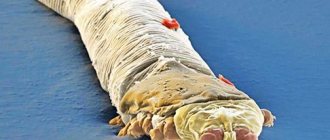
Acariasis is a disease caused by parasitism of arthropods. The uncomfortable symptoms of ear mites should not be underestimated. Timely treatment will prevent dangerous consequences.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
About the Demodex mite
There are two species of these mites found on humans: Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis.
Demodex mites can also live on various types of animals, in particular on dogs, which also suffer from demodicosis. But a person cannot become infected from an animal, since those ticks belong to other species and cannot live on humans. Demodex mites are considered opportunistic. This means that they can live on the skin of a healthy person - their presence does not always lead to the development of the disease. Different studies indicate different prevalence of Demodex. In any case, at least 50% of people are carriers of these mites; some researchers put the figure at 97%. It is believed that among children and young people there are fewer carriers of Demodex mites, the number of carriers increases with age, and almost all older people are affected by this mite.
Demodex lives in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, preferring the face to other parts of the body. Larger mites, Demodex folliculorum, most often target the hair follicles of the eyelashes and eyebrows. Demodex brevis prefers to settle in the sebaceous glands of the wings of the nose, nasolabial folds, and chin. However, mites can also be found on other areas of the skin, including the cheeks, neck, chest and back.
Demodex mites are not visible to the naked eye. An individual of Demodex folliculorum can reach a size of 0.5 mm; Demodex brevis is even smaller - no more than 0.15 mm. Demodex does not like light and is most active at night. The most comfortable temperature for it is 30-40 °C, so the tick becomes active in the spring and summer.
Prevention measures
You can only get rid of a tick in a medical facility. But you can prevent a dangerous situation yourself. The main preventive measures are to maintain immunity, as well as correct behavior when walking in the park or forest. To reduce the likelihood of ear mites infestation, you should follow simple recommendations:
- choose light-colored clothing for walks in nature and arthropod habitats;
- trousers must be tucked into socks or boots;
- You need to wear a hood or headdress on your head;
- tie long hair with an elastic band;
- treat clothing with parasite repellents;
- after a walk, inspect shoes and clothes, open areas of the body;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning of premises;
- monitor your health;
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports;
- follow a daily routine, sleep at least 8 hours;
- eliminate bad habits;
- master emotion control techniques that neutralize stressful conditions.
Causes of demodicosis
In a healthy person, the activity of the Demodex mite is suppressed by the body's immune defense. With a decrease in immunity, there are more ticks, which leads to the development of demodicosis. Also, an increase in the number of mites can be caused by metabolic disorders. Demodex feeds mainly on the secretions of the sebaceous glands, so increased productivity of the sebaceous glands leads to the activation of mites and, as a consequence, manifestations of demodicosis.
Thus, the list of the main reasons for the development of demodicosis may look like this:
- decreased general immunity;
- stress factors (stress and negative emotions contribute to decreased immunity);
- chronic diseases leading to a decrease in the protective ability of the skin;
- increased skin oiliness;
- hormonal changes (in particular during adolescence, when as a result of such changes the viscosity of the secretion of the sebaceous glands increases);
- use of cosmetics with hormonal supplements;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
What procedures provoke an exacerbation?
Even after treatment, the skin is vulnerable to external influences, not to mention skin that has not undergone therapy, since its protective functions are significantly reduced. As noted earlier, other exacerbation factors include some cosmetic procedures:
- phototherapy and laser coagulation - these procedures help to increase temperature and increase blood flow to the skin, and at the same time increase the production of sebum (and this is simply an ideal environment for subcutaneous mites);
- massages, vaporization, ultraviolet exposure (in a solarium, for example) - also contribute to increased sebum production, and therefore should be excluded from the list of procedures until remission is achieved;
- chemical peeling - in the acute stage of the disease, aggressive acids only contribute to the proliferation of mites, however, this procedure is sometimes effective in combating residual effects on the skin (everything is very individual);
- Skin biorevitalization is one of the most popular anti-aging procedures, but during periods of exacerbation of the disease it is contraindicated.
Symptoms of demodicosis
Mites destroy the cells of the follicle walls and sebaceous glands. This leads to the appearance of keratinization, foci of inflammation, and pigmentation. Demodex migrates across the skin, exploring new areas; Thus, with increasing demodicosis, the signs of damage spread over an increasingly larger area. It is also assumed that mites cause sensitization of the body, that is, an allergic reaction is added to mechanical damage.
