How to kill a tick to protect humans and animals. Important actions to take when a tick is found on your body. What is prohibited to do? What danger do infected ticks pose? What to do after removing a tick. How to kill a tick. Tips and tricks.
If it so happens that you find a tick on your body, then you should take the necessary measures to minimize the likelihood of contracting dangerous diseases. An infected individual may not transmit the disease to humans when bitten. This is due to the fact that the virus itself is found in the insect’s saliva, as well as in the fluid of the gastrointestinal tract. When a bite is applied under normal conditions, it does not share saliva with the victim and does not release dangerous fluids from the gastrointestinal tract.
But if the tick is incorrectly removed from the human body or dies before it is removed, then the likelihood of infection increases significantly. You should know how to kill the parasite to prevent infection.
Ixodid tick
There are more than 40,000 species of ticks on the planet. The parasites we fear belong to the Ixodidae group. These opportunists chose the blood of animals and humans as food. They carry human pathogens: tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis (Lyme disease), typhus, tularemia and others. Ticks appear in April and immediately begin to accumulate nutrients while tracking down prey. By the end of summer, their reserves are depleted.
Are all ticks dangerous?
In Belarus, the main carriers of human infections are representatives of ixodid ticks - the forest tick (also known as the dog tick) and the meadow tick. A tick goes through four stages in its development: egg, larva (0.5–1 mm in size), nymph (2–3.5 mm) and adult (7–15 mm).
All stages except the egg require blood feeding and can carry diseases. For clarity, we can say that the larva is similar in size to a small speck, the nymph is the size of a poppy seed, and the adult is a small spider the size of a sesame seed.
If a tick has sucked blood, it increases in size several times . At the beginning of summer, we mainly encounter small ticks (nymph stage), and at the end of summer, more often with adult individuals. The latter bite people less often because they are easier to notice and remove from the body or clothing.
Where do ticks live?
Ticks do not live on trees and do not fall from them, although they can fall by the collar from a small bush. They don’t live on birch trees either, but they love birch groves. They also love pine forests, contrary to the belief that the needles somehow scare them away. Nothing.
In coniferous forests, ticks are attracted to logging operations. But mostly they hang out on the grass, twigs, fallen trees, stumps - do not sit down to rest, losing your vigilance in the hope that a piece of wood will move you away from the grass.
For tent sites, choose trampled areas without grass. Upon arrival at your vacation spot, you can conduct an experiment: wipe off the sweat with a thin towel (kitchen towel, waffle towel) and fan the tops of the tall grass with it. The parasite, if there is one, will definitely react and attach itself.
Do ticks come to life in winter?
Ticks survive at low temperatures, but die in ice, which simply crushes them. Therefore, with the onset of cold weather, they begin to look for a secluded place for themselves where they can wait out the frost. Typically, such places are the crowns of trees, holes in firewood stacked for the winter. As soon as it gets cold, the tick goes into diapause and all its activity slows down. He returns to life only at the end of March. But with all this, a tick can come to life and come out of its diapause if it gets into a warm place, for example, into a person’s house. And he can get there with your help. Of course, he will begin to look for food for himself. You could bring fir cones from the street, where they are hiding; wood for lighting the stove.
How do ticks hunt?
The tick climbs onto a blade of grass, raises its paws and moves them from side to side. Sniffs the air - its olfactory organs are on its paws. It grabs lightning fast and tenaciously using special suction hooks. Thus, the tick cannot jump or fly up; it sticks harmoniously like a burdock. Both males and females hunt; larvae and nymphs do not pose a threat.
It is impossible to distinguish an infected tick by appearance - there are no differences. Both males and females bite, but females stick for a long time.
In the male, a hard shield covers the entire back, in the female - only the front part. This explains the bloodthirstiness of females: they enter more. They still have children to give birth to, they need a lot of food. Males bite quickly, sometimes humans do not have time to notice them. Females hang and drink for up to several days. The sucked tick secretes saliva into the wound, the first portion of which glues the trunk to the skin. This “cement” is also contagious, so you must avoid tearing the tick when removing it. Once attached, the tick moves straight upward from five minutes to an hour (depending on how quickly it finds a good place to bite), during which time it can be noticed and caught.
Long-term observations have shown that tick activity depends on a combination of many factors, so it is impossible to name the most dangerous time of day, time of year, location or weather conditions! You must always be vigilant!
Do ticks live in grass or trees?
Contrary to popular myth, ticks do not fall on us from above from trees, but live in the grass or on bushes, usually not rising above 1 m. They prefer shaded and damp places: the edges of mixed forests, paths, clearings, dead wood and brushwood. And ticks determine the approach of a person or animal by the concentration of carbon dioxide and thermal radiation.
As soon as the future owner approaches them closely, they cling to wool or clothing and crawl (always upward and quite quickly: 15–20 cm per minute), trying to get under the clothing and find a place to attach. And they find it more often where examination is difficult: the back, groin, axillary area, back of the neck and head.
