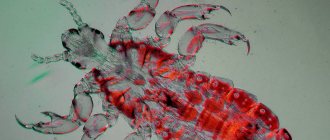
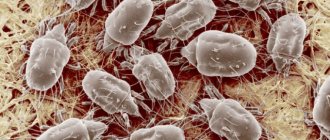
Lice are small parasitic insects on the human body. Their habitat is bed linen, clothing and human hair. The medical name of the disease is pediculosis (lice).
What does a human louse and nit look like (on the head):
- The length of an adult head louse is 2-4 mm , and that of a larva is from 0.7 to 2 mm.
- They are light yellow or brown in color , which helps them hide in the hair and scalp.
- Lice are usually found on the scalp , but can be on the eyelashes and eyebrows.
- They feed exclusively on blood.
- After being saturated with blood , the abdomen turns red, which makes the louse more noticeable.
What is pediculosis
Pediculosis is a parasitic disease, primarily of the skin, and as a result of its damage, of the hair. Moreover, it can be not only the head, but also the body or pubic. These varieties are caused by the corresponding species of lice. Such parasites on the head most often prefer the temples and back of the head, but can quickly spread to other areas.
When bitten, these parasites secrete saliva - after getting into the wound, a person may feel itching (14-36% of cases).
How they appear on a person’s head
The most common way head lice occurs is through close contact with an infected person , as well as wearing hats of such a person or using his comb.
Close contact for the appearance of lice and nits is those actions of an infected and healthy person in which their heads touch. For example, children often play together, after which lice immediately spread throughout the entire group of children.
Nits cannot appear out of nowhere, as they are a consequence of lice infestation, which can only be transmitted from another person.
Also, even if one capsule gets on the head, which happens very rarely, the disease will not be able to develop, since there will simply be no conditions for reproduction.
Capsules appear on the hairline almost immediately after several lice get on it, as the process of reproduction begins.
Head louse under magnification
What lice look like: appearance
Head lice are very small insects, with bodies of grayish-yellow or grayish-white color (sometimes even transparent), having 6 legs with hooks at the ends, with the help of which they move along the hair. Their length is about 2-4 mm (females are larger, and the length of an adult male reaches only 2-3 mm). Externally, they are approximately the size of a sesame seed. They differ from body lice and pubic lice in their shade and longer body.
Photo No. 1. Human louse
These insects can be clearly distinguished when they have just drunk blood, then the body acquires a purple or red tint.
Photo No. 2. Human louse under a microscope
Effective treatment
“Paranit” products are the best choice for the prevention and treatment of head lice. Easy-to-use shampoos, lotions and sprays kill lice and have a number of compelling advantages:
- • many convenient forms of application for your choice;
- • easy distribution of the thick composition throughout the hair;
- • easy rinsing, especially with shampoo-conditioner;
- • pleasant smell, at the same time destructive for lice.
Do not put off treatment for head lice until later. Over time, the disease causes increasingly severe discomfort. Buy products from the “Paranit” line and forget what parasites are!
What nits look like: appearance
It is also important to know what nits look like. The fact is that often infection with pediculosis occurs precisely through the attachment of eggs, hence the long incubation period.
Photo No. 3. Nits on hair
Nits look like small white oval capsules measuring 0.8 by 0.3 mm. They are so small that they seem like regular dandruff. But unlike dandruff, they practically do not wash off and are very difficult to comb out.
Photo No. 4. Nits under a microscope
Pubic lice
The habitat of this type of parasite is the hairy part of the pubis and genitals, but it can also live in the armpits, chest, beard or eyelashes. The limbs of pubic lice are designed in such a way that the insect can be supported on hair with a triangular cross-section. For this reason, pubic lice do not survive on the head.
The length of the insect is from 1 to 2 mm. The legs on a short and wide body are directed to the sides. This type of parasite is inactive; most of the time the louse is in one place, feeding on blood through the proboscis. As a result of their activity, bluish marks remain on human skin. They are usually noticeable in the thighs and abdomen.
