Many people do not know the difference between a bee and a wasp, since the insects are very similar in size and striped body color. But this is not just the first glance. There are a lot of differences between them: habitat, physiology, lifestyle. In the summer, through open windows, striped guests often fly into apartments, houses, and car interiors. To protect yourself and others from painful stings, you first need to understand the difference between a wasp and a bee.
What to do to protect yourself from insect attacks
There are a few simple rules that will help you protect yourself and prevent painful wasp and bee stings.
- If you encounter these insects, remember not to make sudden movements, as this will scare them, which means they will have to defend themselves. You should also not drive away, wave your arms, or try to drive away an insect that has landed on your clothing or your body. They are most likely attracted by the smell and want to explore the area, after which they will leave you alone and fly away.
- When walking in nature, especially in meadows where there are many flowers, do not walk barefoot. Very often there are many stinging insects in the grass.
- We all love to eat outdoors; on our table there are often aromatic fruits and sweet drinks; wasps and bees also like such treats, so when they hear the smell, they will definitely come to visit. Therefore, at the table you need to carefully watch the food you put in your mouth, and also, before drinking a sweet drink, look to see if there are any “guests” there.
- It’s better not to walk around with your hair down in nature; the fact is that insects very often get entangled in such “nets.” If you try to straighten the hair where it is, a bite will follow, because without realizing it, they will think that they are in danger.
- There is no need to give preference to too bright colors in clothes that attract them. They will also be attracted by the floral aroma of perfumes and some odors of decorative cosmetics; they should be as careful as possible.
- If you are driving a car with an open window and a bee or wasp flies in, there is no need to try to drive it out. Just stop and open all the windows, she will fly out of such a trap with great joy.
Who stings more
Not every person can objectively assess painful sensations. Not everyone has been bitten by both animals. American entomologist Justin Schmidt asked this question and decided to compare the sensations obtained from the bites of various insects. Over the course of several years, the scientist subjected himself to attacks by several thousand insects, after which he recorded his observations and sensations. After his experiments, he invented the scale. According to this scale, a wasp sting is like burning the tip of your tongue with a cigarette. He compared a bee sting to a skin burn from an open fire. Schmidt notes that in most cases a wasp sting is more unpleasant, but the peculiarity of a bee sting is that, due to the teeth, the sting gradually goes deeper and deeper into the skin, prolonging the painful sensation.
He compared a bee sting to a skin burn
Interesting anatomy of a wasp
Wasps belong to the suborder Hymenoptera. Just one look at the structure of the wasp allows you to understand why the suborder received such an unusual name: between the chest and abdomen of this insect there is a narrow “waist”, reminiscent of a long thin stalk in some wasps.
Thanks to this feature, wasps can easily fold their body almost in half and sting their prey from almost any angle - this allows them to win fights with other, sometimes even larger, insects.
The wasp's body is divided into three clearly distinguishable segments - head, thorax and abdomen, and has a strong external chitinous skeleton. The wasp's head is very mobile and is crowned with two antennae that perform many functions: they detect odors and air vibrations, with the help of them the insect can evaluate the taste of liquid food and measure the length of the honeycomb in the nest.
The photo shows the head of a wasp at high magnification:
Each wasp is endowed by nature with powerful jaws - mandibles. They serve both to feed on plant foods - soft fruits, berries, flowers - and to kill prey. For example, most hornets, when attacking even such large insects as cockroaches and mantises, practically do not use their stings, but make do with only strong jaws, with which they successfully crush the chitinous coverings of their victims.
In the photo, a wasp caught a fly:
The wasp's flight speed is quite high, but, however, is not a record for insects in general. That is why even well-armed striped predators often become victims themselves - for example, large predatory blackflies and dragonflies.
As for coloration, here too wasps stand out from all other insects due to their worthy diversity. For example, some species of paper and flower wasps have bright, contrasting black and yellow stripes and look unrecognizable.
Other species may have a completely different color: from rich black to turquoise and purple. In any case, the body color of these insects is always clearly recognizable (especially in the animal world) and allows them to avoid becoming a victim of an accidental attack, scaring off many mammals and birds.
The first photo clearly shows what the German wasp looks like - a common species in Europe:
And this photo shows a fire shiner, painted in unusual colors (due to the lack of black and yellow coloring):
This is interesting
It is wasps that have the largest number of insect imitators, which copy their color and appearance for protection from predators. An excellent example is the hoverfly, which looks very similar to a wasp. Birds and mammals, knowing that the body of an insect with black and yellow stripes usually has a dangerous sting, avoid it. Such a wasp fly itself is absolutely harmless.
