The onset of warm days makes it possible to go out into nature, which can often be overshadowed by the discovery of a tick bite on the body. In the hotter seasons, this problem is especially relevant and every year parasites are found even in those regions where they had not previously been noticed.
The bite itself does not pose a danger to humans; the threat lies in the fact that the parasite can be a carrier of the causative agent of serious diseases, the consequences of which are not always correctable.
In order to protect yourself, it is important to know what a tick looks like under the skin and what the difference is between a sucking parasite.
Types of ticks
There are about 54 thousand species of ticks in nature. All of them belong to the arachnid class of arthropods, but only the most dangerous of them feed on the blood of humans, birds and animals. They resemble small bugs, about 3-4 mm long, and have 4 legs with small hooks that help them climb in search of the bite site. Pathogens enter the human blood through the proboscis. The parasite has a well-developed sense of smell, thanks to which it senses the victim at a distance of up to 10 m by the heat emanating from the body and the smell of sweat.
The most famous types of ticks in our region are:
- ixodid (the most dangerous, a carrier of tick-borne encephalitis, lives on the lower branches of trees, low bushes, grass stems, loves shade and moisture, feeds on blood);
- subcutaneous (a source of demodicosis, can live on the human body for many years, feeds on dead cells of the epidermis, becomes active during a period of weakening of a person’s immunity, penetrating deep into the skin, causing burning and itching);
- argas (its habitat is cracks in buildings, bird nests, caves, attacks in the dark, has a painful bite, unlike the bite of the ixodid tick);
- bedding (lives in down pillows, mattresses, blankets, feeds on dead epidermal cells, invisible to the human eye).
Of all the listed species, ixodid ticks are the most dangerous.
Of these, only about 20% are carriers of such serious infectious diseases as:
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- borreliosis or Lyme disease;
- hemorrhagic fever;
- typhus.
Prevention
Prevention of diseases carried by ticks comes down to avoiding bites; in rare cases, vaccination will help protect you.
How to prevent ticks from biting you?
When going outdoors during tick season, the following preventive measures are necessary:
- use clothes with long sleeves and trousers that cover as much area of the body as possible, it is better if the clothes are light in color,
- wear hats,
- carefully inspect your body and clothes after a walk, comb your hair with a fine comb,
- also inspect your pets if they are walking outside (dogs often bring ticks into the house on their fur),
- use repellent before walking in the forest,
- do not tear off branches and try not to touch them, so beware of tall grass and bushes, stay in the middle of the path.
Photo: rawpixel.com / freepik.com
The effectiveness of vaccination, is it worth it?
You can protect yourself from tick-borne encephalitis and tularemia by getting vaccinated.
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis
In Russia, vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is indicated for residents of areas where encephalitis is endemic. You should receive a course of vaccinations in advance, at least 2 weeks before the start of the tick season. The vaccination regimen includes two doses of the drug with an interval of 1-3 months between doses and revaccination after a year. The completed course guarantees a stable immune response for 3 years.
If you missed the vaccination dates or unexpectedly went to a dangerous area, you can take an emergency course of 2 doses of the vaccine with an interval of 2 weeks. Revaccination will also need to be done after a year.
According to studies conducted in Russia, the frequency of development of stable immunity during vaccination according to the traditional scheme is up to 91%, and according to the emergency scheme – 88%.
Important! Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is the most effective measure to prevent this disease. Anyone who is in an area with an increased risk of contracting encephalitis or plans to stay in such a place should be vaccinated.
Vaccination against tularemia
In our country, people from foci of infection and workers in hazardous professions who have a high risk of infection are vaccinated against tularemia (for example, agricultural workers). Vaccination is allowed starting from 7 years of age.
For protection, one dose of a live vaccine administered subcutaneously or intradermally is sufficient. Revaccination is carried out every 5 years. The tularemia vaccine can significantly reduce the incidence of the disease and alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Important! Before vaccination, a doctor’s examination is necessary; the drugs have contraindications for administration. After vaccination, remain under the supervision of a specialist for at least half an hour in case of a sudden negative reaction.
