Ticks have established themselves as harmful insects, which is why many are afraid of them. Basically, these representatives of arthropods are associated with dangerous diseases. So why are they needed, what are the benefits of ticks in nature? To parasitize and carry the infection
There are over 50,000 species of ticks. They are divided into herbivores and pathogens. Few people know that these arthropods are not only carriers of various infections, but also pests, as they cause damage to agriculture and the food industry.
Most mites are saprophages (predators), which provide benefits by destroying other pests. They also feed on soil organic matter, which contributes to its decomposition into humus.
The importance of ticks in nature and human life
There is no place on Earth where ticks are not found.
These arachnid pests live in every part of the globe. The variety of ticks is very huge. To date, about 25 thousand species have been identified. Each species has its own structure, its own way of life, color, size, among them there are mites that harm plants and human health, there are also blood-sucking specimens and simply parasites. Still, we cannot discount the fact that in nature ticks are quite important. The greatest harm to human health is caused by ixodid ticks - they feed on human blood and carry various diseases and viruses with their bite. From an ecosystem point of view, ixodid pests are simply irreplaceable in nature; they act as a regulator of natural selection. How it works? The tick bites a passion that is weaker than itself, and she naturally dies. The stronger insect eats the killed passion and thereby develops immunity. In this regard, nature maintains a numerical balance of individuals.
Features of character and lifestyle
Depending on the species of the tick, its diet consists of different ingredients; sometimes arachnids live quietly next to us, and we are not even aware of such a neighborhood.
Each link of the ecological system has its own function. Millions of ticks inhabit the earth, water, plants and living organisms. They are an integral part of natural balance. Like other representatives of the fauna, arachnids are part of the food chain. What importance do ticks play in nature and human life? Soil species process organic matter in the soil. Through the efforts of small arthropods, fertile humus appears. As food for reptiles, birds and insects, mites contribute to the survival of these species.
Arachnids eat fungal spores, algae and bacterial plaque. Predators reduce the number of insects, nematodes, and worms. This feature makes them plant orderlies. Infecting animals with various diseases is a kind of natural way to control their numbers.
Families that live on agricultural crops, grain and flour reserves, and dairy products are harmful to humans. Ectoparasites of domestic animals and birds are also considered harmful species. Of the total number of existing groups of ticks, only a small part poses a direct threat to human life and health. These are ixodid and argasid species. It is necessary to dwell in more detail on where these ticks live, how they reproduce and feed.
Blood-sucking species
Ticks reproduce in a unique way. Males fertilize females who feed on the animals' bodies. Bloodsuckers hold the record for the number of eggs they lay. One female leaves up to 17 thousand eggs in the ground. It is good that only a small part of the offspring survives. After birth, the larva feeds once, choosing a rodent as its host.
Argas species - the body of the adult is 3-30 mm in size, it is flat and oval in shape. A hungry individual is gray in color, but after feeding it turns purple. Argas parasites live on birds, cats, and bite humans. Their saliva is extremely toxic. Mexicans compare Ornithodorus coriaceus bites to a rattlesnake attack.
Attention. The risk of contracting one of the diseases carried by parasites increases with the amount of saliva carried into the bite site
It is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the body after visiting forests and meadows. If the bloodsucker is removed in the first hours, the likelihood of the virus entering the blood is minimal.
How a tick bites
A special feature of the bite is the simultaneous administration of active painkillers, so the victim does not feel it. Ixodids do not bite immediately; they can search for a convenient place for up to two hours. On the human body the parasite prefers:
- area behind the ears;
- neck;
- groin and armpits;
- scalp;
- small of the back.
A special suboral outgrowth of the hypostome, which has sharp hooks directed backwards, helps to firmly anchor itself in the chosen place. This structure makes it difficult to remove the parasite. With the help of sharp chelicerae, the bloodsucker immerses the head into the skin. Its saliva acts as an analgesic and anticoagulant. You can remove a tick from a person using tweezers, a loop of thread, or a device purchased at a pharmacy.
Where do ticks live?
