Insect feeding
The source of replenishment of vital supplies for lice species is human blood. An adult feeds 4 times a day. Each procedure lasts at least 5 minutes. At one time, the insect drinks about 5 ml of blood.
On a note!
Nutrition plays an extremely important role in the life of insects. Without blood, the female cannot reproduce or lay eggs. Nymphs stop developing and do not move on to the next stage.
Parasites live in a colony, but are not known for their coordinated actions. They eat randomly. With severe infection, unpleasant sensations are constantly present. Nymphs drink less blood per meal, but make more attempts to get food.
Should you tell others about lice?
Getting rid of lice is not a problem, but getting rid of public censure is extremely difficult. A child may be bullied by classmates. Let's face it - this happens almost all the time. Employees of our sanitary and epidemiological station, who treat apartments and houses against lice, often hear stories from parents and see children’s tears. We draw one simple conclusion - confidentiality must be maintained whenever possible.
In the case of adults, everything is the same. Of course, no one will openly blame you. But the subconscious effect that a person is unsanitary will remain. It is necessary to destroy lice quietly and in a family manner so as not to disturb others.
Interesting: children are more susceptible to insect attacks. The reason is weaker immunity. By the way, alcohol, smoking and simply poor health make a person a tasty target.
Types of lice
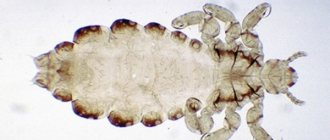
Types of lice There are several types of lice. The most common is the head one. Behind it is the wardrobe, pubic. Outwardly, head lice and body lice are similar to each other. Features of the head parasite:
- body size no more than 4 mm;
- elongated torso;
- the color is light, changes depending on the color of the hair, as well as food;
- the translucent chitinous cover reveals the insides;
- parasitize on the head, and in case of severe infection - on the beard, mustache, and eyebrows.
On a note!
A well-fed louse increases in size, has a rounded body, and a red tint in color.
Body lice parasitize the body. However, they live outside its borders. They lay eggs in folds, seams, bedding, clothing, and underwear. They crawl into biting the human body up to 4 times a day. They parasitize everywhere except the head. The structure of the hairs and whether they are on the body does not matter.
“Typhoid had a bad reputation, but it was dealt with!”
Andries Both, “Catching Fleas by Candlelight” (1630).
Image from the site art.biblioclub.ru Once upon a time, body lice were a breeding ground for typhus, and one of its types, relapsing fever, was carried by head lice. This infectious disease, however, is largely over. Since the end of World War II, typhus outbreaks have occurred mostly in Africa, with three countries: Burundi, Ethiopia and Rwanda.
In the United States, cases of typhus are isolated, and Europe has practically forgotten about this infection.
In Russia, the last case of typhus was documented in 1998, but in 2015, in eight regions of the country, including the Tula, Samara regions and Moscow, epidemiologists identified several cases of Brill's disease (a recurrent form of epidemic typhus), due to with which the chief sanitary doctor of Russia, Anna Popova, called for intensifying measures to combat head lice in medical and children's educational institutions and organizing special washing stations for the homeless.
Judging by the fact that there have been no reports of typhus in the three years since then, the measures were effective, and perhaps the risk of spreading the disease was extremely low to begin with.
The most important good news is that typhus is easy to treat these days. To do this, it is enough to take 200 mg of doxycycline once, regardless of the patient’s age.
You may have heard that a bloodsucker can infect a person with hepatitis B or even HIV infection. This is pure fiction, not based on any facts.
Viruses are broken down by special enzymes of lice and washed away by their saliva, so there is no danger of contracting these terrible diseases through insects.
Bite process
The process of a parasite bite Lice lack a proboscis, thanks to which the blood-sucking insect easily reaches the vessel with blood.
The mouthparts are similar to those of a flea. The insect pierces the cheekbones into the skin, gets to the blood vessels, and injects a special substance so that the blood does not clot. While feeding, the insect lifts its body upward and penetrates with its head as deeply as possible into the human body. After feeding is completed, blood continues to ooze for some time. And at the site of lice bites, characteristic marks remain.
Interesting!
Some people are interested in the question of whether nits bite. The name nits refers to the larva that is located inside the egg, under a dense shell. She is unable to go outside and feeds on the substance left in the egg. After 2 weeks it appears outside. But this is no longer a nit, but a nymph of the first instar. Differs from the adult individual in body size and color. Immediately begins to parasitize.
Mechanical method of diagnosis and treatment
The most important assistant for detecting lice is a comb, or rather a comb with very densely spaced long teeth. They comb their hair to remove lice and nits. This must be done subject to the following rules:
- It is better to comb wet hair;
- It is advisable that it is not the person who has picked up lice who does the combing, but his assistant;
- cover your shoulders with a white towel so that the combed parasites fall on it;
- Combing is best done indoors, which can then be treated with pediculicides, for example, in the bathroom.
