The ichneumon wasp differs significantly in appearance from the well-known insects with a sting and a yellow-black abdomen. It also leads a different lifestyle, is smaller in size and has a different structure. There are more than 100 thousand species of these insects on the planet, but in Russia you can find single representatives of the family. The wasp is a parasite. She lays her eggs on the body of other insects, and the hatched larvae live directly in the host's body. Many people are interested in the question of whether the ichneumon wasp is dangerous, what harm and benefit it brings to humans. We'll talk about this in our article.
Reproduction
The best time for breeding wasps is rainy and warm summer. In such weather, the population increases several times.
After mating, the female lays eggs in the body of arthropods, most often small insects. The size and number of clutches are individual for each species. Typically, about 20 larvae hatched from eggs parasitize the body of one victim. They feed on tissues, which gradually leads to the death of the host by the time of pupation. The larvae spend their “reserves” very sparingly: the victim never dies prematurely, because future riders will die along with it.
Nutrition
Adult megarhyssa perlata, which prefer to consume the nectar of flowers themselves, introduce their larvae into pests that breed in the bark of trees, depositing them in the passages made by these insects.
And ichneumon larvae , being extremely active in search of food, find their own prey, attaching themselves to the body of the victim. Most adult parasites do not eat the flesh of other insects, and some do not even eat anything at all. But they are looking for a suitable object to saturate their larvae.
Prey for parasites can include wasps, ants, beetles and caterpillars, and in some cases scorpions and spiders. Braconids are used to feed barn moths and leaf roller butterflies, but they can also harm people’s supplies, spoiling spices, confectionery, dried fruits, grain and flour.
Life cycle and mechanism of influence on the victim
The ichneumon wasp is a solitary insect; it makes its nest directly in the ground or in plant stems or tree bark. Its lifespan, as a rule, is short: for females it is about a month, and for males it is no more than 10 days. In some species, the larvae can overwinter in the body of the prey host and pupate only in the spring.
For the most part, adults are not carnivores, that is, they do not feed on other insects; For some species, nectar serves as food. But the larvae can be considered true parasites, given how reproduction occurs.
Female wasps lay eggs on the bodies or larvae of ants, wasps, beetles, caterpillars, spiders and even scorpions, on which the hatching larvae feed. During the process of laying eggs, the female parasite sits on top of her victim, resembling a rider on a horse, which gives the name to this entire family.
This parasitic insect has an amazing sense of smell, which allows it to sense even through the thickness of tree bark whether there are beetle larvae there on which to lay eggs.
By laying their eggs on the body of the victim, the females inject it with a paralyzing poison, turning it into a “zombie”. It takes less than a day for about two dozen larvae to hatch on a victim, and only a few days for them to go through all stages of development.
Throughout this period, they feed on the body of their “master”, while maintaining the viability of his body; it dies from exhaustion only before the time comes for the larvae to pupate.
The process of laying eggs
Such parasites are treasure hunters by nature. Distinguished by their excellent sense of smell, they run along dried up tree posts and look for walled-up larvae of longhorned beetles and golden beetles under the bark. At times, riders (insects) fly around the trunk in a curve, looking for the place where a large beetle larva was buried under the bark. And it’s even difficult to imagine how they can feel the larva through such dense bark.
Having found an area, the parasite settles on the bark of a pine tree and begins to pierce it with its ovipositor. Therefore, in most ichneumon races the ovipositors are enormously long; in some species they are even 7.5 times longer than the body. This is a whole drilling device. At first, the insect removes the “case” in which its “installation” was stored to the side, then it stands “on tiptoe” and slowly screws a thin sting into the bark. Along with this, the parasite is forced to spin, screwing the ovipositor deeper.
The drilling operation sometimes lasts several hours. Thanks to its special structure, the thin ovipositor easily passes through the thick bark of a tree, piercing into a hidden prey larva at a depth of 2-3 cm. Then the egg passes through this ovipositor.
Varieties
- Megarissa pearly . A very rare species, is under state protection. Lives mainly in forests. The color is orange, with white and black stripes on the abdomen. The thin, hard ovipositor is twice as long as the abdomen and can even penetrate tree trunks.
- Mutillids are represented by approximately 4 thousand varieties. The habitat is mainly steppe areas. Males, larger than females (their length is up to 3 cm), are dark brown or black in color, while females are orange or bright red with black splashes. The body is covered with thick long hairs. Females do not have wings, which is why they are called “velvet ants”. Unlike other species, they have a long sting, which they use to fight the owners of the nests, where they are going to lay eggs in their larvae.
