We all know about the existence of parasites - protozoa, animals, viruses, bacteria and fungi that need a host organism to survive. There are parasites that humans are susceptible to infection; they are called human parasites. Some of them, as the results of scientific research have shown, can be “carried out” under the skin - in the literal sense of the word. So, in 2014, Piotr Naskrecki, an entomologist and conservation biologist, author and photographer at the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University, discovered that tiny parasites - the human flies Dermatobia hominis - had settled under the surface of his skin and decided to raise them in the name of science.
Stories that will give you goosebumps. Still from Business Insider video
Myiases are parasitic diseases caused by fly larvae in the tissues and cavities of the body of humans and animals.
Types of parasitic skin diseases
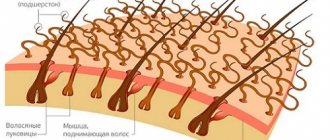
What parasites can live under human skin? The most diverse, including insects, helminths, mites and protozoan single-celled organisms. Lesions of human skin by various types of parasites are classified as a separate category of parasitic diseases .
Each group of diseases is united by characteristic pathogens:
- Protozoan organisms cause protozoan skin diseases.
- Ticks cause acariasis lesions of the skin.
- Insects can cause entomotic skin lesions.
- Helminthic diseases develop as a result of infection with helminths.
All these pathogens of human skin parasitic diseases are equally unpleasant and require diagnosis and treatment. Long-term neglected forms can lead to irreparable consequences from blindness to death. Fortunately, we can add that most of the list of parasites living under human skin is typical mainly for countries with a hot and humid climate.
Bedbugs
They belong to the order Hemiptera and have a sucking mouthparts. They feed on the blood of humans and animals at the larval and adult stages. They attack at night, falling on a person from the ceiling or crawling into bed. They usually bite on exposed parts of the body. By piercing the skin, the bug injects an anesthetic, which makes the bite almost imperceptible. During the day they hide in cracks, under wallpaper, in cracks in floors, furniture, under the upholstery of a sofa or bed. In nature, bedbugs live in damp caves, burrows, and nests of animals and birds.
Kissing bugs, common in Latin America, carry Chagas disease. After a single bite, trypanasomes enter the human bloodstream, which over time can lead to death. Children are the most seriously ill. In adults, the disease is mild. Treatment is effective only at the first stage of the disease. There is no specific vaccination. For personal protection, repellents and curtains over beds are used.
Diseases caused by protozoa
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoan single-celled pathogens transmitted by mosquitoes. A person infected with leishmaniasis becomes a reservoir for further spread of the infection. After a mosquito bite, which is the main host organism for leishmania, a person develops cutaneous or visceral leishmaniasis. Cutaneous leishmaniasis appears as deep ulcers or pustules, as well as extensive skin lesions. The mucocutaneous form of the disease leads to significant deformations of the appearance, especially of the face. Swelling of the airways due to leishmaniasis can be fatal.
Leishmaniasis occurs in 90 countries and is a very common disease in Syria, Iran, Afghanistan, Saudi Arabia, Brazil, and Peru.
Midges and biting midges
These small insects, one of the species of midges, are also representatives of the order Diptera. Midges swarm around a person and get under clothes. When attacking a victim, they bite off a piece of skin and drink blood from the resulting wound. The components of saliva have an analgesic effect, cause itching and allergic reactions. Midges live and breed near fresh flowing water bodies. They attack mainly during daylight hours. At night their activity decreases significantly.
In Africa, the Arabian Peninsula and Latin America, midges are carriers of onchocerciasis, a helminthiasis that leads to vision loss. For personal protection against insects, repellents with a high dose of active substance (30–50% DEET) are suitable, as well as thick clothing with well-fastened cuffs and collars that prevent insects from crawling onto the skin.
Diseases caused by ticks
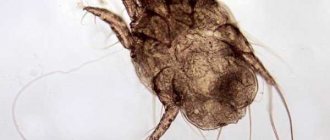
Demodicosis
A disease caused by a parasite that lives under the skin in the sebaceous glands and follicles of living human hair. This is a microscopic mite - demodex. Mainly localized on the eyelids, facial skin, and ear canals. Rarely - on the chest and back.
Infection with Demodex causes complicated acne and dermatitis, which worsens in spring and autumn. The skin looks red, hyperemic, lumpy, inflamed. The ciliated edge of the eyelid is usually swollen, red, the eyelashes are stuck together, there is a discharge in the form of crusts along the edge of the eyelid, and eyelash loss is typical. Sometimes the disease occurs without obvious manifestations, so the tick is considered opportunistic. Typically, demodicosis is exacerbated in people with impaired immunity, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and metabolic disorders.
Scabies
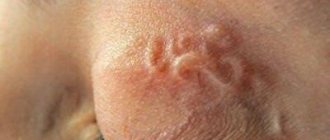
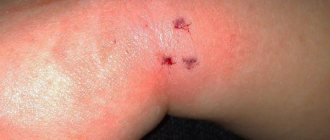
Another widespread disease caused by mites is called scabies. These mites gnaw passages in human skin in which they lay eggs. The development of an adult tick is accompanied by a complex cycle. Usually this process occurs at night, so the itching of the skin intensifies at this time. The main diagnostic symptom of the presence of parasites under human skin looks like double red small dots located nearby. These are double passages gnawed by a tick.
The disease is complicated by various infections that the patient incurs while trying to relieve the itching: streptoderma, nodular seals, blood crusts around scratches, rashes in the form of bloody blisters and other skin lesions. Complicated scabies may resemble urticaria, pyoderma, dermatitis, eczema, and psoriasis.
