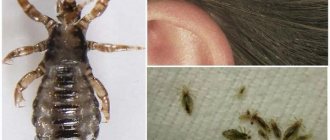
Fleas are representatives of a order of blood-sucking insects that are distributed almost everywhere. Currently, 2086 species are known. When bitten, these parasites cause skin and allergic diseases in humans and animals; In addition, they are carriers of vector-borne infections. Therefore, if you have information about what fleas look like and the dangers of contact with them, you can protect yourself, your loved ones and your pets.
Description, appearance and structure of the flea
Fleas are fairly small insects. Their body length, depending on the species, usually ranges from 2 to 5 mm. The largest individuals grow up to 1 cm. They most often parasitize deer and elk.
If you examine a flea under a microscope, you will notice that its body, covered with a durable chitinous shell, is strongly flattened laterally. This body shape was formed during the process of evolution to make it easier for the insect to penetrate the fur or feathers of the host. The surface of the body is strewn with small spines and bristles. This helps insects stay and move on the animal's fur.
Under a microscope
Those who have ever encountered fleas wonder if they have wings. Indeed, insects move so quickly that it seems that they simply evaporate into the air. In fact, fleas do not have wings. But they have three pairs of legs, with the hind legs being much longer. This makes fleas excellent jumpers.
The mouthparts of fleas are piercing-sucking. There are eyes on the head, but the parasites have very poor vision. They navigate thanks to an excellent sense of smell, as well as with the help of a special sensory organ located on the back of the abdomen. It is called pygidium and is capable of capturing the most insignificant vibrations in the air.
All fleas look the same, the only thing that differentiates them is their size and color, for example, a bird flea is not as dark as a human flea. The body color of parasites can vary from yellowish-red to dark brown, almost black.
Bites and damage caused
The flea's mouthparts are ideally suited for piercing the skin of a warm-blooded animal. A flea bite is quite painful because it is not accompanied by the injection of an anesthetic into the punctured area. Instead, the flea secretes enzymes that prevent the blood from clotting. Meanwhile, the pain of the bite is considered the least of the problems caused by the blood-sucking parasite. In fact, flea bites can lead to the following consequences:
· allergic reaction;
· infection with serious diseases;
· infection of the wound when scratching.
The greatest danger to humans are dangerous diseases carried by fleas. The specificity of the disease is determined by the specific type of blood-sucking parasite. Some species spread helminthic diseases, infection of which can also have serious consequences for humans.
- Fact! The mouthparts of these insects lack a blood-sucking proboscis like those of bedbugs and mosquitoes. In order to get to the blood vessel, they have to literally drill into the layer of skin.
If you notice fleas in your home, immediately take measures to eliminate them. We recommend professional flea treatment for your apartment from our service. Call us or email us and you will never see these parasites in your apartment or on your pet again.
Varieties
To date, scientists have described more than 2,000 species of fleas, which are grouped into 15 families. Fleas are found in animals, birds, and can live in the upper layers of the earth and on plants. A person can most often come into contact with the following species:
- felines are one of the most common species; they parasitize mainly on cats, but can also live on dogs, rodents, and other animals, and also bite people;
- canine fleas are close relatives of cat fleas, they are also not limited to the dog as a victim, they can settle on cats and other pets;
- human - can parasitize on humans, as well as on animals that often come into contact with them (cats, dogs, horses);
- rats - mainly parasitize rodents (rats, mice), small brown insects are very dangerous, as they carry pathogens of many dangerous infectious diseases;
- domestic - this is not a scientific classification, this is the name given to fleas that live in a person’s home; these include, for example, bed or linen fleas ;
- earthen - live on the ground or in the top layer of soil;
- arboreal - prefer to settle at the foot of trees;
- avian – most often parasitize birds, including domestic chickens;
- herbaceous (field) - live in the grass.
These are just a few species from the huge variety of fleas existing on the planet.
Flea control
In case of mass infection, it is worth considering that most folk remedies act as prevention. To destroy parasites, it is better to choose an industrial insecticide or contact specialized organizations. If you decide to do it yourself, do the following:
- Identify the source of the infection. Having established where fleas got into your home, eliminate the possibility of their reappearance: seal cracks and cracks in the floor, walls, and ceiling.
