In this article we will tell you:
- Principles of milk pasteurization
- Types of milk pasteurization
- Milk pasteurization quality
- Stages of pasteurization of milk in production
- Requirements for raw materials for the production of pasteurized milk
- GOST requirements for pasteurized milk
- Conditions for storing and transporting milk after pasteurization
- Which is better – pasteurization or ultra-pasteurization
- Pediatricians' recommendations for consuming pasteurized milk
- Who is not recommended to drink pasteurized milk?
- Shelf life of pasteurized milk in the refrigerator
Pasteurizing milk is a proven way to keep the product fresh and safe for consumption. The pasteurization method, which will soon be 200 years old, is successfully used in large industries and small enterprises.
Milk processing time, temperature conditions, packaging in which milk is packaged, and storage conditions are all important factors affecting the quality of the final product. How milk is pasteurized, read in our material.
What is milk pasteurization?
Milk pasteurization is a technology for disinfecting milk and extending its shelf life, which consists of heating the liquid once at a certain temperature for a certain time.
This technology is already more than one and a half hundred years old - it was first used in the mid-19th century by a microbiologist from France named Louis Pasteur. Actually, the name of the technology came from his last name.
There are various modes of pasteurization of milk - from long-term pasteurization (lasts 30-40 minutes at a temperature of 60 to 80 degrees) to instant (a few seconds at a temperature of 98 degrees). There is also ultra-pasteurization - it takes place at a temperature of more than 100 degrees.
Meaning
The advantages of pasteurization are obvious:
- accessible method;
- not expensive;
- the shelf life of the product increases;
- the environment is disinfected;
- the beneficial properties of the substance are preserved.
People who consume this milk are completely protected from intestinal disorders.
History of pasteurization
French microbiologist Louis Pasteur is the founder of the pasteurization process. In the mid-eighties of the nineteenth century, winemakers turned to a famous scientist with a request to find a remedy that could cleanse wine of harmful and destructive enzymes. The result of a number of experiments was the discovery that you can get rid of harmful microorganisms by heating the wine to a temperature of 55 - 60 degrees. He applied a similar method to milk to clear it of the tuberculosis bacillus.
Pasteurization has taken root and become popular in many countries around the world. It began to be used not only for disinfection, but also to increase the shelf life of dairy products.
What is pasteurized milk?
This is a heat-treated product. It increases shelf life. In the process of industrial pasteurization, milk is heated to 60 degrees for 1 hour or to 80 degrees for half an hour. Under the influence of this temperature, all pathogenic bacteria and microbes that are always present in whole milk are destroyed. During pasteurization, up to 90 or even 99% of microorganisms die (data on this issue vary). Using pumps, milk is cleaned of foreign impurities, then pumped into a separator, where the cream is separated. Then the product is cooled and placed in a special container, packaged and sent to the refrigerator.
The shelf life of the product ultimately increases to a week if stored in a sealed container in the refrigerator. Then the milk sours and curdled milk is formed. At room temperature the product can be stored for only a few hours.
Composition and calorie content
Not a single GOST precisely regulates BZHU and other features of the composition of pasteurized milk - the main thing is that it corresponds to what is indicated on the packaging. Even for fresh milk, these indicators can vary significantly, so it is not surprising that indicators vary markedly between different manufacturers. For this reason, our indicators will only be approximate, and the consumer is obliged to double-check the information by reading the exact content of the substances he needs on a specific package.
Most types of pasteurized milk have the least protein - its amount is in the range of 2.5-3%. On the contrary, carbohydrates are present in the composition the most - 4.5-5.5%, with the most popular value being 4.7%. As for fat content, this component is the most variable, because, as mentioned above, many manufacturers even regulate it artificially - it can fluctuate between 1-6%. Useful components in the form of microelements and vitamins in all types of milk are approximately the same, there is especially a lot of calcium and iodine, copper and strontium, as well as vitamins B and D.
If we talk about the calorie content of a natural drink, then it largely depends on the balance of BJU, especially on the amount of fat. As a result, the energy value can range from a very modest 44 kcal to a much more serious 71 kcal, so those who strictly monitor the calorie content of the foods they eat should be on their guard.
What is the difference between UHT milk?
Recently, on store shelves you can find not only pasteurized milk, but also ultra-pasteurized milk. It is produced using a similar technology, but heats up to a higher temperature of 135 degrees in just 2-3 seconds. The conducted studies confirm that such a short processing time is sufficient for high-quality purification of milk from harmful bacteria. Then it is immediately cooled to +4 degrees.
