Photo of a parasite
The development of civilization served as an impetus for the rapid evolution of parasitic insects. The appearance of the head louse as a separate type of parasite, and then its morphotype - a linen variety called body louse, is due to the behavioral line of humanity.
According to the theory of evolution, body lice are considered a late type of evolution, since clothing, as a substrate for habitation, appeared much later than hair in mammals.
Two representatives of the same form interbreed well with each other, giving new generations of individuals best adapted to modern living conditions. The result of evolution can be considered the reluctance of the linen parasite to settle in the folds of woolen clothing, since a person does not wear woolen products, putting them directly on the naked body.
Externally, the body louse is very similar to parasites that lead their way of life under the scalp. The slightly elongated light gray-yellow body of the linen parasite barely reaches three millimeters in length. Laying eggs in the seams of clothes and on the lint of linen, the blood-sucking insect feeds on human blood, temporarily crawling onto the skin from the folds of clothing.
Unlike the head louse, the structure of the jointed legs of the linen parasite is not adapted to life on the surface of the human body, hair, and the fur of domestic animals.
Like the head form of the parasite, body lice lay eggs, or nits, firmly attaching them with a specific secretion. Thanks to this substance, removing nits from a woven surface is quite problematic - they are firmly glued to the fabric. The linen parasite prefers linen and cotton fabrics, avoiding settling in the folds of smooth and slippery silk clothing.
The appearance of the larva of the laundry parasite is no different from the adult, but is much smaller in size. Just like adult parasites, larvae feed on the blood of the host. A well-fed insect has striking differences from a hungry individual. Its dark abdomen makes it look like a flea, but unlike a flea, a louse does not have the ability to jump.
What does a body louse look like and how is it different from a head louse?
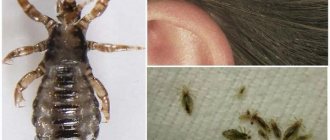
Body louse - or as it is also called, body louse, linen louse - differs from the head and pubic louse in the size and structure of the paws. This is the largest parasite, its size is 3–4 mm. It is similar in shape to hair. The body is oval, elongated. The shell is translucent, the insides are visible through it. Color – gray-yellow, pale. When saturated it turns purple.
The body louse has antennae, thanks to which it easily finds a food source and communicates with relatives. The mouthparts are the same as those of the head parasite.
The lice also have three pairs of legs, but their structure is such that they cannot move along hair with a round or triangular cross-section, like hair and pubic hair, respectively.
Like the head louse, the body louse feeds on human blood. This is a species-specific parasite, that is, it does not infect other species and does not live on animals and birds.
Symptoms of lice in children and adults
The main symptoms of pediculosis are: detection of lice and nits, itching of the skin, the presence of bite marks, scratches and other skin lesions, pyoderma. The cause of itching is saliva, anticoagulants contained in it and excrement of parasites. Antigens of parasites cause an allergic reaction, and contamination of the skin with staphylococci and streptococci leads to the development of pyoderma.
Itching, rash and the presence of lice and nits are the main signs of lice in humans.
Detection of lice and nits
One of the signs of pediculosis is the detection of lice and nits. Because nits exist only on the hair, they are more visible than adult insects, which spend most of their time on the skin. Head lice live on the scalp, most often the back of the head, temple, and on the beard and mustache in men.
Pubic lice live in the pubic area, perineum, scrotum, perianal fold, and rarely along the edges of hair growth on the head, in the armpits, on eyelashes and eyebrows.
Head and pubic lice lay eggs on hair. Body lice lay eggs randomly. They fall onto the fabric of clothing and become attached there. Body lice nits are located in the seams and folds of clothing.
Rice. 3. The head louse has an elongated shape and pigmentation on the sides. After absorbing blood, its abdomen turns purple.
Rice. 4. Head lice can be detected with the naked eye.
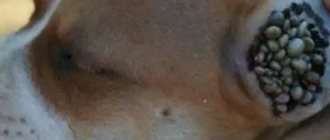
Rice. 5. The photo shows nits on the hair. Clearly visible to the naked eye.
