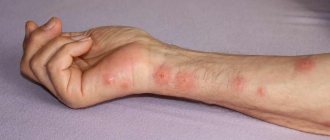
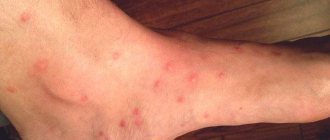
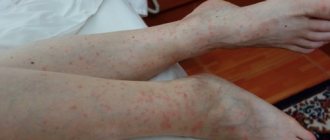
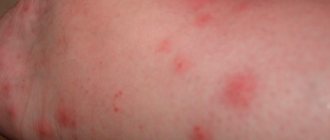
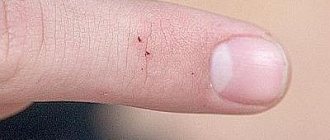
If redness and an itchy rash are detected on the skin, it is necessary to exclude linen lice bites. Small blood-sucking parasites are easily carried on clothing and are well camouflaged in underwear and bedding. The problem can be encountered after visiting a hotel, a hospital ward, or a holiday in a children's camp. Therefore, it is recommended to know the symptoms and treatment features, and remember the rules of prevention at home.
Symptoms of lice
Lice live on various parts of the human body. The main route of infection is through close contact with another person. Head lice most often infect children who spend a lot of time actively interacting with each other.
Body lice are rare these days. Most often they affect people leading an asocial lifestyle and living in unsanitary conditions. The habitat of body lice is in the folds of clothing, the thickness of mattresses, pillows or other pastel objects.
Pubic lice live on the scalp of the genitals and are transmitted from person to person during intimate intimacy.
The main symptoms of head lice include:
- • itching in the area of bites – scalp, back, limbs, lumbar region (occurs on average in 14-36% of cases);
- • the appearance of spots and marks on the skin from bites and scratches;
- • redness of the skin at the bite sites;
- • compaction and swelling of the skin;
- • feeling of discomfort, irritability, worsening sleep
The most common type of blood-sucking insect is head lice. Their active spread is indicated by the appearance of nits on the hair. Outwardly, they resemble dandruff flakes, but unlike dandruff, they are firmly attached to the hair. When you press on a nit, you hear a distinct, specific click.
Insect feeding
These insects feed exclusively on human blood. They need frequent and regular feeding; an adult needs to eat 4 times a day. The saturation process itself lasts about 5 minutes, during which time the parasite absorbs approximately 5 ml of blood.
Blood for an insect is not only food, but also the most important factor in the processes of development and reproduction. Without this product, nymphs cannot move to another stage because development stops. The female individual loses the ability to reproduce and lay offspring.
Nymphs require less food to fully satiate than adults, but at the same time they make much more bites. These insects live in colonies, but no coordinated actions within the family are observed. With severe infection, a person experiences great discomfort.
How and where do lice bite?
To accurately determine the presence of an infestation, you need to figure out where the lice bite. The location of the bites depends on the type of insect.
Traces from head lice bites are especially noticeable in the back of the head. The person experiences itching and a burning sensation. Linen lice crawl onto the human body in order to feed on blood. The locations of their bites are the lumbar region, arms, legs, and shoulder girdle.
Linen lice do not bite hairy parts of the body. The presence of bite marks and itching in the pubic area directly indicates damage to pubic parasites.
Consequences of contact with parasites
Many people don't even realize that body lice bites pose a health hazard. They can bite a person infected with a serious disease and transmit it further. In addition, the insect injects a special substance under the epidermis that anesthetizes and contains antibodies foreign to the human body.
If linen lice bite, the consequences may be:
- Infection in the wound after scratching, suppuration and the appearance of non-healing erosions.
- Insomnia and the development of neurosis with prolonged contact with parasites.
- Characteristic marks that cause embarrassment, forcing one to refuse communication with the opposite sex.
- An allergic reaction that intensifies and threatens with swelling, weakness, and drowsiness.
If lice bites on the skin do not heal for a long time, scarring begins, leaving unflattering scars with a bluish rim.
How they bite: the biting process
To find out how lice bite, pay attention to the characteristics of the insects. Lice cannot fly or jump, but they move quickly. This explains their penetration onto the head or body of a new carrier as a result of close contact
The insect needs a bite to gain access to human blood. The parasite's mouthparts are well adapted for biting through skin. At the same time, the louse secretes a substance into the wound that causes itching. The affected areas are susceptible to inflammation; when scratched, they can become covered with crusts and serve as a “gateway” for infection.
What can you do to treat bites and relieve itching?
Itching can be eliminated only if the parasites are completely eliminated. After pediculosis as a phenomenon is eliminated, itching will no longer bother a person.
There are many ways to combat parasites. For this purpose, both medications and traditional medicine are used. Let's look at some of them.
Therapy
Therapy for pediculosis Treatment of head lice is carried out with special medications.