Encephalitis insurance. Is it worth doing?
If you are not vaccinated and at the same time, due to the nature of your work, you are often in places where ticks live, it is advisable to conclude a voluntary health insurance contract in advance against tick-borne encephalitis. This will allow you not to think about the cost of treating this serious disease in the future.
The cost of the policy usually does not exceed 150-300 rubles. If you insure yourself and get sick, you will not be able to claim cash payments, but the insurance company will have to pay the costs of treatment and rehabilitation. The insured amount can range from 50 thousand to 1 million rubles, depending on the insurance company, insurance program and region. It is within these funds that you will be provided with the necessary medical care.
Typically it includes:
- examination of the victim and removal of the tick,
- laboratory testing of ticks for the presence of viruses,
- administration of immunoglobulin if indicated,
- hospitalization and treatment if the disease occurs,
- restorative therapy.
How to detect the bite site?
Ticks select areas of the body with the softest and thinnest skin, under which there is a network of capillary vessels. There are several such zones on the human body:
- head;
- neck;
- back of the ears;
- groin area;
- armpits;
- small of the back;
- breast.
When examining the body, you should first pay attention to these areas. Very rarely, but still a tick can attach itself to any other place. Once saturated with blood, the tick falls off the bite site. Females are considered more bloodthirsty; they can parasitize on the body for up to 6 days; males need 1-3 hours for this.
The tick lives on bushes, lower branches of trees, and grass at a level no higher than 0.5 m, so it easily gets on the body of an animal or person. He cannot bite through clothing or even nylon tights, so he climbs until he finds an open area of the body. He needs not only to pierce the skin with his proboscis, like a mosquito, but also to plunge headlong into it.
Treatment
Only a specialist can prescribe complete and competent treatment. The first test for demodicosis may show a negative result. The larvae and subcutaneous mites themselves are quite difficult to identify, so it is better to carry out the analysis several times for an accurate result.
Means necessary for both treatment and prevention:
- Vitamin preparations.
- Antiparasitic drugs.
- Immunomodulatory agents.
Medicines often prescribed by doctors for the treatment of demodicosis:
- Ointments: sulfuric, clindamycin, with metronidazole.
Sulfur ointment also shows effectiveness in the treatment of scabies in children.
- Klion.
- Metrogil.
- Amitrosole.
- Alcohol-based products.
Why do ticks need blood?
In order for the female to lay eggs, she needs protein contained in the blood. An insect can suck blood from several minutes to several hours. A hungry ixodid tick weighs 3-15 mg, and a engorged tick weighs 200-1200 mg. At one time, a tick can suck up to 1000 mg of blood.
The size of a hungry tick does not exceed 4 mm, but a saturated one can increase in size up to 1-2 cm. After a bite, the tick does not die like a bee, but continues to develop and multiply.
If a tick simply crawls across the body, then it is impossible to become infected from it. Infection occurs when pathogens enter the bloodstream with the insect's saliva. If a tick is found on clothing, it should be shaken off as quickly as possible, but not crushed.
Just a few steps and no problem
Call or request from the site
You call or leave a request on the website
Clarification of details and cost calculation
Our employee will conduct a detailed consultation and calculate the cost
Departure of a specialist at the appointed time
We will arrive at the time you specify, conduct an analysis and determine the methodology
Processing an object
We will treat the property, protect it from neighbors and give recommendations for prevention.
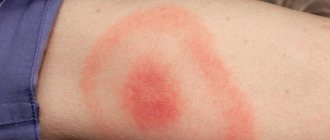
What does a tick bite look like?
In the absence of allergies, the bite site looks like a small red spot with a diameter of about 1 cm. How do you know that the bite was caused by a tick if it fell off after drinking blood? A characteristic feature of the bite of this insect is a single mark of a skin bite; there will be no other similar spots or dots nearby.
Over time, the spot may increase in size and swell if allergies are present. Numerous small bites in one place are characteristic of bedbug and flea bites. The bite of a mosquito and midge is much thinner than that of a tick.