- Pompilid wasps , or road wasps, are found in almost all regions of the world, but are especially fond of hot climates. There are up to 4900 species. Their brown or black body is up to 4 cm long, and the females retract their ovipositor into the elongated narrow abdomen. The second name is explained by the fact that they make their burrows near roads. Females use large spiders to lay eggs.
- Crabronids , or sand wasps, make their nests in the sand. Of the more than 8 thousand representatives of this species, approximately 600 are found in Europe. In appearance, thanks to the black and yellow stripes, as well as their small (up to 2 cm) size, they resemble simple wasps; they have the same well-formed wings and short antennae.
- Scaephids are represented by 800 species, living mainly in warm climates. Their dark-colored body reaches up to 6 cm in length. They build nests in the sand or sculpt them on the walls of buildings. To lay eggs, the female finds a victim, paralyzes it and carries it to her nest.
- Betilids are represented by 1800 species, about a hundred of which are found in Europe. Their narrow body is 1-10 mm long, there are no wings, so they are sometimes mistaken for ants. Such agricultural pests as cotton moth and grape budworm become their victims and breeding ground for the larvae.
Appearance
The size of the insect ranges from a millimeter to several centimeters, their color is also very diverse: there are black, brown, red, striped wasps, etc.
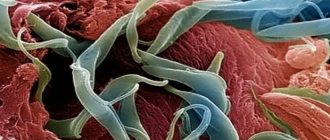
The photo clearly shows what this insect looks like and its characteristic features: a huge ovipositor, sometimes exceeding the length of the body, an elongated abdomen, well-developed wings and long antennae.
Appearance of an insect
Danger
The wasps are dangerous primarily for other arthropods, because parasitism leads to their death. This is the benefit of insects: they often fall prey to other pests that cause damage to human supplies, livestock, and agricultural crops. Equines, often being “super-parasites”, restrain the growth of their population. But is the ichneumon wasp dangerous for humans? The fear of these insects is not unfounded. Their body, like that of wasps, produces poison, so the bites do not go away without leaving a trace. But riders do not attack people just like that and do not lay eggs under human skin: they attack solely for the purpose of self-defense.
The poison is especially dangerous for those who have individual intolerance to the substances included in its composition. In this case, the bite can provoke a dangerous condition - anaphylactic shock. Even in the absence of hypersensitivity to the ichneumon ichneumon venom, soreness and swelling appear on the skin, which lasts for an average of three days.
Prevention from attacks by wasp wasps - careful behavior. If an insect is spotted nearby, there is no need to try to get to know it better or, on the contrary, actively drive it away with your hands. When visiting forests and meadows near water bodies, it is better to wear tight-fitting clothing that covers the entire body.
What to do if bitten by an ichneumon wasp? The action plan is universal for attacks by any insects:
But usually an encounter with an ichneumon wasp passes without any unpleasant consequences.
Riders are insects that are peaceful towards humans and never choose people as objects for parasitism. Their benefit lies in reducing the number of other pests. The only danger is their poisonous bite, which causes discomfort.
The harmfulness of creatures
Why is the earwig dangerous for humans: myth and reality
It’s time to figure out whether the wasp is dangerous for people. No, rather, on the contrary, these insects bring considerable benefits to humans, ridding plantations of bark beetles, voracious caterpillars and spiders. Individuals help protect forests and agricultural lands, maintaining natural balance. Many homestead owners specifically attract creatures to their territory to combat harmful beetles and spiders. Iridescent wasps are able to parasitize a huge number of pests, killing them and thus preventing damage to crops. Protecting food barns and agricultural fields with their help reduces the volume of toxic chemicals, which significantly improves the environmental situation.
It is worth remembering, however, that some species of ichneumon ichneumon bite quite painfully, but their bites pose a potential threat only to allergy sufferers and children.
Basically, this kind of damage does not pose a threat to humans and is completely harmless, so you can safely attract creatures to fight the annoying garden pests.
Wasp rider: what a bite looks like
The insect is not distinguished by aggressive behavior; it stings a person only in exceptional cases in self-defense. You can meet it in damp places - near a pond, in a forest and in a meadow. If you find an individual, you should not try to pick it up.
If an ichneumon wasp has left a sting, redness and slight swelling will appear at the site of the lesion. External manifestations are accompanied by itching. In a sensitive person, when an allergic reaction occurs, a large red spot, severe swelling and a rash develops all over the body.
