Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral disease that can be transmitted to people and animals through an Ixodid tick bite. If it enters the body, the spinal cord and/or brain are affected, and serious disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system develop. The encephalitis virus is curable, but in 25-30% of cases it is still fatal. In addition to people, dogs suffer greatly from encephalitis. Its development is caused by infection with intracellular parasites Babesia canis (canine Babesia), which also enter the animal’s body through a tick bite.
What symptoms may indicate infection with this virus? How to distinguish an encephalitis tick from a regular one? What to do if you are bitten and what measures to protect and prevent infection are there?
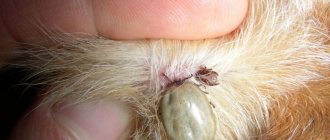
Encephalitis tick and its difference from the usual one: photo
The encephalitis tick and its difference from a normal tick are not visible in any way live or in a photo. An encephalitic tick will look exactly the same as a non-encephalitic tick or one that carries other common tick-borne infections - borreliosis, monocytic ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis.
The main carriers of encephalitis in Russia are two types of ticks: taiga ticks (Ixodes persulcatus) and forest ticks (Ixodes ricinus). They share possessions throughout the temperate climate zone of the country, from the northwestern to southeastern borders. These pests look almost identical.
- The parasites have an oval, flat body 4-5 millimeters long if the tick is hungry.
- Together with the head, the pest acquires a characteristic drop shape, tapering towards the head.
- Ticks are arachnids, so they have 8 legs, not 6, like other insects with which the parasite can be confused.
- Hungry taiga and forest ticks have a dark brown color, with a darker rounded heel immediately behind the head; as a rule, it has a diameter half as large as that of the body.
Due to the small size of the tick, details of its color cannot always be seen; the pest may look like a black or dark brown moving dot, but the shape of the body can still be identified. When the pest drinks blood, it swells to a spherical state and acquires a lead-gray color.
Sequence of actions when detecting an embedded tick on the body
If a tick is found on clothing or on the body, but it has not yet had time to attach itself, but is simply crawling in search of a convenient place, it is enough to simply shake it off. If discovered during a picnic, it is better to kill it - while people remain in one place, the parasite will be able to climb onto someone else again.
It is also useful to read: What diseases do ticks carry?
If a tick has attached itself, it must be removed immediately. Moreover, the faster this can be done, the lower the risk of infection will be.
On a note
In many instructions and literary sources you can find recommendations to go with an attached tick to a clinic or emergency room and trust a doctor to remove it there. This is dangerous advice. As a rule, a tick bite occurs in nature, far from populated areas and hospitals, and you will have to spend at least 1-2 hours on the way to the doctor. While the bitten person gets to the hospital, the bloodsucker will have time to inject an infectious dose of the virus under his skin. But if you remove the parasite immediately after detection, this may not happen. Therefore, you need to remove the tick as early and quickly as possible, even if it is not as aesthetically pleasing and competent as shown in numerous videos on the Internet.
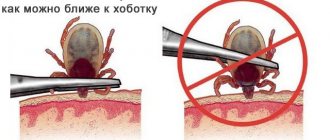
In the optimal case, a person has a special pincer at hand - a device with which the parasite is captured, rotates around the axis of its body and falls out entirely, without the risk of squeezing part of the pumped blood into the wound and without the risk of tearing off the head.
A tick remover is one of the most effective devices for removing ticks.
However, in most situations there is no such ticker at hand. In this case, you need to grab the tick under the body with your nails, turn it at least 90-180 degrees and pull it out. This can almost always be done without tearing off the head, but even if the mouthparts are torn off and remain in the skin, they can be removed with a needle in the same way as a splinter is removed.
It is important to understand that carrying a tick in your skin to the hospital for an hour or two is more dangerous than even in the worst case, tearing off the tick’s head and picking it out with a needle. If the body of the tick is torn off from the gnathosoma, the oral organs remaining in the skin no longer pose an infectious danger to humans: they have no salivary glands (they remain in the body) and no virus. Even such a head can be removed for a long time and carefully, without the risk of infection. If you are afraid to tear a tick, then by the time a person gets to the doctor or makes a homemade tick remover, the parasite will already have time to infect him with tick-borne encephalitis or borreliosis.
However, cases of the parasite's body being torn off from the head are very rare. Both of the most common carriers of tick-borne encephalitis - dog and taiga ticks - do not form a cement sheath around the hypostome in the skin when they bite, and therefore their jaws are easily pulled out and this requires less force than tearing the body of the parasite. That is, if you simply take and tear off a tick, there will almost certainly be no jaws left in the skin.