Ultra-pasteurization extends the shelf life of the product to 6 weeks or more, even when stored at room temperature. After opening the package, it remains fresh for 3-4 days, then it sours, like all other milk.
What is healthier - pasteurized or sterilized milk?
Sterilization occurs at a much higher temperature - up to 150 degrees. Thus, the raw materials are processed within half an hour.
There are 3 main differences between the two types of product:
- Pasteurized milk retains beneficial lactic acid bacteria, while sterilized milk does not contain any beneficial microflora.
- Pasteurized milk can be stored in a hermetically sealed box for about a week (ultra-pasteurized milk - 2 months or more). Sterilized products do not lose their quality for a year after production, if the original packaging is not opened during this time.
- Sterilized milk has less nutritional value than pasteurized milk.
In terms of practicality, sterilized milk wins. It lasts much longer. In terms of composition, a pasteurized product is still healthier.
How long is it stored?
Fresh milk has a very short shelf life, so many consumers sincerely hope that the pasteurized version, which they perceive almost as preservation, will last much longer. Such people will have to be disappointed, because regular pasteurized milk, when sealed, is usually stored for no longer than 3-4 days, and when unsealed it is advised to consume it within 24 hours.
Moreover, even such a short period requires storage conditions in the refrigerator, whereas at elevated temperatures, ripening can occur much faster.
You can slightly extend the life of the product by pouring it into sealed consumer containers or boiling it. In the first case, lactic acid bacteria can “start up” in the liquid even at the time of transfusion, and in the second, the product must be boiled in advance before it has deteriorated and such an operation does not negatively affect the usefulness of the milk.
With UHT milk the situation is radically different - it heats up much more, so there is absolutely no “life” left in it. Thanks to this, such a drink is optimal for delivery over any distance, and even more so it can be stored in the refrigerator. In warehouses and other specialized places, such a drink can be stored for several months, although it should be clarified that in an open package, the rapid formation of a colony of lactic acid bacteria is still possible.
At the same time, you need to understand that the expiration date is an abstract value if you do not know the release date. Ordinary pasteurized milk is a perishable product, so this point must be clarified - the date must be indicated on the packaging in a visible place. By the same expiration date, you can also determine how healthy the drink is, because from all of the above it follows that a truly natural and healthy product cannot be stored for a long time
Conditions for storing and transporting milk after pasteurization
After pasteurization and cooling, milk and cream should be kept at a temperature of 0...+8 °C, and storage is allowed for no more than 36 hours after completion of processing. Compared with pasteurization, sterilization of milk preserves the freshness of the product for much longer - for six months at a temperature of +1...+10 °C or for four months at 0...+20 °C. It is important that the rooms and chambers used for storage are well ventilated and protected from light.
Since the shelf life of milk is short, storage requires special conditions. So, the chamber must be darkened, and the temperature regime must be maintained in it.
The fact is that the sun's rays are able to penetrate several centimeters into milk, while the inner layers of the product are additionally illuminated by reflected light. The most permeable to light is skim milk. Under the influence of the biologically active solar spectrum, milk fat oxidizes first. As a result, peroxides, aldehydes and ketones are formed - all of them, especially the latter, cause the appearance of an oxidized taste. Whereas the greasy taste is a sign of oxidation of oleic acid.
Light also leads to the oxidation of proteins, due to which the amino acid methionine is converted into methional, and milk develops a sweetish taste, which is also called “sunny.”
Exposure to light negatively affects the vitamin composition and biological value of the product, destroying B2, C, A, carotene, etc.
To store milk, it is necessary to ensure a low positive temperature, since in such conditions mesophilic bacteria, namely lactic acid streptococcus and Escherichia coli, cannot multiply if, due to insufficient control of milk pasteurization, they remain in the product. In other words, they remain in an inactive state and, even at high concentrations, do not lead to serious changes in composition.
Even after heat treatment, 1 ml of milk contains up to 200,000 bacterial cells. Some of them are capable of developing at low temperatures, so they try to limit the shelf life to 36 hours. This period is calculated from the moment of completion of pasteurization and assumes storage at a maximum of +8 ° C. Maintaining the temperature makes it possible to restrain the growth of lactic acid bacteria, as a result of which during the sales period the acidity of the milk will be at a level of up to -21 °T, as required by the standard.