Rice. 6. The photo shows pubic lice nits on the eyelashes.
Rice. 7. The photo shows pubic lice in the pubic area of a man and a woman.
Rice. 8. The photo shows lice and body lice nits.
Lice bites
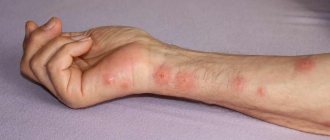
Lice bites are accompanied by the appearance of papules, spots and severe itching. Lice bites with the mouth organ, which pierces the epidermis and sucks out blood. Piercing the skin is carried out using a soft proboscis tube, which is equipped with piercing needles. The proboscis penetrates deep into the skin using rotational movements. The stratum corneum of the epidermis is cut through by the denticles of the terminal corolla.
The cause of itching after lice bites is saliva, anticoagulants contained in it and excrement of parasites. Redness after bites is associated with the development of an allergic reaction. Lice bites, due to the subsequent severe itching, lead to scratching of the skin and infection.
Rice. 9. Lice bites are carried out by the oral apparatus of insects.
Itching is the main symptom of lice
Itching is one of the main symptoms of head lice. It becomes especially noticeable 2.5 - 3 weeks after infection, when the insects have had time to breed. At first, the patient may not pay due attention to it. A person's reaction to itching is not the same.
Intolerable night itching occurs with body lice. Weak, but constant - with pubic. Significant itching is observed with head lice. Its cause is often an allergization of the body to insect bites and its waste products.
The intensity of itching decreases with decreasing sensitization and with habituation. Itching is accompanied by scratching followed by the formation of bloody crusts. Due to constant itching, patients often develop irritability and insomnia.
Rice. 10. Itching is the main symptom of head lice.
Rash due to lice
A lice rash appears a few days after the bites. Redness (erythema) and papules appear at the sites of lice bites. Papules are dense inflammatory infiltrates, in the area of which hyperemia and swelling are noted. The rash with pediculosis at first has the character of acute itchy dermatitis. Next, the scratched areas are torn by hemorrhagic crusts. Severe itching leads to scratching, ulcers, crusts and peeling of the skin.
Rice. 11. One of the main symptoms of body lice is a rash on the body.
Skin damage due to pediculosis
With pubic and body lice, bluish spots (melasma) can often be seen on the skin, the appearance of which is associated with the breakdown of hemoglobin in areas of hemorrhage.
In advanced cases of body lice, areas of massive lice bites become coarser. Pityriasis-like peeling and pigmentation appear on the skin.
With advanced lice, the skin becomes infected as a result of constant scratching. Pustular skin diseases (pyoderma) develop.
With chronic pediculosis, regional lymph nodes enlarge, body temperature periodically rises and anemia develops.
Rice. 12. The photo shows a rash on the scalp and neck due to head lice (right).
Rice. 13. With a long course of head lice, dermatitis develops. The skin at the bite sites becomes thicker and pigmented.
Rice. 14. In the photo there are areas of hemorrhage (melasma) - one of the symptoms of body lice and pubic lice.
Rice. 15. When pyogenic bacteria penetrate through damaged areas of the skin, pyoderma (pustular skin lesions) develops.
Koltun for pediculosis
Koltun (tangled and matted hair) appears with severe head lice. Hair sticking occurs due to scratching of the head with constant release of serous-purulent discharge. Rarely seen nowadays.
Rice. 16. In the photo, tangles are tangled, matted hair that gives off a putrid odor. Formed in advanced forms of head lice.
Lifestyle
The body louse does not live on the human body. These parasites live in the folds of clothing, underwear, bedding and accessories. They move onto the human body to get food, and after satiation they leave. You can see the parasite on the body only during feeding. An adult needs to receive food every 3 to 4 hours, so it goes hunting several times a day.
Body lice eggs are also found in clothes and underwear. They do not deposit nits in human hair or skin. Layers can also be located on the surface of clothing, but more often - in folds, seams, in the thickness of pillows, blankets and mattresses.
