Demodicosis (Demodecosis from Lat.) is a common chronic dermatosis, mainly of the facial skin, caused by parasitism of the glandular acne mite. From 2 to 5% of the population suffer from demodicosis. The disease ranks seventh in terms of incidence among other skin diseases. Demodicosis in humans complicates the course of rosacea (in 88.7% of cases), perioral (around-oral) dermatitis (in 58.8%) and acne in 33%. Among acneiform dermatoses, the disease accounts for 10.5%.
Demodicosis occurs mainly in young women aged 20–40 years, whose incidence is 4 times higher than in men. The disease is rare among children, which is associated with low sebum production. The incidence of disease in people over 45 years of age is due to hormonal changes in the body and somatic pathology.
The genus Demodex contains more than 100 species of ticks, 10 of which are pathogenic to humans, cats, dogs, horses, sheep, pigs, goats and cattle. Ticks that parasitize animals do not parasitize humans. Ticks that parasitize dogs (D. canis) are deadly. They often lead to the death of puppies and weakened animals.
With demodicosis, the skin of the face is primarily affected.
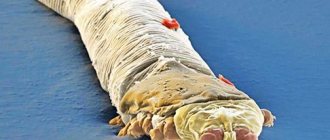
Rice. 1. The photo shows demodex mites under a microscope.
The cause of demodicosis is the acne iron mite
The demodex mite (D. follicullorum) belongs to the genus Demodex, family Demodicidae, suborder Trombidiformes, order Acariformes.
A little history
- The parasite was first discovered in 1841 by two independent researchers Henle (identified the parasite on human skin) and F. Berger (identified the parasite in earwax).
- In 1842, C. Simon identified mites in hair follicles and described the parasite for the first time. Between 1917 and 1923, acarologist Hirst identified 21 species and several subspecies of demodex mites in animals.
- In 1963, L. Kh. Akbulatova described a new species of iron mite, Demodex folliculorum brevis.
Spreading
Demodex mites are the most common parasites living on the surface of the body of humans and animals. They live in the mouths of hair follicles and the excretory ducts of the sebaceous and meibomian glands. Of the 100 known species of Demodex mites, 2 species live on human skin: Demodex folliculorum longus (long) and Demodex folliculorum brevis (short). Contamination of the skin occurs in childhood through contact. The maximum incidence occurs in females aged 20–40 years. At older ages, tick parasitism is registered in 80–100% of the population.
Acne iron mites live in places with high humidity; the parasites do not live long outside the host, are distributed everywhere, and are recorded in all races and in all geographical zones.
Who is at risk?
This disease develops regardless of a person’s age and gender. But there is a certain group of people who are more susceptible to Demodex infection.
Pregnancy
This occurs against the background of decreased immunity caused by:
- diabetes mellitus;
- pregnancy;
- transitional age;
- menopause;
- oncology;
- skin diseases (seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea, acne);
- food intoxication.
People with sensitive thin and oily skin are also at risk.
General characteristics of parasites
Acne gland mites live in the mouths of hair follicles and excretory ducts of the sebaceous and meibomian glands of the skin of the face (T-shaped zone), in the ears, and less often on the back and chest. There is an atypical localization of parasites.
Demodex mites feed on epidermal cells and sebum.
At night, ticks crawl to the surface to mate. Ticks move along the surface of the skin at a speed of 8 - 16 mm/hour.
At the head end (gnathosoma) there is a mouth opening equipped with sharp chelicerae that facilitate the absorption of food (epidermal cells and sebum). Digestion of food occurs under the influence of lytic enzymes.
Rice. 2. Photo of demodex mites under an electron microscope.
Clinical manifestations
Have you suddenly noticed increased skin roughness? Demodectic mange should not be ruled out. There may also be other symptoms:
- skin itching or peeling;
- redness;
- increased skin sensitivity;
- burning sensation of the face;
- The skin felt rough, like sandpaper.