Photo of a hoverfly - the black-striped coloring really gives it a menacing appearance:
It is noteworthy that the body of most wasps does not have such a huge number of hairs on the body, as, for example, bees and bumblebees. This is due to the fact that the last two groups of insects are typical pollinators, and the hairs help them increase the efficiency of collecting nectar on flowers. In the overwhelming majority of wasps, there is no need for such body cover; only some parasitic species have dense pubescence, which saves them from attacks by the owners of infested nests.
This is interesting
Some types of wasps do not have wings at all. Such are, for example, German wasps, parasitizing in the nests of their paper “brothers”. However, the lack of wings does not prevent them from having a sting and very strong poison.
The wasp has five eyes: two large faceted eyes, located on the sides of the head and providing a wide angle of vision, and three small ocelli on the forehead.
The main eyes have a rather complex structure, and consist of a great many individual elements that form a mosaic picture. They focus weaker than, for example, a person's, but perfectly capture any movement of objects in the field of view.
As for the additional eyes, each of them is more similar to a human and even has its own pupil.
In another photo of a wasp under a microscope, you can clearly see the extra eyes on the insect's forehead:
The sizes of wasps vary widely. For example, the giant Scolia from Southeast Asia grows up to 6 cm in length, and the Asian giant hornet is not far behind it - about 5-5.5 cm. But the vast majority of representatives still have sizes that are more standard for insects. In this case, usually (but, nevertheless, not always) the body size corresponds to the degree of danger of the insect.
Functions of the sting and features of bee venom
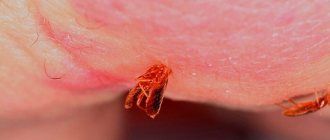
Bees initially had no sting and appeared in the process of evolution. Since this is a modified ovipositor, only females have it. A bee's sting looks like a sharp dark needle. If you look at it under a microscope, you can see numerous notches covering the surface.
The main purpose of the sting is to protect the life of the bee, its home and the lives of other family members. The structure of the sting makes it easier to insert it into the victim’s body and inject poison from a special reservoir.
Clinical signs
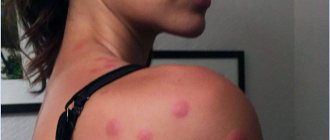
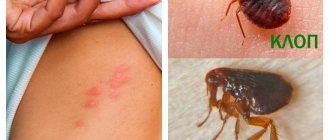
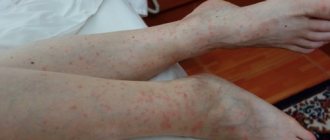
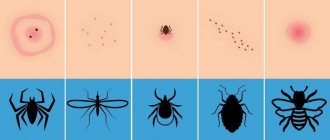
When the sting penetrates the body, a person feels a sharp pain in the form of a strong burning sensation. Sometimes it is difficult to see exactly who has bitten, for example, in the grass, when an insect stings the head or crawls under clothing. But they can be distinguished by the presence or absence of a sting. This is shown in more detail in the table.
Table. Differences between a wasp and a bee:
| Characteristic sign | Bee |
|
| Appearance | The bee is gray or brown, sometimes there are red stripes on the first dorsal half rings | Has a thinner body, bright yellow color with black stripes on the abdomen |
| What does a bite look like? | The sting will get stuck in the skin and escape from the insect's body. It contains a reservoir of poison that pumps it into the body for several minutes | There is never a sting left in the body |
| Number of bites | One individual can only sting once | The wasp can do this repeatedly |
| Unpleasant sensations | The pain is strong at first, then subsides. The swelling hurts and itches for several days. | Pain lasts longer, swelling has similar symptoms, but the sensation of pain and discomfort is slightly greater |
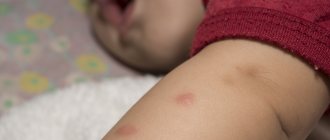
This is what a wasp bite into the soft tissue of the eyelid looks like
The general characteristic signs of the bite of any poisonous hymenoptera insect in our latitudes (wasp, bee, bumblebee, hornet) include:
- sharp pain;
- first, a red papule is formed with a red dot in the center (wasp) or with a sting (bee);
- within 30–60 minutes, local swelling and hyperemia forms around the site of penetration of the poison;
- During the first 12-24 hours, the area may swell more, especially if it is soft tissue, such as the cheek, calf, thigh, shoulder area, etc., on the fingers, nose, ear and other places where there is mainly skin and no muscle or fiber swelling, usually less;
- after the swelling has stabilized, the pain subsides, but does not go away completely, this is especially felt upon contact;
- itching appears;
- after 3–5 days, negative signs normally completely disappear.