- Don't forget that fleas are carried by animals on their fur. Rid them of parasites and take measures to ensure that the infection does not recur. Use special collars, sprays and long-term exposure products for this.
The flea collar is impregnated with a product that repels parasites from your pet. - Using the chosen product, carefully and scrupulously treat the property.
Treat premises against fleas using protective equipment: gloves and a respirator. All residents of the apartment, including pets, must block access to the premises during treatment.
To prevent fleas from reappearing, consider several factors:
- Killing adult insects will not rid your home of fleas. When choosing a product, give preference to what kills them at all stages of development.
- Process the room without missing a single centimeter. Parasite eggs and adult insects can hide anywhere, even under the ceiling.
- The residual effect of the drug used lasts up to 1 month. During this period, avoid wet cleaning, otherwise the parasites will survive.
- Carry out the treatment in the morning. Since the room should be closed at this time, it will take time to ventilate it later.
Whenever possible, go beyond just gloves and a respirator when working with chemicals: use full-body protection - Prepare the room in advance - open access to baseboards and other hard-to-reach places, remove fabrics that can be washed (furniture covers, curtains, capes), remove carpets from the walls, bolsters and mattresses from beds and sofas.
- If the room is heavily infested, in addition to the main drug, use long-acting powders, scattering them after treatment in places where fleas are most likely to appear.
Take flea control measures at the first sign of fleas. Parasites are fertile, and if you leave everything to chance, then after a while your home will be overflowing with bloodsuckers.
Photo gallery: types of flea control products
The most popular products in the fight against fleas are emulsions.
Modern flea treatments are available in aerosol form for convenience.
Safe for people and animals, but effective against fleas, pyrethrum powder is poured into all hard-to-reach places in the house.
To rid pets of fleas, medications in the form of shampoo, drops, tablets or anti-flea collars are used.
When dealing with fleas, it is important to remember that local destruction of parasites is wasted time. Treating a pet or the only ottoman favored by fleas will not give any results. Use the information received, do not forget about preventive measures, and fleas will not bother you.
Lifestyle and behavioral characteristics
Most often, fleas parasitize animals that have a permanent shelter. Those who use a nest, burrow or other shelter occasionally from time to time are less likely to be attacked by bloodsuckers. Usually the flea does not live permanently on the victim's body. She jumps on it to feed and then returns to the litter of the nest or burrow.
Infected animals
There are so-called “stationary” ectoparasites. They parasitize animals that have no shelter. In order not to lose the owner, such fleas do not leave his body. Most often this applies to fleas of marsupials and artiodactyl mammals. Another reason for permanent residence on the victim’s body is the need for regular nutrition.
The vast majority of fleas are not too picky in choosing a victim and can parasitize various animals. The exception is fleas of bats, which recognize only this species of animal as a host.
Common types
Bloodsuckers are distinguished primarily by the host on which they live. The most common:
- rat fleas, divided into 2 varieties - European and southern, more common
- cat and dog fleas
- human fleas
- chicken fleas
In the absence of a specific provider, the parasite will be content with the blood of any other warm-blooded animal. Insects actively feed on the blood of not only domestic animals, but also livestock and poultry - chickens, pigs, horses and cows have fleas.
The division based on habitat is quite arbitrary. Basement fleas are rat or cat fleas. Household fleas are usually represented by bed or linen fleas, which also cannot be called separate species. The concept of “indoor fleas” - they can be considered absolutely identical to the definition of “household fleas”. The same can be said about the erroneous definition of the concept “genital fleas” as a separate species. But the same bedding is not a separate species, although it is often cited in the literature in precisely this understanding. Most often, fleas in the bed belong to one of the common species, usually human, cat or dog parasites. Linen fleas are the same collection of different species that have inhabited the apartment - dog, cat and rat. A conditional type, which can mean all types of parasites living in the house, but those who have chosen carpets as their home - carpet fleas.
Methods of movement and jumping characteristics
Fleas move in several ways. They:
- jumping;
- crawl;
- running.
Parasites cannot fly due to the lack of wings.
Jumping is the main movement option for fleas. Jumping fleas move so quickly that it is almost impossible to follow them. It seems that the insect has simply disappeared. This is understandable, because at the moment of jumping the flea reaches a speed of up to 2 m/s.