Sucking lice.
Less than 500 species. Wingless; oral appendages modified for sucking and piercing (piercing-sucking oral apparatus); retract when not in use; thoracic segments are fused; tarsi unsegmented; claws single; churches are missing; metamorphosis is incomplete; at all stages – ectoparasites of mammals. They are highly adapted to parasitism: there are no free-living stages, and they quickly die when separated from the host. Morophologically more specialized than biting lice. Pediculus humanus and Phthyrus pubis are human parasites.
Life cycle
A nit is a capsule, an egg in which an insect larva develops. Its dimensions are no more than 1.5 mm; it can be difficult to discern nits; their accumulation looks like sand. The egg is translucent, attached to the surface with the help of a sticky secretion secreted by the female. Within 7–10 days, a larva, a nymph, emerges from the nit. In 7–10 days, it goes through several molts and becomes an adult, ready for reproduction. Females live up to 45 days, males - up to 30 days. An adult female lays 4 – 5 eggs per day.
How do they reproduce?
Reproduction occurs sexually. The only condition for successful procreation is the most comfortable microclimate. In this case, this refers to 30°C and small deviations from them. At 15°C, the development of nits stops, and at -10°C they die completely.
This classification of lice is characterized by a very short life span. Males most often cannot even live for more than a month. Females are superior in these indicators for several weeks, which is approximately 45 days in total. Many believe that this difference is due to the greater functional importance of females. Every day they lay about 4 eggs. In total, about 100-140 young organisms reproduce over the entire life cycle.
The larvae mature relatively quickly. As soon as they are born, they immediately begin to absorb human blood and molt for the first time. After 5 days they experience a second molt, after 8 days the situation repeats and eventually the nymphs become sexually mature individuals. Then they actively reproduce and within a few months they can replenish their colony several hundred times.
Why are body lice dangerous?
Body lice bites when they puncture the skin and suck out blood are painless. When these insects pierce the epidermis, they inject a substance into the wound that prevents the blood from clotting and at the same time relieves pain. After this effect wears off, when the louse becomes saturated and moves away from the bite site, the wound begins to itch unbearably.
Even one louse leaves several new bites on the body per day, and if their population grows, there will be many wounds on the skin. Body lice bites are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- redness;
- swelling;
- swelling;
- dried traces of blood on the wound.
With a large number of bites, areas of the skin acquire a blue tint.
The parasite can bite through the skin on any part of the body, but most often bites appear:
- on the neck;
- behind the ears;
- on shoulders;
- on the upper back;
- on the chest.
Lice bite both adults and children, but it is easier for them to pierce children's skin, so children are the most desirable victim for them.
Why are lice bites dangerous?
- severe itching;
- when scratched, the bite sites do not heal for a long time;
- wounds become infected;
- parasites are carriers of typhoid fever and other diseases;
- a person becomes nervous and restless from constant itching;
- allergic reactions, which are expressed by severe swelling, increased body temperature, inflammation of the lymph nodes and other signs.
Body lice infestation is called body lice. This is a disease that needs to be treated.
Symptoms
Most often, people infected with parasites find bites that are accompanied by itching and rashes. At the initial stage, such manifestations may not be given much importance, but as the lice spread, the area of affected areas on a person’s skin will only increase, causing more and more discomfort and causing unpleasant consequences.
In such a situation, it is necessary to consult a specialist as soon as possible, but if for some reason the trip to the doctor is delayed, you can use the elimination method. First, you need to understand what the clinical picture is - an allergy or actual bites. The allergy affects larger areas and looks like continuous redness, and the bites are local in nature. In addition, body lice bites have a pronounced puncture point in the center of the inflamed area.
