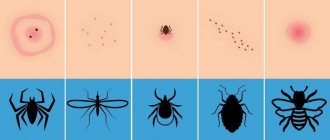
All pet owners have experienced flea bites. If treatment is not started in time, the parasites actively multiply and bite people. Flea bites appear as red marks on the skin that are itchy and sometimes painful. Children often develop secondary infections because they scratch the bites. Some types of fleas are dangerous because after bites serious symptoms may appear.
Let's look at what flea bites look like - photos and symptoms, whether the bites of basement, earthen and bed fleas differ from each other. We will also find out what is remarkable about duck and sand fleas, and how their bites affect people.
What fleas bite people
For fleas, regardless of species, humans are not a priority host. The body of dog, cat and other types of fleas (including human) is adapted for comfortable living in the fur (or feathers) of animals. Therefore, in an apartment, pets are the first to suffer from these parasites.
But at the same time, fleas are not adherents of a strict diet; for them, it is not important whose blood they feed on. If a person is bitten by a flea, it means that he was simply caught on the way first. Owners of cats or dogs are more likely than others to find bite marks on their legs, although sometimes parasites appear even where there are no animals.
The conventional division of fleas into basement, house or bed fleas is not a scientific classification. Among the people, such names have become firmly established, but they imply the areas of individual populations, and not biological species
By appearance, cat flea bites cannot be distinguished from dog, rat or human bites. A person's symptoms will be the same. Of course, the bites of house and bed fleas are no different from the bites of ground fleas and basement fleas. The consequences of a bite will depend not on the type of flea, but on whether the insect is infected with a pathogen, as well as on the person’s immunity. The exception is sand fleas, which use human skin to breed offspring.
Which ants bite - black, red, red, house and flying?
All types of ants bite. Another thing is what the consequences may be. Information has been provided above with the symptoms and effects of known and common types. I would like to add a few words about flying ants.
- Yes, they really do have wings. But this feature is not observed in all species. And this is precisely the feature that occurs during the mating period. It happens in both males and females.
- They cause discomfort with their flights, but they will not attack a person without a threat to life. Moreover, their bites are practically painless and do not have any negative consequences.
Interesting Facts! After mating, the winged males die, and the female then gnaws off her own wings. Only virgin individuals can show off their wings.
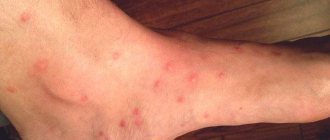
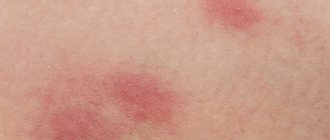
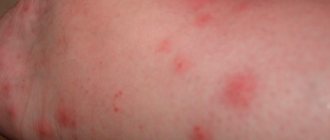
What do flea bites look like on the human body?
When attacking people, fleas leave bites mainly on the ankles, feet and legs - as far as the height of the jump.
As a rule, the site of a flea bite first looks like a small red dot, around which a halo of reddened skin then appears. Redness remains on the skin sometimes for a couple of hours, and sometimes for a couple of days. In some cases, flea bites cause a long-term allergic reaction that lasts for weeks or even months.
Flea bites in children
Children's skin is more delicate than that of adults, and the immune system is just developing, so the protection against infections is weaker. Therefore, flea bites on a child’s body cause a more severe reaction.
Children are more vulnerable, and the development of an allergic reaction in them requires close attention. Vomiting and diarrhea, difficulty breathing, dizziness and chills are possible symptoms of a severe allergy to flea bites in a child. In addition, children constantly scratch itchy bites, and this is fraught with secondary skin infections. If symptoms of bites do not subside, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment
Immediately after an ant bite, avoid panic and take an antihistamine (for example, Suprastin) to avoid an allergic reaction. If possible, call an ambulance and, most importantly, treat the puncture with an antiseptic/alcohol, which will prevent infection.
The treatment method is selected based on the body's response. It is advisable to have it prescribed by a specialist.
First aid
The further condition of a person depends on the first actions after an insect bite. Even if you are in the forest, provide first aid to the patient. What to do:
- Move away from the anthill, shaking off the ants.
- Wash the puncture sites with soapy water or, in extreme cases, water for 10 minutes.
- Treat with any antiseptic and apply ice/cold compress. As an alternative, it is permissible to use plantain juice, lemon juice, soda solution, and salt brine.
- If your legs are affected, elevate them to reduce the risk of severe swelling.
- Give the victim warm tea or clean water in large quantities.