- How dangerous is a karakurt bite and how to reduce its negative consequences
- How dangerous is a brown recluse spider bite?
- How dangerous is a spider bite?
Folk remedies
Symptoms disappear completely within a week. All this time the sore spot hurts and itches. To speed up tissue regeneration, folk remedies are used. They are also used if it is not possible to treat the wound with professional antiseptics.
- Baking soda. Making pasta. Add a little water, mix, apply to the bite area until dry.
- Laundry soap. Foam should be applied to the bite. Leave for 5 minutes.
- Plant juices. Celandine, dandelion, plantain, and aloe vera are used.
- Toothpaste. For medicinal purposes, a hygiene product with menthol is used. Leave on skin for 5 minutes. Instead of paste, use shaving foam.
- Onion. Squeeze out the juice or apply the paste to the sore spot. The product neutralizes poison and prevents infection.
On a note!
The juices of potatoes, carrots, beets, lemon, and grapefruit have anti-inflammatory properties. They make compresses, lotions, and simply wipe the wound.
Behavior and nutrition
Bees, bumblebees and the vast majority of wasp species are social insects; they lead a gregarious lifestyle. But bumblebees fly alone in search of food, and they can do this in the early morning, when the rest of the Hymenoptera have not yet recovered from sleep. Bumblebees warm up their bodies in a special way and go in search of food with the first glimpse of dawn, managing to collect nectar before other insects.
Bees stay in a small group, and wasps often circle in flocks of up to 2-3 dozen individuals. Bumblebees and bees collect pollen and nectar from flowering plants, and wasps feed on both plant and animal foods, often very intrusively and aggressively declaring their rights to any piece of food they find.
As soon as you cut a watermelon on the veranda in the summer or start making jam in the kitchen, the wasps are right there: they circle around the table, sit on your hands and food brought to your mouth. They willingly chew the meat into small pieces and take it to the hive to feed their larvae. Wasps, especially large ones, often kill bees and take their honey.
What to do if stung by a bee
The sooner you remove the sting, the less poison will enter the body. First aid may include one of the following:
- removing the sting with a clean sewing needle;
- applying a cotton pad soaked in a solution of alcohol and water to the sting site;
- wetting the affected area with salt water and potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate);
- stretching using cut raw potatoes.
After removing the sting from the body, it is necessary to treat the site of the attack with hydrogen peroxide or alcohol, make a cold compress to subside the swelling, and take an antihistamine.
Bee venom can pose a serious threat to human health. At the same time, the benefits of its use in medicine, thanks to its powerful antibiotic and antibacterial properties, have long been proven.
Who bites harder?
Hornets and wasps are the most aggressive; they have a thin sting with which they pierce the skin deeply several times. The bite is painful and burning, the affected area swells greatly. This may cause an allergic reaction. Wasps are also able to give a signal for the entire swarm to join them. These insects continue to live after being bitten.
It is difficult to anger a bee, but it leaves a sting in the body, striking only once, and subsequently dies. Bees sting only in extreme danger. Their bite is not so painful.
The most benevolent of all is the bumblebee; he attacks in exceptional cases. Its bite is less painful. Only the female has a sting; she does not lose it, and sometimes bites several times. A bumblebee sting can cause severe allergies and fever, and is especially dangerous for children.
Antihistamines
The active components reduce histamine levels, stop the pathological process, and eliminate allergy symptoms. Apply a thin layer twice a day. Contraindication is individual intolerance to the components. Do not use longer than 7 days. To enhance the effect, take tablets, syrup, or drops for oral administration.
Effective means:
- Claritin;
- Suprastin;
- Diazolin;
- Fenistil-gel;
- Psilo-balm.
Average price 300 rub. Available without a prescription.
On a note!
In case of a severe allergic reaction, as well as if antihistamines do not help, hormonal drugs are prescribed.
What you need to know about OS
These representatives do not have a strict scientific name. They belong to the stem-bellied order. They are divided into single representatives, since flower wasps and shrews, as well as social ones, which include hornets, they live only in colonies, and a swarm can number up to several thousand individuals.
They are quite aggressive, but this applies to insects. They are peaceful towards people, and, like bees, will not attack a person without any reason. Attacks on people often occur because they create a situation that threatens insects, so they try to defend themselves.
It is worth knowing that they have not only stings, but also very powerful jaws, which they use more often. When attacking their victims, they use their jaws, which are quite enough to win, but they use their sting in very rare cases. When attacking a person, they can use both jaws and stings.