The fact is that the insect’s proboscis is quite short and in the process of digging into the skin the parasite has to immerse part of its head inside, thereby enlarging the puncture hole. It is also easy to distinguish between a bedbug bite and a body louse bite. Bedbugs bite people in open areas of the body that are not covered by any clothing, usually the arms, legs and neck. But body lice, on the contrary, attack those areas of the body that come into contact with clothing: shoulders, back, armpits, stomach and lower back, hips. Moreover, the areas least likely to be affected are areas where there is hair.
A special sign of the bites of these parasites is a change in skin color, which is characterized by the appearance of bluish spots. This fact can be explained by the fact that when a body louse bites, it injects a special enzyme that destroys hemoglobin in the blood; it is its breakdown products that accumulate under the skin and give it a blue tint. It is worth keeping in mind one more feature: damage to the skin by these parasites looks very much like flea bites, however, body lice bites differ from the latter in their random arrangement, and not in a characteristic chain, according to the principle of which bed bugs also usually bite.
After making sure that the body is covered with bites, you need to examine your sleeping place, bedding and clothes. As a rule, adult lice can be seen with the naked eye, but lice eggs can only be seen by a person armed with a magnifying glass. When these parasites are detected, the fight must begin immediately, without waiting for possible complications.
How can you get body lice?
Contrary to popular belief, body lice are not limited to people who lead an asocial lifestyle. Of course, due to the fact that such people do not have access to washing and heat treatment of clothes and linen, it is difficult for them to get rid of body lice. But you can catch body lice not only from them.
You can become infected with body lice:
- using personal belongings of infected people;
- in crowded places;
- in direct contact with patients;
- in shops and markets when trying on clothes;
- on long-distance trains;
- in social institutions - hospitals, kindergartens, health camps, etc.
Unfortunately, treating public areas with a large flow of people does not always provide protection from insects.
Body lice do not have wings, they cannot fly, but they move quite quickly. They can cover a distance of 50 cm in just a minute, so they do not need very close or prolonged contact with a carrier of the parasites to become infected.
Treatment for body lice bites
Bites from bloodsuckers must be treated with alcohol-based products:
- balm “Rescuer”;
- alcohol lotion, cologne;
- "Star" ointment.
The bite may cause an allergic reaction in some people.
In this case, symptomatic treatment should be used:
- antihistamines (“Tavegil”, “Suprastin”);
- painkillers (“Phenobarbital”, “Nurofen”);
- headache remedies;
- decongestants.
How to get rid of lice
These parasites are often confused with fleas or bedbugs. The type of bites and other symptoms are similar, and besides, they all do not live on humans.
If there is a suspicion of infection, it is necessary to inspect the bed and frequently worn clothing, paying attention to folds and gathers. This is where parasites can hide. Traces of vital activity - excrement, dead insects, empty nits - are also found in textiles.
If even small traces are found, it is necessary to begin a comprehensive fight. First, you need to wash all your linen and clothes. Before washing, you can soak items in a pediculicide solution. Insects die at temperatures above 40 degrees, so to be safe, it is advisable to wash items at 60 degrees or more for at least 30 minutes. You also need to iron the items, paying attention to the seams and folds so that there are no nits left in them. When unfavorable conditions occur, they can fall into a kind of hibernation and then continue their life cycle.
In summer, when it’s hot, you can take out linens, pillows, blankets in the sun. Lice are afraid of direct sunlight and high temperatures.
Temperature treatment also works in the opposite direction, that is, lice can be frozen out. In winter, you can dry things after washing in the cold.
You can use a steamer to treat mattresses, pillows, blankets, sofas and other upholstered furniture where pests may also be present. You can take things to the dry cleaner. This is especially effective for carpets, bedspreads and other heavy textiles.
Cabinet furniture, for example, cabinets for storing clothes and bed linen, must be treated with insecticides. A vinegar solution is suitable for these purposes. You can also use professional products - pediculicides, for example, Medilis-Super or Medilis-Malathion. They are suitable for treating any surface, that is, they can be used to treat cabinets, other furniture, and wash floors, window sills and other places where pests may be found. The treatment must be comprehensive, since with selective etching, lice can simply move to another place. Without shelter in underwear and without food, a louse can live up to a day, and then continue to parasitize and reproduce. To prevent this, you need to treat all possible places where the pest can hide.