The tick's saliva causes an allergic reaction, causing itching, burning, and mild pain at the site of the bite, but this is a completely normal reaction of the body. The danger is when a peculiar red circle has formed around the bite site, which is one of the signs that the tick is infected with borreliosis. The spot will increase in size and can remain on the body for up to 30 days. The diameter of the spot can reach 6 cm.
Diagnosis of demodicosis
With severe symptoms, diagnosing the disease is not difficult. You can suspect the presence of a tick during the initial examination, but to verify the diagnosis, a scraping is taken. In laboratory conditions, sebum and crusts are examined, and the presence of mites or traces of their activity is detected. After this, treatment is selected, which directly depends on the stage of the disease.
In order for the test results to be reliable, it is not recommended to wash your face, go to the bathhouse, or use cosmetics the day before taking them. Otherwise, the scraping may turn out to be unremarkable, and accordingly, the doctor will not be able to prescribe treatment.
Characteristic symptoms of a bite
Attention!
If you notice the slightest symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. A tick bite is determined not only visually. If the insect has been infected, symptoms may appear within 2-4 hours after the bite:
- chills;
- feeling of aching in joints and muscles;
- temperature increase;
- drowsiness;
- fear of light.
For people with allergies, the following are added:
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness;
- chills;
- swelling;
- lack of coordination.
One of the main signs that a tick is infected is an increase in body temperature to 38-39°C. This can happen either a few hours after the bite or 7-10 days (average incubation period) after it.
Features of the reaction of children and pregnant women to a tick bite
When children are bitten, the symptoms are somewhat different. The bite site itself takes on the appearance of a red spot measuring 7-10 mm. Immediately within an hour, body temperature may rise to 37-37.5°C. After 3-4 hours the following symptoms will be observed:
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- chills.
If such signs appear, the child must be urgently shown to a doctor with an explanation that he was in nature (forest, field, park area) and the possibility of a tick bite cannot be ruled out.
The first signs in pregnant women appear after 3-4 hours:
- temperature rise to 38-39°C;
- decreased blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- headache;
- weakness;
- fear of light.
In this case, the expectant mother should also definitely contact a medical facility.
Where to get vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis in Krasnoyarsk?
You can get vaccinated or have a tick tested in the city of Krasnoyarsk at the medical office. Here you will be greeted by helpful staff who will tell you how to get diagnosed, get vaccinated and make an appointment with a specialist.
You can register in one of the ways convenient for you:
- Online on our website medyunion.ru. Fill out the electronic form, indicating your contact information, doctor's specialization, and a convenient date and time for your appointment.
- Request a call back by indicating your name and phone number. Our managers will call you back within 15 minutes and answer your questions.
- Call the medical clinic reception at phone number +7.
What to do if you find a tick?
Very often the tick does not have time to fall off when a person discovers it on his body. In this case, you should know several prohibiting rules:
- Do not pour oil or alcohol on the tick and expect it to crawl out. It will not crawl out, and such an action will provoke an additional injection of saliva into the human blood, which increases the risk of infection.
- Burn the tick with hot objects, cigarettes or caustic liquids (gasoline).
- To sharply pull out the insect, in this case the head and proboscis will remain in the body, which leads to suppuration of the bite site.
- Use a needle or tweezers for extraction without disinfecting them.
- Try to crush the tick (this way you can drive it even further and stimulate a new injection of infected saliva into the victim’s blood).
The best and most correct option is to seek help at the nearest hospital or emergency room. In this case, the extraction will take place under sterile conditions, and the parasite itself will be sent to the laboratory for clinical testing.
Why choose us?
Readiness to immediately come to you on any day and at any time of the day.
Conclusion of a formal contract. Guarantee for all work performed. We are responsible for the safety and quality of processing.
Strict compliance with SanPin. Disinfection center specialists use BAYER and BASF products that are safe for you and your pets.
The complexity of the object for us is not a matter of increasing the cost. Our prices are the ideal combination of price and quality for the service provided.
The symbiosis of our own developments and insecticides with a cold or hot fog generator guarantees 100% effect.
Maintaining confidentiality and anonymity. You can be sure that no one will know about the treatments carried out by the disinsection station