Further actions depend on whether the bitten person has been vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis. A vaccinated person only needs to remember the date of the bite to be tested for Lyme borreliosis infection in about a month. If there is no vaccination, then the sequence of actions should be as follows:
- After removing the tick from the skin, it must be placed in any tightly closed container, or, in extreme cases, in a bag, which is then tightly tied;
- After this, you need to find out whether the region in which the bite occurred is dangerous for tick-borne encephalitis. In fact, you can become infected with this infection anywhere in the temperate zone of Eurasia, from Sochi to Vorkuta, but in some zones the epidemiological threshold is relatively low, and the likelihood of infection is higher than in others. You can find out using special maps; they can be easily found on the Internet. If the bite occurred in a dangerous region, the tick must be taken to a special laboratory, where it will be examined for infection with the virus. Further actions will depend on the results of the study;
- If a tick is infected with a virus, the bitten person must be given anti-encephalitis serum (the so-called emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis). It reduces the risk of developing the disease (although it does not completely protect against it), and if it does develop, the disease will be milder and most likely will not lead to serious consequences. If the virus could not be detected, it means that the tick is not encephalitic and there is no danger of developing the disease for humans. There is nothing else you need to do in the near future.
This kind of serum is sometimes used for emergency prevention of TBE.
In any case, after a bite, you need to monitor your own condition for a month. If any nonspecific symptoms of the disease develop, you should consult a doctor and tell them when the bite occurred.
How to distinguish an encephalitis tick bite
As is the case with the insect itself, visually the bite of an encephalitis tick is no different from a regular bite. In both cases, the pest’s absolutely identical body sticks out of the wound, while its head is deep in the skin. The only and most effective way to distinguish an encephalitis tick bite from a regular tick bite is to submit the pest for analysis to a laboratory.
note
Red ring-shaped spots around the bite appear due to infection with Lyme disease (borreliosis), not encephalitis.
Encephalitis can be divided into two subtypes: European and Far Eastern.
- European encephalitis, as a rule, “starts” in the body in 2 stages. Symptoms appear within 2-4 days, then there is a lull for about a week, and on days 8-9 the central nervous system is damaged.
- The Far Eastern subtype develops faster, the symptoms that appear do not disappear, they only get worse over time, and it is this type of encephalitis that more often leads to death.
In both cases, symptoms appear 1-3 weeks after the virus enters the bloodstream. Analysis of the tick allows you to determine whether it could have infected you with encephalitis even before the first symptoms appeared. This greatly facilitates both the further course of the disease and its treatment.
In Moscow and the Moscow region, ticks are accepted for analysis:
- Private laboratories - Gemotest, CMD, Invitro and others.
- Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in North-East Administrative Okrug.
- Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Mytishchi.
You need to submit the pest to the laboratory as soon as possible after the bite, preferably on the same day. Tick analysis is carried out everywhere for a fee. Diagnosis of 4 infections, including encephalitis, will cost about 2,000 rubles. Results can usually be obtained within 1 to 2 days. It is also possible to do an analysis only for encephalitis, but it is still advisable to choose a comprehensive option in order to exclude the possibility of infection with other diseases. Borreliosis, anaplasmosis and ehrlichiosis are more often transmitted than encephalitis, and they also need to be diagnosed in time to avoid serious health consequences.
note
Different laboratories may have different requirements for the state of pests (only live/any), containers (only special containers for analysis/any container) and execution of related documents. Look for current requirements and conditions for submitting ticks for analysis to the organization where you will order the service.
Features of the bite
The parasite bites using a hypostome, which looks like a proboscis and allows it to attach to the victim and feed from it. It is also a sensory organ. Most often, ticks bite in the groin, lower back and armpits, abdomen, neck, chest and ears. At the affected area, due to the influence of the parasite’s saliva, a local inflammatory process and an allergic reaction in the form of redness occurs. No pain. Sometimes the skin at the site of the bite does not change. But evidence that it was there is an attached insect.
The site of the tick bite is characterized by slight redness
To determine when to be wary of tick bites, you need to focus not so much on the season as on the temperature and humidity. The most favorable weather for them is from +5 °C and air humidity from 80%. Such conditions are typical for May-June, as well as late August and early September. If the temperature exceeds 22 °C, parasites rarely crawl out of their shelters.
Having studied in advance the tick-borne encephalitis incidence map, you can decide whether it is advisable to vaccinate
Usually insects bite in cloudy weather before rain. You should be wary of them before 8 a.m. and at late times of the day—after 7–10 p.m. Ticks do not rise to a height of more than 50 cm, so they jump onto the victim from the grass or bushes. The parasite spends a long time looking for a place to bite. Sometimes you can remove it even before biting the skin.
The male tick does not attach itself, but quickly bites, feeds and falls off. But the female sits on the victim until she is completely saturated and increases in weight almost 100 times.
