms are one of the most common human parasites, which are a roundworm (nematode). Most often, pinworm infection occurs in children, but it also occurs in adults.
The pinworm is a white parasite, small in size and round in shape. Female specimens measure 8-13 mm in length, 0.5 mm in thickness, oblong in shape and have a straight tail, pointed at the end.
This feature of the tail of the female parasite explains its name - “pinworm”, from the word “sharp”. The male pinworm is much smaller: its length is 2-5 mm, its thickness is 0.2 mm, its tail is curved, unlike the female pinworm.
Photo of worms. Infestation of humans with pinworms is called enterobiasis, and occurs mainly due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules (insufficient hand washing). Pinworms primarily live in the small intestine and upper part of the large intestine, but in some cases they can also migrate to other organs and organ systems.
The female helminth, having entered the human body orally and mated with the male representative of the nematode, migrates to the large intestine, where she receives the necessary nutrients for life and the maturation of eggs from undigested food debris.
After 4 weeks, the female pinworm begins migrating into the rectum at a speed of 12 cm per hour, crawls out of the anus and lays about 5,000-15,000 eggs in the perianal area, which after 4-6 hours are fully mature and ready for the further life cycle.
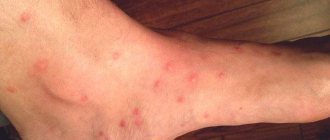
This process may be accompanied by itching, which prompts the infected person to scratch the anus, and thus contribute to the further spread of parasites that fall from under the nails into food onto the hands of other people (especially for children who are in very close contact with each other and not always observing the rules of personal hygiene).
Pinworm infection occurs from person to person, through dust with parasite eggs, or objects touched by the patient. Pinworm eggs can also be transferred to food by cockroaches and flies.
Eggs also remain on linens, clothes, and beds, which explains their rapid spread. Due to the fact that the life cycle of the worm is very fleeting, and infection occurs from person to person, it is quite difficult to get rid of parasites, since in addition to taking anthelmintic drugs, it is necessary to treat the patient’s personal belongings and isolate him from other carriers of the nematode.
Excretory system
The structure of an earthworm in longitudinal and transverse sections. Paired tubules of the excretory system are visible
The excretory system of an earthworm consists of paired tubes in each body segment (with the exception of the terminal ones) (Fig. 53).
At the end of each tube there is a funnel that opens as a whole, through which the final waste products (represented mainly by ammonia) are discharged out.
Roundworms - what they look like in the human body (Photo of worms)
Ascaris is a large, spindle-shaped, red-yellow parasite, reaching 40 cm (females) and 15-25 cm (males) in adulthood. Without suction cups or other fastening devices, the roundworm is able to move independently towards food masses. The eggs laid by the female parasite are excreted in the feces.
Infection with ascariasis occurs when mature eggs are ingested along with water or unwashed vegetables and fruits that have soil particles on them. After the eggs penetrate the intestines, mature larvae emerge from them.
Then, penetrating into the intestinal wall, they reach the heart through the bloodstream, and from there they enter the lungs. Through the pulmonary alveoli, the roundworm larva again enters the oral cavity through the respiratory tract.
Photo of worms. In the intestinal phase of their existence, roundworms, endowed with the ability to spiral movements, can penetrate even the narrowest openings. This feature of the parasite often leads to the development of quite serious complications (obstructive jaundice or pancreatitis)
Once ingested again, the parasite reaches the small intestine where it develops into an adult. The worm lives for 12 months, then dies and is excreted in the feces. One or several hundred individuals can live in the intestines of one host.
Find out more: Tapeworms - symptoms and treatments in humans
Allergens released by roundworms can provoke severe allergic reactions. A large number of adults can cause intestinal obstruction, and worms that enter the respiratory tract sometimes cause suffocation.
Spirobranchus Giganteus
Yes, yes, you didn’t think so - Spirobranchus Giganteus is not a plant, but a living creature. It is often called the “Christmas Tree Worm” - and, admittedly, it really looks like a forest beauty.