Milk freezes at -0.55 °C. Due to a drop in air temperature to -10 °C, it can freeze with the formation of ice crystals in the peripheral layers. Dry substances are displaced by crystals into the middle part of the product - there their concentration increases significantly, while the freezing point drops. As a result, even when kept at low temperatures for a long time, the milk does not freeze completely.
When the proportion of salts in the still liquid part increases to a certain level, salting out of the proteins occurs, that is, the destruction of the hydration shell of the protein with coagulation of the latter and the formation of a precipitate. As a result, the product tastes watery.
To deliver pasteurized milk, it is necessary to use refrigerated trucks or vehicles with an isothermal/closed body - this is stated in the instructions for the transportation of perishable goods. Today, the supply of this product to large cities and industrial centers occurs exclusively using road and rail tanks. The use of the latter makes it possible to completely mechanize loading and unloading. And the insulation layer provided on their walls prevents the milk from heating up or getting too cold.
Mechanical shocks during the transportation of milk lead to partial destruction of the protein shells of fat globules, which causes disruption of the fat emulsion, churning of fat and the formation of butter grains. Such problems can be avoided by leaving no free space in the tanks.
Features of the method
Pasteurization of milk involves heat treatment of the drink. The heating process occurs up to 63-100 degrees Celsius (the exact temperature indicator is determined by the chosen method). The heat treatment method is named after the scientist Louis Pasteur from France, who was able to apply the technique to eliminate microorganisms in liquid. The effectiveness of pasteurization is determined by the temperature and duration of exposure of milk under a certain regime. Despite the lack of boiling, only pathogenic bacteria are eliminated. The optimal temperature regime of heat treatment preserves the beneficial milk microflora and the optimal characteristics of the drink (consistency, taste and smell).
To successfully destroy pathogenic bacteria, you will need to carry out the procedure correctly. Sterile containers and equipment must be used. If sterilization is carried out at an unsatisfactory level, there is a risk of up to one billion bacteria entering the drink with further active reproduction. As a result, the number of microbes will reach a million per milliliter.
Pasteurization is recognized as an effective and inexpensive way to disinfect the resulting drink for further fresh consumption or the preparation of dairy and fermented milk products.
The effect of pasteurization on the properties of milk
During pasteurization, profound changes in the physicochemical and biological properties of milk are not observed. The content of protein and vitamins does not change significantly. Organoleptic parameters such as smell, taste, color, consistency remain the same. Therefore, it is believed that the nutritional value of the product remains almost the same level.
However, as a result of heat treatment, some processes in milk still occur. The degree of changes in physicochemical characteristics depends mainly on the heating temperature and holding time. Heat denatures milk proteins. The most sensitive are serum ones, for which it is enough to exceed the threshold of 65 °C. Casein has higher stability. Vitamins are partially destroyed, especially those soluble in water, and enzymes are deactivated. Phosphorus and calcium salts pass from a soluble to an insoluble state and precipitate.
When planning pasteurization, it is necessary to choose a method so that changes in the components of the product that affect its nutritional value are minimal.
Ultra pasteurization
This process is also a heat treatment of a dairy product to increase its shelf life. UHT milk can be drunk unboiled, and this is a definite advantage over its pasteurized counterpart. The boiling process leads to the destruction of all beneficial qualities, as well as the decomposition of proteins and a change in the absorption of calcium.
For ultra-pasteurization, special closed containers are used. The essence of the process is that the milk is brought to a temperature of 133-153 degrees, this temperature is maintained for two to three seconds, and gradually cooled to 4-5 degrees. This type of treatment leads to the death of all microorganisms.
Ultra-pasteurized milk does not sour, but retains all its beneficial qualities, since the heat treatment process does not negatively affect the state of vitamins, main lactic enzymes and mineral salts.
UHT milk can be stored for up to two months in a closed package, even without a refrigerator, at a maximum room temperature of +25 degrees.
An open box can be stored for no more than five days. After five days, UHT milk begins to taste bitter and acquire an unpleasant odor.
Modern technologies make it possible to produce ultra-pasteurized milk, which is not inferior in its beneficial qualities to whole fresh milk.
Pasteurization methods
There are 3 methods of pasteurization:
This method is called long-term pasteurization. Milk must be heated to a temperature of 63-65°C and pasteurized for half an hour;
This method, otherwise called short-term pasteurization, involves heating the product to a temperature of 72-75°C. After holding for 15-20 seconds, the heat treatment should be stopped; During flash pasteurization, milk should be brought to a temperature of 85-90°C without further holding.