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.
The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
Other tests
We recommend reading
Parasites of ciliates: description of representatives, danger to humans
03/29/202003/29/2020ecoliv94
Do lice jump on people's clean hair? Do they know how to fly?
08.03.202008.03.2020ecoliv94
Types of amoebas in humans: description, class, type and order, appearance and structure
03/07/202007.03.2020ecoliv94
Trichomonas Hominis in humans: description of the parasite, mating cycle, routes of infection
03/07/202007.03.2020ecoliv94
What to do if a wasp bites a person?
In some cases, hypersensitivity to the sting of a parasitic wasp wasp has been recorded. An allergic reaction occurs in young children and people with reduced immunity. To prevent anaphylactic shock or angioedema, it is recommended to provide first aid to the victim in a timely manner.
Symptoms and consequences
Most often, a wasp sting does not show up on the skin. But with a strong concentration of toxins that the insect injects during an attack, a slight redness appears. Itching and swelling may also occur. The most dangerous consequence of an encounter with a rider is considered to be scratching the wound. In this way, a person can independently introduce an infection. Symptoms of infection are swelling and tearing of the stung area, the formation of an abscess, and a rash.
If redness does not go away after 5 days, you should consult a doctor. To determine the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, the victim is given a referral for a scraping from the bite site, a general blood and urine test.
First aid
After a wasp attack, you should wipe the bite site with an antiseptic. Fukortsin, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide or alcohol (vodka) are suitable for this. If pain occurs, you can take analgesics and antispasmodics. To prevent the development of swelling, redness and rashes, anti-inflammatory medications are needed.
Allergic reaction
An allergic reaction is rare because when a long-tailed wasp stings, it injects a minimal amount of toxin that is not dangerous to humans. But there is always a risk of developing severe swelling or hives. Young children need to be especially closely monitored. If signs of intolerance to poison appear, you should urgently take antihistamines (Suprastin, Loratadine, Zodak), and then seek help from a doctor.
How to deal with insect pests: plant protection methods
In order not to disturb the natural balance, try to give preference to means of controlling plant pests that would not harm beneficial insects and birds. The main thing in protecting plants from pests is a system of preventive measures: it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. The main role is given to plant care activities, from the purchase of planting material to wintering or storing in storage.
Crop rotations prevent the accumulation of pathogens and pests in the soil and create conditions for normal growth and development of plants. It is known that nasturtium, mustard, and calendula, which release phytoncidal substances, help cleanse the soil of infection. Therefore, it is recommended to alternate planting bulbous plants with these annuals. The plants are returned to their original site after 5-6 years.
How else to deal with plant pests in the garden? An important point is soil preparation. In poorly drained, humus-poor soil, plants are more likely to get sick, grow weakened, and are attacked by pests. Before planting a flower garden, the area must be cleared of debris: branches, stones, wood chips, etc. Deep digging of the soil in the flower garden in the fall will help get rid of the larvae and eggs of harmful insects (cutworms, wireworms, earwigs) overwintering in it. When using composts or manure, you need to be careful not to introduce Mayweed, which often settles in compost heaps, into the flower garden. The larvae must be carefully selected and destroyed; they can be fed to chickens. Boxes for seedlings must be disinfected annually (with a solution of potassium permanganate or boiling water), and the soil in them must be changed (it is better to use ready-made mixtures for seedlings).
For most ornamental plants, areas with light, loose soils are more suitable. Heavy acidic soils, which promote the spread of fungal infections, are limed. To do this, fluff lime is added in the fall at the rate of 100-200 g per 1 m2.
If you purchased healthy planting material, then there will be much fewer problems. Therefore, it is better to make purchases in specialized stores. Try to avoid thickening the plantings; in such conditions, the plants lack nutrition and excess moisture appears, which also leads to the proliferation of pests and pathogens. It is necessary to systematically remove weeds, as they are a reservoir for many diseases and pests. In addition, they thicken plantings and compete with cultivated plants for nutrients.
Plant debris (foliage, stems, fallen flowers) often become a haven for pests. You cannot leave trash near plants. Carefully rake it and destroy it.
What kind of wasps are found in Russia?