They live in almost all tropical seas of the World Ocean. It is very common to see people using these worms to decorate their aquariums. Spirobranchus Giganteus look stunning thanks to their colorful tentacles.
Whipworms - what they look like in the human body
This type of parasite is quite rare in central Russia. Whipworms often live in the southern regions, since the eggs of this worm love warmth. Most infections are observed in rural areas. Whipworm eggs live in the soil.
Infestation occurs through hands, contaminated soil particles, and poorly washed vegetables and fruits. As a result of infection, a disease occurs - trichocephalosis. Whipworm parasitizes the intestines. This worm causes anemia, as it feeds on human blood, and severe abdominal pain.
To diagnose trichuriasis, the rectum and sigmoid colon are examined with a special device (sigmoidoscopy). In this way, accumulations of parasites in the intestines are detected. Treatment of the infestation takes a long time, since the whipworm eggs are protected by a dense shell.
The eggs of the parasite are excreted in the feces, but they are very small and cannot always be seen even under a microscope. Only with very severe infestation is it possible to detect eggs in a stool test. They are shaped like a barrel and have a brownish-yellow color.
There are holes on both sides of the egg. What do worms look like in feces? They are very difficult to detect alive in feces, since whipworms cannot live long outside the human body. Only with anthelmintic therapy can you notice dead white worms in the feces.
Pseudoceros liparus
In the coral reefs of the Pacific and Indian oceans you can find incredibly beautiful worms of lavender, sky blue or purple colors. Pseudoceros liparus cannot cause any harm to humans; they are completely harmless worms. They grow up to six centimeters and look like alien creatures. It's hard to believe that nature can create such unusual beauties.
Liver fluke - what it looks like in the human body
The parasite that causes opisthorchiasis is a flatworm that reaches a length of 7-20 mm. It should be noted that more than 50% of cases of infection with liver fluke (also called cat fluke) occur among residents of Russia.
In the acute phase of helminthiasis, the patient experiences pain in the upper abdomen, body temperature rises, nausea, muscle pain develops, possible diarrhea, skin rashes. The larvae of the parasite begin to develop after the eggs enter fresh water (from the snails that swallowed them). Then they penetrate the body of the fish (carp, crucian carp, bream, roach).
Photo of worms. Human infection occurs by eating contaminated fish meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment. The larva of the liver fluke from the small intestine penetrates the bile ducts and the gallbladder, fixing there with the help of two suction cups.
The chronic course of opisthorchiasis is manifested by symptoms of hepatitis, inflammation of the bile ducts, cholecystitis, disruption of the digestive tract, nervous disorders, weakness and increased fatigue. The parasite leads to the development of irreversible changes, and even after its expulsion, the patient continues to experience chronic inflammatory processes and functional disorders.
Arrangement of the worm house
If you want to start breeding earthworms at home, you need to equip a spacious worm barn in advance. The structure should become a comfortable home for the spineless, where they can live, eat and perform their biological duties.
A wooden box, a trough, an old bathtub and other similar structures can be used as a container. Experienced gardeners recommend placing high-quality open compost in the container. However, the ground must be protected with netting to prevent mass consumption of eukaryotes by birds and other natural enemies.
Proper worm care involves preparing suitable fertile soil. About 40 centimeters of compost should be placed at the bottom of the box, after which it should be filled with warm water. Next, you should create a straw bedding and wait a few days until the substances are completely absorbed. After completing these steps, you can put the worm into operation.
Finding the first group of worms to move is not difficult. It is enough to go to your own garden or vegetable garden and dig up a small layer of soil. Individuals living in the upper layers tolerate movement into the worm nest better than all others. Invertebrates are also sold in specialized gardening stores.
Settlement is carried out in several stages. The first thing a gardener needs to do is dig a small hole and then place a bucket of worms there. After this, the animals are covered with straw or burlap. In a week you will be able to notice the first results of the worms taking root.
To prevent the death of the colony, it is necessary to regularly monitor them. If the creatures demonstrate an active lifestyle, it means that they have managed to settle down normally , and everything is fine with them.
