A rather interesting question is how many legs a spider has. A very large number of people confuse these animals with other arthropods, in particular insects or mites. Therefore, this article will answer not only the question of how many legs a spider has, but will also make a comparison with ticks, since the latter also belong to arachnids.
It is especially important to consider that the ability to distinguish our hero from a tick is also important in practice.
In particular, the latter are carriers of a large number of diseases or simply provoke allergic reactions in the body.
Both the arachnids and the other have eight legs, but they can be distinguished even externally. What to say about internal features related to behavior or other aspects of his life. Well, let's figure out from the very beginning what spiders are in order to figure out how to distinguish them from ticks.
Origin of the species and description
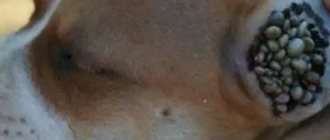
Photo: Mite
The tick is an arachnid animal that feeds on the blood of animals and humans. Nowadays, there are a huge number of varieties of this species, up to 40 thousand.
But two types play a significant epidemiological role:
- taiga tick - its habitat is the Asian and partly European parts of the continents;
- European forest tick - habitat is the European mainland of the planet.
Video: Tick
To this day, scientists have not come to a consensus on where exactly ticks came from and from whom they originated. The main thing is that over a million years of evolution they have practically not changed. The fossil mite is very similar to the modern primitive specimen.
The main hypotheses for the origin of ticks today are the following:
- neotenic origin. Ticks could have originated from chelicerate animals, which were many times larger, but were at an early stage of their development;
- origin from floating larvae of creatures that were unable to move and did not have a central nerve core;
- occurred by truncating the life cycle of an animal that was more specialized.
The latter hypothesis was even directly confirmed. Thus, a chelicerate animal was found with a clutch of hatched eggs. The larvae of these eggs are very reminiscent of ticks, incl. have the same number of legs.
Arachnids are part of nature
Each link of the ecological system has its own function. Millions of ticks inhabit the earth, water, plants and living organisms. They are an integral part of natural balance. Like other representatives of the fauna, arachnids are part of the food chain. What importance do ticks play in nature and human life? Soil species process organic matter in the soil. Through the efforts of small arthropods, fertile humus appears. As food for reptiles, birds and insects, mites contribute to the survival of these species.
Arachnids eat fungal spores, algae and bacterial plaque. Predators reduce the number of insects, nematodes, and worms. This feature makes them plant orderlies. Infecting animals with various diseases is a kind of natural way to control their numbers.
Families that live on agricultural crops, grain and flour reserves, and dairy products are harmful to humans. Ectoparasites of domestic animals and birds are also considered harmful species. Of the total number of existing groups of ticks, only a small part poses a direct threat to human life and health. These are ixodid and argasid species. It is necessary to dwell in more detail on where these ticks live, how they reproduce and feed.
Blood-sucking species
The ixodid or encephalitis tick is the most dangerous species for humans. These parasites are found everywhere, even in Antarctica, where they live on penguins. Ixodids are quite large individuals - female 3-4 mm, male 2-2.5 mm. On the back of the imago there is a dense scute; in the male it covers the entire back, and in the female only one third. The color of the head, legs and body is dark, from brown to black. When saturated with blood, the female increases significantly in size (up to 100 times) and changes color to gray.
Ticks reproduce in a unique way. Males fertilize females who feed on the animals' bodies. Bloodsuckers hold the record for the number of eggs they lay. One female leaves up to 17 thousand eggs in the ground. It is good that only a small part of the offspring survives. After birth, the larva feeds once, choosing a rodent as its host. After molting, she becomes a nymph. To transform into an imago (adult) one more feeding is necessary. In total, ixodid ticks suck blood three times in their life. Most species change hosts, the last being a large animal or human.
Attention. In Russia, two types of blood-sucking ticks are considered the most dangerous - the taiga tick and the dog tick.
Argas species - the body of the adult is 3-30 mm in size, it is flat and oval in shape. A hungry individual is gray in color, but after feeding it turns purple. Argas parasites live on birds, cats, and bite humans. Their saliva is extremely toxic. Mexicans compare Ornithodorus coriaceus bites to a rattlesnake attack.
What diseases do ticks carry?
After a parasite bite, you can become infected with several dangerous viral and infectious diseases:
- tick-borne encephalitis virus;
- tularemia;
- Lyme disease or borreliosis;
- relapsing fever;
- Marseilles fever;
- monocytic ehrlichiosis.
Attention. The risk of contracting one of the diseases carried by parasites increases with the amount of saliva carried into the bite site. It is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the body after visiting forests and meadows. If the bloodsucker is removed in the first hours, the likelihood of the virus entering the blood is minimal.
How a tick bites
A special feature of the bite is the simultaneous administration of active painkillers, so the victim does not feel it. Ixodids do not bite immediately; they can search for a convenient place for up to two hours. On the human body the parasite prefers:
- area behind the ears;
- neck;
- groin and armpits;
- scalp;
- small of the back.