The sting of these individuals is very smooth and, unlike bees, does not have serrations, so they can inflict several bites without harming themselves at all. Regarding the harm to human health of poison, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
If there are chronic diseases, a weakened immune system, or if there are allergic reactions, the body will have a hard time tolerating the incoming poison; the situation is further aggravated by the fact that one individual can sting repeatedly.
When using the sting, a smell is released that is heard by relatives, so it is likely that they will come to the rescue. Each bite is accompanied by severe pain, swelling, redness and inflammation.
The structure of the sting
Both types of insects have similar defense mechanisms. However, there are certain differences. If you carefully examine the structure, you will notice that wasps are characterized by a smooth sting with small serrations at the end. Usually the insect stings once, but can do it again. Bees have a strong, jagged sting. In this case, the large teeth are directed upward.
External differences between wasps and bumblebees
Let's understand in detail how a bee differs from a wasp and a bumblebee. Since we perceive 90% of information about the outside world with our eyes, let’s start with what we see, or rather with our appearance. The difference in size and body structure between the bumblebee, wasp and bee is significant. What are their external differences?
Wasps
Common wasp (Vespula vulgaris).
The body is thin and elongated, smooth, slightly lowered in the area of the abdomen and head. The chest and abdomen are connected by a thin bridge (this is where the expression “wasp waist” comes from). The front of the chest and head are black. The abdomen is brightly colored with black and yellow wide stripes. The wings are thin and transparent. There are antennae on the head. The body length is no more than 1.5 cm. Hornets, which are the largest representatives of wasps, can grow up to 5 cm in length.
A bee and a wasp differ in the structure of their sting. The wasp's weapon is similar to a needle - it easily enters the skin and is freely removed. When attacked, the insect can sting up to 5 times.
Interesting facts about OS
- Fact No. 1. Wasps living in a large colony know each other by sight. At the same time, insects living in small families do not have this ability.
- Fact No. 2. Not all of them build nests. There are species that prefer to live in burrows in the ground.
- Fact No. 3. One bee colony can produce more than 20 kg of honey per month. A wasp colony of the same size will collect at most a teaspoon.
Hornets
Common hornet (Vespa crabro).
The body structure is similar to wasps (it’s not for nothing that they are closest relatives). The color is also black and yellow (sometimes dark brown and yellow). Of all the insects described in the article, hornets have the most powerful jaws and the largest sizes. Any hornet is 2-3 times larger than a bee. They grow up to 5 cm in length. It is difficult to confuse an insect of this size with another. In flight it buzzes quite loudly. The sting is smooth. A hornet can sting many times. And given its size, it can be assumed that much more poison gets into the wound than when attacking smaller “relatives”. A hornet sting is more dangerous and painful.
Interesting facts about hornets
- Interesting fact #1. It is suspected that eastern hornets are capable of converting sunlight into electrical energy. But how insects use this is still unknown.
- Interesting fact #2. The ancient Mayan warriors used hornets as weapons of mass destruction. With the help of throwing devices, they threw hornet nests with all their inhabitants into the ranks of the enemy. Angry insects sowed panic, unrest and mercilessly stung everyone they came across.
- Interesting fact #3. Oddly enough, the hornets themselves are not aggressive. They only attack if there is a direct threat.
Bees
Honey bee (Apis mellifera).
The size of a normal bee is equal to or slightly smaller than the size of a wasp. The color is also striped, but paler. Some breeds of bees are completely grayish. The transition from chest to abdomen is smoother. The shape of the head is triangular. Unlike the wasp, the body of the bee is covered with hairs, which act as organs of touch. The paws are thick, black in color, with small hairs. Body length is about 1 cm.
Bees form a family consisting of three types of insects: the queen bee, the worker bee and the drone. The queen bee can reach 2.5 cm in length. In wasps, the queen is forced to take care of herself on her own.
Interesting facts about bees
- Interesting fact #1. Regular honey bees have 5 eyes. Two large compound and three simple eyes. Compound eyes consist of a large number of facets and are located on the sides of the head, and simple eyes are located on the crown of the head (in the drone, the simple eyes are somewhat shifted to the forehead).
- Interesting fact #2. Bees do not perceive the color red. That is why, when checking the condition of the hives in the winter hut in winter, beekeepers use red lights.
- Interesting fact #3. No matter how far a bee flies in search of nectar from its hive, it will always find its way home.
bumblebees
Moss bumblebee (Bombus muscorum).