To improve adaptation to the new environment, the worms need to be fed only after 3-4 weeks. However, the heated liquid should be placed in the worm chamber at least twice a week.
Trichinella - what it looks like in the human body (Photo of worms)
The causative agent of trichinosis is a small round helminth, reaching 2-5 mm in length. Infection occurs when eating poorly cooked meat (pork, bear, wild boar). Penetrating into the intestines, the parasite larva matures in 3-4 days to the state of a sexually mature individual.
The lifespan of the worm is 40 days, after which the parasite dies. By boring through the intestinal wall, the larvae penetrate the bloodstream and spread to all organs of the human body, settling in the muscles. In this case, the respiratory and facial muscles, as well as the flexor muscles of the limbs, are most often affected.
In the first days after the invasion, patients complain of abdominal pain.
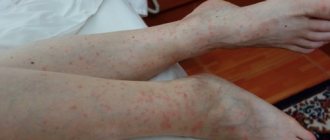
Then, after about 2 weeks, the body temperature rises to 39-40 C, itchy rashes appear on the skin, muscle pain develops, and the face swells.
During this period, in case of massive infection, there is a significant risk of death. After about a month, recovery occurs. The parasite is encapsulated in a spiral form, after which it dies within two years.
Habitat
Earthworm and its movement in the soil. The anterior end of the earthworm's body from below.
During the day, earthworms stay in the soil, making tunnels in it. If the soil is soft, the worm penetrates it with the front end of its body. At the same time, he first compresses the front end of the body so that it becomes thin, and pushes it forward between the lumps of soil. Then the front end thickens, pushing the soil apart, and the worm pulls up the rear part of the body.
In dense soil, the worm can eat its way through the soil through its intestines. Lumps of soil can be seen on the surface of the soil - they are left here by worms. After heavy rain has flooded their passages, the worms are forced to crawl out to the surface of the soil (hence the name - earthworm). In summer, worms stay in the surface layers of the soil, and in winter they dig burrows up to 2 m deep.
Wide tapeworm - what it looks like in the human body
This is one of the largest helminths, reaching a length of 10-20 meters. The disease caused by this parasite is called diphyllobothriasis. The development cycle of the worm begins with freshwater fish or crustaceans.
Photo of worms. Reaching the small intestine, the parasite attaches to its wall and grows to a sexually mature individual within 20-25 days.
The larva enters the human body, which is the definitive host of the broad tapeworm, along with caviar or infected fish fillets.
Diphyllobothriasis occurs against the background of disorders of the digestive tract and B12-deficiency anemia.
Echinococcus - what it looks like in the human body
For this parasite, humans are the intermediate host. The worm parasitizes the human body in the form of finna. The definitive host of Echinococcus is a wolf, dog or cat.
Find out more: Worms in an adult: signs, symptoms and treatment regimen
Infection occurs through nutritional routes through contact with animals and environmental objects contaminated with Echinococcus eggs. After entering the intestine, oncospheres (six-hooked larvae) develop from them. From the intestines they enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body.
Photo of worms. The “favorite” places for parasitism of the worm are the liver and lungs. Settling in these organs, the larva turns into a finna (echinococcal cyst), which, gradually increasing in size, begins to destroy nearby tissues.
Often, echinococcosis during the diagnostic process is mistakenly mistaken for a tumor of benign or malignant origin. In addition to mechanical effects (compression of organs and blood vessels), rupture of an echinococcal cyst sometimes occurs. This condition can cause toxic shock or the formation of multiple new cysts.
The importance of invertebrates
The importance of black worms for the biosphere is quite difficult to overestimate. It is worth clarifying that these invertebrates eat dead tissue of plant origin and waste products of various animals. Next, they digest it all and mix the resulting mass with the soil. Humans have learned to use this feature of black worms for their own purposes. Thus, he receives the most valuable fertilizer - vermicompost, or vermicompost.
Alveococcus - what it looks like in the human body
This parasite, considered a type of echinococcus, is the cause of one of the most dangerous helminthiases (alveococcosis), which is similar in severity to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Infection occurs when oncospheres (eggs with mature larvae) penetrate the intestines.
