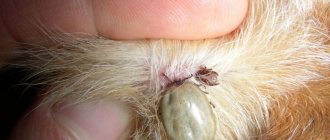
Ixodid ticks, like other representatives of the species, belong to the arthropod family and are relatives of spiders and scorpions.
Having a smaller size (from 1 to 10 mm), these insects have developed into a separate class, the number of different species in which is more than 1 thousand.
- Ixodid tick shape
- Stages of insect development
- Nutrition
- Habitat and distribution
In all corners of Russia except the Arctic, this family is represented by hundreds of different species, and they are localized differently in natural areas. High numbers of ticks in various regions are achieved due to their parasitism. Insects survive by feeding on the blood of people and animals.
General information
The arachnid has many varieties and is distributed everywhere. Adults rarely reach a size of 3 mm, average values vary between 0.1−0.5 mm. The female tick does not have a long body. She has it even a little shorter than the male. Some people mistakenly believe that tick larva and nymph are two names for the same developmental stage.
Adults have 4 pairs of legs, while juveniles have fewer. Depending on the structure of the body, leathery and hard varieties are distinguished. The former are characterized by complete fusion of the head and chest, breathe through the skin and trachea, the latter have a shell, and the head is movably attached to the body, breathing is carried out using special spiracles.
A distinctive feature of the arachnid is the absence of eyes. They navigate in space through a developed sensory apparatus, which allows them to sense the smell of the victim at a distance of up to 10 meters.
There is a classification depending on the way arachnids feed. There are two large groups:
- Saprophages feed on organic debris. They are considered useful and participate in the formation of humus. There are separate subspecies that harm plants, agricultural crops, flour and grain reserves. Saprophages include dust, arachnoid, flour, granary, subcutaneous, and ear saprophages. The last two species parasitize the human body and cause significant discomfort.
- Predators parasitize plants, animals, and humans. When attached to the victim, they crawl under the skin with the help of their paws and detach only after saturation. They can remain on the victim for quite a long time. The bite can be dangerous.
Both species are often found in human homes and at work, cause significant harm, and are difficult to remove.
Prevention
You should adhere to strict hygiene rules, change towels daily, iron pillowcases, disinfect your razor, glasses, and thoroughly wash personal items that come into contact with your face (scarves, handkerchiefs). This is especially important during treatment to prevent infection of other family members.
Never use other people's cosmetics and personal hygiene products. Do not dry yourself with someone else's towel or handkerchief. Keep the room clean, wash bedding frequently and drain pillowcases.
If you have already suffered from an illness, be attentive to your health. The slightest problems can provoke the resumption of demodicosis.
It is better to start treatment at an early stage, then there will be no complications and good results can be achieved in combating the parasite. To increase the protective functions of the body, a balanced diet, exercise, and walks in the fresh air are necessary.
Taking vitamin complexes in the autumn and winter, eating fresh fruits and vegetables will help boost immunity and improve the condition of the skin and increase its protective functions.
Types of parasites
In nature there are more than 40 thousand species of arachnids. Scientists divide them into 2 superorders: parasitiforms and acariforms. The former include ixodidae, argasaceae, gamasidae, nuttaliaceae, the latter include freshwater, armored, acaridia, feather, marine, scabies, thyroglyphoid, sarcoptiformes.
These are not all varieties, but the most popular. Each type has its own characteristics and differences:
- Ixodid ticks are the most common. They are distinguished by a shell covered with hard plates, often reaching 2.5 cm in length, which is considered almost a record among all species. They live in places with a temperate climate, prefer to constantly be in foliage and grass, and become more active with the arrival of the first warm days after a long winter. The life cycle of ixodid ticks is no different from other individuals. Females are very fertile and can lay up to 17 thousand eggs per season. They parasitize humans or animals and can feed on the blood of the victim for up to 3 weeks.
- Argas arachnids are characterized by a soft body, a small head that is almost invisible. They are of normal size and parasitize birds and animals. Sometimes they attack a person, the bite is painful, causing a rash and irritation.
- The armored variety lives on trees and soil, is small in size, and has a solid body. It does not attack humans; it feeds on carrion, mushrooms, and plants. It poses a threat to domestic animals because it carries helminth eggs.
- The gamasid mite lives in the burrows of rats and mice, parasitizes them, as well as poultry. It is small in size and lives up to 6 months. Produces toxic saliva that causes irritation when it comes into contact with the skin of birds and rodents.