Unlike everyone else, the bumblebee is a calm, shaggy fat fellow. Not aggressive. Attacks only in case of self-defense or defense of its nest. Its dimensions are more impressive than those of wasps and bees. Yellow-black wide stripes are visible on the body. The head is slightly lowered down. Some have completely black or reddish stripes. One of the distinctive features is the hind legs, or rather the lower legs. They have long hairs along the edges, which form a collecting apparatus, the so-called “basket”. Only females can boast of such a basket.
If you can roughly imagine the sizes of a bee, wasp and bumblebee, then it is better to show the size of a hornet in the photo. It will be clearer this way. After this, you are unlikely to confuse him with someone else.
The difference in size between a hornet and a wasp.
How does the sting work during a wasp attack?
If you doubt whether a wasp has a sting, put on a thick glove and catch it by its wings, and then press on its abdomen. The sting will be pulled out with each press and then hidden back.
It looks like this video:
During an attack, 0.3-0.4 mg of poison gets under the skin. Since the venom flows down the outer walls of the stinger, it is necessary that it penetrates deep into the skin, otherwise the attack will be ineffective. How many times does a wasp sting? Until all the poison is used up. 4-5 times if the bites find a target, and several hours if you simply provoke the sting to be pulled back and forth in laboratory conditions.
Differences between these insects
There are a number of signs by which you can easily determine what kind of insect is flying around - a bumblebee, a wasp or a bee.
The first sign is hairiness, which is distributed among insects in the following order:
- First place goes to bumblebee.
- Second place goes to the bee.
- Third place goes to the wasp.
If a bumblebee and a wasp are the same size, then they can easily be confused by color, but in any case the wasp’s body will be “bald.” Bees occupy an intermediate position in terms of hairiness, so for those who do not understand this, it may seem that the body of a bee is also devoid of hairiness. In fact, if you look closely, her body is covered with bristles, but they are not so long, so they are not too noticeable.
The coloring options for insects are so numerous that it is not difficult to distinguish between a bumblebee, a wasp and a bee. The bee is distinguished by dark brown shades. In cartoons, there is a certain stereotype, which is why honey collectors are drawn with stripes. If you look closely at the images of insects, their difference immediately catches your eye.
Bumblebees and wasps can have completely monotonous colors, including stripes. There are glossy wasps, which are distinguished by rainbow colors, and typhias, for example, are painted in a monotonous black color. However, most people believe that wasps have exclusively classic colors, with a predominance of yellow and black stripes. It should be noted that representatives of other families that do not have similar coloring can be dangerous and can bite just as painfully.
First aid for a bee or wasp sting
Bee and wasp stings are considered very painful. In addition, they can provoke serious allergic reactions. To avoid negative health consequences, it is important to provide first aid to the victim. To do this, it is recommended to do the following:
- Examine the bite area for diagnostic purposes. When a bee stings, you can see the sting in the wound. However, the wasp does not leave him. Under no circumstances should you press or scratch the damaged area. This will lead to accelerated entry of toxic substances into the systemic bloodstream.
- Rinse the bite site to remove dirt and remaining venom.
- Pull out the sting. This can be done with a needle, tweezers or pin. However, they must first be disinfected. If such devices are not at hand, you can try to pull out the sting with your fingernails. However, first you should wash your hands well and sanitize them.
- Disinfect the bite site. This can be done with hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, alcohol, iodine or regular soap.
- Take an antihistamine. In this case, the wound should be treated with antihistamine or antiseptic ointment. To do this, you can use “Psilo-balm” or “Fenistil gel”. When swelling occurs, it is recommended to drink Tavegil, Suprastin, Claritin.
- Remove swelling. To do this, it is recommended to drink plenty of water throughout the day. With the help of liquid, it will be possible to remove toxic substances from the body and improve the general condition. You can also apply a cool compress to the bite area. This will help remove the swelling.
In severe cases, you need to call an ambulance. In order for her to arrive, it is recommended to do the following:
- Apply a tourniquet above the bite area. This will prevent the subsequent spread of toxic substances.
- If you feel short of air and feel hot, remove tight clothing, lay the victim down and provide fresh air.
- In case of severe swelling in the neck area, shortness of breath and fainting, cover the victim and cover with heating pads filled with warm water.
- If there is no pulse and breathing stops, begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Consultation with a doctor is required in the following situations:
- bitten by more than 3 bees or wasps;
- the bite was on the face area;
- a wasp or bee stung in the larynx area, lip or tongue;
- before this, cases of angioedema or anaphylactic shock after an insect bite were recorded;
- Nausea and vomiting appeared, convulsions or fainting occurred after the bite.