Encephalitis tick: symptoms and treatment
If you suspect that you have been bitten by an encephalitis tick, symptoms and treatment should only be diagnosed and prescribed by a doctor. All you need to do immediately after the bite is to have the pest tested. If encephalitis pathogens are found in a tick, you should immediately seek help and, within 4 days after the bite, carry out emergency prevention - administer immunoglobulin. Further treatment is prescribed only by doctors. Encephalitis should not be left to chance and self-medication. It could cost lives.
If for some reason after the bite you did not take the tick for analysis, but it still infected you with encephalitis, this may be signaled by the following symptoms for 7-21 days:
- Temperature from 38° and above
- Strong headache
- Muscle weakness
- Neck muscle tension
- Nausea, vomiting
The symptoms are in many ways similar to intoxication of the body and a number of other viral diseases, but in this case they are necessarily preceded by a tick bite. While feeding, the pests remain on the victim’s body for 3 to 10 days. The likelihood that a tick will leave you on its own after drinking blood is extremely low - it is impossible not to notice it on your own body for so long.
Are tick larvae dangerous?
The tick goes through several stages: egg, larva, nymph and adult. Many people believe that ticks are dangerous only at the stage of sexual maturity, but this is not entirely true. Both the nymph and the larva are capable of moving independently, albeit over short distances. The easiest prey for them is small rodents. But they still pose a threat to humans.
Even tick eggs can be dangerous. Ticks are not born with the virus, they receive it. This can be done in two ways: by biting an infected victim or together with the mother’s blood. In the second case, even the tick eggs are already infected.
Even though they cannot attack on their own, there is still a threat. The female lays her eggs in a dark, secluded place, but she often does this on grass and leaves. And in turn, livestock chews the grass and leaves. Thus, the eggs can penetrate the animal’s body and then it becomes a carrier. This largely applies to cows and goats. Milk from a cow with the pathogen will also be contaminated. The only way to kill the virus is by boiling it.
How to protect yourself from encephalitis ticks
If you are traveling to a region or area where encephalitis ticks live, you may want to get vaccinated against this disease in advance. Insurance companies also issue policies for tick bites, which can include a wide range of related services.
Any measures to prevent tick bites also remain relevant - use protective repellents and acaricides, wear closed clothing in the forest, take care of your summer cottage and, if necessary, order treatment from the SES for ticks and other pests. By combining all available methods of protection against encephalitis ticks for a specific situation at once, you can provide yourself with maximum protection.
Treatment of the disease
The treatment regimen directly depends on the patient’s symptoms, and even those who have been vaccinated should consult a doctor. During the acute period, you need to lie in bed under medical supervision until the symptoms disappear. It is important to follow a diet developed by a doctor depending on the degree of damage to the liver and gastrointestinal tract, as well as take ascorbic acid to improve the functioning of the adrenal glands and liver.
The cause of the disease can be overcome by anti-encephalitis immunoglobulin. It gives a positive effect within one or two days: the temperature drops to normal, the general condition improves, and meningeal symptoms become weaker. You can replace it:
- leukinferon;
- homologous polyglobulin;
- reaferon;
- serum immunoglobulin;
- ribonuclease.
To rid the body of toxins, vitamins, solutions of sodium chloride and glucose are administered intravenously. If the patient suffers from poliomyelitis, meningoencephalitic and polyradiculoneuritic forms of the disease, additional treatment methods are needed. If the cranial nerves are not affected and there are no disturbances of consciousness, prednisolone is prescribed. Along with the glucocorticoid, a gentle diet and potassium salts are prescribed.
Anti-encephalitis immunoglobulin and its substitutes are used to treat encephalitis.
Possible complications of encephalitis
The disease is dangerous not only due to its manifestations in the active phase, but also due to its possible complications. These include:
- meningitis;
- mental problems;
- dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system;
- deterioration of hearing and vision;
- constant headaches;
- fecal and urinary incontinence.
With proper rehabilitation, the negative consequences gradually disappear, but this takes time. After a severe form of the disease, they disappear within several years, after a moderate form - two to three months, and a mild one - within 2-5 weeks.
Ways of infection by ticks
Encephalitis ticks feed on the blood of any mammals, as well as birds. In the area where the disease is spreading, arthropod hunting objects are often infected with the encephalitis virus. When feeding on the blood of the victim, the tick also “drinks” the virus. This is the main way ticks become infected with encephalitis. The second way is transmission of the virus from the female to her offspring.
The arachnoids themselves do not care whether they have an encephalitis virus, so there is no way to recognize an infected bloodsucker “by eye” in the field.
On a note!
The only way to find out whether a tick is encephalitis or not is to submit it to a laboratory.