- The subcutaneous species poses a threat to humans and animals. It parasitizes under the skin for several years, consuming dead epidermal cells as food. It reproduces quickly; viable tick nymphs appear 2-3 days after laying eggs.
Such species are common and cause harm to animals, humans, and agriculture. They differ in that they are difficult to remove.
Factors influencing the population size of Sarcoptes scabiei hominis
The population size of scabies mites is influenced by a number of factors:
- The itching that accompanies scabies suppresses the population. Taking antipruritic drugs (antihistamines and ointments with corticosteroids) leads to an increase in the number of strokes.
- The number of scabies in people whose production activities are associated with petroleum distillation products - gasoline, kerosene, aftol diesel fuel, etc., decreases. These substances have a powerful anti-scab effect.
- The number of strokes is significantly reduced with active mechanical destruction of ticks, which occurs during bathing.
- The use of anti-mite agents in low concentrations or incomplete treatment of the body slows down the formation of scabies, which contributes to the chronicity of the infectious process.
Rice. 16. In 50% of men, scabies affects the genitals and skin of the buttocks.
Scabies mites are contagious at different stages of their development.
Diet of scabies mites
Scabies itch feeds on scales of the stratum corneum of the epidermis. The period of activity of parasites occurs in the evening and at night.
Daily rhythm of scabies mite activity
A strict daily rhythm of activity can be traced in the life of scabies. During the day, ticks are at rest, and in the evening and at night the parasites begin to actively gnaw through passages (1 - 2), located at an angle to each other. In each of the moves, the female lays one egg. In the roof of each of the passages the female makes an exit hole through which the future larva will come out. All scabies ducts have a convoluted shape and consist of segments called the diurnal element.
In the second half of the night, the female feeds intensively, and freezes during the day. All females perform the same actions synchronously.
Each person's skin reacts differently to the activity of mites. However, in all patients, the parasites cause the same symptoms - severe itching in the evening and at night. As a result of insect bites and the impact of their metabolic products on the body, papular-vesicular rashes appear on the skin. Contamination of the areas, which occurs as a result of scratching, leads to the development of pyoderma.
The presence of circadian rhythms of scabies mites explains the prescription of anti-scabies medications at night.
Rice. 17. Itching is the main symptom of scabies.
Other types
There are other types of parasites. The scabies mite is a common one. Causes scabies in humans and animals. Life expectancy is no more than 6 weeks. During this period, the female can lay many eggs, which turn into nymphs quite quickly.
Ear mites do not pose a threat to humans. It mainly harms animals. It lives in the auricle, feeds on its secretions, causing severe itching, irritation and inflammation.
Scratch infections often occur. The dust species often lives in blankets and pillows. It does not parasitize humans; it feeds on dead skin cells, accumulations of dust and fluff. Life expectancy is 4 months. During a season, a female can lay more than 35 thousand eggs. It often provokes the development of asthma in a person.
Spider mites are safe for animals and humans; they are herbivores and feed on plant juices. The only danger of this species is the spread of gray rot, which is destructive to plants. The marine species does not threaten animals or humans; it parasitizes marine life. Lives in salt and fresh water, in stagnant bodies of water. The predatory tick poses a danger to any other species, since it feeds on its relatives. Sometimes such individuals are specially introduced into greenhouses to destroy the harmful spider species.
The granary or flour species does not pose a threat to humans, unlike the blood-sucking species. It is considered a serious pest; it can destroy grain reserves, contaminating them with waste products. The pasture parasite is dangerous to humans and animals. Lives in forests, sometimes in the steppe, near populated areas. Carries serious diseases, for example, plague, fever, encephalitis, brucellosis. Animals are also threatened by dog ticks, which live everywhere and cause serious discomfort.
Epidemiology of scabies
The incidence of scabies has increased over the past few decades. The reason for this is the increase in migration processes, the increase in the number of patients with immunodeficiencies and self-medication. The peak incidence is observed in the autumn-winter period. Each type of scabies mites parasitizes only a specific host.
Ticks that live on animals can transfer to humans, but they cannot survive on them for a long time. Parasites spend the main part of their life intradermally. Outside the human body, ticks quickly die from dehydration.
Scabies infection
Source of infection. The source of scabies infection is only a sick person. The scabies mite is transmitted only from person to person.