Many people are interested in what to do if a child is bitten. If your baby experiences shortness of breath, nausea, high fever, heart rhythm disturbances, headache, or convulsions, you should immediately consult a doctor. If only local irritation and slight swelling are observed, standard care measures are sufficient. It is important to consider that children's bodies are more prone to developing allergies.
Wasps and bees are considered fairly similar insects. However, they also have many differences. The difference concerns appearance and lifestyle. The differences also affect the structure of the sting, the nature of the bites, and feeding habits. In addition, the benefits and harms that these types of insects bring differ.
Life activity
Wasps and bees differ primarily in their habitat. Bees can be found in flowering, flooded meadows. They are the most welcome guests of the spring garden. A good harvest is largely their work.
Wasps are more willing to eat fruits, berries, and sweets. And not necessarily fresh. They can confidently be found on rotting food waste. Given this feature, you need to be careful. They carry bacteria and fungi. They become a source of infection of healthy plants.
READ Worms in cats - photos with names, description
Even the larvae have differences: the toilers feed theirs with honey, royal jelly and pollen, while the aggressors need protein. To do this, other insects are destroyed.
Seeing a wasp near the hive, beekeepers begin to take protective measures. Otherwise, you can lose the precious families of working women.
Wasps are not capable of producing any useful product; they make their hives from a variety of waste. The food of wasps is quite varied. They will not disdain either fruits or nectar. The diet of wasps also includes delicacies, which include flies and other small insects.
Benefits of bee venom
Every product that bees produce is beneficial to humans.
Bee venom is no exception; it is used to relieve symptoms and treat various diseases. Bee venom is associated with painful sensations after a sting - burning and itching. But products made on its basis have a positive effect on the human body - nature has created many healing agents. Thus, thanks to the unique composition of bee venom, they increase hemoglobin levels, normalize blood clotting, lower blood pressure, and improve performance. The best effect can be achieved by combining the poison with useful health procedures - for example, sunbathing and swimming.
What do insects look like?
Wasps and bees from the order Hymenoptera.
Biologists have classified wasps in the suborder of stalked bellies, which belong neither to ants nor to bees.
- Bees have a round yellow body with black stripes, covered with hair. The colors are washed out and not too bright.
- The mouth has a special proboscis with which the insect pulls out nectar.
- The shape of the abdomen depends on the height of the position in the bee colony. Honey collectors have an ovoid abdomen, and the uterus is elongated. The belly of drones is rounded.
- The paws are dark in color, thick, with baskets for flower nectar.
- Bees have two compound eyes on the sides of their triangular head, which are not their only organs of vision.
- On the parietal and frontal lobes there are simple 3 eyes in the form of black dots or triangles. It turns out that bees have 5 eyes, two types of vision: simple and faceted.
This number of eyes allows you to see from all sides at once, the picture turns out three-dimensional.
- The shape of the wasp's body resembles that of an ant, and its color resembles that of a bee.
- The body is slightly elongated, drawn across the chest, and has no fibers. The color is bright, the colors are saturated: there are clear boundaries between the yellow and black stripes.
- The insect's eyes are located on the sides of its head. The wasp sees from both sides at once. On the forehead there are two segmented whiskers with olfactory organs, thanks to them the insect orients itself, moves, and sees when it is dark. With the help of its whiskers it senses dampness, cold, warmth and even the presence of gases in the nest.
- The mouth has strong jaws for grinding rough food and building nests.
- The tarsi are thin, without pollen baskets.
The body of insects is covered with a protective chitinous shell. Externally, a wasp and a bee are similar only at first glance. If you look closely, the differences become more noticeable.
Types of insects
Biologists have described more than five hundred species of bees that are found everywhere, not only living in Antarctica and deserts.
Important types of bees and wasps:
- single;
- public.
Solitary insects do not make nests.
Social wasps are divided into oviparous (queens) and non-oviparous workers.
Bumblebees are a type of social bee. They are larger than a normal bee. On their bright yellow body the villi are thick and long.
What does a bumblebee look like?
Autumn is the time of flight of young bumblebees. By winter, the males die. Females burrow into the ground and spend the winter there.
Bumblebees inhabit the empty homes of rodents and birds.
The main difference from their relatives is that in the box for raising larvae, not one, but several individuals can mature at once.
Prevention from a bite
People with allergies to bee venom should exercise increased caution. It would be a good idea to take the following precautions:
- Wear a protective suit or closed clothing with long sleeves. Although insects can sting through fabric, in some cases it can still provide protection.
- Do not wear perfume or wear bright clothes both when working in the apiary and when going out into nature. It attracts insects.
- Do not go close to the nests of wasps and wild bees, or the apiary without a protective suit.