The human body temperature is ideal for the reproduction of pubic lice. The female lays eggs at a temperature of 20-40 °C. The number of eggs per day is 2-4 pieces. Under normal conditions, females live about 17 days, and males - up to 22 days. Outside the human body area, lice quickly die
Ways of infection with pubic lice:
- • sexual contact is the main route of infection;
- • wearing clothes of an infected patient, using his personal belongings;
- • staying in crowded places, namely in a sauna, bathhouse, swimming pool, solarium - infection in this way rarely occurs.
Reproduction
A single mating of adults leads to complete insemination of all eggs of the female, who will be able to lay more than hundreds of nits over the rest of her life. Re-pairing is not required.
If just one fertilized female louse lands on a person's hair, after two weeks there may be 10 to 50 lice on the head.
Within a few hours after insemination, the female begins to lay eggs, attaching them to her hair, about 2-5 eggs per day.
Louse lays eggs on hair
After 7–11 days, the upper lid of the egg bursts and the nymph hatches. She begins to suck blood almost immediately after hatching, thanks to which she reaches adulthood in 8 days. If the louse does not find a food source, after about 18 hours it loses its ability to suck blood due to dehydration and dies.
Body lice
Body louse is also called linen or bed louse. From the name of the parasite one can infer its habitat. The length of the louse is more than 4 mm in the female and approximately 3.5-3.7 mm in the male. Body lice are larger in size than pubic parasites.
Body lice periodically leave their habitat and move onto the human body to feed. The results of bites are clearly visible on such parts of the body as the back, neck and lower back.
The female lays approximately 6-14 eggs per day. To reproduce, the insect requires an air temperature of 27 to 35 °C.
This type of parasite, although it feeds on blood, does not live on the body. The most common habitats are bed linen, blankets, rugs, folds of clothing, and the inside of mattresses or pillows. The female also lays eggs in these places.
Infestation with body lice occurs much less frequently than with head parasites. Typically, the victims of bed insects are people who lead a sloppy lifestyle and do not have permanent housing. Infection occurred in the past during military events, in crowded places where there were no opportunities for proper hygiene
Life cycle
In its development, the head louse goes through several stages:
- Females lay white eggs - nits. They attach very well to the hair right at the very roots. Sometimes you can see dead nits that are brown in color or empty ones that are light in color and look like dandruff.
- Nits grow from 7 to 9 days. Then it develops - a nymph, the so-called cub.
- After 10-12 days, the nymph turns into a mature louse, which is ready to reproduce and give birth. The louse lives for 28-30 days, and during this time they lay 200-300 eggs.
What do they eat?
There is a misconception that lice feed on dead particles of the epidermis. In fact, they are blood-sucking parasites. For normal life, they need human blood, which they feed on. How long do they live?
In general, the lifespan of these parasites is only 38 days, but this is quite enough to give birth to offspring.
Contrary to popular belief, head lice can live outside the host's body for some time, although for a relatively short time. They need to feed approximately 4-5 times a day, but can live without food for up to four days. However, in most cases this period is only 2-3 days. But usually this is enough for lice to find a new “master”. They do not jump or fly, but they move very quickly, developing speeds of up to 20-30 cm per minute, which explains the high risk of contracting lice in close contact with carriers
However, much depends on the ambient temperature. If it is about +10°C, the parasites leave the person, since they cannot live in such conditions. And at negative temperatures they will die within a couple of hours. True, this only applies to those insects that are outside the human body, since such a low temperature never occurs on the scalp.
How dangerous are lice?
Lice can become carriers of serious diseases such as relapsing fever and Volyn fever. But these diseases arise in wartime, during mass epidemics or in places where there are large crowds of people in the absence of hygiene rules. In modern civilized conditions, the likelihood of such diseases is extremely low.
Scratching bite sites causes microtraumas, and they, in turn, can become sites of infection. Constant itching negatively affects the child’s mental state, he becomes irritable and restless, loses sleep and appetite.
Head lice infestation worsens the condition of the hair, causing brittleness and excessive hair loss.
Where do lice come from: the main methods of infection
There is only one way to transmit head lice - through direct contact with a person with lice.