How is scabies transmitted? Paths of distribution. Direct contact with a sick person accounts for 90% of all cases of disease, half of which occur through sexual transmission. A secondary role is played by the indirect route of transmission of infection - through household items (bed linen, clothing, washcloths, towels, toys, sports equipment, etc.). Infection with scabies mites can occur in a wide variety of places - baths, trains, hotels, hospitals, etc. The rarity of indirect transmission of scabies mites is associated with the weak resistance of parasites in the external environment:
- young females and larvae play a major role in the transmission of infection, but at ambient temperatures below 22°C and humidity below 35% they do not live for more than 4 days;
- at a temperature of 60°C, the death of ticks occurs within one hour;
- in boiling water and at temperatures below 0°C, insects die instantly;
- sulfur dioxide vapor (sulfur dioxide) kills parasites in a couple of minutes;
- the most favorable environment for the existence of Sarcoptes scabiei outside of humans is house dust, natural fabrics and wood products;
- Insect eggs are the most resistant to anti-mite substances.
Overcrowding, low culture and lack of basic hygiene skills contribute to the spread of scabies.
Rice. 2. Direct contact with the patient accounts for 90% of all cases of the disease.
Rice. 3. Sexual transmission of infection accounts for half of all cases of diseases that arise through direct contact with a sick person.
Development and reproduction
Most ticks lay eggs and only some species are viviparous. The most interesting will be the development cycle of blood-sucking individuals. The whole process occurs in several stages:
- eggs;
- larvae;
- immature individual, or nymph;
- sexually mature ticks, or adults.
The female lays eggs in late spring or early summer. At one time their number reaches 2-3 thousand. The shape is varied, the most common are oval, round, oblong.
After about 2-3 weeks, the eggs hatch into larvae that look like adults, but have several differences. The most pronounced will be the number of legs. Adult ticks have 4 pairs, while larvae have only three. Some varieties have a transparent shell and no bristles on the body.
The larvae choose small rodents, lizards, and hedgehogs as their permanent habitat. They parasitize until they become a nymph. Typically this period is no more than 7 days. After moving to the next stage, the parasite leaves the victim. It is worth noting that even if the larva falls under water, its viability remains for a month. The bite of the larva is dangerous for humans, especially if the individual is a blood-sucking species.
Scabies lesions
Foci of the disease are family and collective.
- The leading factor in the epidemiology of scabies is the family outbreak. In 90% of cases of disease, the pathogen is introduced into the family by one of its members, much less often - by relatives and friends who do not live in the family. The primary sources of infection in family outbreaks are persons aged 17–35 years, most often children and husbands. In half of sick adults, infection occurs through sexual contact. The direct route of infection (contact with a patient) is the main one. Indirect transmission of infection (through household items and bedding) occurs in 13% of cases.
- Organized communities in which scabies can be transmitted are divided into two groups. The first group includes groups where people have common bedrooms (orphanages, dormitories, boarding schools, etc.). The incidence of scabies in such groups is two times lower than in families.
The second group includes teams where all members are in contact with each other during the daytime (kindergartens, schools, secondary and higher educational institutions, work collectives). Collectives of the second group do not pose an epidemiological danger.
Family outbreaks of scabies are the main sources of patients in society.
Nymphs and adults
The tick nymph has 4 pairs of limbs, just like the adult. It reaches 2 mm in length, moves quickly, and chooses animals of different sizes as temporary residences. Scientists note that most varieties of parasites in the nymphal stage spend a period of cold weather, and after the onset of heat they turn into an adult tick. Not all species pose a danger to humans. Most blood-sucking nymphs are considered a health hazard. They carry various diseases, for example, Lyme disease, encephalitis and others.
After a year, the nymph turns into a male or female. Some types of parasites live for more than 4 years and gradually develop during this time. They eat no more than 4 times during the entire period. That is why, of the many larvae, only a minority reaches maturity.
Adults do not live long. After being introduced to any animal or entering a home, they lay eggs and die. Today, it is becoming increasingly difficult for parasites to live in human homes, since a large number of objects made from non-natural materials deprive them of the opportunity to settle down normally and reproduce. In addition, there is a huge selection of products on sale that allow you to get rid of unpleasant neighbors yourself.
Varroatosis: infection of bees
The Varroa mite has spread to every continent except Australia. Without human help, infected bee colonies usually die within 3 years.