Dairy farming is one of the profitable industries in agriculture. Products obtained from cows are not only tasty, but also healthy. However, few people know how many beneficial substances actually are included in milk and what to do to ensure that the fat content is at the desired level. We hope our article will help you figure this out.
The fat content of a cow's milk is one of the main indicators of the quality of this product. It’s not without reason that milk packages focus buyers’ attention on fats, proudly “protruding” this indicator on a unit of dairy product.
Some people buy pasteurized store-bought milk, while other consumers prefer a natural product from the owners. However, such ideas are just the tip of the iceberg - to learn more about milk, you need to become more familiar with the fat content and know what it depends on and how it is increased.
Fat content
The norm for the fat content of milk in a cow is 3.4%. A higher percentage allows you to increase the cost of production. Farms work to maintain this important indicator not lower than the stated norm; factories also control the quality of raw materials: the fat content and quality of cheeses, butter, and sour cream will depend on the chemical content that is included in milk.
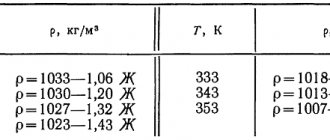
Based on accepted standards, the acceptable fat content of domestic cow's milk is 3.3−6%. As for the product in its natural form, the latter figure of more than 6-8% may indicate the presence of vegetable fats in it.
What is the fattier milk?
Fattier milk
and towards the end of lactation.
Fat content is increased by: legumes, cake, wheat bran, fodder and sugar beets. The vitamin and mineral supplement “Zdravur Mu-Mu” also significantly increases the fat content of milk
.
Reducing the amount of hay sharply reduces the fat content of milk
.
Interesting materials:
What is the suffix in the word little? What punctuation mark is placed after the words Namely? What are the reasons for borrowing words from other languages? What are the characteristics of a word? When is the word extreme used? When can words be hyphenated? When did the word Airbus appear? When did the word Uzbek appear? When is word analysis based on its composition? When is S put at the end of a word?
Concept and meaning
Milk fat refers to the fat globules found in the milk of farm animals. It is a product with a high level of saturated acid capacity.
If a cow produces a small amount of milk, then its fat content is high. Otherwise, the cow can only boast of a large milk yield, but small percentages of nutrients.
There are two types of indicators. Take a package and you will see the relative percentage of fat content of cow's milk in one liter. It is used most often when assessing the quality of a product. This % is higher when the cow is characterized by low productivity.
The Jersey cow has the highest numbers - the relative fat content reaches 14%. The milk yield of this breed is small, and the total amount of fat during the entire lactation period does not exceed 700 kg.
Complications
During severe calving, the fetus may get stuck in the mother's perineum; if it is not removed in the first hours, it will die, and possibly the adult too. Removal requires at least two people and special chains and forceps; using them without a veterinarian is highly not recommended; incorrect and inept movements will only cause damage.
Special reference books and magazines can help beginners. Experienced livestock breeders give various advice here, including what to do after the cow calving. According to most, it is necessary to watch her for the first few hours.
There is a possibility of so-called paresis occurring immediately after childbirth; its manifestation is similar to the symptoms of paralysis. The animal's ears and sacrum become cold, it cannot stand up and moans protractedly. Calcium is used for treatment; it is injected into a vein or subcutaneously. The cause of the disease may be obesity, an unbalanced diet or an improper diet. Such unpleasant situations most often occur in adults.
How to increase the fat content of a cow's milk
You can increase the level of fat in a product in order to make it even more tasty and nutritious, as well as to increase its selling price.
Secrets to increasing your score:
- Diet. An increase in fat can be noted when feeding the animal fresh green grass. In summer, if possible, the cow should be grazed on pasture.
- Udder massage. It must be carried out before each milking. This procedure will stimulate the secretion of stagnant milk, which contains the highest fat level.
- Milking “foremilk”. Typically, milk obtained in the first seconds of milking has less fat.
- If you milk it into a separate container, the amount of fat in the subsequent product will automatically increase. In addition, this trick will increase the hygiene of the process. The animal must be carefully “milked” to the last drops.
It is in residual milk that the fat level is highest.
To increase the fat content of milk it is recommended:
- Form a basic diet of roughage and succulent feed, rich in sugar, fiber and starch - carbohydrates that play a key role in the formation of milk fat;
- Introduce sodium acetate into the intestines (150-300 g per day), which increases the content of acetic acid - the material for the formation of fat cells;
- During the stall period, add sugar beets to the food (about 2 kg per 1 liter of milk) or similar products with a large amount of “fast” carbohydrates, which increases the fat content by up to 0.5%;
- Short-term addition of brewer's yeast (3 kg for 3 days) increases fat content by 0.2-.03% for one and a half months;
- Feeding with iodized salt to stimulate the thyroid gland.
Factors affecting the percentage of fat in cow's milk
There are several of these factors. These are the genetic potential of the animal, feeding diet, age and season. Each of them affects fat content, reducing or increasing it.