Heat treatment (at 80-85°C) changes the taste and aroma of milk. When exposed to temperature, some elements contained in milk change their physical and chemical properties, and accordingly the composition of the product changes slightly.
For example, the gases contained in milk evaporate, the acidity of the product decreases slightly (by 0.5–1 °T), changes also affect the salt composition (phosphate salts become insoluble). Heating devices used in the production of pasteurized milk may become coated with burnt deposits caused by milkstone deposits. Calcium salts slow down the coagulation of milk, which requires the addition of an artificial solution of calcium chloride. When milk is processed using flash pasteurization (when the temperature is above 85°C), casein begins to change. And albumin protein tends to denature already at 60-65°C. Vitamins are the most resistant to heat treatment, especially when the access of oxygen to the pasteurizer is limited.
Experts do not recommend boiling pasteurized milk, as this changes the composition of the milk, reducing the content of nutrients and vitamins A and C. You can pasteurize milk at home in a water bath. When heating the water in a saucepan to 63-65°C, turn off the heat, let the milk stand for 20-30 minutes, and then cool it by placing it in cold water. During the heating process, it is necessary to constantly stir the milk.
Long-term
The most gentle method of processing milk. Pasteurization takes place automatically at enterprises. The equipment is equipped with an artificial intelligence program that does not fail. Maintenance personnel at dairy plants work around the clock, monitoring the entire technological process on monitors: heating temperature, degree of filling of tanks, time.
Treatment takes 30 minutes at 63-65 °C. During this time, all pathogenic microorganisms die, while lactic acid microorganisms remain.
Short term
This is high-temperature pasteurization - a kind of shock for the product. For 15-20 seconds the temperature in the tanks reaches 72-75 degrees.
Mini pasteurizers
Mini pasteurizers are available for home use. They are designed for milk volumes from 15 to 200 liters, the maximum heating temperature inside the device is 92 degrees. Typically, home pasteurizers come in the shape of a cylinder with a handle. Pasteurized homemade milk can be stored for up to ten days.
The weight of the device depends on the internal volume. The minimum weight of a pasteurizer designed for 15 liters is six kilograms.
Types of pasteurizers
According to the mode of action on the product, all units are divided into two groups: direct and indirect.
Among indirect ones, thermal ones are more common, in which milk is heated by intermediate coolants: hot liquid or air, steam, flue gases.
Other installations of this type are electrical. According to the method of heat transfer, they are either elemental or inductive.
Direct pasteurizers heat the product using ultraviolet or infrared radiation, as well as ultra-high frequencies. This also includes electrode and hydrodynamic devices.
The latter are divided into fluid friction devices, cavitation devices, and units in which both fluid friction and flow turbulence are used.
In addition, there are capacitive and flow-through pasteurizers. The former operate in a cyclical manner and are therefore ineffective. The second has a much smaller number of technological operations and their duration.
In industry, four types of pasteurizers are most often used: plate, tubular, steam with displacement drums and baths for long-term pasteurization.
The baths are designed to heat milk for 30 minutes. Temperature - 63 - 65 °C. Their main disadvantage, in addition to low productivity, is the possibility of microorganisms (thermophiles) multiplying in the product.
Therefore, all over the world they prefer units for short-term and flash pasteurization that heat the raw materials to a higher temperature - steam, tubular and plate.
For milk, the latter are considered the best, but with the help of tubular ones you can pasteurize viscous products. Steam and electric devices have low efficiency and problems with scale in boilers.
In direct-acting units, the heat source is the hydraulic resistance of the rotating fluid or electric current.
Among them, the most popular are installations in which milk is disinfected using ultraviolet radiation and pasteurized using infrared radiation (2.9 - 3.2 microns).
Microwave devices use waves with a frequency of more than 3000 MHz. The energy utilization factor reaches 0.8. The disadvantage is the complexity of the design. The efficiency of electrode heaters is up to 98%. However, they are not safe or reliable.
Milk pasteurizer
A pasteurizer is equipment designed for heat treatment of a dairy product. There are a number of requirements for pasteurizers:
- They must destroy all pathogenic bacteria,
- Ability to process a variety of products
- Preserve the unique qualities of processed products,
- Avoid product loss during processing,
- Be made from materials approved for use in the food industry.
