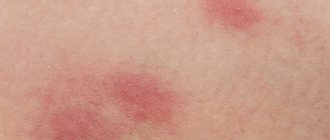
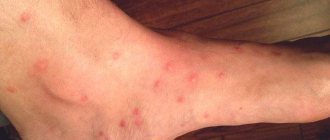
What do bites look like?
One of the “signposts” of an unpleasant neighborhood is the detection of traces of insects. For this reason, it is important to know exactly what the skin lesions left by linen, bed and body lice look like.
Believykh
Linen lice bites are localized in areas of slight hair growth - lower back, buttocks, neck, upper back, abdomen. During the feeding process, the insect moves throughout the human body, moving away from the previous site of the lesion. For this reason, traces of pests are located in groups, but do not form a “path”.
The site of the skin lesion turns red and swells. When in contact with items of clothing, the spots begin to itch. When scratched, they become dense and ulcers appear.
The wounds take a long time to heal. Unlike an allergic rash, the redness of the skin does not subside after using antihistamines. To get a good look at what a bite from linen lice looks like on the body, you should arm yourself with a magnifying glass - this is a common spot on the skin with a black mark in the middle.
Video
What do bed bug bites look like?
Bed
The bed louse is not interested in the hair area of the human body. Unlike its relatives (pubic and hairy individuals), the bed parasite is larger in size - 3-5 mm.
Most bed lice bites occur in the armpits, on the hips and lower back, between the shoulder blades, and on the neck . The lesions are not localized in a specific way; they are located chaotically and are presented as single swellings with a dot in the center.
After saturation, the parasite turns red-brown, increases in size and begins to resemble a flea.
Clothes
Body lice bites cluster around the neck, waist, upper back, armpits, groin and abdomen. Externally, the affected area is similar to a bed lice mark. Over time, single spots on the body become bluish.
Methods of transmission of pediculosis
A person on whom lice live, regardless of the degree of his infestation, is a source of lice infestation.
There are the following ways of transmitting pediculosis.
Contact path. Possible through close contact with an infected person. Lice crawl onto the body, hair, things of a healthy person, or parasites may be shed (accidentally or specially) onto a new host from an old one. It is very easy to become infected with head lice.
Sexual path. This is the main method of pubic lice infestation. During close contact of the pubic areas, the flats move to a new host.
Through care items, such as mattresses, pillows, scarves, hats, hoods, underwear, hairpins and elastic bands, washcloths, towels, combs, etc. After using care items by a person infected with lice, lice may remain on them for some time. the next time the items are used, they may crawl onto a new owner. Also, nits can mature in things and objects, which over time turn into adults. As a rule, head lice are transmitted through hats, pubic lice through underwear, and clothing through underwear.
Through the water. Infection occurs in places where a large number of people bathe, both in water (pool, sea, river, lake) and on land. These insects can live in water for almost 2 days, and while swimming they may well find their way to a new owner. Also on the beach they can crawl out of the sand.
Once they reach a new host, lice crawl to easily accessible places for parasitism. And depending on what stage of the life cycle the insect is at - a larva or an adult - after maturation or immediately, it begins to reproduce, that is, to lay nits. Each adult louse lays eggs every day throughout its life: a body louse - up to 16 pieces per day, a head louse - up to 4, a pubic louse - up to 3.
So, having settled on a new host, lice are ready to quickly spread to everyone around him. Body and head lice spread most quickly in places with large crowds of people (prisons, military barracks, communes, dormitories, public transport, children's groups) and in places where unsanitary conditions flourish and people do not take care of things, care items and the body (antisocial families, homeless habitats, shelters, places of deprivation of liberty, as well as places without unhindered access to water).
A place where at least one person is infected with head lice is called an epidemic focus.
Why do children most often get head lice? The fact is that they come into contact with other children every day and do not keep a distance from each other during games. Also, children often confuse their belongings or personal hygiene items with other people's and may sleep on each other's pillows. There may be lice on toys (most often soft ones).
How lice bite
Answering the question of how bed lice bite, you can give a similar answer to the question regarding other types of insects. The principle is identical : the parasite’s mouth is made up of jaws that resemble stilettos.
By biting, the louse pierces the skin with the help of its jaws and injects a little enzyme into the resulting wound, which prevents human blood from clotting. It is this substance that causes irritation, itching and redness at the site of the lesion.
Once the integrity of the skin is broken, the insect begins to search for an artery, which will become a source of nutrition. The pest sucks, clinging as closely as possible to the human body - its back part rises slightly.
The adult repeats the meal every 2-3 hours. After finding out how linen lice bite a person, it is worth moving on to the logical section on the correct treatment of lesions.
What are nits
Cocoons form around the eggs laid by female insects. Head and pubic lice lay their eggs on the hair, to which they attach using a special secretion. The cocoon with the egg inside is called a nit.
Nits on hair.
The body louse randomly lays eggs, they fall on clothes, underwear, where they are attached to the seams and folds.
The nits are white, spindle-shaped, and size 0.4–2 mm. They are not transmitted from one person to another.
The photo shows lice and nits.
The picture shows the development cycle of lice.
Eggs of pubic and head lice mature in 7–10 days. Bed lice larvae take longer to mature due to frequent cooling of linen and clothing.
When the nit is opened, the cap falls off and air enters through it. The latter fills the cocoon at its base and gradually displaces the larva, which is called a nymph. She molts three times, after which an adult should emerge.
What do lice look like inside nits?
Products for treating bites
In most cases, you can cope with the symptoms of an insect attack on your own. The help of a specialist is necessary if a clear allergic reaction occurs - a person’s temperature rises, chills, headache, nausea, etc.