The fluctuation in size is similar. Both groups have representatives invisible to the naked eye with a body length of 0.3 mm. They have the same number of limbs - 4 pairs of walking legs. They have spikes and suction cups to hold them on the host's body. Both species are armed with claw-like processes - chelicerae. Most arachnids are covered with a chitinous shell. Their respiratory organ is the trachea; only small species breathe with their whole body.
And a few more facts:
- The smallest tick measuring 0.08 mm is listed in the Guinness Book of Records.
- In the absence of food, the argas species engages in omovampirism - it sucks blood from an engorged individual.
- The number of ixodid ticks is controlled using hedgehogs. Animals cannot get rid of the parasite on their own. Observers count how many parasites cling to a hedgehog per hour.
Benefits from ticks
Even bad associations between people and pests do not negate the fact that arachnids actually bring benefits to the ecosystem.
- Agriculture.
Everyone knows that there can be damage that ticks can cause to agriculture, but there are still benefits from them.
Most mites are small saprophages; they process organic matter, which significantly increases soil fertility, which is an important unit for agriculture. A predatory mite can destroy other individuals that cause more damage to the crop, for example, spider mites. It can destroy your crop almost completely within a season. Another benefit of mites is that they can clean flowers and plants that have been infected with fungi from them, which gives them strength and recovery for further development. Interesting fact. Some types of mites are used to make different types of cheese. - Medicine.
There is also a particular interest in mites in this industry. Enzymes contained in the saliva of arachnids (anticoagulants) actively work to reduce the intensity of the blood clotting process. Also, doctors are interested in tick antigens, which work to form antibodies and other protective reactions in the victim’s body.
In the ecosystem, ticks are also the connecting link of the entire chain. Frogs and various birds feed on ixodid ticks.
Natural enemies
There are a large number of means of combating parasites. Nature also made sure that their numbers did not grow indefinitely. Arachnids are an important link in the food chain for many insects, birds and other animals.
Natural enemies that feed on ticks in nature and thereby control the arachnid population include:
- frogs;
- other types of arachnids;
- birds (sparrows, thrushes, starlings and others);
- ground beetles;
- dragonflies;
- ants;
- wasps;
- riders.
Natural enemies for ticks in nature are also fungal spores, which have a detrimental effect on them and cause fungal diseases in them. Therefore, it is so important to prevent large-scale burning of grass and treatment of large areas with acaricides. This will lead to disruption of the natural balance and as a result, not only the parasites themselves will die, but also their enemies. In addition, most of the tick eggs will survive, which will lead to their rapid reproduction and spread.
What harm do arachnid pests cause?
As mentioned earlier, the most dangerous tick is the ixodid tick. There is also the taiga (encephalitis) tick, which is also a carrier of encephalitis and other dangerous diseases that can cause serious health problems. There are confirmed cases of deaths from bites of these particular types of ticks. These types of arachnids feed only on blood. When bitten, the virus and the causative agent of the disease enter the human body along with the saliva of the tick. In addition to these two types of dangerous mites, the following types can be contagious: subcutaneous mites or scabies. There will be no lethal outcome from their bite, but diseases such as scabies or dermatitis are guaranteed.
Where can I take a tick for analysis? Moscow laboratories
Listed below are laboratories where you can submit ticks for analysis in Moscow and the Moscow region; they conduct tests for encephalitis, borreliosis and other infections.
- FBUZ "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the City of Moscow": metro station Alekseevskaya, Grafsky lane, building 4 (entrance from the yard, 2nd floor). Telephone
- Branch of the Federal State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Moscow": metro station 1905 Goda Street, Krasnogvardeisky Boulevard, building 17 building 1. Telephone: 8 (499) 256-24-40
- Institute of Poliomyelitis and Viral Encephalitis: Moscow Region, Vnukovo, Moskovsky village. Telephone
- Children's Clinical Hospital No. 13 named after Filatov: metro station Barrikadnaya, Sadovaya-Kudrinskaya street, building 15. Telephone
- Infectious Clinical Hospital No. 2: Sokolinaya Gora metro station, 8th Sokolinaya Gora Street, building 15. Telephone
Types of ticks
In general, harm to humans can be caused not only by parasitic ticks, but also by completely harmless ticks. Their sizes are so small that they can be anywhere (in the garden, in the house, in bed, in things, in clothes, in food, and so on). Flour mite
- eats cereals and its ability is that it spoils a huge amount of food.