Pasteurizers are divided into several types according to their main characteristics. So, according to their design, they are divided into open and closed. And depending on the work process, they can be periodic or continuous. In the dairy industry, continuous pasteurizers are more commonly used, but for the production of any canned products, a batch pasteurizer is more often used.
Another difference is the type of heat treatment. Some pasteurizers use sterile steam in the process. This method involves subsequent cooling of the milk in a special vacuum chamber. Others use a heat exchanger. The built-in regeneration department of which provides for a cooling process.
The usual package of a pasteurizer includes:
- Working capacity,
- Milk and water pumps,
- heating system,
- Pipelines,
- Remote Control.
Plate pasteurizers are more popular. They are able not only to quickly heat a dairy product, but also to maintain it for the required amount of time at a certain temperature and then cool it. The plate pasteurizer consists of:
- pasteurization column,
- Plate heat exchanger with cooling device,
- Centrifugal pump,
- Pipeline,
- Control systems.
- Long-term pasteurization bath
This device is capable of heating the product up to 95 degrees. A typical long-term pasteurization bath set consists of:
- double-walled bathtub with built-in electric heaters,
- control unit,
- motor,
- drain tap,
- pipe for pouring milk.
This type of pasteurizer is available in several versions, capable of holding from 60 to 2100 liters at a time. The average weight of a pasteurizer is 75 kg, and the weight of a device for pasteurization of 1000 liters is 340 kg.
Effectiveness of disinfection
Pasteurization of milk is aimed at eliminating pathogenic microbes. To do this, the drink is heated once. It is mandatory to observe a certain temperature regime and focus on the holding time. Mesophilic bacteria die most quickly, but other microbes may remain active. If the liquid is stored at a temperature less than +8 degrees, it is possible to get rid of pathogenic microflora, the product becomes of high quality and useful. The development of remaining bacteria stops if the drink is stored properly.
The effectiveness of pasteurization depends on the microflora and composition of the drink being processed. For this reason, the initial quality of the product is taken into account. Subsequently, storage conditions determine the final effectiveness of disinfection. If timely cooling does not occur, microorganisms continue to develop. To increase the efficiency of heat treatment, it is recommended to cool the milk received after milking to +3 degrees to timely eliminate most bacteria. Violation of storage temperature activates the development of microflora, so pasteurization technology becomes less effective and it will be difficult to improve the microflora in the future.
To ensure a successful procedure, equipment and inventory are disinfected. If the preparation was unsatisfactory, the composition of the product will be worse due to the continued activity of bacteria. An increase in the content of enterococci in milk after pasteurization indicates unsuccessful heat treatment of the product, which remains dangerous.
Milk obtained through ultra-pasteurization can be stored without refrigeration at room temperature for up to 4 months.
Shelf life of pasteurized milk in the refrigerator
The length of time milk remains fresh depends largely on the container. A plastic bottle does not retain its properties for as long as special packaging.
For long-term storage, cardboard packaging is used, which provides maximum protection of the product from contact with oxygen, forming a hermetically sealed vacuum. But this is only possible until the moment the pack is opened.
GOST 32922-2014 “Pasteurized cow's milk” does not have specific expiration dates for pasteurized milk. But the temperature requirements are established:
- up to +2…+6 °C during storage;
- up to +10 °C during transportation;
- Freezing is not allowed.
But at home, you can easily put the milk in the freezer to preserve it for 1–6 months. When you need it again, it is recommended to defrost it in the refrigerator. It is also worth thinking about using the most suitable cookware in advance. Practice shows that a plastic bottle is most convenient, although it cannot be filled to the brim. Otherwise, the liquid will expand as it cools and tear the plastic. It is for this reason that you should abandon glassware. Once a glass container cracks, drinking milk from it will be dangerous due to the possibility of small fragments.
Pasteurization in industry
Nowadays, for industrial heat treatment of products, TEK hydrodynamic units are used, which are also suitable for mixing, homogenization (breaking fat globules into smaller ones), emulsification (producing emulsions by separating the drop-liquid phase from supersaturated solutions, vapors). Manufacturers offer different models of equipment, so each enterprise can choose the most suitable option. It is assumed that it is possible to shut down the plant’s boiler room and organize the procedures at minimal cost.