As part of the question of how to treat lice bites from linen, bed and clothing lice, it makes sense to consider the features of the use of medicines and folk remedies
Medicines
At home, parasite stains can be treated as follows::
- any ointment containing hydrocortisone (relieves swelling and discomfort after a bite);
- hydrogen peroxide (has antiseptic properties);
- homeopathic medicines (with tea tree oil, calendula);
- Fenistil gel (relieves severe itching).
If the patient develops purulent formations indicating the development of an infection, the patient may require antibiotic therapy (Doxycycline, Lincomycin, etc.) as prescribed by the doctor.
Other medications prescribed by the doctor include the antiseptics Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, antihistamines Zodak, Suprastin, etc.
Universal products will help you get rid of linen, bed and clothing lice.:
- Paranit;
- Pediculen;
- Para Plus and others
Folk remedies
Folk help for lice bites is also appropriate.
Among the possible “helpers” in eliminating the primary symptoms of insect bites:
- soap solution. Helps relieve the first unpleasant symptoms, disinfects;
- alcohol or vodka diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio. Disinfects and prevents infection from penetrating into the deep layers of the dermis.
Effective treatment
The most effective and safe means include “Paranit”. Its action is to block the respiratory system of lice and nits. The active substances dimethicone and mineral oils have no effect on humans, but are harmful to insects.
Advantages of the product:
- • the result has been confirmed in clinical trials and experience in various countries;
- • the possibility of using the “Paranit Sensitive” product for hair treatment in children over 1 year of age and pregnant women;
- • available in various forms – shampoo, lotion, spray – it’s convenient to choose the best option
- • in most cases, one application is sufficient to eliminate lice;
How to distinguish lice bites from other insect bites
Single bites of clothing, linen and bed lice are very easily confused with the site of a bite, for example, of a bedbug.
There are some "landmarks" that can help identify the pest.:
- The louse leaves behind chaotically “scattered” spots, unlike the bug. The latter tries to bite at a distance of several centimeters - a “chain” of spots is obtained.
- An insect bite differs from the lesion left by a flea in the absence of obvious pain at the time the skin is damaged. If a flea bites, this process is accompanied by intense pain. He learns that a person has been bitten by a louse several hours after contact. In addition, fleas often leave visualized “tracks” on the victim’s body.
- Ticks, unlike lice, leave behind a large area of damage (a swollen red circle). To eliminate the feeling of hunger, the tick needs to eat from several hours to several days; lice do not eat for that long.
- Mosquito bites differ from marks on the body left by lice in the absence of a darkened hole in the center in the affected area.
In some cases, insect marks are confused with manifestations of scabies, which is caused by scabies mites. However, in this case there are no visible traces of skin puncture at all.
Head louse
The head louse is usually localized in the occipital, temporal regions, beard, and mustache in men. The legs of insects are adapted for attachment to precisely such hairs with a circular cross-section.
Arthropods have an oblong shape. The length of the male is 1–3 mm, the female is 4 mm. The insects are gray in color and turn red or purple after ingesting blood. The oral apparatus of lice is formed by piercing needles enclosed in a proboscis that turns out of the oral cavity. The latter is pressed tightly against the skin during an insect bite. The saliva of parasites contains an enzyme that prevents blood clotting.
Lice feed twice a day, the female absorbs about 0.7 ml of blood per meal, and the male - a third of this volume. Without food, arthropods die within 2 days.
The female lays 5 eggs per day, from which lice of subsequent generations appear. After 6–10 days, head lice reach sexual maturity.
The lifespan of lice is from 28 to 32 days.
In the photo you can see what head lice look like.
The optimal temperature for head lice to reproduce is 28 °C. When the temperature drops to 22 °C or rises to 35 °C, the vital processes of insects slow down sharply. At temperatures above 44 °C, the head louse dies.
Danger of bites
The danger of bites from linen and other types of lice lies in the likelihood of a person becoming infected with dangerous diseases. The infection process takes a few seconds.
Among the pathologies carried by lice:
- relapsing fever (manifested by skin redness, intoxication of the body, attacks of fever);
- typhus (occurs against the background of destructive vascular changes);
- Volyn fever (manifests as acute pain in muscles, bones) and others.
Bites from body lice and other types of lice can also cause an acute allergic reaction, which in some cases leads to anaphylactic shock - the patient needs urgent medical attention.
For this reason, if suspicious spots appear on the body, it is necessary to promptly exclude linen lice bites.
Body louse - structure, life cycle, reproduction, nutrition, habitat
Body lice have been parasitic for 70,000 years, they are dangerous insects, they carry various diseases - typhus, fever and others.
Life cycle – 16 days. An adult female can lay up to 10 eggs per day, that is, about 300 in her entire life. The life expectancy of the parasite is 1.5 months.
- larvae are laid;
- hatching process;
- after the first molt a nymph is formed;
- the nymph molts two more times;
- the larva becomes an adult.
Lice reproduce sexually.
Video: body lice (lice)
Preventive measures
Preventing the spread of lice involves regularly checking suitcases upon returning from a business trip or traveling, and washing stale items of clothing.
To protect yourself from insects, you can put a cotton pad soaked in hellebore water or lavender oil in the closet with your linen. You should visit beauty salons and hairdressers with caution and pay attention to the disinfection of instruments.
Lice live in the folds of people's clothing, bedding and other textile household items. Pests can be detected not only visually, but also by the appearance of bites on the body of household members.
The affected areas are presented in the form of red swellings on the skin, which are characterized by a chaotic location. The bites itch, and ulcers remain at the scratch site.
Medical care for those affected by the active life of parasites should be followed by no less active pest control. You can carry out all the necessary activities yourself or contact specialists.