You need to spread white paper or cloth, tilt your head in its direction and start combing your hair from the back of your head forward. The teeth of the comb should go through the hair and touch the scalp. Parasites will comb out onto the paper and get stuck between the teeth of the comb.
Please note that combing is a way to detect parasites and reduce their numbers, but not to get rid of them completely. This method of control is suitable for very small numbers of insects and nits, if the infection has occurred recently. Combing is also used to remove lice and nits from a child, for whom pediculicides cannot be used. In this case, you can not resort to special means, but try to simply comb out the parasites. The procedure must be carried out several times, combing the entire head and trying not to leave a single adult or nit on the head.
If pests are found, you can’t just leave them. Pediculosis does not go away on its own. You can get rid of them using special pediculicides, for example, produced by MediLIS Laboratory LLC: Malathion, Permifen, Super, Bio. They destroy parasites and nits. Instructions for use are included with each product; they are easy to use and effective.
Features of bites with pediculosis
A lice bite looks like most of the many marks left by blood-sucking insects. In the warm season, lice bites on the body are confused with mosquito and flea bites. It is difficult to distinguish even with careful inspection.
Lice bites on the head are the main symptom of head lice. When damaged areas are detected, suspicion immediately falls on these parasites.
During the cold season, lice bites on humans can be confused with bed bugs. It is necessary to pay attention not to the bite itself, but to its location:
- Bedbugs always leave a path with a couple of punctures. They bite mainly on the shoulders, arms, legs, neck, and back.
- A lice bite looks a little different. Traces of damage to the skin are located randomly. Unlike bed bugs, the stomach and face also suffer if these are bites of linen lice.
How does infection occur?
These insects are unusually tenacious and can live in bedding, mattresses or crevices of wooden floors for years. Detecting an infection right away is almost impossible. Only after the parasites occupy several piles of linen in the closet and begin to rapidly multiply in the mattress can they be noticed.
It is a mistaken opinion that linen (body) lice are the lot of marginalized people. You can become infected in transport, in a store, and even in a queue. Wherever there is a large crowd of people and they touch each other's clothes, transmission of infection is possible.
Places where the risk of infection is highest:
- Bedding in long-distance trains (especially blankets and pillows, which are not always properly disinfected).
- Trying on clothes in a large shopping center or second-hand stores.
- When visiting a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool, it is also quite possible to bring home this “gift”.
- Children often bring lice from camps and sanatoriums, along with parasites in their hair.
- In a hotel whose administration does not comply with established hygiene standards, there is also a risk of infection.
- In emergency hospitals, especially in the emergency department, do not leave items on chairs or benches. In such places, the risk of infection increases several times.
You shouldn’t go to extremes either; the percentage of the probability of infection with this type of parasite is no more than twenty.
Where to look for evidence - signs of lice
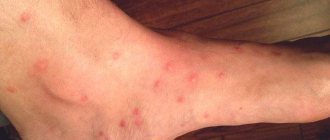
Head lice bites remain on the scalp, behind the ears, and on the neck. A photo of lice bites on the head is presented below. With an average degree of infection, red spots with slight swelling remain. There is dried blood in the center. Since severe itching occurs after lice bites, additional scratches, sores, and wounds appear on the head.
Head lice bites
On a note!
Head lice bites cannot be confused with other insects, so you can immediately begin treating head lice.
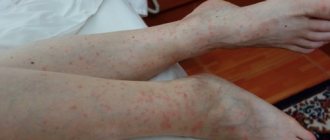
Body lice bites remain on different parts of the body. It is important to determine who you are dealing with in order to select effective methods of control. Photos of linen lice bites can be seen below. Characteristics:
- red spots, swelling, inflammation remain;
- in the center of the pimple there is a dark dot of dried blood;
- unlike bites from bed bugs, fleas, and mosquitoes, there is slight swelling;
- lice bites are scattered;
- with severe infection, many small spots appear; the entire body can be bitten;
- easy to detect in bed and clothes.
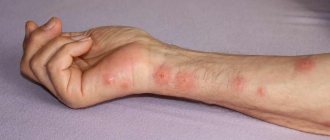
Pubic lice bites Pubic lice bites remain in the genital area. On the pubis, groin, within the anus. With a large number of parasites, marks appear on the stomach along the hairline, and in men on the chest. They can parasitize in the armpit and bite in this area. A louse bite is a small red spot. But when scratched, it increases in size, becomes inflamed, and thickens.