Proper heat treatment in the dairy industry of a product eliminates pathogenic bacteria from the composition and improves taste characteristics. Clumps of high-molecular compounds are crushed by cavitation bubbles. At the same time, a reduction in energy costs is guaranteed.
Modern installations are configured taking into account what the pasteurization temperature should be and the further conduct of each stage and the exit of liquid from the installation. Careful process control increases the efficiency of the product heat treatment procedure. Modern pasteurizers (hydrodynamic units) heat liquid in volume. A new class of pasteurizers eliminates product burning.
In industry, pasteurizers with several sections (3, 4 or 5) are used. In this case, the main parameters of the installations are taken into account.
- The temperature of heat treatment and cooling must be set before the start of the procedure. This is required to effectively disinfect the product and eliminate all unwanted bacteria from the composition.
- Raw milk must enter the regeneration (recuperation) section for first processing. The optimal product temperature is 10-35 degrees.
- The separator is used to clean the incoming drink. In this case, heating occurs to 37-45 degrees (the initial indicator is taken into account).
- The hot water temperature is then set for pasteurization. The maximum permissible indicator is taken into account when carrying out pasteurization. In this case, the water should be hotter than milk.
- The next stage is cooling. It is recommended to take into account the time of year and local conditions to properly configure the equipment used. Usually milk should be colder than 9 degrees. For this, water (artesian, tap, ice) or brine can be used.
The pasteurizer, which is a plate heat exchanger, must be functional and reliable. The equipment must be configured taking into account how milk is pasteurized in production. This is required for careful control over the heat treatment of milk.
Types of pasteurization
Heat treatment of milk can be carried out under different modes. In each case, certain features of the procedure are taken into account.
- Long-term pasteurization is aimed at guaranteed suppression of pathogenic microorganisms. During the procedure, the properties of the milk remain original, but the vital activity of microbes is almost completely suppressed. The method is labor-intensive, so it is used in exceptional conditions. The pasteurization temperature is 65 degrees. The main difference is the lengthy procedure, as it takes about half an hour. Traditionally, special large bathtubs are used, characterized by double walls. This method is considered one of the best, because its effectiveness is maximum (99%).
- Short-term pasteurization is carried out according to a more accessible scheme and involves the use of only hot water. The procedure is based on heat exchange. The milk is heated to 71 degrees and then kept for 40 minutes. Efficiency reaches 98 percent, so this method is considered one of the best.
- In high-temperature pasteurization, milk is heated instantly without further holding. The minimum temperature should be 85 degrees. This method resembles a short-term one, but exposure is not expected. Heating is carried out not only using hot water, but also steam. Suppression of saprophytic microflora reaches 99.5 percent. Nowadays, due to its specificity, this method is practically not used, but it can be effective for cream, which is subsequently used to make butter.
- Ultra-high temperature pasteurization involves two stages of the procedure. Initially, the temperature is raised to at least 70 degrees (but not more than 80). Then heated to 135-150 degrees using steam. In this mode, milk should be processed in less than one minute.
When carrying out any procedure, it is important to observe the correct parameters of the selected mode. This determines how effective the selected types of pasteurization for milk processing will be.
Pasteurization of milk at home
Even though pasteurization seems like a complicated process, it can be done at home. So, how to pasteurize milk without special industrial installations? The process is carried out in several stages.
Pasteurization of milk at home
- Fresh milk is poured into a basin and the heat is turned on to maximum. The milk must be constantly stirred so that it heats evenly.
- When the milk reaches 72 degrees, turn off the heat and cover the pan with a lid. It should infuse for no more than 30 seconds.
- After this, the container with milk is transferred to a bowl of cold water and cooled to 22-38 degrees.
That's it, pasteurization is complete, and you can consume high-quality milk without bacteria.
The slow cooker can also be used for pasteurization. Modern models have a special “Pasteurization” mode. Milk is simply poured into the multicooker bowl and the “Pasteurization” mode is set. There is no need to control the process, the multicooker will do everything and at the end will notify you with a signal that the work has completed.
Interesting! Modern multicookers have a “Pasteurization” mode, which allows you to process the product at home without any difficulties.
Pasteurization is an effective process of disinfecting milk before its subsequent consumption or processing. It also allows the milk to be stored better. This processing technique is used for milk that is sold or consumed at home. If pasteurization is carried out correctly, the milk will remain healthy, but will not contain pathogenic microorganisms. This product is of high quality and pleasant taste, and most importantly, it is absolutely safe for consumption.