The main symptoms of demodicosis are:
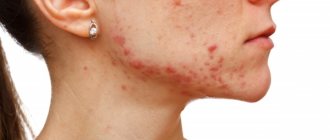
Acne (acne)
Juvenile acne in most cases is a manifestation of demodicosis.
Skin redness
Redness may be accompanied by swelling of the skin.
Itching
Itching with demodicosis usually intensifies at night, when mite activity increases.
More about the symptom
Skin changes
Progressive demodicosis leads to changes in the skin: roughening, peeling, and the appearance of thickenings similar to scars. In the advanced stage, the skin takes on an earthy color.
Blepharitis
When Demodex affects the eyelashes, signs of blepharitis (inflammation of the ciliary edge of the eyelids) develop: the eyelids begin to itch, turn red, swell, and may stick together. The eyes water, inflammation spreads to the conjunctiva - conjunctivitis develops. Loss of eyelashes is observed.
Lifestyle Features
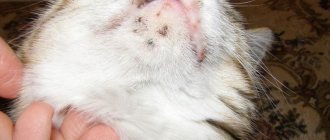
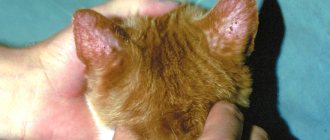
Ear mites infect the outer ear and parasitize in the ear canal, feeding on human waste products. Like its other relatives, the parasite, when it gets on human skin, grabs onto it, adapts to the “host” and no longer leaves it voluntarily. Infection is expressed by redness of the ear, acne, inflammation and the feeling of parasites under the skin.
In addition to the fact that the ear mite leads a parasitic lifestyle, it is a carrier of bacteria harmful to the human body and provokes infectious infections. The type of ear mite determines the type of infection. There are several types of common parasites that actively attack human skin.
Methods for diagnosing demodicosis
The symptoms of demodicosis coincide with the symptoms of some other diseases (dermatitis, allergies). Acne with demodicosis is similar to the manifestations of rosacea (rosacea disease). Therefore, laboratory diagnostics are necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Demodex analysis
The material for analysis is a scraping from the skin. If the eyelids are affected, eyelashes are taken for analysis. Next, a microscopic examination is carried out, which is designed to detect tick individuals or eggs.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Appearance of an insect
To recognize the enemy, you need to know what ear mites look like.
Ixodid ticks. Parasitomorphic arthropods parasitize the skin of humans, birds and animals. They are carriers of dangerous diseases (borreliosis, encephalitis).
There are 3 stages of development of the parasite: larva, nymph, and sexually mature individual - adult. Representatives of the species can rarely be found in humans, since their development cycle is not determined by only one place: if the females feed on the blood of humans and animals, then after mating, they try to lay larvae in the depths of the earth.
Demodex mites. Small mobile parasites with a body size of no more than 0.4 mm. The body is elongated, transparent. A representative occurs in 90% of people.
Average life expectancy is 20 days. At temperatures below +15 °C it becomes numb and cannot reproduce. If the temperature rises above +48°C, the tick dies.
Demodex parasites may not manifest themselves for a long time and only when the body’s protective functions decrease, they begin their active life in the ears and on the skin of a person’s face.
Arags mites. Adults of arags mites are small in size. The habitats of parasites are caves, cluttered attics, basements, haylofts, and farms.
Moves with dust particles. When dust settles on a person's skin, mites cling to it and thus become attached. There are 17 species in nature. All representatives are very hardy, as they can live up to 11 years without food.
Ways of infection by parasites:
- eating dirty vegetables;
- direct contact with parasites (visiting abandoned places, attics and caves);
- drinking water from an unknown source;
- swimming in a pond with dirty water.
When traveling to exotic countries, strict adherence to hygiene rules is recommended. Ear mites may not be the only problem brought from distant countries. On such a trip you can become infected with dangerous helminths.
For your information!
Dangerous helminthiasis brought from overseas countries can affect human eyes. If this happens, you will have to not only be treated with medications, but also surgically remove the adults, as well as their larvae.
During its “conscious” life, an ear mite can provoke mite sensitization. In this case, the human body will become more sensitive to irritants.