The length of a flea's jump reaches 50 cm. This distance exceeds the length of the insect's body by 120 - 150 times. The flea jumps not only far, but also high – it can cover a distance of 30 cm.
Scientists are still studying how the flea jumps. Research shows that at the moment of jumping, the insect's body contracts like a spring. Then the long muscular hind legs are used, with which the flea pushes off the surface and abruptly begins to move in the desired direction.
An interesting fact is that a hungry flea can jump non-stop for several days in search of a victim.
Causes of fleas in humans
Surprisingly, the main carriers of human fleas are animals. Even without direct contact between humans and animals, fleas can easily enter a person’s home. It is enough for him to be close to the place where the parasite carrier dropped the insect. If a flea is hungry, it will definitely jump on a potential food source. It often happens that residents of the first floors also become victims of fleas - rats and mice live in the basements of apartment buildings - carriers of these harmful insects. And since fleas are incredibly jumpy, it is not difficult for them to get into the apartment through cracks.
Let's highlight the main routes of flea infection:
- From the basements;
- On clothes, shoes;
- From the attics;
- From other warm-blooded organisms (people, animals).
Reproduction and life cycle
To successfully reproduce, fleas need food and favorable environmental conditions. Sexual intercourse occurs when the female climbs onto the male's back. She draws his genital claw into the spermatheca and receives the seed. The fertilization process lasts about 15 minutes, but sexual intercourse can last several hours.
Soon after fertilization, the female lays eggs. She does this in small clutches of 10–15 eggs. The flea forcefully pushes out the eggs, which scatter in different directions. Thus, competition between hatched larvae is reduced and they have a greater chance of survival.
Reproduction
The flea development cycle includes 4 stages:
- egg – develops in 5–14 days depending on temperature and humidity;
- larva - a translucent worm emerges from the egg, experiences three molts, during each of which it increases in size;
- pupa - the flea larva hides in a cocoon, where its further development occurs from 2 weeks to a year (at this time the insect does not need nutrition and is resistant to external conditions and mechanical influences);
- imago (adult) - having hatched, it immediately begins searching for prey.
How dangerous are fleas to humans?
The appearance of fleas in an apartment ultimately leads to unpleasant consequences, and unpleasant bites are only a small part of how things can turn out.
The enzyme contained in the saliva of a flea not only causes swelling at the site of the bite, but also causes unpleasant itching and can take a long and painful time to heal. In this case, an infection can get into the wound. Moreover, complications in the form of severe allergic reactions are possible.
There is a high possibility of contracting one of the diseases carried by fleas. Fleas can transmit more than 25 diseases to humans, including bubonic plague, typhus, encephalitis and hepatitis. Fleas also spread worm larvae and are intermediate hosts for parasitic worms such as hookworms.
Poor health of the pet with possible complications, including infestation with worms. Constant itching from bites makes animals nervous. The pain is excruciating. Various skin diseases are possible, the treatment for which will also cause suffering to the animals.
Where do they live?
Fleas are hardy and virtually invulnerable insects that adapt well to various environmental conditions. This partly explains the fact that fleas' habitat includes all continents. The habitats of most species of parasites are temperate and subtropical zones, but fleas live even in Antarctica, parasitizing local inhabitants - penguins and seals.
Some species do not leave the host's body, others live in nests and burrows, and others settle in the ground or on grass. Fleas often live next to people, living in basements and even apartments. In most cases, at home they parasitize pets, but sometimes they also attack people. In rare cases, fleas can even settle on a person’s head, hiding in the hair.
habitats
A common misconception is that fleas live on the body of their prey. This is far from true. Fleas jump onto the body of an animal only to eat; the rest of the time they prefer to live in more comfortable conditions. Various types of blood-sucking parasites choose comfortable places to live in the apartment. Earth and sand fleas prefer to stay close to the floor. Therefore, most often their nests are located behind baseboards, in carpets and paths. Cat and dog fleas are found in the animal's bedding and can sometimes be found in soft toys.
What do they eat?
The answer to the question of what a flea eats will depend on whether we are talking about an adult insect or a larva. Parasite larvae consume decaying organic compounds as food. Their diet includes flea excrement, particles of dead plants, even dust.
The diet of adult fleas is not so varied. Their only food is fresh blood; without it they cannot develop and reproduce. Absolutely all fleas are blood-sucking, regardless of their species.