How is it different from sterilization?
Milk can be pasteurized or sterilized. What is the difference?
Sterilization and pasteurization are two different processing processes. To choose the right product in a store, you need to understand their differences.
During pasteurization, milk is heated at temperatures of 65-100 degrees. The higher the temperature, the shorter the processing time.
When sterilizing, the product is processed at 120-150 degrees for up to half an hour.
There are no harmful bacteria in sterilized milk, but there are no beneficial ones either! And beneficial microorganisms are preserved in a pasteurized product.
Sterilized milk can be stored for a long time, up to a year, but only under the right conditions. But pasteurized milk can last no more than 2 weeks.
The nutritional value of a pasteurized product is lower than that of a sterilized product. Pasteurized milk can be used to make lactic acid products.
It sours well, but sterilized milk does not sour, but simply becomes bitter. As you can see, sterilization and pasteurization of milk have significant differences.
How long does milk last after pasteurization?
We figured out what sterilized milk is. Now let's talk about the shelf life of a product that has undergone this heat treatment.
Fresh milk does not last as long as many of us would like. Therefore, when purchasing pasteurized milk, consumers sincerely believe that due to this heat treatment, the product is almost preserved at the factory, which means it is able to retain its beneficial properties and freshness for a long time. But, unfortunately, everything is not as cloudless as we wanted.
The shelf life of regular pasteurized milk in sealed form is no more than 4 days, and after opening the package it begins to sour within 24 hours. Let’s say more, even with such a short shelf life, the product should be kept in the refrigerator, because at room temperature it will lose its beneficial properties even faster and turn sour.
Advice! It is possible to extend the shelf life of pasteurized milk by pouring the product into an airtight glass container or by boiling it. In the first case, lactic acid bacteria can appear in the liquid even at the time of transfusion, and in the second, the product should be boiled in advance, before it becomes unusable, and such a procedure does not negatively affect the usefulness of the milk drink.
Speaking of ultra-pasteurization, the situation here is significantly different - milk is heated to critically high temperatures, which negates the existence of any viable microflora in it. Yes, milk no longer has beneficial properties, but its shelf life is already quite impressive, allowing it to be transported from the manufacturer to different points far removed from it, without fear for the preservation of the taste of the product.
In warehouses and other specialized places, UHT milk can be stored for several months. In open packaging, the shelf life is reduced, but, unlike a pasteurized product, we are not talking about several days, but about several weeks.
It’s worth understanding right away that if you don’t know the production date of a product, then the expiration date is an abstract value. Pasteurized milk is a perishable product, and therefore this aspect of the issue should be clarified - the release date and expiration date are indicated on the container.
Using the same shelf life, it is also possible to determine the benefits of the drink. So, from all of the above it follows that a truly natural and most healthy drink cannot be stored for a long time.
At what temperature is it advisable to store pasteurized milk? The standard temperature for refrigerators is 6-8°C. Under such conditions, the product is able to retain its beneficial properties throughout the storage period specified by the manufacturer.
Infrared pasteurizers
Infrared pasteurizers are used in a variety of fields. They are used to pasteurize milk from cows with mastitis. This dairy product is not suitable for humans, but is well suited for feeding calves. Another area of application is increasing the shelf life of bottled milk. Infrared pasteurizers are divided into three groups:
- Capacity up to 300 liters per hour,
- Capacity from 500 to 1500 liters,
- Capacity from 2000 to 500 liters.
How to choose healthy milk in the store?
There are many varieties of pasteurized milk . Therefore, in the store you should first look at the production date and expiration date. If it has expired or will expire soon, it is better to refuse the purchase.
Plastic bags are not suitable for long-term storage of the product. They are also not strong enough. Plastic transfers foreign taste and odor to milk. Glass bottles do not have this disadvantage, but it is better to choose products in cardboard bags. They are great for long-term storage.
You should also study the composition. If it says whole milk, it is a natural product that has been heat-treated. Whole milk can be diluted with reconstituted milk - made from dry powder. It is not necessarily of poor quality, there are simply fewer useful substances in such a product.
There is an easy way to check the quality of milk. You need to drop a drop of it into a glass of water. If it sinks to the bottom, the milk is whole; if it spreads, it is diluted.
Good pasteurized milk does not have sediment, but this can only be checked at home after opening the package.
Antibiotics are often found in imported milk. If it does not sour for a long time, it means that these substances are in the product, as well as acidity stabilizers. It is clearly not worth buying it - it will not bring any health benefits.