Treatment methods for demodicosis
Treatment of demodicosis is a long process. On average it takes 4-6 weeks, but in some cases it may take several months.
The difficulty of treating demodicosis, in particular, is that the most effective anti-mite remedies are quite toxic. Therefore, means for the treatment of demodicosis are selected individually, depending on the degree of damage and the patient’s condition.
Treatment must be comprehensive. The course of treatment includes both local and systemic therapy.
Local therapy
Local therapy for demodicosis is aimed at suppressing the activity of the mite. Without the use of local therapy, treatment success cannot be expected.
Systemic therapy
Systemic therapy for demodicosis involves measures to strengthen the immune system and normalize metabolism.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
How is ear mites treated?
Before starting treatment, you need to determine which type of parasite is the source of the disease. For this purpose, you need to contact an otolaryngologist, who will conduct an examination and, if necessary, take ear discharge for analysis.
When treating hearing diseases caused by parasites, the following techniques are used:
- Procedures for washing the ear canals. For this, saline solution, an aqueous solution of ethanol, or hydrogen peroxide are usually used. This method is most often used to destroy argas and ixodid ticks.
- The use of physical procedures that relieve inflammation, treat skin lesions and block the proliferation of parasites. This is done using laser coagulation, electrophoresis, liquid nitrogen and ozone therapy.
- Performing mechanical suction of mites from the auricle and ear canal.
- Treatment with Ornidazole and Trichopolum, which help destroy parasites.
- The use of ointments for the manufacture of which tar, zinc or sulfur is used. They have a detrimental effect on parasites, reduce ear pain and reduce inflammation.
- Taking antihistamine medications. To block the allergic reaction resulting from the activity of mites, Zodak, Suprastin or Citirizine are used.
In addition, the doctor may recommend multivitamin preparations, with the help of which the lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body is compensated.
Question answer
Is demodicosis contagious?
Yes, you can become infected with demodicosis through kissing, hugging, using the infected person’s things, his hygiene products, etc. But this does not mean that you will show signs of illness. As we have already said, the tick is found in almost all adults, it’s just that most are carriers. For the development of the disease, other additional factors are needed.
Is it possible to get demodicosis from animals?
Animals, like people, suffer from this mite. However, there are several dozen types of pathogens - and each lives only on its own host. In other conditions it dies. Therefore, you cannot catch the disease from a dog or other animal.
Which pillows are best for preventing demodicosis?
It is best to choose synthetic fabrics to prevent demodicosis. The mite lives well in feather and down pillows, but it is extremely difficult for it to take root in synthetic ones, especially those that are regularly cleaned.
Folk remedies for treatment
Folk remedies for getting rid of ticks
You cannot use independently even the remedies that have been tested by someone. Fighting ear mites is allowed only after consulting a specialist. Otherwise, dangerous complications and a direct threat to human health and life are possible.
Effective ways to combat ear mites:
- Salt with lemon. Mix 1 teaspoon of each component and apply to affected areas 2 times a day. Leave the resulting slurry for 10 minutes and wipe with a cotton pad.
- Tincture of calendula. It should be dripped 1 drop into each ear.
- Garlic lotions. Pass the garlic through a press and apply to the skin, leave for 10 minutes, rinse and wipe with a dry cloth.
- Tar soap. Leaves no chance for parasites. Grind the soap and dissolve it in a small amount of water to obtain a concentrated solution. Moisten a cotton swab and leave it in your ear for at least 15 minutes.
- Alcohol-containing solutions. They are an emergency response method. If a tick has clung to the skin, it will help to wash it with an alcohol solution. Often used as first aid.
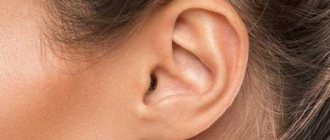
Can a tick get into the ear?
When the weather warms up, the number of tick bites increases sharply, which is explained by the greater hunger of the ticks. At this time, people should be more careful about themselves and their loved ones in order to detect the parasite in time.
Most often they like to climb:
- on the inside of the arm;
- under the knee;
- behind the ear;
- on the head;
- into the nose.
He will crawl from place to place for a long time until he finds the most convenient place to bite. It is precisely because of this that he is easily able to climb very high. Often, in search of food, an individual can get into the ear canal. It can rarely creep beyond the border of a person's outer ear. To fully support life, it definitely requires oxygen and enough space for growth.