Ticks do not bite painfully because they secrete special anesthetic substances into the wound. Further, the task of the tick is clear and prosaic: to get your blood - after all, it feeds on it. The entire process from crawling onto your pant leg to receiving your first red blood cells takes about two hours.
Why are there more and more ticks?
It turns out it's not the mites at all. They themselves are quite harmless. They were slandered. Ticks are carriers of infection; they are victims, not criminals. They are infected by small forest animals. If our country is completely enslaved by ticks, the number of cases may not increase, but even decrease. But if mice or hedgehogs are enslaved, epidemics are inevitable. In recent years, there has been an increase not in ticks, but... in mice. There are many reasons for this. For example, the amount of household waste in parks and forested areas attracts small rodents. Climate change - the warmer the winter, the higher the likelihood that both ticks and small animals will survive the winter well. Logically, after the frosts that tormented us this winter, there should be less of both. But if you ask a doctor from a vaccination center or an insurer, or a representative of a pharmaceutical company about the “tick-borne” situation, they will, of course, answer you with horror in their eyes: there are more and more ticks every year, MORE!
How to protect yourself from ticks? Anti-tick products
The main protection is proper clothing and timely inspection . When going to the “mite area” (uncultivated territory), seal your body as best as possible: thick cuffs on the sleeves, elastic bands. Tuck your T-shirt into your pants and your pants into your socks. Ideal clothing: thermal underwear type. Those who like to roll around in the grass can get a tick on the collar, so the collar should not be loose. Experienced tourists secure the sleeves and legs with elastic bands - any that attract you aesthetically, even if they are “monetary” will do. On his head is a bandana and a thick hat. Avoid tall grass, bushes, and do not sit on fallen trees, spruce branches, or logs. Examine each other every 15-20 minutes, paying special attention to all sorts of body folds and the neck under the hair. Check your clothes.
Tick repellents are divided into three groups: repellent - repel ticks, acaricidal - kill, insecticidal-repellent - kill and repel.
The first group includes products containing diethyltoluamide: “Biban” (Slovenia), “DEFI-Taiga” (Russia), “Off! Extreme" (Italy), "Gall-RET" (Russia), "Gal-RET-kl" (Russia), "Deta-VOKKO" (Russia), "Reftamid maximum" (Russia). They CAN be applied to the skin as well as clothing. Read the instructions, they indicate when to reapply the product.
The second group includes products containing permethrin: “Pretix”, “Reftamid Taiga”, “Picnic-Antiklesh”, “Gardex aerosol extreme” (Italy), “Tornado-Antiklesh”, “Fumitox-Antiklesh”, “Gardex-Antiklesh” , "Permanon". They CANNOT be applied to the skin. Only for clothes. All these drugs are extremely poisonous! Do not spray clothing on yourself or breathe in the toxic cloud. Remove it, process all the edges (cuffs, collars, trousers, hems of trousers), dry it, and only then put it on.
When you return home, do not throw things (in backpacks, bags) into the room - first inspect and shake them somewhere on the balcony or above the bathroom. The same applies to bouquets of flowers. Do not let pets run around the house after a natural outing; carefully inspect their fur for uninvited guests.
How can you protect your pets from ticks?
Alexander Ocheretny
deputy editor-in-chief of the newspaper "Palyaunichy i rybalo"
“I’ve been keeping dogs all my life, but I’ve started protecting them from ticks in completely radical ways over the last 18 years,” says Alexander. – Previously, you could forget to treat the dog and hope for luck, but now no, it won’t work that way.
For example, I can remove about 50 ticks at a time from my current dog; You yourself understand that an unprotected dog is now a suicide bomber. Moreover, if we talk about means of protection, then I am inclined to those drugs that are taken orally by the dog: I feel calmer when the dog is protected for a long time - the ticks cling, but die on it.
On a short-haired and light-colored dog they are better visible - ticks are black or reddish in color, they are easier to collect. For example, my previous dog, Drathaar, was “mite-colored”, plus thick fur - it was difficult. And now I have Italian spinone: it’s light, and it’s much easier.
How to remove a tick? Can I remove it myself?
The sooner you remove the tick, the better. There is a chance that he has not yet managed to infect you. Also, your body can cope with a small amount of the virus on its own, but not with a large amount. If you are in the city, immediately go to the emergency room (a list of emergency rooms in Yekaterinburg with addresses and telephone numbers is below). If this is not possible, remove the tick yourself.
How to remove a tick yourself: Buy a special hook for removing ticks at the pharmacy or use any other clamp (tweezers, strong thread). Do not squeeze the tick with tweezers, so as not to squeeze the contents of the salivary glands into the wound. Twist the thread closer to the trunk, stretch the ends and twist, rotating around its axis. We apply force to twisting, not pulling, so as not to tear - we pull just a little. If it does tear, cauterize the wound with alcohol and pull out the head like a splinter using a hot needle. When removing the tick, pull it strictly perpendicular to the plane.