GOST requirements for pasteurized milk
GOST 32922-2014 “Pasteurized cow's milk - raw materials. Technical Specifications" applies to pasteurized cow's milk - a raw material that is made from raw cow's milk using pasteurization at the factory.
According to its organoleptic characteristics, the product of interest to us must have the following characteristics.
| Index | Characteristic |
| Appearance | Opaque liquid, no sediment, a small amount of cream may settle, which disappears when stirred |
| Consistency | Liquid, homogeneous, non-sticky, without protein flakes or lumps of fat |
| Taste, smell | Characteristic for this product with a taste of pasteurization, without foreign tastes and odors |
| Color | Uniform white or creamy tint |
For pasteurized cow's milk - raw materials, the following physical and chemical indicators have been established:
| Indicator name | Norm |
| Minimum mass fraction of fat, % | 2,8 |
| Minimum mass fraction of protein, % | 2,8 |
| Minimum mass fraction of skimmed milk solids (SMF), % | 8,2 |
| Maximum acidity, °T | 21 |
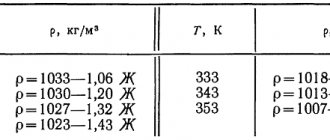
| Minimum density, kg/m | 1027 |
| Cleanliness, group, no less | II |
| Heat resistance, group, not lower | IV |
| Temperature of the product upon release from the enterprise, °C | 4±2 |
It is worth emphasizing that after using any pasteurization method, phosphatase cannot be present in milk.
Toxic elements, pesticides, mycotoxins, dioxins, melamine, antibiotics, radionuclides, and genetically modified organisms are also considered potentially dangerous. Their share in the composition of pasteurized milk cannot exceed the indicators established by the requirements or legislative and regulatory legal acts of the states that have adopted the above standard.
We recommend
“What types of milk are the most popular: what the Russian population drinks” Read more
If we talk about mesophilic aerobic and facultative anaerobic microorganisms, coliform bacteria, the genus Salmonella, Staphylococcusaureus, Listeria monocytogenes, then in pasteurized cow's milk subject to further processing, their quantity also cannot exceed the indicators established by the requirements or legislative and regulatory legal acts of states using the standard.
Influence of environmental factors on microorganisms
1. What groups of microorganisms are distinguished depending on their optimal growth temperature?
According to the temperature optimum for growth, three main groups of microorganisms are distinguished:
1.
Psychrophiles - grow at temperatures below +20 0 C.
2
. Mesophiles - grow in the temperature range from +20 to +45 0 C (often the optimum is at 37 0 C).
3
. Thermophiles - grow at temperatures above +45 0 C.
List methods of sterilization using high temperature.
The death of cells of bacteria, fungi, yeast and viral particles during sterilization at high temperatures occurs either as a result of cell combustion or as a result of coagulation of the protein structures of microorganisms.
The following methods of heat sterilization are distinguished: calcination, boiling, dry heat sterilization, wet heat sterilization (autoclaving), sterilization with flowing steam.
Indicate the objects to be pasteurized, the temperature at which it is carried out, and the duration.
Pasteurization involves the destruction of only vegetative forms of microorganisms in the material and is used in the food industry. Widely used for easily perishable food products (milk, juices, syrups). In this case, short-term heating to 90-92°C for 2-5 seconds or longer heating to 70-75°C for 5-10 minutes is used. Materials processed in this way are considered pasteurized, but not sterile, as they contain spores.
4. What nutrient media are sterilized using the fractional method?
The fractional method is used to sterilize nutrient media whose properties change at temperatures above 100 0 C - these are media containing proteins, carbohydrates and other substances that are easily changed by heating; they are sterilized fractionally with flowing steam.
5. Which apparatus is used for dry heat sterilization?
Dry heat sterilization is carried out in air sterilizers (formerly called “dry heat ovens” or “Pasteur ovens”).
6. In what cases is the tyndalization method used?
Tyndalization is fractional sterilization. It is used for media that deteriorate when exposed to temperatures above 100°C.
Indicate the temperature that is created in the autoclave at a pressure of 0.5 atm.
List physical methods of sterilization.
Methods of the physical method of sterilization include drying, burning and calcination, boiling, pasteurization and tindalization, hot air (dry heat), ultrasound, ultraviolet and radioactive radiation, high frequency current, sunlight.