Treatment of the body when infested with body lice involves the use of pediculicides. They come in the form of a spray, lotion or soap. You need to wash your entire body, including your head, diluted in the required proportion or ready-made. Since lice do not live in hair, one such treatment will be enough to wash away all the pests. Skin damage, scratches, and ulcers in their place are treated with conventional antiseptics and wound-healing drugs.
When dealing with lice, it is necessary to take appropriate safety measures. For example, chemicals should not be used in the presence of pregnant or nursing women or children under 5 years of age. When using special medications, you must be careful and strictly follow the instructions. It is forbidden for the products to come into contact with the mucous membrane. Do not inhale them, as they are toxic in high concentrations.
In general, fighting body lice is easier and faster than fighting head lice. The main thing is not to leave untreated clothes, linen or places where they are stored. If body lice appear on one family member, then you need to treat the belongings of all household members.
How to deal with these insects?
To get rid of body lice, serious measures should be taken, the list of which includes both treating things and using body products. The whole set of activities will look like this:
- collect all contaminated items and wash them automatically at the maximum permissible temperature. In this case, it is necessary to add one of the modern insecticidal agents;
Advice! If you are unable to do this, then it is recommended that you take your clothes to the dry cleaner.
- treat the body with a pediculicidal preparation and wash it off after the time specified in the instructions;
- After these procedures, you must put on clean clothes, and hang previously infected and washed items on the balcony and leave them in direct sunlight for two weeks.
Recommendation! It is very important not to put washed items next to those that have not yet been processed.
Body Treatment Products
To combat body lice on the body, you need to choose a reliable remedy. These include shampoos, lotions and sprays:
- Para Plus;
- Nittifor;
- Nit Free.
They must be applied to the body, paying special attention to the affected areas, it is advisable to wrap it in plastic (you can use cling film) and wash it off after a certain time. Various preparations may indicate a time period ranging from 10 to 45 minutes.
On a note! Folk remedies for body lice include vinegar and kerosene, but they can cause burns on the skin, and the effectiveness of such drugs is much lower than special ones.
How to treat clothes?
Previously, the same kerosene was used to treat clothes against lice. It was added to the water in which the laundry was soaked, then the whole thing was boiled, after which the lice were guaranteed to die. However, this method has a number of negative features:
- It is not advisable to add kerosene to the washing machine;
- when washing by hand, you must wear rubber gloves, as the solution can cause a negative skin reaction;
- during boiling, kerosene vapors evaporate, which can lead to poisoning;
- It is quite problematic to remove the smell of this substance from clothes.
Therefore, today, in order to kill body lice, they choose easier-to-use and highly effective anti-pediculicidal drugs:
- Medifox. The active ingredient is permethrin, which is harmful to insects and relatively safe for humans.
- NOC. An antiparasitic agent that has anti-pediculosis and insecticidal effects. Paralyzes insects by disrupting the permeability of the membranes of their nerve cells.
- Buzzed. Shampoo that is effective against head and body lice.
- Pedilin. Contains malathion and tetramethrin. Penetrates into the body of insects through the chitinous cover and causes their poisoning.
- Karbofos. Nerve-paralytic insecticide. It is highly effective, but its price is also quite high.
Important! Remember that the treatment of the body must be carried out simultaneously with the treatment of things. This will reduce the risk of re-infection.
Natural remedies
The following recipes may be useful for body lice that have not yet developed to a serious extent. These methods are simple and, as practice shows, give positive results quite quickly.
- Repellent plants are very often used to combat various parasites, and in the case of body louse they also come to the rescue. According to observations, these insects cannot tolerate the smell of tansy, so it is recommended to hang bunches of grass in places where the patient’s clothes will be ventilated after treatment. Additionally, this plant can be placed in closets with bedding and underwear.
- The same tansy can be used to treat the body of an infected person. A decoction is prepared from it, which is used as a rinse and used after bathing.