Crabronids (sand wasps)
Compared to the tropics, the Russian climate is poorly suited for most riders. And yet, in Russian latitudes they are also found, although less frequently. The most common types:
Lifestyle and habitat of long-tailed wasps
The predominant habitat of most of the 100 thousand species of ichneumon wasps present today is the tropics. In temperate latitudes (in Russia) only a few varieties can be found. What they all have in common is the laying of eggs or larvae on or directly into the body of caterpillars and other insects. Not everyone is capable of stinging.
Wasp wasps do not look too threatening, especially those found in Russia. Their size ranges from 3 mm to 3 cm in length, and the chance of meeting the largest representatives is extremely low due to their extreme rarity. All types have different colors: from translucent to rich black.
Wasp rider
For your information! The insect has 6 legs, an elongated abdomen ending in a sharp ovipositor, a thin waist, transparent or colored wings, most similar to the wings of a dragonfly. There are species of wasps without wings at all, very similar to ants. A wasp with a long tail looks interesting.
Riders do not have a sting. Instead, there is a long ovipositor. However, the insect is quite capable of causing harm, since a special poisonous secretion is released from the ovipositor. Having pierced the skin of the enemy with its sharp end, the wasp injects poison, which has a paralyzing effect, although it does not pose a danger to the life of the insect. All riders are parasites, which are divided into 3 groups:
- ectoparasites that attach eggs and larvae to the body surface of other arthropods;
- endoparasites that introduce eggs into the body of other insects, using paralyzing poison;
- superparasites that are capable of infecting their own kind.
Preventing an attack
The main prevention of a rider attack is considered to be careful behavior in nature. You should not come into contact with the parasite, try to catch it or kill it. When getting ready for a picnic or to a pond, you should wear thick clothes with long sleeves. It is better to treat children's skin with repellents, which will also protect the baby from bites of mosquitoes, other wasps, and midges.
Wasps are parasites that are harmless to humans and attack only insects. Fertilized females hunt for caterpillars, beetles or other wasps to lay their eggs. The hatched larvae are very voracious and can completely destroy the prey in just 5-6 days.
Source
How dangerous is an insect?
The ichneumon wasp is not dangerous to humans and never stings for no reason. The bite is practically painless and is easier to tolerate than an attack by a regular wasp. A slight redness remains on the skin. Also, do not be afraid of parasitism and the appearance of larvae under the skin. Humans are not hunted or food for the long-tailed parasite.
Gardeners and gardeners often use parasitic wasps to protect their gardens from other parasites. Predators attack caterpillars, leaf beetles and other sucking beetles that harm crops. Flowers are planted around the site to attract equestrians.
Features of behavior
The insect's lifestyle is classified as a solitary wasp. Its behavior is associated with obtaining food, searching for potential victims, and laying eggs. The wasp rider does not form nests and does not live in large families. Individuals do not communicate with each other, do not give each other signals about danger or the location of victims.
Wasp rider
The insect leads an active lifestyle during the daytime; at night it prefers to hide among grass, leaves, and sit on a tree. She tries to stay away from the person’s house because nothing attracts her there.
The imago feeds on fruit juices and nectar, and some representatives of the genus do not need to replenish food supplies at all, but live no more than 14 days. Iridates are called predators because of the need to lay eggs in the body of other insects, arachnids, and worms.
The wasp rider is not distinguished by its aggressive disposition, but it senses its prey even under the bark of trees. Often it goes into the soil to search, digging holes, as sand and earth wasps do.
Biology
Female during oviposition.
The larvae of the wasp fly parasitize the larvae and pupae of horntails. Females have the ability to search for horntail larvae located deep in the wood (up to 40 mm). Then, using a long ovipositor, she drills into the wood and lays eggs on the larvae or in the passages they make. Adult larvae of the wasp pupate directly in the horntail tunnels and overwinter. One generation is replaced per year.
- Striganova B. R., Zakharov A. A. Five-language dictionary of animal names: Insects (Latin-Russian-English-German-French) / Ed. Doctor of Biology sciences, prof. B. R. Striganova. - M.: RUSSO, 2000. - P. 285. - 1060 copies. — ISBN 5-88721-162-8.