A special suboral outgrowth of the hypostome, which has sharp hooks directed backwards, helps to firmly anchor itself in the chosen place. This structure makes it difficult to remove the parasite. With the help of sharp chelicerae, the bloodsucker immerses the head into the skin. Its saliva acts as an analgesic and anticoagulant. You can remove a tick from a person using tweezers, a loop of thread, or a device purchased at a pharmacy. The main rule is to remove it completely, avoiding leaving the head under the skin. The bite site must be disinfected with alcohol or chlorhexidine.
Attention. The number of people infected with encephalitis is 2-6% of those bitten by the ixodid species.
Where do ticks live?
The habitat of nymphs, larvae and adults is the forest floor, grass or low shrubs. They climb to the tops of plants, waiting for a new host. The parasite smells a person at a distance of up to 10 m.
Ticks: common features and differences between family members
Due to their small size and external similarity, ticks are mistakenly classified as insects. In fact, they belong to the class of arachnids. Their body has a solid structure without division into the chest and abdomen. The main difference between species is the number of limbs; insects have 3 pairs of legs. How many legs does a tick have? It has 8 legs or 4 pairs.
Ticks (Acari) belong to the phylum arthropods. Like other members of the group, they have a chitin-containing cuticle (body membrane). The main feature of this type is paired limbs consisting of several segments.
According to the way they feed, representatives of the Acari family can be divided into several groups:
- Parasites are individuals that feed on secretions and tissues of the host. These include blood-sucking Ixodidae (ixodid) species.
- Saprophages - feed on organic debris. Most representatives of this group live in the soil and forest floor, for example, oribatid mites.
- Phytophages are creatures that live and feed on plants. They are often pests, a prime example being the spider mite.
- Predators are individuals that hunt prey. What do predatory mites eat? Their diet includes small insects, worms, nematodes and their own relatives. People grow and use the arachnid predators Phytoseiulus and Amblyseius to destroy pests.
Life cycle of ticks
Arachnids, regardless of species, go through the same developmental path: egg, larva, nymph, adult. How long does a tick live? Their lifespan ranges from several months to two years. Most families grow and die quickly. The longest-living representatives of the genus Acari are armored and ixodid ticks. Blood-sucking parasites, in the absence of nutrition and unfavorable conditions, can slow down all body processes for a long time.
The state of diapause occurs in winter at any stage of development of ixodid species. In summer, at high temperatures and lack of moisture, they also freeze. Cases have been recorded where an adult tick was in a state of diapause for up to 8 years.
What types of animal are there?
In total, there are more than 54,000 different species of ticks, which are grouped into 6 orders (Opilioacarida, Holothyrida, Ixodida, etc.). Thus, on the territory of the Russian Federation the following types of ticks are most often found:
- encephalitic;
- ixodid;
- argassy;
- gamas;
- subcutaneous;
- scabies;
- bed.
Attention . Judging from the point of view of danger, the entire set of tick species can be divided into two groups: those that do not pose a danger to people (for example, bed ticks) and individuals that pose a threat to human health, and sometimes life (encephalitis, ixodid ticks, etc. .).
Who or what is a tick
Small, six-legged and crawling. Who is this? Definitely some kind of insect. In fact, when answering the question whether a tick is an insect or an animal, you need to choose the second option. These peculiar creatures belong to the animal world and are arachnids. Unlike spiders, there are no poisonous mites. That is, they do not use the secretion of their salivary glands to kill the victim.
The Latin name for ticks is Acari. The name refers to the entire subclass. And the branch of zoology that studies these arthropods is called “acarology”.
Interesting!
Ticks are not insects, but traditionally many acarologists are members of the Russian Entomological Society.
People often classify any small multi-legged life form as insects, so this confusion will continue in the future. The Akari subclass is also similar to insects in stages of development that are usually absent in more developed forms of life. There are four such stages in arthropods:
- egg;
- larva;
- nymph;
- adult.
Depending on the type of tick, the nymph also has from 1 to 3 stages of development.
Who are spiders?
Spiders are a fairly large order of arthropods that have at their disposal animals that live in various parts of our planet. How many of these animals are there? In the latitudes of the former USSR alone, there are 2888 species. In some latitudes they are harmless, they have eight legs or four pairs of paws (as we understand), this is the same thing. Spiders are mostly engaged in creating webs. The implementation of this difficult task is required of them because they catch prey in such nets.
Then they run with their nimble legs to the insect caught in the net, and there they eat it. This is to briefly describe these habits. What do spiders look like? No wonder many people confuse them with insects. To some extent, they are very similar , since they belong to arthropods. But it is very easy to distinguish a spider from an insect. The latter has only six legs, while the spider has eight. This is the main difference. The body of spiders consists of a cephalothorax with an abdomen located at its other end.