There is no need to act outrageously over the tick, as many “experienced” people do - you should not lubricate it with oil, burn it, or otherwise contribute to its death. Before death, he will release all sorts of rubbish into the wound, possibly infected. Someone claims that when smeared with oil, the tick suffocates (does not die) and releases the victim. Experience shows that he doesn’t care about oil. If you are not sure that you can pull out a tick, get to the doctors.
This is what a drunk tick looks like
How to pull out a tick
If the attached insect was found in the forest, far from civilization, then you can eliminate the tick on your own. It must be remembered that any careless movement can lead to rupture of the insect, and if the head of the tick remains in the body, then this is very dangerous.
To properly remove a blood-sucking parasite, it is recommended to resort to one of the following methods:
1. Using tweezers (tweezers) . The instrument is treated with any antiseptic (you can use vodka) or heated over a fire. Using sterile forceps, carefully grasp the tick as close to the surface of the human body as possible. You should not grab the parasite by the abdomen, as it will easily come off the head. Having captured the “bloodsucker”, they begin slow rotational movements counterclockwise, trying to “unscrew” the tick.
2. Using thread . If you don’t have tweezers or forceps at hand, you can resort to using regular thread. Make a small loop. This “lasso” is thrown over the tick, trying to move it as close to the body as possible. Lightly tighten the loop, securing the insect. Then they begin to slowly twist the bloodsucker in the opposite direction clockwise.
3. Manual method . This is the most dangerous method. Since ticks can serve as a carrier of infection, it is necessary to protect yourself as much as possible from the risk of infection. Therefore, it is recommended to wear gloves or protect your fingers with gauze when removing the parasite. The insect is grabbed with the nails right next to the victim’s skin and gently twisted. It is important not to crush the tick.
After pulling out an insect, many people make a colossal mistake. They simply throw away the parasite. In the future, they are very worried whether the tick was infected. To protect yourself from such experiences, the elongated insect must be preserved (in an ordinary jar with a lid) and delivered for research. The analysis will take 1-2 days.
What to do next?
If you are not vaccinated against encephalitis, two weeks after the bite you can do a blood test for antibodies; if you are vaccinated, this is not necessary. Monitor your condition carefully. Lyme disease testing is done three weeks after the bite.
In any case, after a bite, go to the nearest medical center. Get direct instructions from doctors! Blood is tested for tick-borne encephalitis in any laboratory, including paid ones. The tick can be immediately tested for infections that it carries (the list of laboratories in Yekaterinburg is below).
What diseases appear due to such “neighbors”?
Inconspicuous bugs belong to saprophytes, that is, microbes that eat dead tissue in the body. They will not live on the surface of the human body , feed on his blood, they do not like infections. However, for those who have lung diseases or asthma, ticks in the bed will be dangerous, making it simply unbearable to be inside their own apartment. The bug itself is not dangerous, but its feces, located where a person sleeps, are an aggressive allergen and can cause exacerbation of asthma attacks and lung diseases.
If allergies appear, such as hives, swelling, runny nose or cough , during frequent attacks of bronchial asthma, a person should conduct allergy tests for the presence of dust mites, which are done in the laboratory. In most cases, this seemingly harmless saprophyte turns out to be the culprit of allergies. When the examination result is positive, then every effort must be made to get rid of the small insect.
You need to know that saprophytes do not like both high and low temperatures . This will help you successfully get rid of ticks in your bed. Therefore, when there is such an opportunity, one of the effective methods of getting rid of unnecessary parasites is to expose mattresses to the cold in winter, and in summer they should be exposed to the rays of the sun. The old method that grandmothers used when cleaning wool carpets will help perfectly: the carpet is laid out on a cover of snow and the dust is knocked out of it using a cracker. Those who care about their health should:
- constantly carry out wet cleaning in the apartment;
- wash bedding accessories in hot water;
- store sheets, pillowcases and duvet covers in a dry place;
- From time to time it is recommended to ventilate the pillows; after 2–3 years of use, it is advisable to change them;
- also, once every ten years, you need to replace mattresses, which are a favorite haven for house mites in the bed;
- When fighting insects, follow the basic rule: do not allow dust to accumulate in large quantities in the bedroom and other places.
How to deliver a tick for analysis
Place the tick in a glass container with a piece of cotton wool or cloth moistened with water, and cover with a lid. For microscopic diagnosis, the tick is delivered to the laboratory alive. Even individual fragments are suitable for PCR diagnostics. If it is not possible to immediately take it for analysis, store it in the refrigerator, but no more than two days.
The results of a tick study should not be taken as absolutes. A tick can be infected, but a person cannot. A tick may be harmless, but a person will get sick because he missed the bite of an infected tick (several ticks bit him at the same time). And so on. As experts say: the diagnosis is given to a person, not a tick. Even if the test is negative, still monitor your condition.
The appearance of ticks in the apartment
Where can ticks come from in the house? From simple dust generated in domestic conditions, which accumulates anywhere, from the cover of animals living in the house. These insects can breed:
- in a blanket made from wool and other materials of natural origin;
- in the bedspread;
- in a feather pillow;
- in upholstery of upholstered furniture;
- in carpets and mattresses filled with cotton wool.