If anaphylactic shock or angioedema occurs, act immediately, as the condition can be fatal. First aid provided before the arrival of doctors - algorithm of actions:
- Apply a tight bandage above the bite.
- Lay the victim down so that his head is on his side. Otherwise, the person will choke on vomit.
- If the patient is indoors, open the windows to provide fresh air.
- Unfasten top buttons, untie belts, remove jewelry, etc. so that nothing is constricting your body.
- Measure your blood pressure. If necessary, give appropriate medications (for high/low blood pressure).
- If the heartbeat weakens, perform chest compressions or perform artificial respiration.
Quincke's edema, like anaphylactic shock, occurs against the background of an allergic reaction, so it is important to take antihistamines (allergy sufferers usually always have them with them).
Medical supplies
To alleviate the victim’s condition, the doctor prescribes one of the following remedies (or in combination, depending on the symptoms):
- Telfast;
- Zyrtec;
- Tavegil;
- Claritin.
Among the adverse reactions of all the described drugs, mild dizziness, weakness, and headache are observed. Duration of treatment is at least 3-4 days.
For local use (itching, burning and other symptoms are eliminated), ointments and gels are used:
- Gel Lorizan. The active substance (loratadine) blocks histamine H-1 receptors. Already 40-60 minutes after use, the burning sensation, itching is relieved, and swelling is eliminated.
- Fenistil gel. Affects the allergen, neutralizes itching and pain.
- Gel Cetrilev. It is based on plant components and silver nanoclusters, due to which, in addition to relieving unpleasant symptoms, it allows other agents to quickly penetrate the epidermal tissue.
- Psilo-balm. Antihistamine gel, which is applied several times a day.
For severe itching, burning and redness of the skin, the following medications are used:
- Golden star in the form of a balm. Quickly cools and soothes.
- Menovazine in solution form. It not only relieves irritation, but also relieves pain due to the content of anesthesin and novocaine.
- Cream Rescuer. Tourists often take it on the road, as it is intended for use against insect bites.
- Menovazine in ointment form. Acts in the same way as Menovazin.
- Boro-plus cream. It is considered a powerful antiseptic, which additionally stops inflammatory processes and promotes wound healing.
For disinfection, it is permissible to apply ointments:
- Levomekol;
- Ichthyol;
- Heparin;
- Tetracycline;
- Vishnevsky.
It is strictly forbidden to use zinc-based products, since formic acid is rich in this element.
Apart from an allergic reaction due to individual intolerance to one of the components, these drugs do not cause side effects.
For severe allergies to ant bites, the following remedies are used:
- for external use – Sinaflan, Flucinar;
- for oral administration - Diazolin, Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Fenkarol (first generation drugs), Loratadine, Levocetirizine, Astemizole, Desloratadine (second/third generation drugs);
- use vinegar solution as a compress.
If urticaria occurs, the doctor prescribes glucocorticosteroids. For detoxification, infusion is used, hyposensitizing substances are introduced.
Adherents of homeopathy use the following medicines:
- Caladium seguinum. Relieves pain and burning.
- Ledum palustra. Removes swelling and itching.
- Apis mellifica. Used for severe pain thresholds and allergies.
- Belladonna. Anesthetic antiseptic.
Surgery
If blisters form, do not puncture them. When they burst spontaneously (accidentally), treat with hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin solution. The best option is to visit a hospital, where a surgeon will open the blisters at a professional level.
Surgery is prescribed when suppuration occurs due to infection of the wound. The purulent exudate is opened and removed.
After pumping out fluid and pus from the inflamed area, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment, which eliminates the formation of scars, cicatrices and, most importantly, the progression of the infectious disease.
Traditional methods
There are situations when there is no pharmacy kiosk or hospital nearby. For example, in a remote village, in nature, in a summer cottage, etc. There are also people who prefer to use exclusively traditional medicine.
For these cases, the following recipes exist:
- Soda slurry. Combine baking soda with warm water to form a creamy mass. Lubricate the bite area within a radius of 3-5 cm, leave for 7-10 minutes, then rinse.
- Aloe. Cut a 3-year-old leaf from the plant, wash it and peel it. Mash the pulp with a fork, place it on a piece of gauze folded in several layers, and apply it to the wound. Secure with a bandage for at least 60 minutes.
- Lemon. A simplified method: cut a slice and apply it to the bite. If possible, squeeze out the juice, soak cotton wool in it, and make a compress.
- Salt. For 50 g of salt, take 1 tbsp. l. water. Stir thoroughly until completely dissolved. Place on a bandage, as in the case of baking soda, and leave for 15 minutes.