Symptoms
If we talk about the symptoms, they are not different in anything special and are typical for all parasitic diseases of this kind:
- Redness. The first sign of pediculosis is the appearance of small red spots, which at first are not accompanied by anything. Very often, people do not even suspect the presence of parasites on their bodies, citing the fact that the spots were formed as a result of skin friction, excessive sweating or food allergies.
- Itching. Lice feed exclusively on the blood of their host, on whom they parasitize, and to do this they have to bite through the skin. While the louse is small, the itching is almost imperceptible, but after 2-3 days, the itching becomes unbearable.
- Bite marks. If the problem is not identified in time and treatment is not started, the skin becomes covered with visible wounds. When several lice bite in one place, blood stagnates in the subcutaneous tissue, it does not clot well and a small bruise appears. Thus, on the body you can see small wounds with baked blue blood.
- Nits. Lice tend to multiply and lay small black larvae covered with a white capsule - nits. They are very firmly attached to the roots of the hair and it is almost impossible to wash them. You must use a special brush for combing. How to distinguish dandruff from nits, read on our website.
- Deterioration of hair condition. Every time you bite through the skin, blood microcirculation in the upper layers of the epidermis is disrupted and blood flow worsens. This deprives the hair of adequate nutrition, the hair follicles become weak, begin to come to the surface, and the hair actively falls out.
Interesting fact: lice do not grow in dyed hair. Naturally, parasites can migrate to such hair, but they will not stay there for long. Ammonium thiaglycol, which is included in all paints, has a detrimental effect on insects. But it is worth remembering that lice staining should not be used as a medicine. If paint gets on open head wounds, you can get severe chemical burns and cause allergies.
Danger of lice
Lice bites provide a lot of inconvenience and discomfort.
- The affected areas are very itchy. The itching intensifies at night, as parasites become more active at this time.
- A person suffers from insomnia, decreased ability to work, daytime drowsiness, and headache. Constant itching makes it difficult to concentrate and irritates the nervous system. Puts you in an awkward position in front of others.
- Scratching leaves scratches and infection enters the wounds. Ulcers and lumps appear. The addition of a secondary infection is dangerous for the development of other dermatological diseases.
- The substance that the louse injects into the human body provokes a severe allergic reaction. It manifests itself as unbearable itching, redness, burning, and rash. If a person has a tendency to allergies, the situation requires immediate treatment. Antihistamines and antiallergic drugs are prescribed.
Preventive measures
Preventing the spread of lice involves regularly checking suitcases upon returning from a business trip or traveling, and washing stale items of clothing.
To protect yourself from insects, you can put a cotton pad soaked in hellebore water or lavender oil in the closet with your linen. You should visit beauty salons and hairdressers with caution and pay attention to the disinfection of instruments.
Lice live in the folds of people's clothing, bedding and other textile household items. Pests can be detected not only visually, but also by the appearance of bites on the body of household members.
The affected areas are presented in the form of red swellings on the skin, which are characterized by a chaotic location. The bites itch, and ulcers remain at the scratch site.
Medical care for those affected by the active life of parasites should be followed by no less active pest control. You can carry out all the necessary activities yourself or contact specialists.
Therapy
Therapy for pediculosis Treatment of head lice is carried out with special medications.
To get rid of lice, treat the hair with a pediculicide, put on a special cap, and wait for the time specified in the instructions. Nits and dead individuals are combed out. To consolidate the result, it is recommended to re-treat after 14 days. It is also possible to destroy parasites using folk remedies. Therapy for linen lice is carried out somewhat differently. The main effort is directed to processing bedding and things. Wash at high temperature, chemically treated. Take a shower with tar soap or a special shampoo that contains insecticides against lice.
Pediculosis pubis is the easiest to treat. It is necessary to shave the hair on the pubis and genitals. Treat bites with alcohol. Or apply a special product and rinse off after the time specified in the instructions. They wash clothes, bedding, and underwear.
In each case, disinfestation is carried out in the house. The bites themselves can be treated with Zvezdochka balm, Bepanten, Fenistil gel, and calendula tincture.
Prevention
In order to minimize the risk of infection, precautions should be taken, namely:
- • regular washing of the head and body, adherence to general hygiene rules;
- • regular examination of the child's head, especially if he attends school or kindergarten;
- • familiarizing children with the rules of hygiene and maintaining a safe distance when playing and communicating;
- • regular change of bedding - to prevent infestation with body lice;
- • exclusion of casual sexual relations in order to prevent infection with pubic lice;
- • applying drops of tea tree oil or lavender behind the ears, the smell of these products repels insects
Unfortunately, following normal hygiene rules does not guarantee complete protection against lice infestation. The main method of prevention is maintaining a safe distance when communicating with people whose appearance is suspicious.