Genetic level
In some dairy breeds, selection was and is being carried out for such characteristics as milk fat content. The best representatives are selected for breeding, and their offspring inherit the desired traits. However, even among purebred cows, phenotypic deviations from the standard are possible.
Belonging to a breed to some extent guarantees a certain percentage of fat content, since this characteristic in cows is inherited.
Feed base
The potential inherent in a cow by nature and breeders can only be shown by proper feeding. If the animal is underfed or the feed does not contain enough important mineral components, the fat content will be affected.
The food a cow eats at home also matters. Fat in the body of ruminants is formed from acetic acid, the source of which is fiber obtained by animals from grass, hay, and silage. If there is not enough roughage in the cattle diet, the production of acetic acid is reduced and the fat content is reduced. The minimum fiber content in the diet of dairy cows should be 16-18%. Hay in the diet should be at least 50%, grain – no more than 15% (if you exceed the norm, lactic acidosis may develop).
Maintaining the optimal ratio of sugars and protein (1 to 1), sugars and starch (1.5:1) in the cattle diet improves conditions for the rumen microflora, which enhances fat synthesis. The optimal level of starch in the diet of dairy cows is no more than 28%. If carbohydrates in the diet are less than 20% or more than 40%, fat content may decrease by 1%.
Finely ground feed reduces the amount of fat, since due to the small size of the particles they are quickly removed from the proventriculus. Therefore, you need to cut root vegetables and vegetables into small pieces so that the cow can swallow them. To increase fat content, cattle are fed with mixed feed and crushed corn. You can add a little sugar to the corn mash. Boiled potatoes (not raw, they contain a lot of starch), beets and carrots in small portions are added to the food. All vegetables must be cleared of soil.
Age characteristics
How much fat milk contains depends on the age of the cattle. Practical studies show that fat content, like milk yield, increases until the 5th calving, and becomes maximum in the next lactation. In older cows, these characteristics naturally decline. In first-calf heifers it is lower than in cows that have given birth repeatedly, which is also considered normal.
See also
Technology for raising replacement young cattle and maintenance rulesRead
Season
The fat content is lower in summer than in winter. This depends on feeding succulent food in the warm season and drinking a large volume of water. The liquid entering the body makes the milk thinner.
How to determine fat content at home
It is not easy to accurately determine the fat content of milk without equipment. You can only get an approximate figure at home yourself.
To determine the amount of fat, carry out the following steps: Take a transparent glass, wash it well and dry it. Set the line at 10 cm. Pour in fresh milk and leave for 8 hours in a warm room;
After time, use a ruler to measure the layer of cream that appears on top. Now you need to calculate one indicator.
10 cm is taken as 100% fat content. Now you can calculate the amount of fat in your milk. However, it is important to remember that this result is not 100% accurate.
Description of the technique
To independently determine the fat content of breast milk, a young mother needs to stock up on a ruler, test tube and marker in advance.
Next, follow these steps: Taking a pre-washed test tube, measure a distance of 10 cm from the bottom on it. This distance must be marked with a marker, preferably black; After this, the young mother should pour expressed breast milk into the test tube. It must be remembered that to evaluate and obtain a reliable result, you need to use the rear portion of mother's milk. Measuring fat content in foremilk is inappropriate, since this portion of milk does not normally contain an increased amount of fat; The test tube is installed in a vertical position using a special stand or tripod. In this position, the container is kept for 7 hours at room temperature. The tube is not closed; After the milk has settled, a creamy layer forms in it, which must be measured using a ruler. Each millimeter division of the ruler is equivalent to 1% milk fat content
Before starting the assessment, it is important to consider that milk expressed from an overfilled breast will contain an order of magnitude more fat.
The World Health Organization has described the gold standard for the fat content of human milk as 4%. If this indicator has shifted up or down within 1-2%, then this is not a reason for serious worries. The body of each breastfeeding woman is individual, so quality indicators are closely related to many factors.
The described technique cannot always reliably determine the amount of fat in breast milk. An equally important indicator of the quantitative composition of this product is the baby’s weight gain. If a child does not gain weight well and is often capricious, this indicates malnutrition.
Conditions of detention and milk fat content
The fat content of milk is influenced by all factors important for the healthy development of the animal:
- Optimal temperature conditions;
- Healthy humidity and ventilation;
- Frequent milking intervals.
Long daily walks in cold weather and grazing in summer make it possible to achieve an optimal and stable level of milk fat content for a particular cow.
In hot weather, the quality of milk decreases, in cold weather it increases. The best performance is achieved at a temperature of 10-16 degrees.
The last portions of milk are always the fattest. Frequent milking with additional “massage” irritation of the udder ensures the most complete removal of milk from the udder, and therefore its best fat content
Contraindications
Lactose is not fully absorbed by every body, and its individual intolerance becomes a contraindication to drinking cow's milk.