Many people believe that it is possible to become infected through household items - for example, by sharing combs. But in fact, in medicine these cases are considered rather as an exception to the rule, since lice are not transmitted this way
At the same time, personal hygiene is not important for parasites. Lice “select” both clean and dirty hair with approximately the same frequency. Experts even believe that clean hair attracts these insects more, since in this case there is less secretion from the sebaceous glands on the human skin, which prevents lice from feeding.
What threat do they pose?
The immature nits themselves do not pose a threat, with the exception of the unattractive appearance of the hair and white formations in it. But when the louse begins its parasitic life, symptoms appear that can significantly worsen the quality of everyday life. These symptoms include:
- almost constant itching of the scalp;
- infection of scratches and wounds, their infection and suppuration;
- sleep disturbance;
- inability to concentrate;
- irritability, nervousness.
Sometimes typhus or age-related typhus can become a complication of pediculosis. Infection of damaged skin after a louse bite, which is dangerous to health, occurs as a result of contact with the waste products of parasites, that is, with liquids and feces. The main unpleasant consequence of infestation with lice and nits is constant discomfort and apparently dirty hair.
How to understand that there are lice
In order to take timely action, you need to know what lice bites look like. After all, the appearance of scratches in their place is one of the most important signs of infection. However, this is not the only manifestation. Pediculosis is characterized by such symptoms as:
- • severe itching at the site of the bites
- • the appearance of small grayish-bluish spots on the skin;
- • scratching;
- • the presence of white nits in the hair.
Since infection can penetrate through scratching, pustules and inflamed areas may appear in their place.
Symptoms
How can you tell if there are nits? Symptoms of the disease, as a rule, are invisible immediately after its appearance, since they are not very pronounced and a person simply does not consider it necessary to pay attention to them. Despite this, it is possible to detect signs of head lice in the first days of infection.
The following symptoms of infection exist:
- Constant itching that does not go away even with strong scratching of the skin.
- The presence of bites, since the entire diet consists of human blood. To prevent the bites from healing, the parasites inject a special secretion that interferes with the blood clotting process.
- Slight tingling, like a mosquito bite. The sensations of a mosquito bite and a louse bite are the same.
- The presence of white bodies in the root part of the hair.
Of the above symptoms, the most noticeable is itching. Most often, it is this that becomes the reason for contacting a medical specialist or conducting a thorough examination of the head at home.
Are there nits without lice?
Such a case is possible, but very rare. The discovery of empty nit capsules, where there are no longer living individuals, makes you think carefully about the situation. The answer to many questions is that measures to combat head lice were applied either on purpose or by luck.
There are no living specimens on the head, as they died as a result of some impact. One of the types of such effects is painting with a mixture containing hydrogen peroxide, or bleaching hair, as a result of which the peroxide destroys lice and nits.
Basic methods for removing lice
To treat head lice, several methods are used at once: their combined use gives the greatest effect. This:
- • Mechanical method, which involves removing nits. They are combed out using special metal combs with very fine teeth. These combs can simply be washed regularly with soap and water.
- • Chemical. To do this, products are used that help dissolve the adhesive base that helps nits stick to the hair.
- • Physical method. It mainly involves temperature exposure. Since the death of lice is possible at temperatures above +30°C, after washing the hair, it is recommended to dry it with hot air using a hairdryer. You also need to wash pillowcases and bed linen at the appropriate temperature, but boiling textiles is unnecessary.
But folk remedies for lice like olive oil are not always effective. They provide a certain sliding effect, which makes combing easier, but have no effect on the parasites. Alcohol damages the shells of nits, but it has virtually no effect on adult parasites. While such a traditional method as using kerosene, although it kills insects, can even cause severe poisoning in humans, so it is better to abandon it altogether.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
How to get rid of nits at home, traditional methods
Worms in an aquarium: what they look like, reasons for their appearance in fish, how to get rid of them
What lice and nits look like on human hair, in adults and children
Treatment of head lice and nits at home with folk remedies
Worms in the human body: in the intestines, liver, head, eyes and under the skin
How to get rid of lice and nits with vinegar at home: treatment methods