Any of these essential household items accumulate dust, and mites thrive in such conditions. Inconspicuous creatures in bedrooms take advantage of the fact that the bed linen is not changed every day , the bedspread is not washed often and is also washed, and the surface of the floor under the bed is washed, well, if once a week.
Favorable conditions for the spread of mites are considered to be dust accumulating in the house, the warmth of the human body and constant humidity maintained by the body.
Plier sizes
Ticks in bed are so small that they can only be seen using a microscope. They look like simple bugs with six legs. Their body is a little short of half a millimeter . The limbs of ticks are equipped with peculiar suction cups, thanks to the presence of which they are securely attached to the surface, therefore an attempt to get rid of them using a simple vacuum cleaner will not give the desired result. Dead cells of the human body are the main source of nutrition for the inhabitant of the bed. Without even realizing their existence, those who are in the bedroom very often live together with ticks.
What diseases does a tick carry?
Tick-borne encephalitis. Viral disease. Incubation period: 3-25 days. Characterized by high fever, headache, and convulsions. Despite the danger of the disease, some survive it without any special consequences, but in general the risk of serious complications is very high.
Lyme disease. Bacterial disease. A person introduces Borrelia by scratching a wound. Therefore, the bite site should be thoroughly washed. The disease is treated with antibiotics and there is no vaccine against it. Incubation period: 1-20 days (usually 7-10) days. The main symptom: after 7-10 days, the spot at the site of the bite spreads, malaise, headache, and nausea appear. Lyme disease is no worse than encephalitis, but quite the opposite, since humanity has learned to fight bacterial infections, unlike viral ones.
Contrary to popular myth, infected ticks do not differ from their counterparts in color or other markings.
Do you always need to take an antibiotic after a tick bite?
This is a question with which it is better to consult a doctor.
Considering that the transmission of infection requires the fulfillment of several conditions at once, and side effects from the use of antibiotics are more common than the disease itself, emergency antibiotic prophylaxis after a tick bite is not carried out in Europe.
In our country, this issue is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health No. 338 of 2016, which states that emergency antibiotic prophylaxis is carried out individually as prescribed by a health worker - but no later than 72 hours after a tick bite.
Therefore, in situations where the tick has been on a person for more than 12 hours, appears to be engorged, and was difficult to remove, it is worth discussing the use of medications with a doctor you trust.
In any case, after an encounter with a tick, you should monitor the site of the bite for a month, as well as the general condition of the victim. The appearance of redness at the site of contact or high temperature with aching bones, nausea and (or) headache are reasons to consult a doctor.
When and how to administer immunoglobulin
An injection of gammaglobulin (immunoglobulin) is administered within three days from the moment of the bite. There is no point in placing it on the fourth day or later. If you are vaccinated, but you are bitten by several ticks at once, an injection is also given. Immunoglobulin does not provide a 100% guarantee against infection, but it softens the course of the disease. The cost is paid by the patient himself (about 700 rubles), children under 16 years old and pensioners are free. Course: three injections. It is important to know that the administration of immunoglobulin is an emergency measure and has its side effects. It can lead to a weakening of the immune system in the future, as there is a powerful rise and then a decline. After the injection, you need to monitor your condition. Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers should discuss the issue of administering immunoglobulin with a doctor, since this drug has not been tested in this population, and the risk must be justified. There is stupid advice about giving an injection as a preventative measure before resting - the condition may worsen. And you don’t need to bring immunoglobulin with you either. Although some people use a special container for storing ampoules with a cold element (for example, if they live in the country for a long time) or simply store them in the refrigerator door.
From the rusmedserver memo (rusmedserv.com):
We DO NOT RECOMMEND the use of immunoglobulin for emergency prophylaxis in camping conditions. This is a protein drug that can cause a severe allergic reaction (even fatal), which is impossible to cope with in the field without special training and medications. In addition, immunoglobulin requires strict adherence to storage conditions (+2 - +8ºС), which is very difficult to comply with in field conditions.
Is it possible to touch a tick with your hands?
If a pest is detected on the skin, it is recommended to immediately visit the hospital to receive first aid. After extraction, the insect is sent for examination, which should confirm or deny the presence of dangerous viruses. You should resort to removing the tick yourself in the absence of qualified assistance.
An insect getting on the skin and moving through the body without a bite does not pose a threat, since it is impossible to become infected with dangerous diseases in such a situation . When containing the parasite, you need to follow basic safety rules. A small risk arises when, when crushed, the contents come into contact with the skin with signs of damage (an open wound, a cut).
Once on the body, the parasite begins to choose the best place to penetrate. The insect can bite, but suction does not occur. It is at such a moment that an infection can be introduced into the victim’s body.
Interesting! The insect's proboscis resembles a bolt that is screwed in due to a fine thread.
Do I need to take antiviral drugs or antibiotics when bitten by a tick?