Lactose favors the formation of a putrefactive environment and sometimes causes digestive problems. The chemical composition of milk becomes depleted when boiled, but in its fresh form it is contraindicated for infants due to contamination with bacteria.
Milk is contraindicated for people with salt deposits in blood vessels
For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and pancreas, it is worth replacing the consumption of fresh products with fermented milk.
Types of fat content
The assessment of the quality of natural milk is determined by the milk fat content, which is measured as a percentage.
Today, there are several types of this product, which are divided depending on the percentage of fat in its composition.
This indicator is significant for different foods, as well as other areas of use. Did you know? If it is not possible to purchase cow's milk of a certain fat content, you can take goat's milk.
It has an indicator of 4 to 9%, in addition, it contains the same amount of useful elements and is digested in the same way as cow's milk.
Categories
- up to 1% - low-fat, drunk by people who avoid fatty foods;
- up to 2% - a low percentage, but the most popular product used in various fields; 3.5% is the average norm when determining the indicator of a paired product immediately after milking;
- from 4.5 to 6% - high fat content, which is produced only by certain breeds of cows;
- 10% - maximum fat content, presented in the form of cream.
The fat content of cow's milk is a distinctive feature of this product, for which it is valued by the consumer. Increasing the fat content of homemade milk is not so difficult; it is much more difficult to properly care for the animal in order to prolong maximum lactation and constantly receive a high-quality fatty product.
How beneficial is this drink for our body?
The problem of milk consumption is associated with new scientific research data, which talks about the accumulated evidence of harm caused to health by this product.
The campaign against cow's milk could lead to a decline in the population, which had already declined significantly in the 1990s.
Many doctors associate it with a variety of medical problems. However, there are no fewer scientific and medical facts that support the general concept of the usefulness of this product.
Lactase enzyme deficiency
The absorption of food is determined by the synthesis of certain enzymes, the presence of which is determined at the RNA level and arose as a result of the adaptive reactions of the human body associated with traditional dietary habits. The lactase enzyme is responsible for the digestion of milk, a deficiency of which was found in 15% of Russians, almost 100% of those living in Siberia, 6% of Ukrainians, and on average 25% of Europeans. The absence or deficiency of lactase leads to disruption of the digestion process of dairy products in the gastrointestinal tract.
Lactase deficiency does not exist as a medical diagnosis
This enzyme helps process sugar. Problems with milk digestion can be detected even in infancy during breastfeeding. Lactase deficiency can be treated with enzymes. Children are prescribed Lactase Baby, the drug helps cope with feeding problems. Adults can also undergo enzyme therapy.
The value of a glass of milk
Lactase deficiency is classified into several types:
- primary – when the production of the enzyme is reduced, but when the cells that produce it (enterocytes) are not damaged;
- transient - when the production of enzymes is associated with defects in fetal development, typical for premature babies;
- secondary – with damaged enterocytes, these cells can be damaged during inflammatory processes in the intestines of various natures. Cell synthesis can be restored after treatment.
The causes of lactase deficiency in children and adults are usually different
If for residents of Siberia the deficiency is associated with the lack of cow's milk in the diet, then for residents of “prosperous” dairy regions it is a question of damage to enterocytes by an infectious process - parasitic, infectious in nature and/or dysbacteriosis. If the restoration of enterocytes can be secondary, then the restoration of immunoactive cells (of which about 80% of the total number is located in the intestine) cannot be ignored.
Africans have a lean physique due to a lack of protein foods
It is worth noting that lactase deficiency is typical for 90% of Latin Americans, 95% of Africans and 25% of Europeans. It is often associated with genetic factors and the processes of human maturation. Also, in some cases, part of this enzyme can be removed from a store product, since dietary supplements and medicines are produced on its basis.
Harm or benefit of beef (milk) fat
Milk or beef fat is assessed by medicine as one of the most harmful, leading to clogging of blood vessels with cholesterol plaques.
The problem of atherosclerosis is not as superficial as some experts want to present it. It is classified as a disease characteristic of modern humans, associated with several factors:
- with inflammatory processes in vessels of an infectious nature, “detaining” cholesterol as a result of decreased tone and impaired blood circulation in the vessels;
- with direct deposition of cholesterol on the walls;
- with a lifestyle disorder and, as a result, a decrease in the intensity of blood circulation, which also leads to excessive deposition of cholesterol on the walls during periods of local lipid imbalance.
Cholesterol on the walls of the vessel
Experts emphasize that cholesterol is an important chemical element, a kind of energy source for cells of the immune and nervous system, and is also involved in muscle metabolism. It is not a by-product or a harmful product.
Dairy products are a source of high-energy fats that the body needs, but with a systematic lack of plant components in the diet, the balance of lipoproteins is disrupted. The body has redundant mechanisms to combat deposits on the walls of blood vessels: with intense blood circulation, which occurs during intense work, movement, running, and also when visiting a Russian bath. From this we can conclude that atherosclerosis is not associated with milk fat, but with lifestyle and nutritional deficiencies leading to an imbalance of lipoproteins.