To get rid of lice, treat the hair with a pediculicide, put on a special cap, and wait for the time specified in the instructions. Nits and dead individuals are combed out. To consolidate the result, it is recommended to re-treat after 14 days. It is also possible to destroy parasites using folk remedies. Therapy for linen lice is carried out somewhat differently. The main effort is directed to processing bedding and things. Wash at high temperature, chemically treated. Take a shower with tar soap or a special shampoo that contains insecticides against lice.
Pediculosis pubis is the easiest to treat. It is necessary to shave the hair on the pubis and genitals. Treat bites with alcohol. Or apply a special product and rinse off after the time specified in the instructions. They wash clothes, bedding, and underwear.
In each case, disinfestation is carried out in the house. The bites themselves can be treated with Zvezdochka balm, Bepanten, Fenistil gel, and calendula tincture.
The main methods of treating pediculosis
Combing
For this action you will need a special comb with fine teeth. Use it to comb out strand by strand for at least 30-40 minutes. To enhance effectiveness, the comb is soaked in vinegar, which helps destroy the secretion by which nits are attached to the hair. The disadvantages of the method include its duration and low efficiency. It is usually used to eliminate residual nits on hair after processing.
Wrap
To get rid of parasites, apply the prepared mixture to the hair, wrap it in a towel and leave it for a certain time. Cranberry juice, a combination of kerosene, shampoos and vegetable oil, a vinegar solution, and masks of crushed garlic and onions can be used as an active mixture. After the mixture is washed off, you need to comb your hair to avoid any remaining nits.
The disadvantages of this method include the risk of skin damage and burns. This is especially true for kerosene. Its prolonged presence on the hair will effectively eliminate lice, but can cause allergic reactions and even skin burns.
Rinsing and washing hair
Washing your hair with regular shampoos will not help get rid of parasites. Products such as tar or dust soap are more effective. After washing your hair, rinse your hair with decoctions of mint, wormwood, and wild rosemary. But this method is only applicable for minor lice infestations.
A haircut
This is the simplest and most radical method of eliminating parasites, in which they die, deprived of their natural habitat. Boys and men have their heads shaved, girls have their hair cut as short as possible.
Shaving and cutting with further combing are effective methods, but they are not suitable for girls who do not want to lose long hair.
Most traditional methods do not guarantee complete elimination of infection and usually require repeated use. Some may be unsafe or not suitable for use in children or pregnant women
The use of folk remedies is justified in cases where a person does not have access to more effective and safe medications. If you decide to use folk remedies, you need to be extremely careful and perform all actions under the supervision of a doctor.
Head louse
This is the most famous subspecies of this parasite, as many have suffered from it. Bites are detected quite easily. At first they look like normal redness, but as the colony grows and the lice feed, they merge into bluish spots.
Typically, bites can be found between the hair, as well as behind the ears and on the part of the neck where the hair ends. In men, lice can live in the beard and mustache, if any. In some cases, these parasites can even live in eyelashes or eyebrows, but such cases are rather the exception and show that the infection is already very strong.
Treatment methods are more varied in comparison with the pubic and veil subtypes. But, the main method is still shaving the hair from the head. If this method is not considered, then you need to purchase a special anti-lice shampoo at the pharmacy and use it. It is also necessary to comb your hair with a fine comb to remove nits from it.
ATTENTION: When infected with any type of lice, you need to examine your neighbors in the apartment to exclude their infection, or to take timely treatment measures. Inspections are carried out four times a month, every ten days.
How long do lice bites itch?
Bites can itch for up to three days; this is a purely individual indicator, depending on the body and skin condition, as well as the level of hygiene. The main thing is not to scratch the bites.
Prevention
In order to minimize the risk of infection, precautions should be taken, namely:
- • regular washing of the head and body, adherence to general hygiene rules;
- • regular examination of the child's head, especially if he attends school or kindergarten;
- • familiarizing children with the rules of hygiene and maintaining a safe distance when playing and communicating;
- • regular change of bedding - to prevent infestation with body lice;
- • exclusion of casual sexual relations in order to prevent infection with pubic lice;
- • applying drops of tea tree oil or lavender behind the ears, the smell of these products repels insects
Unfortunately, following normal hygiene rules does not guarantee complete protection against lice infestation. The main method of prevention is maintaining a safe distance when communicating with people whose appearance is suspicious.
Effective treatment
The most effective and safe means include “Paranit”. Its action is to block the respiratory system of lice and nits. The active substances dimethicone and mineral oils have no effect on humans, but are harmful to insects.
Advantages of the product:
- • the result has been confirmed in clinical trials and experience in various countries;
- • the possibility of using the “Paranit Sensitive” product for hair treatment in children over 1 year of age and pregnant women;
- • available in various forms – shampoo, lotion, spray – it’s convenient to choose the best option
- • in most cases, one application is sufficient to eliminate lice;