Antibiotics are taken only after a positive blood test result for borreliosis. If a tick has infected you with encephalitis, antibiotics will make the disease worse. Drugs like Anaferon, Arbidol and the like have no effect against TBE (tick-borne encephalitis). There is not a single drug against TBE in the world; vaccination is considered the only method of prevention. Doctors do not have a consensus on the drug Yodantipirin. It is actively advertised, but yodantipyrine has not undergone testing appropriate to international standards and cannot be considered a remedy against TBE. The substance antipyrine is not harmless, quite toxic. According to the principle “it’s better than nothing”, you can take it with you to the forest and, in case of a bite, take it according to the scheme, but keep in mind that there are more positive reviews about yodantipirin in advertising articles than from venerable doctors who are extremely skeptical about it .
Information from the Rusmedserver memo:
Clinical trials of the domestic drug yodantipirin do not meet modern requirements for assessing the effectiveness of a drug. This drug CANNOT be recommended for use. Recommendations for taking iodantipyrine instead of immunoprophylaxis should be considered a mistake.
Infection of pets
If you find a tick on your pet, you should follow the same recommendations as in the case of a person. Do not touch the insect with bare hands or treat the bite site. Be sure to contact a veterinarian, as infection is also possible.
In the case of animals, they are attacked by parasites much more often, so you should use specialized means that prevent infection. In addition, it is not always possible to carry out inspections after each walk, and it is not so easy to notice them in wool.
When choosing a specialized product, you need to take into account the animal’s weight, age, presence of diseases, and general condition. An incorrectly selected drug can harm the animal.
Tick vaccinations
The only remedy with a guarantee of safety against tick-borne encephalitis is vaccination. Discussions are raging on the Internet: is vaccine advertising a desire to make money from their production? Undoubtedly. But the fact is that ticks are unusually resistant to various chemicals: hikers share stories of how ticks calmly crawl over treated clothing without writhing in agony. And there are no products for children at all due to their extreme toxicity.
Vaccination scheme against tick-borne encephalitis
Vaccination takes place in two stages: the interval between the first and second vaccination is from one to seven months. Immunity to tick-borne encephalitis is developed two weeks after the second vaccination. The next vaccination is in a year, then one every three years. Accelerated vaccination scheme: administer two vaccinations with an interval of 14 days; you can go to the forest two weeks after the second vaccination.
In 2022, clinics will offer domestic vaccines (Klesch-E-Vac, EnceVir), for children and adults. Vaccinations against tick-borne encephalitis are well tolerated and provide a high protective titer of antibodies.
Don’t forget that you are ONLY vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis, so you still need to follow all protective measures.
Vaccination does not guarantee complete protection; approximately five out of a hundred people still get sick. But without critical complications.
Contraindications: any acute disease, for example, acute respiratory infections, or exacerbation of a chronic process. The vaccination is carried out a month after recovery. Allergy to chicken egg white is also contraindicated. During pregnancy, vaccinations against tick-borne encephalitis are not given; there are no restrictions for breastfeeding women.
Are all ticks encephalitic?
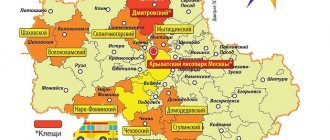
In Russia, the main carriers of tick-borne encephalitis are two types of ticks: taiga and dog ticks. The taiga tick is most often found in the forests of Siberia and the Far East, while the dog tick is found in the European part of Russia. An area where 1% of ticks are infected with the encephalitis virus is considered dangerous or endemic. As a rule, local authorities of Rosportebnadzor inform the population about which areas are dangerous at certain times, usually in early spring and early summer. Tick activity begins when the soil warms up to 5-7 degrees, that is, somewhere in April, and the largest number of bites occurs on the warm days of May and June.
How to calm down?
If you have been bitten by a tick, and you are shaking from the convulsions and immediate death floating in your mind’s eye, remember: even if the tick has an infection, it does not mean that you will 100% get sick. History knows many cases when a tick became infected, but the person ultimately remained healthy. There are a lot of nuances here. It happens that there are unbearably many ticks in a certain area, but the encephalitis level is low. It is not so easy to pick up a sick tick; the number of infected individuals varies from year to year, but on average in the Urals (approximately) 5-9% of malicious spiders are carriers of diseases. Not every second one.
The most important thing is not to panic. It is masterfully pumped up by manufacturers of vaccinations and repellents, and insurance companies. An ordinary consumer in his life has to be “infected” by many myths inflated by marketers. We are already massively “sick” with dysbacteriosis, cellulite and many other invented diseases. Panic sentiment is clearly visible in forums where mothers of children under one year old communicate: is it possible to vaccinate a child at 6 months? At 8 months? If a mother leaves a child under one year old in the “tick” zone unattended for 15 minutes or longer, then the mother should be given injections, immediately and any kind - just for tone.
Are animals a risk factor?
The need to feed on blood has developed in the tick in the process of evolution a very wide range of donor hosts - from rodents and birds to dogs and humans (for example, in the USA the most common tick is called the deer tick).