- When walking, you should pay attention to the presence of large concentrations of stinging insects. It is better to leave such places in time.
- If there are such nests at your dacha, it is better to call specialists and get rid of them.
Bees are peaceful insects that sting only in exceptional cases. It is better to avoid large concentrations of them, be careful and not provoke them. In case of a bite, first aid must be provided and doctors must be called.
0
0
Copy link
Lifestyle
Insects also differ in their lifestyle:
- The flight of a bee is soft and leisurely. The nectar collector needs to visit many flowers without missing a single one. The wasp flies rapidly, at high speed, but can freeze in the air for a moment;
- All insects prefer to live in families, which mainly consist of ordinary workers, one queen and drones.
Domestication and Taming:
- Man made comfortable hives for domestic bees. Working individuals produce wax from which they build honeycombs;
- Wild individuals make their nests in tree cavities and mountain crevices.
Wasps also live in groups, where responsibilities are clearly distributed between them. Sometimes they prefer to live as hermits. Their nest is round, as if made of thin crumpled paper. In fact, they prepare it from rotten wood and dry plants.
Dirt and small debris are used to build the nest. They attach their nests to the walls of a house, large tree branches, thick grass, even in a thick plant stem, a discarded mitten, or a piece of cardboard.
In what situations does a bee sting?
For those who plan to live in the country for a long time, this question is especially relevant. Bees use their weapons extremely rarely - only in exceptional cases, and not for attack, but for defense, when they encounter a serious threat. But there may be other circumstances:
- Strong smell. Sensitive olfactory receptors help to recognize the aroma of flowers over vast distances. An insect may attack if it senses something unusual and frightening - for example, the strong aroma of perfume or sweat.
- The smell of smoke. Instinctively, the insect senses danger, because such a smell may indicate a forest fire. Therefore, she tries to escape and in panic can sting everyone who meets on the way.
- Clothing in dark colors. Beekeepers note that bees react differently even to the color of clothing - dark shades cause aggression in them.
- Poison from other bees. If you are bitten by one bee, then others may attack - they will feel the poison, which will be a signal for an attack.
Stages of development
Wasps lay their larvae in such a way that they cannot fall out of the nest. This is also prevented by the thick body, which clogs the honeycomb like a cork in a bottle. The adult, after completing the pupation process, simply straightens and climbs out. The female uses a special substance to attach her egg to the honeycomb, which allows the small larva to remain safe. After she gets fat, she is kept in the nest by her large body mass and lack of waist.
The life cycle of the larva lasts about two weeks. Then a thick cocoon forms around it and the pupation stage begins. After 10-14 days, this stage also ends - an adult is born.
Wasps are not particularly fond of children. If difficult times of hunger come, adult insects eat the contents of the cocoons.
There is an interesting feature in the life of these pests. When the adult cannot obtain insects for food, the larva secretes nutrients to support the life of the colony members. In this way the number of individuals in the nest is regulated. This usually happens during cold weather and prolonged rainy weather.
If the homeowner decides to finally deal with the annoying and dangerous invaders, then he should take into account the peculiarities of the development of the larvae. Young wild wasps fly out of the nest a few weeks after the larvae emerge. This is necessary to determine the timing of re-treatment of the colony with chemicals. Only after disinfestation has been carried out 2-3 times can it be said that all insects have been destroyed.
Found a hive of wild wasps - prepare for bites
Many people believe that wasps attack only if they are provoked, for example, by hitting the nest or trying to catch an individual with your hands. But this is a misconception. Insects defend their territory; at the slightest visible danger, they fiercely defend their offspring and the hive. And if tactile contact with a pest accidentally occurs, it will immediately attack. Unfortunately, a wild wasp sting can cause serious harm to health, especially if the attack is widespread.
In addition to the fact that they can carry E. coli, you should be wary of the following troubles:
- Severe pain at the site of the bite.
- Severe tissue swelling (allergies)
- Increased body temperature.
- Obstruction of the airways.
- Tearing.
- Fever and weakness.
- Anaphylactic shock.
There are cases when a person simply died after being bitten by these dangerous insects, especially their overseas “brothers”. The thing is that wasps, for example hornets, release strong poison through their sting when they pierce the skin. Of course, they don’t want to kill us, it’s just that in the wild this is how they paralyze their prey. To alleviate the condition of the bitten person as much as possible, he is given an antihistamine and pain reliever.
Diet
Harmless and sluggish-looking wasp larvae are insectivores. They themselves are not able to hunt and get their own food, but they willingly eat parts of insects that are delivered to them by adults.
