Quite often there is such a thing as itching of the scalp, which haunts many people. Immediately thoughts appear that there are lice on the head, since lice, even today, is a fairly common disease. Children especially suffer from head lice, since they are actively in contact with each other, being either in a preschool institution, or at school, or in any other institution. It is not problematic for an adult to catch this disease by standing in line or visiting a gym or other crowded event. If, as a result of the examination, it turns out that there are no lice or nits, then the question remains and becomes no less serious.
Causes of itchy scalp and hair loss
Hair thinning can be observed under the influence of various factors, the most common of which are:
- hormonal changes;
- endocrine diseases;
- improper care of strands;
- deficiency of nutrients;
- long-term infectious diseases, especially those accompanied by a prolonged increase in temperature;
- taking certain medications (for example, contraceptives, antihypertensive drugs, steroids).
If this phenomenon is accompanied by itching, various dermatological diseases, fungal or bacterial infections, parasitic infestations, allergies, and autoimmune disorders often occur. The head can also itch due to dandruff: in this case, thinning hair occurs as a result of insufficient access of nutrients to the follicles.
In addition, the clinical picture of hair loss and itching of the scalp can be observed with burns or mechanical injuries. This phenomenon is dangerous due to the risk of scar tissue forming in place of the hair, after which natural restoration of its growth (without surgical intervention) in the affected area will be impossible.
Diagnosis of itchy scalp and hair loss
After examination, the trichologist prescribes diagnostic procedures, which may include:
- scalp scraping;
- general blood analysis;
- determination of hormone levels;
- blood chemistry.
Itching and hair loss in women are often associated with hormonal disorders, so based on the results of the examination, a consultation with an endocrinologist may be recommended.
Dry skin
If the skin does not have enough moisture Dry skin, it may itch and flake. Perhaps you don't drink enough water, wash your hair too often, or use harsh shampoos.
What to do
Drink more. Use mild shampoos with hyaluronic acid or natural oils. After washing, additionally moisturize your skin with a toner containing glycerin or aloe. Get a head massage at least once a week. And don’t forget about a hat: in winter you need to protect your skin from the cold, in summer from the heat.
Treatment for hair loss and itching
The course of therapy may include:
- antihistamines;
- means for sebum regulation;
- antifungal, antiparasitic drugs;
- strand growth stimulants (minoxidil, finasteride);
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- mesotherapy, plasma therapy, laser treatment and some other clinical techniques.
The specialist will prescribe the optimal treatment schedule and also recommend effective ways to prevent recurrence of the problem.
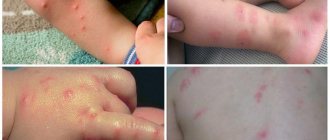
Hives
Hives usually go away after a few hours or days, but may appear again / dermline.ru
These red, itchy bumps can appear anywhere. Hives can be caused by allergies to food, medications, insect bites, pollen, animal dander, latex and other materials. But it can also be chronic - its causes are unknown.
What to do
Hives often go away without treatment. But if it comes and goes periodically for six weeks, it's time to see a doctor. He will prescribe medications that will reduce symptoms.
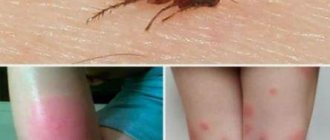
Lice
In fact, lice are small and almost transparent, so they are not easy to notice among the hair / yachist.ru
They run on the head, bite and cause itching. At the same time, anyone can become infected, because parasites are easily transmitted by touching hair or through personal belongings. So, just in case, have someone look at your head.
What to do
Wash your hair with shampoo containing pyrethrin or permethrin. Just read the instructions carefully and follow the directions, otherwise you may cause skin irritation. Comb out nits with a fine comb. Be sure to wash clothes and bed linen in hot water (at least 54 °C), and then iron.
If home treatment does not help, you will need the help of a dermatologist. He will examine you and prescribe stronger remedies.
How to deal with itchy scalp?
It is possible to completely get rid of such a nuisance only if its key cause is found and eliminated. But you can reduce the intensity of itching by using the following means:
In addition, you should refuse (at least temporarily) from dyeing your hair, using mousses, hairsprays and styling gels, and blow-drying your curls. It is recommended to exclude fatty and heavy foods, sweets, carbonated drinks, coffee and alcohol from the diet, and consume fresh vegetables and fruits, cereals, fish and seafood.
To maintain normal skin moisture, you should drink about one and a half liters of water daily.
Scabies
If this is her, not only the head will itch, but the whole body. Moreover, it will be so strong that it will be impossible to sleep. In addition, a rash or scabs will appear.
What to do
Scabies does not go away on its own, it must be treated Scabies Slideshow: Symptoms, Cause, and Treatments. First, go to a dermatologist, he will tell you what to do and prescribe medications.
To kill scabies mites, a cream or lotion containing permethrin, lindane, benzyl benzoate, crotamiton, or sulfur is usually prescribed. Antihistamines and cool compresses are prescribed for itching.
Internal causes of childhood dermatitis
The disease can be provoked by:
- hereditary predisposition to allergies;
- concomitant atopic diseases - bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines;
- eating food with preservatives, dyes, flavorings;
- stress.
More often, the disease develops in people with white, dry skin; dark skin, oily, suffers less often.
Folliculitis
This is the name for inflammation of the hair follicles. It looks like red bumps or pimples with a white head around the hair.