- Photo
- Photo (inaccessible link)
- Rhyssa persuasoria
- Riders
Lifestyle
Wood wasps form a hive, build oval-shaped nests, stay together, and feed the larvae together. In early spring, the young queen looks for a favorable place to build a future nest. The material for construction is obtained from wood. He spits saliva, waits a couple of minutes until the top layer softens, pulls off the thin film with his powerful jaws, and chews. The result is a viscous sticky mass, from which the female initially builds the leg, and then the first combs.
forest wasp
Lays eggs in each individual cell. After a few days, larvae appear from there, requiring a large amount of protein food to feed them. The female hunts beetles, flies, spiders, bees, and small insects. Breastfeeds offspring for about 14 days. At the end of the cycle, the larva pupates, after 2-4 days workers appear, on whom the queen entrusts the responsibilities of building the nest, arranging it, feeding the larvae, and protecting the hive. She herself only lays eggs.
At the end of August, special larger combs are added to the nest. There the queen lays special eggs, from which sexually mature females and males are born. At the beginning of autumn, the young generation mates. The males die, the females look for a secluded place for wintering under the bark of trees, in the cracks of wooden buildings.
Fighting methods
In the garden or garden
- Pour boiling water over the area where insects accumulate;
- lay out the traps in the form of wet rags on which the two-tails will be collected, then destroy the traps;
- dig the area deeply in the fall, this will help reduce the number of unwanted guests next year;
- Earwigs are afraid of the smell of vinegar; you need to place sponges soaked in vinegar on the area for washing dishes.
Readers interested in earwigs may also find articles about the following pests useful: fruit flies, bedbugs, woodlice, nematodes, cicadas, mole crickets, Colorado potato beetles, dust mites, potato moths.
Ant Bullet
Paraponera clavata is a species of large tropical ants from the genus Paraponera Smith, and the subfamily Paraponerinae (Formicidae), which have a strong sting. Called the bullet ant because victims of the bite compare it to being shot from a gun.
A person bitten by such an ant may feel throbbing and constant pain for 24 hours after the bite. Some local Indian tribes (Satere-Mawe, Maue, Brazil) use these ants in very painful rites of initiation of boys to adulthood (which leads to temporary paralysis and even blackening of the stung fingers). During the study of the chemical composition of the poison, a paralyzing neurotoxin (peptide), called poneratoxin, was isolated from it.
What do beneficial parasites usually eat?
Most species of such insects do not eat meat. The adult rider (insect) eats the nectar of flowers and hunts to continue its lineage. There are mature individuals that do not feed on anything at all. However, parasites are very fond of drinking, gathering near lakes and feasting on dew. They exist for no more than 2 months, some of them are evening or nocturnal insects. But at the same time, the favorite and main food of riders are:
- mealybugs;
- cicadas;
- sawflies;
- scale insects;
- aphid;
- bedbugs;
- pest butterflies;
- flies;
- whiteflies;
- burners;
- beetles;
- blood aphid.
Many will be interested to hear the answer to the question: “Is the insect rider dangerous for humans?” Absolutely not, and on the contrary, these parasites play an important role in nature, protecting garden plots with fruit trees and vegetables from the invasion of various pests.
Eulophus
Such a parasitic ichneumon is an external group insect of the winter moth caterpillars, some specimens of butterflies, the ancient moth, leaf rollers, cutworms, moth moths, fruit moths, and others. At different periods, the death of winter moth caterpillars was noted at 27-37% from this parasite.
Beneficial ichneumon insects fly out of cocoons after overwintering, in the second half of May, at the stage of mass flowering of cherries, pears, mid-season varieties of currants, apple trees, cherries and plums. The flight of the parasite lasts approximately 2 weeks and ends at the beginning of the summer season. Eulophus are fed with nectar from weeds and flowers of fruit crops in garden plots. Since the winter moth caterpillars are absent from the garden at this time, the insects look for the larvae of other pests (leaf rollers, cutworms) and infect them.
By August, the larvae of the new generation have already finished feeding, pupate, firmly attaching themselves to the leaf, and after leaf fall ends, they move to the winter hut in fallen leaves or make their way into the surface layer of the earth.
Siafu Ants
Siafu (Dorylus). These nomadic ants mainly live in East and Central Africa, but are also found in tropical Asia. Insects live in colonies that can number up to 20 million individuals, all of them blind. They make their journeys with the help of pheromones. The colony does not have a permanent place of residence, wandering from place to place. During their movement to feed the larvae, insects attack all invertebrate animals. Among such ants there is a special group - soldiers. They are the ones who can sting, for which they use their hook-shaped jaws, and the size of such individuals reaches 13 mm. Soldiers' jaws are so strong that in some places in Africa they are even used to secure stitches. The wound may remain closed for as long as 4 days. Usually, after a Siafu bite, the consequences are minimal; you don’t even need to call a doctor. It is true that young and elderly people are especially sensitive to the bites of such ants; deaths from complications after contact have been observed. As a result, every year, according to statistics, from 20 to 50 people die from these insects. This is facilitated by their aggressiveness, especially when defending their colony, which a person can accidentally attack.