- If you do not want to use special preparations to heal wounds on the skin that appear as a result of bites, then in this case you can prepare an effective remedy yourself. To do this, you need to combine baby cream or rendered pork fat with a mixture of angelica powder and white hellebore rhizomes in a 4:1 ratio. The resulting ointment is applied to the affected areas until they are completely restored.
Since the main source of food for body lice is human blood, they die in the absence of a host for a long time. It is for this reason that body lice is most common among people who lead an asocial lifestyle and, for a number of reasons, do not have the opportunity to keep their linen clean and observe the rules of personal hygiene. At the same time, it is precisely this specificity of the existence of this type of lice that makes the fight against them often simple and quick, when in case of minor infestation it is enough just to limit the parasites’ access to the host’s body, wash clothes automatically at the maximum permissible water temperature and hang them out in the cold or scorching sun. And it is not at all necessary to use any chemicals. We hope that we have helped you figure out how to get rid of body lice. If you approach this issue seriously, you can get rid of annoying insects literally in one day. And don’t forget that it’s always easier to prevent their occurrence than to fight them afterwards. Therefore, try to avoid contact with unkempt people and do not spend the night in dubious places. Practice good hygiene and teach this to your children.
Prevention of head lice
Prevention of lice is not an absolute guarantee of protection against them, but it does help prevent their rapid development and spread. If you notice pests in time, fighting them will be quick and will not require too much effort.
It is believed that lice do not like strong odors, so bedding and clothing storage areas can be scented. Essential oils or bunches of dried plants are suitable for this. The strongest aromas:
- tea tree;
- geranium;
- mint;
- tansy, etc.
It is worth saying that tansy is a traditional means of combating lice of all types. It's quite effective. Therefore, if there is a possibility of infection, for example, if not very clean people live in the neighborhood, then you can hang bunches of tansy in your apartment or put them in closets. Tansy solution can be used to treat things or wash a person. You can even bathe children in it (in a small concentration and avoid ingestion or getting into the nose).
If you have been to a place where you could become infected with body lice, or have been in contact with a carrier of lice, upon arriving home you should treat your clothes - wash and iron them. You can also wash yourself with dust or tar soap. There is no such thing as too much caution.
Causes and routes of infection of parasites
Not only lice, but also other insects appear in the house in unsanitary conditions. Their appearance is especially important if in the house:
- lack of personal hygiene;
- lack of order;
- dirty things;
- improper storage of laundry;
- general use of personal hygiene items and things;
- use of a shared bed for sleeping.
If there are soft toys nearby, then parasites can also live in them. The favorite materials of lice are cotton, wool, and natural fabrics with an uneven surface.
Life activity
Bed lice need human blood to thrive. To do this, 3-4 times a day they crawl onto the body, pierce the skin, sucking out up to 5 µl at a time. When a linen louse bites, it secretes saliva containing enzymes that prevent blood clotting. These enzymes cause specific reactions on the skin: pain, irritation, allergies.
The lifespan of one individual is on average 38 days. Every day, a linen louse lays 12-15 eggs (nits), which amounts to several hundred over the entire period. The embryo turns into an adult sexually mature louse in 5-7 days. If apartment types of bedbugs are active at night, then the linen louse also bites during daylight hours.
They actively reproduce in warm conditions (+31…+32ºC), withstand temperature fluctuations from 0º to +40ºC. At moderate temperatures (+10...+20º C), linen louse survives without food for up to 1.5 weeks, nits - much longer. They die when heated above +44ºC.
Body louse development cycle.
Life period
Incubation period
After contact with the human body, the louse lays an egg coated with a special substance. The shell protects the contents of the capsule from mechanical damage and exposure to chemicals. The entire structure is tightly attached to a thread.
On average, nit development takes seven days. Throughout the entire period, the egg does without food and oxygen.