What to do
You can cure Folliculitis, a mild form of folliculitis, at home:
- Apply gauze moistened with warm water or saline solution (1 teaspoon of salt per 2 cups of water) to your head.
- Wash your skin with antibacterial soap twice a day.
- Use an over-the-counter antibiotic cream or gel to fight the infection.
Your condition should improve in a few days. If the bumps and itching don't go away, it's time to leave home treatment and go to the hospital.
List of the most popular means
The whole variety of remedies for itching of the scalp can be divided into two large groups: pharmaceutical remedies and folk remedies. The first ones are good because they work the first time, but they are bad because they are quite expensive. Folk remedies are very cheap, but in order to alleviate severe itching of the head (without dandruff and without obvious symptoms of seborrhea), you will have to be patient. Folk remedies have a cumulative effect, and a person feels obvious relief only a month after the start of regular use.
The most popular drugs from the pharmacy:
- Line of drugs "Sulsena".
- "System 4".
- "Psoril."
- medicated shampoos - Nizoral, Sebozol, etc.
Among the folk methods for itchy scalp (without dandruff and without obvious symptoms of mycotic lesions or seborrhea), oil masks, compresses with egg yolk, rinsing with an infusion of oak and chamomile bark, salt and soda scrubs are effective. You need to use them on a regular basis, then you will definitely see results.
How it manifests itself
Symptoms can manifest themselves in different ways and depend on the location of the allergen penetration and the characteristics of the body’s reaction. There are several types of allergies.
Respiratory or breathing:
hay fever or allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, other respiratory diseases and bronchial asthma. A runny nose, itching, nasal congestion, cough and swelling of the mucous membranes appear. We have already written how to distinguish an allergic runny nose. The most severe manifestations develop with bronchial asthma: wheezing in the lungs, severe coughing, and it becomes difficult to breathe.
Contact:
urticaria, eczema, Quincke's edema, which affects the skin, subcutaneous tissue and mucous membranes. A rash of different shapes and sizes, skin itching, and peeling appear. With urticaria, pinkish spots appear raised above the skin, and with Quincke's edema, the eyelids, neck and entire face swell.
Food:
after eating an allergen, there may be both skin rashes and gastrointestinal disorders.
Insect
allergy occurs after contact with insects or their waste products, for example, honey.
Medicinal
. Appears after treatment with certain drugs: painkillers, antibiotics or other medications.
Atopic dermatitis.
This is a separate disease that is not always associated with allergies. Periods of clear skin may not be related to nutrition, then allergies have nothing to do with it. It most often occurs in children, but in some cases occurs for the first time in adults. Usually begins after neuro-emotional overstrain and stressful situations or exacerbation of a chronic disease.
Preventive measures
In order for a child to stop constantly scratching his head, the cause should be eliminated as quickly as possible and existing diseases should be cured. But even after the situation has returned to normal, regular prevention of skin lesions should be carried out. Moreover, doing this is not so difficult:
- The child's head should be washed regularly and very thoroughly.
- It is necessary to select gentle detergents that suit his age and hair type.
- When washing, it is important to use only special children's products.
- It is necessary to comb the hair only with his own comb, and it is very important to convey your requirement to the teachers.
- It is important to wash and iron children's bedding, towels and hats regularly.
- It is necessary to ensure that the child’s head comes into contact only with natural materials.
- During walks, it is necessary to constantly monitor the baby and stop attempts to play with sick animals.
Preventive measures can also include a balanced diet, taking multivitamins, and regular sunbathing. And if problems are discovered, you should not let the situation take its course. Timely consultation with a specialist will help improve the situation and avoid additional problems.
How to recognize pediculosis?
The first alarm bell for parents is information that a case of lice infection has been discovered at school (kindergarten, camp, etc.). If your child has had close contact with someone who is sick, it is possible that lice have settled on their head. Frequent scratching of the head should also raise suspicions - itching occurs at the sites of parasite bites. Allergic reactions to insect saliva and excrement may also occur. You can check if your child has lice as follows:
- Comb your hair from the roots with a fine-tooth comb.
- After combing each strand, carefully examine the teeth.
- If a dark moving “dot” is found on the surface, most likely it is a louse.
- Place the find on a white napkin for better viewing and recognition.
Rating of the best remedies for atopic dermatitis
To treat atopic dermatitis, use special children's products recommended by a dermatologist. During exacerbations, medications are prescribed for oral administration, application to atopic areas and general body care:
- preparations for removing allergens from the body - Enterosgel, Lactrofiltrum, Enterodes;
- skin softening products – Atopic cream for daily care;
- drugs that relieve itching - Panthenol spray;
- bathing products - soft shower gels for atopic dermatitis should be purchased at the pharmacy: dermatologists recommend using Atopic bathing gel from head to toe.
Dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis
Dandruff is the result of overactive sebaceous glands. It is not harmful in any way, but may be accompanied by Dandruff itching. Seborrheic dermatitis, a chronic inflammation of the skin called Seborrheic dermatitis, has the same symptoms, but whitish scales can appear not only in the hair, but also on the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids and chest.
What to do
If you just have dandruff, a shampoo containing one of these ingredients will most likely help:
- zinc pyrithione;
- salicylic acid;
- selenium sulfide;
- ketoconazole;
- coal tar.
Such shampoos must be used strictly according to the instructions.
If the problem is seborrheic dermatitis, you will have to take Seborrheic dermatitis medications that your doctor will select.