- Ammonia alcohol. Use only as an antiseptic. Mix in a 1:1 ratio with water, lubricate the bite every 10 minutes.
- Toothpaste. Use mint paste as it is extra cooling. Squeeze out the amount of a match head and lubricate the puncture. Leave until dry, then rinse with warm water.
- Milk. There are 2 options: soak gauze in milk, apply for 15 minutes, or make frozen milk cubes and wipe the wound with them. Do not use store-bought milk - only natural cow's milk.
- Activated carbon. Make a paste out of it to lubricate the affected area. Grind the tablet to a powder, add a little water or milk, apply to the puncture. Wrap the top with a plastic bag and a bandage. Keep for at least 30-40 minutes.
- Echinacea. The solution is sold in pharmacies. Take orally as directed. Used for allergic edema. The tincture can be used as a lotion.
- Essential oils. Give preference to tea tree and camphor. Lubricate the itchy area every 40-60 minutes.
- Butter. It should be at room temperature, that is, softened. Rub into wounds 3 times a day. The quality of the product must be high.
- Raw potatoes. Peel the root vegetable, rinse, cut into a thin slice. Apply to the area of inflammation and secure with adhesive tape. There is another option - grate the peeled tuber, place it in an even layer on gauze, and place it on the bite site. Keep it for 40-50 minutes.
- Onion. Peel the vegetable, chop finely, squeeze out the juice. Soak a cotton swab or small piece of gauze in it. Attach, wrap in plastic, wrap with a bandage. Keep for at least 30 minutes.
- Plantain and parsley. Grind the plants washed under water and apply the pulp to the wound. You can squeeze out the juice and make a compress, wrapping it in plastic wrap.
- Vinegar. It is advisable to use apple juice. Dilute vinegar with clean water in a 1:1 ratio. Soak a piece of gauze in the solution, apply it to the bite for 20-30 minutes, wrap it in plastic and a bandage. Change the compress 3-6 times a day.
- Vodka. If there are no antiseptics on hand, take regular vodka or alcohol, moisten cotton wool, and lubricate the puncture area. If you use alcohol, dilute it with a little water to avoid burns.
- Soap. Use mainly household brown. Grate on a fine grater and mix with water until a paste forms. Apply to the skin, cover with plastic wrap, and wrap with a bandage. Keep it for no more than 20 minutes. Otherwise, peeling begins. If this is not possible, simply wipe the inflamed area with a piece of soap soaked in water.
- Herbs. Make a decoction of nettle, chamomile, mint, parsley, and birch buds. Make compresses from it. Keep them for 40-80 minutes or more.
What can't you do?
There are a number of actions that are prohibited from performing after an ant bite:
- try to squeeze out the poison yourself;
- comb puncture sites;
- cut off the epidermis;
- touch the wound with your hands;
- apply non-disinfected tissues and other objects.
Consequences of flea bites
An increase in the body's sensitivity to flea bites is called sensitization. Depending on the frequency of previous bites, a person’s reaction proceeds through 5 stages of sensitization
- There are no previous contacts with fleas - there will be no reaction to the bite
- All subsequent flea bites cause a delayed or late reaction
- The frequency of bites increases - both immediate and late reactions appear
- Flea bites continue - the intensity of the late reaction decreases and eventually only immediate reactions appear
- With a further increase in the frequency of bites in the body, complete desensitization is achieved, and the person acquires immunity to bites
In most cases, flea bites do not lead to serious consequences. In adults, as a rule, the matter is limited to unpleasant sensations. But for those people who are prone to allergies to insect bites, the following manifestations are possible:
- Edema
- Unbearable itching
- Painful skin irritation
- Swelling of the face or lips
- Labored breathing
- Nausea
Scratching bites leads to secondary infections, so the essence of first aid comes down to relieving the itching. Here is a partial list of treatments after a parasite attack:
- Hydrocortisone
- Vinegar
- Antihistamines
- Calamine lotion
- Tea tree oil
In addition, fleas that parasitize sick animals carry plague, typhus and other infectious diseases. If a person experiences excessive redness, severe pain around the bite, or swollen lymph nodes, this indicates the development of an infection. Such symptoms require immediate medical attention.
First actions after the attack
First aid for a bite
How to treat an ant bite depends on the reaction of the immune system and the complexity of the consequences, but the first steps after an insect attack are the same.
- If you are bitten by an ant, do not panic. What to do - disinfect the wound. Children often intuitively use their own saliva for these purposes. In the absence of disinfectants, this decision is correct. Saliva is a natural antiseptic, but before applying it, it is recommended to wash the wound with clean water.