Unlike some other blood-sucking insects, both female and male fleas feed on blood. The parasite sucks blood once every 2-3 days, and males become saturated faster than females. Eating can last from a few minutes to 2-3 hours. Very often, fleas suck out much more blood than they can digest. While eating, their abdomen swells and the insect increases in size.
Flea bite
Dangers posed by pests
As a reward from bloodsuckers, people can get not only all sorts of local reactions on the surface of the skin, but also some dangerous diseases. They are carriers of tuberculosis, rat typhus, tularemia, listeriosis, and plague. Their consequences, if someone is unlucky enough to become infected with one of the ailments, can be very dire.
Scientists are confident that each insect is quite capable of giving people one of several hundred ailments that exist in the parasite’s body. There is no need to panic, because it is rare that a bloodsucker bite can lead to any disease. It is dangerous if bites appear on the body due to a sand flea. In this case, the risk of becoming infected increases significantly. With a strong bite, the affected area often transforms into an abscess. Bloodsuckers of this type are able to get under the skin and carry out reproduction there, as well as harmful life activities.
Video
How long do they live?
The type of flea, environment and living conditions significantly affect life expectancy. Fleas can live from 2-3 months to 2 years. Dry air and heat shorten the insect's lifespan. So, at air temperatures above +30⁰С, the life cycle is reduced by almost half - the insect simply dries up. At lower temperatures, the development of the parasite occurs more slowly, which means it lives longer.
The absence of a host, oddly enough, also does not shorten the life of fleas. They can go without food for a long time (several months), they simply become less active and stop reproducing. Under normal conditions (optimal temperature, humidity and sufficient food), fleas most often live about 2-2.5 months.
How to get rid of it?
Parasites must be combated; modern drugs will help even in advanced cases. First you need to determine where the insects in the house come from. So, if fleas were brought by pets, they need to be treated. If parasites are coming from the basement or from neighbors, seal the existing cracks. To get rid of fleas at home, we recommend using modern insecticidal preparations that do not have a pungent odor and do not harm people and pets.
Chemicals
Since a flea cannot eat the bait, insecticidal preparations are produced in the form of a spray, powder, or aerosol. All means affect the nervous system of the parasite and paralyze it.
The most popular and effective are:
After killing the insects, you need to do a wet cleaning by adding ammonia or eucalyptus essential oil to the water. It is advisable to place branches of wormwood and lavender under the bed.
Folk remedies
You can get rid of insects using folk remedies. They are allowed to be combined with chemicals or used for preventive purposes.
Important! If you are unable to remove the fleas on the second attempt, it is recommended to contact the sanitary and epidemiological service.
Thus, fleas pose a great danger. They affect not only animals, but also humans. At the first sign of insects, disinfestation should be carried out.
Source
Destruction of fleas in the apartment
If one or two individuals are found in an apartment where there are no pets, it is quite possible to get by with traditional methods of getting rid of fleas. Fleas do not tolerate strong odors; the leaves of wormwood or Persian tansy are most often used; pine sawdust or shavings, a mixture of table salt and soda, or ordinary turpentine are suitable. The main thing is to endure these odors steadfastly and patiently or leave the apartment for a couple of days.
However, folk remedies will no longer help against a large colony of fleas in an apartment or house; professional flea disinsection using modern preparations will be required.
The destruction of fleas in an apartment, in a house, in a basement is carried out using special equipment that allows you to get instant results. Modern certified preparations for killing fleas will not leave parasites a single chance, without causing any harm to children and pets.
What does a flea bite look like?
For people who have not encountered these parasites, it is very difficult to distinguish them from the bite of other insects.
Flea bites are very itchy
But it is necessary to know what they look like if they become infected so that proper treatment can begin.
If you look at photos of people who have been bitten by fleas, you will see that most often bites appear in certain places on the body. People like to feast on the neck and waist; The popliteal fossae and lower parts of the legs are also bitten. They bite where the skin can be easily broken through. You can monitor the emerging skin itching, swelling and redness. They have peculiar bites - along one line at a distance of about 2 cm. The person begins to instantly feel pain during the bite.
Common symptoms:
- the appearance of red bumps;
- itching begins;
- the tubercles have an inflamed appearance.
It is important to know: the child’s body is bitten in different places, since their skin is delicate and it is easier for a flea to bite through it.