Therefore, dog owners need to be especially careful: ticks that stick to their pets while walking can spread to humans.
Thus, American scientists who studied households in areas where ticks are often found found that if there is a dog or cat in the house that roams freely on the street, then the likelihood of finding a tick on one of the household members is twice as high as in families without pets.
To be fair, it should be noted that more frequent exposure to ticks on oneself has not led to an increase in the incidence of tick-borne infections among pet owners.
Where to submit a tick for analysis in Yekaterinburg
Laboratory point: st. Gagarina, 49 362-87-87, Mon-Fri 8:30-15:30 (break from 12:00 to 13:00) Cost: tick-borne encephalitis virus antibodies - 300 rubles. Lyme borreliosis - about 700 rubles. tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme borreliosis, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis - 1000 rubles.
Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology: st. March 8, 177a 210-48-26, Mon-Fri 9:00-16:00 (break from 12:00 to 13:00) Cost: tick-borne encephalitis virus antibodies - 300 rubles. Lyme borreliosis — 677 rub. tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme borreliosis, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis - 1000 rubles.
Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Ordzhonikidze district: st. Avangardnaya, 5a 307-42-99, 307-40-77, Mon-Fri 8:30-16:30 (break from 12:00 to 13:00) Cost: tick-borne encephalitis virus antibodies - 300 rubles. Lyme borreliosis — 667 rub. tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme borreliosis, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis - 1000 rubles.
Where to go if bitten by a tick (list of emergency rooms in Yekaterinburg)
Let us remind you that you cannot delay this! Firstly, the tick needs to be removed as quickly as possible, and secondly, if you go to the emergency room, say, 4-5 days after the bite, there is no point in giving immunoglobulin! In addition, the specialist will remove the tick correctly.
Leninsky and Verkh-Isetsky district (South-Western part) - MBU GB No. 36 “Traumatological”: st. Saperov, 3, tel. 257-57-01, 251-40-51 (24 hours a day)
Verkh-Isetsky and Zheleznodorozhny districts - MBU Central City Hospital No. 2: st. Chelyuskintsev, 3/5, 389-90-71 (24 hours a day)
Oktyabrsky, Zheleznodorozhny (center), Verkh-Isetsky (except for the South-Western) districts - MBU GB No. 36 “Traumatological”: st. Bazhova, 124, a, tel. 350-25-82, 350-32-59 (24 hours a day)
Oktyabrsky district (Kompressorny village) - MBU GB No. 36 “Traumatology” (emergency department): st. Central, 2, tel. 252-00-12 (24 hours a day)
Kirovsky district - MBU Central City Hospital No. 7: st. Vilonova, 33, tel. 341-73-03 (24 hours a day)
Ordzhonikidze district (Elmash) - MBU Central City Clinical Hospital No. 23: st. Old Bolsheviks, 9, tel. 389-93-40 (24 hours a day)
Ordzhonikidze district (Uralmash) and Zheleznodorozhny district (sorting) - MAU GKB No. 14: lane. Suvorovsky, 5, tel. 380-13-95, 380-13-93 (24 hours a day)
Chkalovsky district (Khimmash) - MBU Central City Hospital No. 20: st. Zoya Kosmodemyanskaya, 42, tel. 258-22-34 (24 hours a day)
Chkalovsky district (except Khimmash) - MBU Central City Clinical Hospital No. 24: lane. Rizhsky, 16, tel. 297-92-85 (24 hours a day)
All districts of the city (child population) - DGP No. 13: st. Eremina, 15, tel. 388-30-18, (daily from 8:00 to 20:00)
First children's emergency room - Children's hospital No. 13 (Daily from 08:00 to 20:00)
st. Butorina, 10, 1 floor, tel.+7 (343) 388‒30‒18 (inquiry) +7 (343) 289‒88‒00 (contact center)
Danger to humans
These blood-sucking creatures pose a great threat to humans, as they can infect dangerous diseases. In this case, it does not matter at all whether it is found on the body, or whether it drank blood and fell off on its own; it is its bite that is dangerous. Therefore, it is very important to contact medical institutions when it is detected.
If you manage to save the insect, you can submit it for analysis, which will show whether this individual is infected. If you remove it from the body yourself, then you need to put it in a glass container along with a piece of damp cloth, which will not allow it to dry out. Analyzes are carried out with live insects, which allows you to obtain accurate results. If the parasite is dead, burst, or there is only a fragment of it, then research can be carried out, but the result will not be accurate.
In cases where you have not noticed the tick itself on your body, then symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately. These parasites can transmit diseases such as encephalitis and Lyme disease.
Lyme disease
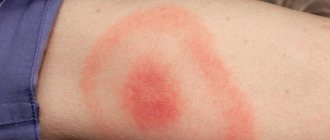
This disease is manifested by such symptoms as fever, headache, body aches, weakness, and a cough and runny nose may also appear. These symptoms are similar to a cold or even the flu, so a person may not think about having a dangerous infectious disease. The main sign that you definitely need to pay attention to is the appearance of a large red spot on the body, which has a clear outline.