- If you rub a slice of lemon over the bite, the burning sensation from the ant bite will subside. For the same purpose, raw potatoes or the juice of this vegetable are used.
- At home, treatment for ant bites begins with washing the affected area with soap and water. It is recommended to use laundry soap for therapeutic purposes. Then treat with medical alcohol or any tincture containing it. Tinctures of calendula, valerian, and motherwort are excellent for these purposes.
- If the itching does not subside, you should prepare a paste of baking soda and salt and apply it to the sore spot.
How to distinguish a bug bite from a flea bite
Bedbug and flea bites are similar in that they cause redness, itching and allergies. It is difficult to determine which bites are from fleas and which are from bedbugs by the appearance of the red spots. The differences lie in the following nuances: on what parts of the body the bites appeared, at what time of day, and whether they were accompanied by pain.
- If fleas leave bites in 90% of cases on the legs, then bedbugs leave bites all over the body. In addition, after fleas there are often clusters of 2-3 marks, and after bedbugs there are lines of 3-4 bites.
- Bedbugs feed at night, and people notice bites the next morning, and fleas bite regardless of the time of day.
- Bedbug bites are painless, thanks to the anesthetics in their saliva, but fleas bite painfully.
Why are ant bites dangerous?
Local insects are dangerous in rare cases. What can happen:
- Eye damage. Ants do not bite the visual organs, but if they are localized in the face area, formic acid can enter the eyes (the shot reaches 30 cm), which burns the retina.
- Scars. Occurs due to scratching.
- Infection. Insects are carriers of pathogens. Failure to provide first aid after a bite (if the wound is not treated with an antiseptic) causes suppuration. Cholera, helminthiasis, salmonellosis, dysentery, diphtheria, and typhoid fever may develop.
- Hives. It is a scattering of red blisters.
- Quincke's edema. Severe swelling in the nasolabial area, ears, eyes, lips, larynx, throat, vocal cords. Other symptoms are hoarseness, difficulty breathing, soreness. In severe forms, Quincke's edema is fatal if help is not provided immediately.
- Anaphylactic shock. Occurs with severe allergies. The patient loses consciousness and blood pressure rises. Just as in the previous case, death is possible.
Preventive measures
Of course, it is impossible to foresee absolutely everything, but some simple recommendations for prevention can protect a person from the dubious pleasure of being offended and bitten by an ant. First of all, you need:
- Do not approach various apiaries without special clothing.
- When going out into nature or going into your garden, you should be careful with “ant houses”.
- When sitting down in nature, you should make sure that you are not positioned on the strategic path of a heap of ants.
Prevention
Special preparations for insects (horseflies and gadflies)
If you do not treat the skin with special anti-bite products, then getting rid of blood-sucking insects in natural conditions is quite problematic.
Below are recommendations on how to avoid gadfly bites:
- use special repellents that can be purchased at pharmacies and, in the summer, in supermarkets;
- Place mosquito nets on the windows, do not leave the entrances to the premises open;
- Keep a close eye on small children who may be attacked by insects;
- try to plan your vacation away from livestock farms and grazing areas;
- It is advisable to always have a first aid kit with the necessary first aid preparations on hand;
- insects are attracted to dark woolen clothes, so wear light-colored pants and shirts, try to cover your arms and legs when walking in the forest or meadow;
- these insects do not like strong odors, so perfumes and deodorants repel horse flies and gadflies, but attract bees and wasps.
What to do if bitten by a gadfly
If the process of introducing parasites into the body is already underway, then you do not need to treat the bites yourself, make sure that no additional allergies arise and, leaving everything, go to the doctor. What to do if you are bitten by a gadfly should only be decided by a specialist, since in most cases, without surgical intervention, the consequences can be more or less tragic.
The gadfly is an extremely dangerous fly, but in reality this whole terrible process, described above and somewhat reminiscent of horror films about the development of alien life inside people, happens in reality very, very rarely. Gadflies living in Russia prefer to reproduce at the expense of cattle and animals, but some threat to people still exists and cases of human infection with larvae are still recorded every year.
Bodfly bite: larvae
The body length of the larva depends on the stage of its development and varies from a few millimeters to 2–3 centimeters. At any age, it uses its jaws, so the bite of a gadfly at the larval stage is quite noticeable. You can read more about what a gadfly larva looks like here
, however, remember that it enters the body in the form of an egg, the size of which does not exceed 1 millimeter. In the form of a worm-like creature, it can only be seen at the moment of its natural exit from the body or early removal during surgery.