Benefit or harm
Benefit
June beetle and bread beetle are extremely harmful insects, and typhia larvae can reduce their numbers.
In some years, Typhia morio parasitized in large numbers on the larvae of the bread beetle, and managed to form two generations in a year. This wasp lays eggs on beetle larvae
second year forgings. The still legless white wasp larva manages to molt several times and transition from a soft-bodied form to an arthropod. Sucking out the larva of the kuzka completely, it spins a cocoon on it, pupating inside it. Thus, typhus emerges from the first-generation pupa after several weeks have passed since the formation of the cocoon. In the second generation, both in autumn and winter, it does not degenerate into a pupa and pupates only in the spring.
Studying this species, it can be assumed that the reproduction of femorata and morio species is the reason for the appearance and disappearance of the beetle (in parallel with the reproduction of other parasites).
Many insect reference books list typhiid wasps as beneficial insects.
Harm
Usually wasps do not attack people first, but their attack can be provoked by a violation of the wasp family’s place of residence, a collision with a wasp, or any other contact.
The bite site may be inflamed and painful, swelling and an allergic reaction of varying degrees may occur.
In difficult cases, it is necessary to consult a doctor for help and an injection of an antiallergic drug.
Short description
Flies belong to the order Diptera. Unlike other insects, they have only one pair of membranous wings. The movable head is quite large in size, and the oral apparatus is a special proboscis. The purpose of the hind wings is to regulate balance.
The special skeleton of these pests and strong muscles allow them to develop high speed in flight and stay in the air for quite a long time. In addition to natural flies, synanthropic flies, which exist near humans, are considered widespread. Among them, the most famous are, for example, true flies, blue, green and gray blowflies and hoverflies.
Features of house flies
These pests are prominent representatives of synanthropic insects - those whose life is connected with human habitation. People constantly struggle with this type of fly. There are many quite effective means for this, but it is not yet possible to get rid of insects once and for all. Unlike bedbugs and cockroaches, flies are exclusively diurnal.
What are blowflies?
These insects got their name because they breed on animal corpses. According to the color of the back, there are gray, green and blue blowflies. The appearance of gray pests resembles ordinary house flies. Adult females do not lay eggs. They immediately hatch the larvae, having previously selected a suitable place for them, which can be the decomposing body of an animal, fruit rot or manure.
Green (carrion) flies have a beautiful appearance, despite the fact that they are partial to carrion and various impurities. They feed on rotting organic matter, where females lay eggs - up to 200 at a time. The resulting larvae leave the carrion and hide in the soil to pupate. This stage lasts 1-2 weeks. After this time, an adult fly emerges from the surface.
What are hover flies?
However, not all flies are pests. Hover flies are very reminiscent of wasps - both in external characteristics and in their behavior. In summer, they can most often be seen near Asteraceae or umbelliferous plants. The body of the insect is covered with black and yellow stripes, and on the semicircular head there are large dark brown eyes. The diet of adults consists of flower nectar.
The female lays approximately 100–180 eggs at a time, so 2–4 generations of these insects can develop during the season.
Hover flies are beneficial insects because they destroy aphids, which cause irreparable damage to trees in the garden.
Some gardeners try to create all the conditions for flies of this species to breed in their areas. To do this, they specially plant umbrella plants, such as carrots, dill or parsley.
Philanthus - bee wolf
Representatives of this species are distinguished by large heads with powerful jaws. Bee wolves are quite strong and large. The wasp's chest is black, there are 1-3 white stripes on its back, and its belly is bright yellow.
The bee wolf is a killer of honey bees.
Philantes were called bee wolves because they kill honey bees. When a bee collects nectar, the philanthus suddenly rushes at it, wraps its paws around it and stings it in the neck, after which the bee dies. After this, the bee wolf makes rhythmic movements with its paws and squeezes honey out of the bee's crop, and then licks it off with its tongue. When the bee wolf completely devastates the bee, he takes it into the hole, in which hungry offspring are already waiting.
Bee wolves cause serious damage to beekeepers when they settle close to hives, since the bees do not leave the hive and stop producing honey. In such a situation, the queen bee does not lay eggs, and the colony gradually weakens.