This parasite, considered a type of echinococcus, is the cause of one of the most dangerous helminthiasis (alveococcosis)
There, the embryo emerges from the egg and, penetrating the intestinal walls, penetrates the bloodstream. Further, through the bloodstream, the parasite spreads throughout all tissues and organs of the body (most often localized in the liver). It is there that the main stage of development begins in the larvae (a multi-chambered bladder, laurel cyst, is formed).
Photo of worms. Each chamber contains the embryonic head of the parasite, which continues to gradually develop. Laurocysts are very aggressive formations, constantly growing due to enlarging vesicles, and also have the ability to grow into the liver, like cancer metastases.
Due to disruption of blood vessels, nearby tissues undergo necrotic changes. Spreading to nearby structures, the alveococcus forms fibrous nodes with inclusions of multi-chamber blisters. This condition can last for several years, and therefore requires mandatory surgical intervention.
Schistosoma - what it looks like in the human body (Photo of worms)
Schistosoma is a blood fluke that belongs to the class of trematodes and, depending on the species, causes various schistosomiasis. This is a flat dioecious helminth, reaching 4-20 millimeters in length and 0.25 mm in width. The body of the schistosome is equipped with 2 suckers - oral and abdominal, they are located close to each other. Female schistosomes are longer and thinner than males. The male has a longitudinal groove on his body, with its help he holds the female. Their eggs are 0.1 mm in diameter, oval in shape, and have a large spike on the surface of one of the poles.
Human worms, schistosomes, choose humans as their final host; in their bodies they parasitize in the small veins of the colon, abdominal cavity, uterus, and bladder. Worms feed on blood and partially absorb nutrients through the cuticle. Schistosome eggs are transported to the intestines and bladder, where they mature and are excreted along with feces or urine. In freshwater waters, a larva emerges from the eggs - a miracidium; its intermediate host is mollusks. In the body of a mollusk, metacercariae develop into cercariae in 4-8 weeks.
Lifestyle of invertebrates underground
Black thin worms are nocturnal. The fact is that it is at night that they can get a large amount of food. So, you can observe their maximum activity. Some worms crawl to the surface of the earth in order to consume food, however, they rarely emerge completely from their burrows. Especially black small worms prefer to always leave their tails underground. During the day, invertebrates are accustomed to plugging their own holes with various objects, for example, tree leaves. They often drag small particles of food into their home.
Pork tapeworm - what it looks like in the human body (Photo of worms)
The pork tapeworm, like the bovine tapeworm, has 4 suckers on its body, but in addition to this, the body of the helminth is also equipped with a double crown of hooks. Strobila reaches two to three meters in length. The pork tapeworm has a three-lobed ovary; the uterus has from 7 to 12 branches on each side. A characteristic feature of this helminth is the ability of the segments to crawl out of the anus. After exiting, their shell becomes dry and bursts, so helminth eggs enter the external environment. The intermediate host of tapeworm can be pigs and humans. Photo of worms.
The main owner is a person. Intestinal parasites in humans include the pork tapeworm, the helminth is located in the intestines of the patient, where it lays its eggs. Infection occurs through consumption of invasive meat.
How to treat
Today, a parasitologist has over 10 anthelmintic drugs in his arsenal, which have their own specific activity against various types of worms.
The main drugs for the treatment of worms:
- Piperazine (10-30 rub.);
- Pyrantel - Helmintox (80-120 rub.);
- Pirantel (30-50 r);
- Nemocid, Combantrin Mebendazole - Vermox (90 rubles);
- Vermakar, Mebex, Vero-Mebendazole, Thermox, Vormin (20 rubles);
- Albendazole - Nemozol (120-150 rubles);
- Gelmodol-VM, Vormil Levamisole - Dekaris (70-90 rubles);
- Carbendacim - Medamin (70-90 rubles);
- Pyrvinium embonate - Pyrivinium, Pyrkon, Vanquin.