Depending on the species, there are differences between individuals:
- feed themselves;
- feed on social wasps.
The larvae of European and Asian hornets cannot feed without the help of adults and cannot actively move inside the nest. They only slightly rotate their heads looking out of the honeycomb. The diet of adult insects includes flower nectar, sweet berry and fruit juice. And the younger generation prefers animal food, which is chewed for them by wasps and delivered directly to the nest. The excrement remains inside the cocoon until it completely transforms into an adult insect. Having spread its wings, the young individual leaves the nest, and the workers remove the secretions.
After the autumn fertilization of the female, wild male wasps die. In the vast majority of cases, females prepare small nests in the form of a depression in the ground or a paper shelter that is attached to walls or trees. The adult attacks and paralyzes any insect with poison and delivers it to its shelter. This is where the wasp egg is laid. After hatching, the individual begins to feed on insects. She does this in such a way that the “food” remains viable for a long time.
What does a wasp larva eat:
- caterpillars;
- butterflies;
- cockroaches;
- slugs;
- bees;
- spiders;
- little mice;
- small lizards.
Each species prefers different types of insects for laying eggs. Some eat only spiders, others like bedbugs. Some wasps lay eggs directly into a living insect. As the larvae mature, they eat their prey from the inside. Over time, the insect dies, and the young, fully formed individual climbs out.
What not to do
After a bite, it is forbidden to squeeze out the poison, since such actions contribute to the spread of the toxic substance and the penetration of a secondary infection. It is forbidden to scratch the wound or rub it for the same reason. You can't drink alcohol. Alcoholic drinks dilate blood vessels, increase blood circulation, which contributes to the spread of poison through the blood.
Remedies to help relieve inflammation from a wasp sting
When pathogenic microorganisms enter the wound, a secondary infection develops. At the site of the bite, suppuration and ulcers appear, and the scale of inflammation increases. In this case, it is prohibited to use hormonal external agents. Treatment is carried out with local antibiotics. An effective, affordable remedy is Levomekol, Tetracycline ointment. They also use combined hormonal agents containing an antibiotic - Elokom S, Fluorocort.
Wasp larvae as food reservoirs for adult insects
Interestingly, in times of famine, adult wasps belonging to collective species can use larvae as sources of food (more precisely, the nutrient fluids they secrete).
At each feeding, the adult passes chewed food to the larva, and in response it secretes saliva, which the feeder feasts on. Even if the adult wasp did not bring food, the larva will still share its secret with it. This phenomenon is called trophallaxis, and is a way to maintain the viability of an entire colony of insects during periods of prolonged rain or cold weather in the north.
The photo shows how an adult wasp feeds larvae:
Finally, the wasp larvae themselves are of gastronomic interest to many animals. Birds (for example, bee-eaters) willingly steal larvae from nests that are beginning to be built. Bears and honey badgers also enjoy destroying such nests.
And in Japan, there is a traditional dish called jibatinoko, which is wasp larvae boiled with sugar and soy sauce.
During the difficult war years, it was insects that allowed many Japanese not to die of hunger.
Methods of treatment with bee venom
Treatment can be carried out in different ways. Patients are given subcutaneous injections, ointments based on bee venom, and special baths are prescribed. Bee stinging is popular. It is important to carry out any procedures only as prescribed by an apitherapist, as there are many contraindications.
Bee venom is actively used in medicine for:
- vascular diseases;
- migraines;
- hypertension of the first and second degrees;
- intercostal neuralgia.
How does a bee colony work?
Some owners identify the inhabitants of the hive with other pets - goats, chickens, piglets - which is not entirely true. Bees, like ants, belong to the so-called “social” insects: a bee individual cannot survive alone, and a community of different individuals exists as a living system, a single superorganism.
Its basis is the nest, the uterus, worker bees, drones, and brood. Each element of the system performs certain functions and at the right moment, after all vital resources have been exhausted, is replaced with a new one.
And here the question arises: why do insects that hatched from the same eggs and had the same parents have different life spans - from 6 weeks to 6 years? Let's take a closer look at what affects the lifespan of three key figures - the queen bee, the worker bee and the drone.
You will find answers to questions about how relationships are built in a bee family and which bees make honey in the article on our website.
How long does a bee live after stinging a person?
Once a person is stung by the shoulder, death occurs within seconds.
The lifespan of a bee after stinging a person is only a few seconds. In the event of an attack not on people and animals, but on insects with a soft chitinous cover, there is a high chance of surviving by easily removing the sting after a bite.
A bee may not always use its weapon. If there is a lot of honey in its abdomen, then it is unlikely to sting.