This disease affects the nervous and lymphatic systems. It is very important to start treatment at an early stage, since brain activity suffers, memory may deteriorate, and disturbances in thinking processes occur. The facial nerves are also affected as they are damaged.
If the correct treatment is applied, the disease can be completely cured. In situations where treatment is not applied, complications occur, which in severe forms are not always amenable to treatment.
Tick-borne encephalitis
This disease is very dangerous with complications. Encephalitis manifests itself with the same symptoms as the previous illness, only there is no reaction in the form of a circle on the skin.
If left untreated, the nervous system is affected; this process can occur as early as a week after infection. The person experiences severe headaches and epileptic attacks may occur. Next, internal organs are damaged, the liver, kidneys, etc. are destroyed.
Regarding children, the disease poses an even greater danger for them, since children cannot correctly describe their condition and talk about their feelings, which for parents does not allow them to create a complete picture and correctly respond to the situation. It is very important after each walk in nature to pay maximum attention to examinations and, at the slightest suspicion, consult a doctor.
In addition to the above diseases, ticks also carry other dangerous infections, which include typhoid, ehrlichiosis, fever, tularemia, etc. The diseases are treatable, the main thing is to seek medical help in time, then you can avoid serious consequences.
Hemorrhagic fever
By the name of this pathological condition, one can understand that its main symptom is a sharp increase in temperature to extreme values (39...40°C). In addition, signs characteristic of viral diseases appear. When a blood test is performed, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia are often diagnosed based on changes in its composition. One of the main signs of hemorrhagic fever is a violation of the integrity of the walls of blood vessels.
As a result,
their permeability increases, which contributes to redness of the outer integument.
Hemorrhagic fever after a tick bite
Viral infections
Tick-borne encephalitis is one of the dangerous viral infections that affects the peripheral and central nervous systems.
At the onset of the disease, chills and fever begin, then damage to the meninges, fever, vomiting, drop in blood pressure, and arterial hypertension occur. Possible death.
Infection with encephalitis occurs when the parasite sucks blood . The male tick sucks blood for a short time - several hours. But the female stays on the skin for many days. The incubation period of the virus lasts 1-2 weeks. During this period, the affected person may not experience any symptoms.
Next, a fever appears, which lasts acutely and is characterized by a very high temperature - up to 40 degrees . Severe headaches, dizziness, hallucinations, and muscle pain appear. Vomiting and nausea are possible. Confusion and deafness often occur. Complications of the disease include paralysis of muscles and nerves.
The disease is treated by administering ready-made antibodies, which are obtained from the blood masses of donors. In the first hours after the bite, it is especially important to administer immunoglobulin. Treatment with antiviral drugs, ribonuclease and interferon is also used.
Ixodid tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) is transmitted by ixodid ticks using saliva. The incubation period of the disease is 7-14 days.
Early symptoms of infections are fever, inflammation of joint tissues, erythema migrans, and elevated temperature. The disease affects the organs of vision, heart, blood vessels, and central nervous system. The course and outcome of the disease depends on timely access to doctors. Chronic borreliosis is especially difficult to treat.
- supportive and anti-inflammatory therapy;
- taking antibiotics;
- consumption of vitamins;
- prescription of immunomodulators.
Medicines are prescribed that relieve intoxication and regulate the functioning of internal organs.
Tick-borne typhus is another disease transmitted by insects. The disease is especially often caused by taiga ticks in Siberian regions.
The incubation period of the disease is 4-5 days. Further, the disease manifests itself as muscle pain, fever, and tissue necrosis. The disease has a favorable prognosis. In most cases, Tetracycline and antiviral drugs are prescribed for treatment.
Microbial infections
Ehrlichiosis is an infection transmitted through the saliva of a parasite. A focal infection is caused when an insect attaches itself to a person.
If you find a mark from a tick bite, you must go to the hospital. When bitten, Ehrlichia penetrates the bloodstream and causes the development of an inflammatory process.
Monocytic ehrlichiosis is characterized by:
- abdominal pain;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- hyperesthesia;
- chills;
- catarrhal symptoms;
- feverish condition.
In case of illness, it is important to periodically check the blood picture - complications such as leukopenia, anemia, lymphocytopenia are possible . Whole blood and serum are taken for research. Treatment of the disease is prescribed even before laboratory results are obtained. The main drug in therapy is Doxycycline.
Ixodid ticks also cause granulocytic anaplasmosis. The disease is caused by an intracellular parasite carried by ticks. Together with the insect's saliva, anaplasmas enter the bloodstream and infect neutrophils.
As a result, various inflammations develop in the internal organs. The acute course of the disease is characterized by severe kidney damage - proteinuria develops. Treatment comes down to eliminating the pathogen and symptoms of the disease.
Rickettsial infections
Mountain fever is an infection caused by an Ixodid tick bite. The causative agent is rickettsia bacteria. The disease is expressed in general intoxication and fever.