Infection usually occurs through prolonged contact with sick people (it has been proven that to become infected with scabies, skin-to-skin contact lasting up to 30 minutes is required; one should not discount the fairly low probability of infection when using common household items).
Forest bloodsucking Moscow region
With the arrival of spring, insects, including bloodsuckers, become more active, trying to go through the next cycle and give birth. The abundance of greenery and leaves is an ideal place for breeding, especially near bodies of water. Therefore, going out into nature, visiting a dacha or going into the forest carry considerable danger. While horseflies, mosquitoes, and flies can be easily protected from or simply driven away, a small tick penetrates into the most inconspicuous crevice.
In the forests of the Moscow region, as well as in the entire central zone, in recent years there has been an increase in the number of encephalitis ticks. Although, according to the latest data, no more than 6% of insects are carriers of the virus, and 2-6% of those bitten become ill, the consequences of the infection can be very severe, even fatal. In addition to tick-borne encephalitis, insects can spread borreliosis. Since 2010, the number of infected regions in Russia has increased by 1.5%, although the number of infected people has not increased due to prevention.
Diseases caused by insects
All skin diseases caused by dipteran insects are collectively called myiases.
Wolfarthiosis
The disease is caused by an insect called Wohlfarth fly, which lays larvae in mucous membranes or wounds on the human body. The larvae destroy tissue, secreting a special enzyme, causing severe pain, necrosis, swelling, discharge of pus and gangrene of the affected tissue. They usually parasitize the eyes, nose, and ears. Wohlfarth fly is widespread in countries with hot and temperate climates.
Mosquitoes
These dipterous insects inhabit all continents except Antarctica. In total, about 3,000 species are known. Mosquitoes live wherever there are conditions for reproduction. The mosquito larva and mobile pupa require a fresh body of water with warm water: puddles, wetlands, lakes, ponds, garden water tanks, damp basements of buildings.
Only females attack humans. They need blood to mature their eggs. Males feed on flower nectar. When choosing a victim, mosquitoes are guided by smell and temperature. When they bite, they pierce the skin, insert their proboscis into the smallest capillaries, and secrete a portion of saliva containing an anesthetic and a substance that prevents blood clotting. These insects are carriers of more than 50 different infections: viral, bacterial and parasitic.
Diseases caused by helminths
Dirofilariasis
A disease caused by round helminths. The source of infection is domestic animals - cats and dogs. The carrier is a mosquito. After its bite, sexually mature nematodes begin to develop in the human body, which, as a rule, parasitize under the human skin. The site of the insect bite becomes hard, inflamed and itchy. A characteristic feature of the pathogen is its ability to move under the skin, so the disease is accompanied by a feeling of moving, crawling inside the inflamed seal. Sometimes the nematode can be seen under the skin; cases of an individual emerging from the mucous membrane of the eye are described.
Accompanying symptoms may be allergic reactions, increased body temperature, nausea, and weakness.
Strongyloidiasis
A disease caused by parasitic larvae that burrow under a person’s skin as soon as he or she walks barefoot on the ground. Foci of incidence of strongyloidiasis are found in Georgia, Ukraine, Krasnodar, and Stavropol. Roundworm larvae burrow through the skin and migrate underneath, causing red, itchy skin and the development of red blisters.
Three infection strategies
There are 3 known types of transmission of infection from insects to humans.
Contact method The first route of infection is the simplest and most invisible. A fly, cockroach or other arthropod is capable of carrying millions of pathogenic microbes on its body, leaving them on food and household items. Through contact, insects spread all kinds of intestinal infections, typhoid fever, cholera, dysentery, trachoma, polio and other serious diseases.
Transmissible method Blood-sucking insects, piercing the skin, infect a person with pathogenic bacteria, viruses or protozoa. In this case, humans and flying bloodsuckers are links in the same food chain. The causative agent of the disease lives either in the body of an insect or in the blood and organs of a person, completing its life cycle in the body of one of the “hosts”. Typically, the natural source of such infections is wild mammals or birds. And insects are just transport for moving from the body of one warm-blooded organism to another. Examples: tularemia, malaria, borreliosis, encephalitis, plague.
Scratching an Itchy Bite Finally, sometimes itching is a contributing factor to infection. The insect pierces the skin, leaving an itchy wound and infected excrement around it. A person scratches the bitten area and thereby rubs the remains of the bloodsucker’s vital activity or hemolymph (tissue fluid) of a crushed insect along with pathogenic microbes into the skin. Some types of helminthiases and epidemic relapsing fever spread in a similar way.
Treatment recommendations
General recommendations have been developed for the treatment of diseases caused by one or another human subcutaneous parasite. The most relevant for our region is the treatment of strongyloidiasis, scabies and demodicosis. Treatment is prescribed after diagnosing the disease and only by a specialist. Some complications and manifestations of the disease require an individual approach to treatment.
- It is recommended to treat helminth infections with Naftamon, Praziquantel and other antiparasitic drugs.
- To treat scabies, benzyl benzoate ointment, Spregal cream and other effective remedies are used. In the fight against scabies, a treatment regimen and a system of preventive measures for contact persons have been developed.
- Treatment of demodex is carried out with comprehensive measures to strengthen the immune system, treat gastrointestinal diseases and other procedures. Ointments are used directly on the skin to treat scabies, as well as various cosmetic procedures.
Subcutaneous parasitic diseases require treatment efforts, so it is better to prevent infection by applying basic rules of personal hygiene . It is a good idea to know the common symptoms that accompany such diseases so as not to come into close contact with sick people.