Depending on the location of the lesion, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Eye shape. Demodicosis of the eyelids is accompanied by itching, pain, and blepharitis. The eyes quickly get tired, the eyelids swell, and the eyelashes fall out. There may be inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes - conjunctivitis.
- Damage to hairy areas. Irritation, itching, and peeling of the skin appear. The hairline becomes sparse and then the hair shafts fall out completely.
- Damage to the porioral and ear areas. The skin becomes rough and itchy.
Then there may be signs of dermatitis: redness, irritation, swelling of the tissue. Based on skin manifestations, two types of demodicosis are distinguished:
- Erythematous. It is characterized by the appearance of red spots on the face a week before the full picture of the disease. It resembles a mosquito bite that is a little itchy and itchy. Then the spots increase in size and the skin becomes oily.
- Papular-pustular. Against the background of redness and irritation of the skin, pustules appear. Gradually they grow, the surface of the dermis becomes uneven, bumpy, painful and itchy. The peculiarity of demodicosis is that the pustules are located nearby in the form of a chain. Itching is most pronounced at night during the parasite's breeding season.
Demodicosis can be combined with other pathologies, aggravating their course. Let's look at the main ones that occur most often.
Rosacea
Numerous studies have reported increased levels of parasites in patients with rosacea. Human demodicosis can manifest as a dry type of rosacea and is called rosacea-like demodicosis.
Let's look at the main differences
| Rosacea caused by Demodex | Common rosacea |
| Characterized by dryness, flaking of follicles, superficial vesicles and pustules | Characterized by oily skin, lack of scales and deeper skin lesions |
| Full recovery after treatment | Doesn't go all the way |
Demodectic rosacea completely goes away after the therapy prescribed by the doctor.
If you do not wash your face or oversaturate the skin with oil creams, then demodicosis on the face intensifies. This is due to the fact that ticks feed on lipids and begin to actively reproduce. In addition, the sebaceous ducts become clogged and rashes appear.
Dermatitis
With dermatitis, itching appears on the face, there may be redness, rash, papules, pustules, acne, comedones. In some people, dermatitis may present as a dry, flaky, rough face without papules or pustules.
Steroid dermatitis and rosacea
Appears when using corticosteroid drugs. Due to their use, local immunity decreases, and D. Folliculorum begins to actively reproduce.
Androgenetic alopecia
Mites can contribute to baldness. In the affected area, inflammatory processes around the sebaceous glands are activated, followed by the development of fibrous tissue and changes in hormonal levels. The sebaceous glands increase in size, producing large amounts of lipids. Hair follicles become depleted and hair stops growing.
Madaroz
This is what is called eyelash loss. The mite penetrates the follicles on the eyelids, causing inflammation and swelling in them. Eyelashes become thin and brittle and then fall out.
Predisposing factors
The subcutaneous mite on the face is contagious, but the likelihood of infection in the infected person is extremely low. Weakened or pathologically weak immunity contributes to the development of demodicosis. The body is unable to restrain the vital activity of microorganisms, and symptoms appear.
Contribute to the development of demodicosis:
- chronic fatigue;
- stressful situation;
- exhaustion of the nervous system;
- heredity;
- oily skin type, improper functioning of the sebaceous glands;
- hormonal disbalance;
- metabolic disease;
- poor facial hygiene;
- squeezing pimples;
- alcoholic drinks;
- smoking;
- abuse of fried, spicy foods;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- pregnancy;
- liver pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics and other medications;
- frequent colds with high fever;
- taking hormonal medications;
- pathologies of the endocrine system, abnormal functioning of the thyroid gland;
- tendency to allergies;
- intestinal diseases;
- fungal infection;
- chronic pathologies.
Causes
On a note!
The risk of developing demodicosis increases with simultaneous exposure to unfavorable factors.
Treatment
Before making a diagnosis, dermatologists prescribe microscopic examinations. An eyelash or hair is carefully pulled out from the eyebrows and examined under a microscope. If a demodex mite is detected, the doctor prescribes special treatment.