When the week comes to an end, the larva appears. She is unable to immediately leave the capsule, so she chews through it, while simultaneously accumulating carbon dioxide in the lower part of her body, which pushes it out. In appearance, it does not differ from a nit in any way except for its size.
You can find out how long the incubation period of pediculosis in humans is on our website.
Stages of larval development
After hatching, the parasite attaches itself to the hair and begins to actively feed. The transition to the next stage of development can take from one to ten days. Over time, the larva begins to look more and more like an adult, but its size is still small and its reproductive system is undeveloped. When the first stage comes to an end, the future louse sheds the old chitinous shell and becomes covered with a harder shell.
After this procedure, a nymph is formed, which goes through two stages of development. Each of them ends with a moult. The chitinous shell is not elastic, so when it becomes too small, it is shed. The evolution of the nymph lasts five days. At this stage, the reproductive system is formed.
The transformation of a nit into an imago (adult) takes about 16 days. The period increases if living conditions are unfavorable.
Features of reproduction
Parasites can begin to reproduce within a few hours after the completion of the last stage of evolution. The mating process takes from 20 to 70 minutes. The female receives seed material, which is stored in the abdomen and used as needed.
She has no need to enter into contact with her partner again, since these reserves are enough for the entire life cycle. The male dies 7–10 days after mating.
The future larva forms very quickly; as it moves along the oviduct, it becomes covered with a dense protective shell. After 24 hours, the female glues the nit to the hair or fabric, depending on the habitat. This happens as follows:
- The louse clings to a thread or hair with its paws using claws located at the ends of the paws.
- Strains the abdominal wall and squeezes out a little sticky substance.
- An egg hatches from the back of the abdomen and is placed in an already prepared area.
- The adhesive substance hardens, forming a reliable shell.
How lice reproduce, their rate of development, read on our website.
Important! It is much easier for parasites to reproduce when their owner is not trying to get rid of them. The female does not have to wait for a suitable partner to appear, so the process of laying eggs goes faster. Stopping the insect population in this situation becomes much more difficult.
How long do they live
The lifespan of a louse usually does not exceed 46 days. This indicator may change up or down depending on the sex and type of animal.
Parasites survive by consuming the blood of their host 2 to 6 times a day. Without a power source, they cannot last more than 55 hours.
Lice never feel hungry, so sucking blood is a way for them to calm their instinct.
Help with bites
Having discovered bed lice bites on a person, the following tips will help alleviate the victim’s condition.
- The first thing that means treating linen lice bites is maintaining hygiene. It is necessary to take a hot shower, thoroughly washing off any parasites that have entered the body. In some cases, pediculicidal drugs with antiparasitic properties are used, which are used according to the instructions. Wash off the composition from the skin using a detergent.
- Hydrogen peroxide, Zvezdochka balm, tar soap or Rescuer will help reduce itching and relieve inflammation of damaged areas.
- If allergies occur, it is necessary to take antihistamines and gels that relieve the allergic process.
- Symptomatic therapy is necessary for skin complications and the development of pustular lesions.
The feeding habits of lice.
The anterior edge of the head forms an oral cone, bearing on its front part several strong, curved teeth. When starting to feed, the louse presses the cone into the host's skin and begins to extend its mouth parts, including its buccal teeth. The teeth are used to cut through the horny outer layer of skin, and when the lip is fully extended, they are positioned so that their cutting edges face away from the central axis of the lip. During feeding, the lip and teeth serve to anchor in the host's skin. The stylets extend and probe the host tissue until they penetrate a blood vessel, usually a venule, at which point the louse begins to suck blood.
Hematophagy is associated with weak sclerotization of the integument of lice. The ability of lice (and fleas) to transmit prokaryotic pathogens may be related to the way they digest food. In contrast to mosquitoes, lice quickly hemolyze red blood cells, the remainder of the bloody meal remains liquid, and they do not have a peritrophic membrane. Blood coagulation and the presence of a peritrophic membrane appear to prevent the transmission of prokaryotic pathogens, but allow the transmission of eukaryotic parasites (Plasmodium falciparum).