Special signs of the disease are:
- microinfarction;
- pathological changes in blood vessels;
- necrosis of cellular endothelium;
- blood clot formation;
- inflammatory process of arterioles.
As the infection progresses, an extensive measles rash appears. In the severe stage, the disease takes on a hemorrhagic form. The disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the kidneys and interstitial myocarditis.
Rocky Mountain fever is the most severe rickettsial infection.
At the onset of the disease, the following begins:
- nosebleeds;
- lymph nodes become inflamed;
- joints are affected.
There is headache and prostration of consciousness. A characteristic sign of the disease is damage to the central nervous system. Pneumonia and gangrene of the extremities may occur.
The treatment of mountain fever involves antibiotic therapy and drug relief of hemorrhagic changes and thrombosis.
Medications to normalize the temperature and antibiotics Doxycycline, Levomycetin, Tetracycline are prescribed. Heparin is administered intravenously using a dropper. Treatment is carried out in a hospital inpatient unit.
Coxiellosis (Q fever) is a rickettsial disease caused by tick bites. The causative agent of the disease can be found in dry tick feces. A person becomes infected with a fever from a tick bite. The incubation period lasts up to 17-19 days.
Then the symptoms begin:
- muscle pain;
- wheezing in the bronchi;
- bradycardia;
- heat;
- headache;
- eye pain.
Treatment boils down to eliminating the pathogen with antiviral therapy and eliminating symptoms. Recovery with proper treatment occurs after 2-4 weeks. However, in some cases, a relapse of the disease is possible.
Protozoal infection
The tick is a carrier of protozoa, bacteria, and viruses, so the appearance of a protozoal infection after a bite is not uncommon. The intestinal form of infection affects the entire gastrointestinal tract. Very often, with a mild course of the disease, a person does not pay attention to periodic attacks of loose stools and abdominal pain. No intoxication or increase in temperature is observed.
In severe cases, the stool may contain blood streaks and be jelly-like. Extraintestinal forms of the disease are manifested by damage to the liver, lungs, and brain.
Treatment of the pathology includes the use of Doxycycline, antibiotics, Etoftamide, Chloroquine. The prescription of medications depends on the form of the disease.
To prevent diseases, it is important to follow preventive measures when visiting the park area. There is a wide variety of parasite species in nature. It is important not to leave exposed areas of the body without clothing when walking in the forest, and also, if possible, apply insect repellents to the body.
What is “tick insurance”?
If you have a high level of anxiety, or the trip to the “tick nest” happened suddenly, you can insure yourself against the consequences of a bite. The insurance company will then pay for the gammaglobulin injections and subsequent treatment if needed. Typically, the cost of insurance depends on the amount of coverage. What to look for when choosing insurance:
- Read the terms of the contract carefully. What is an insured event: one tick bite or several during the season.
- The amount of insurance, and whether it will be enough for you to examine and treat several people, if necessary. An important nuance is whether Lyme disease is included, or the insurance guarantees compensation for treatment only in case of encephalitis.
- Which medical institutions are indicated in the contract (the more addresses, the better). Ask whether you will be paid for medical services provided in an item not specified in the contract - this should also be stated.
- Conclusion: the wider the insurance program, the more reliable the insurer, the better.
Ticks and children
Children are the most delicious object for ticks, they are so close and attractive. And they smell. In hot weather, it is better to strip a crawler that is not yet running as much as possible; it is easier to see a tick on a bare body. Or put him in lighter clothes. On the head - a bandana or hood. If you find an embedded tick, try to pull it out (as already described above) and immediately contact the nearest medical center. Immunoglobulin is administered to children under 16 years of age free of charge.
Ticks are difficult to scare and even more difficult to kill, which is why all repellents are pure, unadulterated poison. There cannot be a “non-allergic”, safe, gentle, natural tick repellent. Can not be. Only in advertising. Therefore, anti-tick products are applied to children FROM FIVE years of age exclusively on clothing. You can also treat the stroller itself: wheels, sides. Do not buy your child milk from an unknown goat. Do not buy any country dairy products for your child unless you are sure of the manufacturer (roadside vendors). Goat's milk contaminated with encephalitis, if not boiled, is guaranteed to make a person sick.
Have ticks already appeared?
Belarus is not the most tick-populated country, but our tick season begins early - in 2022, the first bites were recorded in the Brest region already in February. According to the Ministry of Health, the number of calls to the country's medical institutions regarding tick bites increased by 5% over the past year, and their number in nature increased by 8%.
This, by the way, is a pan-European trend due to climate change, an increase in the number of rodents and other reasons (now there are ticks even in the northern regions of Norway).
It is often said that there were no ticks in Belarus before, but this is not true: there were fewer of them because they were fought with aggressive chemicals, primarily with DDT, which is notorious for its side effects.
Modern chemical agents that kill ticks are much less toxic, but have less effect.
In a word, we need to get used to the fact that ticks are our neighbors, although unpleasant, and we need to know how to live next to them so as not to harm ourselves.