Remedies against demodex:
- Sulfuric ointment;
- Xin Fumanlinq cream;
- Demalon ointment;
- metronidazole tablets, they should be taken in combination with ointments for demodicosis;
- Some dermatologists prescribe benzyl benzoate cream, which is used to treat scabies mites. When applying the ointment to your face, you need to be careful not to get it in your eyes. It is also worth considering that benzyl benzoate bakes the skin very strongly for 15-30 minutes.
The most common drug for treating demodex mites on the face is sulfur-containing ointments. The tick does not survive exposure to sulfur preparations. However, there is a drawback of this treatment - an unpleasant, persistent odor. You should adhere to strict hygiene rules and promptly wipe the affected areas with sulfur-containing preparations. Then, after 6-7 days, the disease demodicosis, caused by a parasitic animal organism, disappears.
After the symptoms of the disease disappear, it is necessary to continue treatment with sulfur preparations to prevent relapse. It is recommended to undergo cosmetic procedures after treatment. Make nourishing masks and regularly moisturize your skin with spray or cream. Along with an ointment containing sulfur, it is necessary to use antimicrobial tablets metronidazole, which enhance the effect of treatment.
Ointments and creams
- Ointment with metronidazole (Klion, Metragil);
- Ointment with clindamycin or erythromycin;
- Spregal (esdepalletrin-pyrethroid) in the form of a spray;
- Demalan ointment;
- Sulfuric ointment;
- Benzyl benzoate;
- Preparations with azelaic acid;
- Sodium thiosulfate;
- Sulfur-tar alcohol;
- Yellow mercury ointment;
- Ichthyol;
- Lindan;
- Amitrazole;
- Crotamiton.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods include kerosene. It is applied to the affected area and is not washed off for 2-3 days. Kerosene creates a moisture-proof film under which the tick suffocates. Badyaga is also often used, which relieves inflammation and resolves seals.
Calendula is used to reduce inflammation. The alcohol solution promotes wound healing and skin restoration after demodicosis. You can prepare a decoction of tansy flowers and instill 2-3 drops into each eye 3-4 times a day. Improvement will be noticeable 5-6 days after the start of treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
At first, the disease develops asymptomatically. As the number of parasites increases, as well as with their mass death, the first manifestations appear. Determining infection with demodicosis is problematic, since the manifestations are similar to other dermatological pathologies - allergies, dermatitis, psoriasis. You need to pay attention to the following manifestations:
- acne - acne;
- rosacea;
- redness, thickening of the epidermis on the face;
- edema;
- nose enlargement;
- pore expansion;
- itching;
- peeling;
- tightness;
- pigmentation;
- spider veins;
- skin color changes to gray, burgundy;
- the skin becomes lumpy and loose;
- small sores;
- hair loss;
- itching on the head;
- heaviness of the eyelids;
- purulent accumulations in the corners of the eyes, sensation of a foreign body;
- blepharitis.
When using hormonal drugs for allergies, there is no therapeutic effect, there is temporary relief or aggravation of the situation.
Prevention
You should adhere to strict hygiene rules, change towels daily, iron pillowcases, disinfect your razor, glasses, and thoroughly wash personal items that come into contact with your face (scarves, handkerchiefs). This is especially important during treatment to prevent infection of other family members.
Never use other people's cosmetics and personal hygiene products. Do not dry yourself with someone else's towel or handkerchief. Keep the room clean, wash bedding frequently and drain pillowcases.
If you have already suffered from an illness, be attentive to your health. The slightest problems can provoke the resumption of demodicosis.
It is better to start treatment at an early stage, then there will be no complications and good results can be achieved in combating the parasite. To increase the protective functions of the body, a balanced diet, exercise, and walks in the fresh air are necessary.
Taking vitamin complexes in the autumn and winter, eating fresh fruits and vegetables will help boost immunity and improve the condition of the skin and increase its protective functions.