Dust pest
– feeds on epidermal debris and dust.
If you are "kissed" by a dust mite, you may develop asthma (especially those with allergies). Ear mites
– this species harms pets.
They feel a huge itch in the area of the ears and are able to scratch them until they bleed. Spider mites
are a species that all gardeners and indoor plant lovers fear.
It is capable of destroying all seedlings, so it is necessary to take action in time. The most distinguished group of mites is the oribati mites.
They can be found in forest soils.
They feed on rot (plant debris). This type of arachnid can harm livestock; they are carriers of tapeworm. Chicken mite
- they feed on the blood of birds and chickens. They go hunting mainly in the dark. Birds often die from lack of blood.
What do they eat?
Where ticks live and what they feed on is of interest to many people who want to prevent encounters with these arthropods. According to the type of nutrition, arachnids can be divided into:
- Saprophages that feed exclusively on organic debris.
- On predators that parasitize plants and animals.
Feeding on plant juices, mites cause significant damage to agriculture. Scabies and field arachnids eat particles of human epidermis. Granary feeders feed on decaying plant remains, flour, and grain. For subcutaneous mites, the food is the fat of human hair follicles, while ear mites consume fat from the hearing aids of animals.
Having taken their place on a branch or blade of grass, blood-sucking predators await their prey. Having waited, they attach themselves to it using paws with claws and suction cups, and then gradually reach the feeding site. The victim of arachnids is usually not only humans, but also other representatives of ticks.
Parasites are carriers of infectious diseases, so their bite can be fatal to humans. Arachnids can go without food for about three years, but once they receive food, they increase in weight several times.
What do forest ticks eat?
They feed on the blood of various animals, including human blood.
Everyone knows that ticks cannot jump to a height of more than 1 meter. Therefore, when they attack a victim, they try to get to the soft tissues and climb higher. Females are more voracious than males. The female can drink blood without stopping for about 7 days in a row, when three days is enough for the male.
The tick bite itself is not felt, since when they pierce the skin they inject special saliva that blocks the pain and thus the victim does not feel the bite and may not immediately recognize that the tick is on her.
How does a tick sense its prey? They have a very developed sense of smell. If the victim stops for a few minutes in the forest. The tick will immediately smell it.
How are you doing with encephalitis today?
Ticks
If you adhere to conspiracy theories, then it is much easier to see a conspiracy in today’s explosion in the number of ticks
Even in the area of encephalitis 40 years ago, precautions were taken more for the sake of being on the safe side. It was difficult to “find” a tick in the forest
Today for 1 sq. km, researchers remove 40 pieces. arthropods. And ordinary citizens complain that after every walk with their dog, they take off at least 5 of these arachnids from them and themselves.
Where there is no encephalitis, piroplasmosis is rampant. And the number of ticks infected with this disease significantly exceeds the number of encephalitis ones.
If the treatment of forests with pesticides is not restored, then all hope remains only on the very natural factors that restrained the spread of encephalitis before the invention of insecticides.
How to protect yourself from tick bites
If you go to the forest to pick mushrooms or just relax, it is important to understand that you can encounter ticks there. How to protect yourself from pests?
- If you are camping outdoors, be sure to close your tents well. Before you go to bed, check everything thoroughly for insects.
- Pay attention to clothes and shoes. It is more difficult to notice a tick on dark clothing than on light-colored clothing; try to wear light-colored clothing. Also pay attention to the fact that there are elastic bands on the cuffs, jacket and pants. It is best to have a hood on your head (this way the tick will fall to the ground, and from the hat there is a high probability of rolling onto your neck).
- Relax in nature during the day when it is light.
- Be careful when lifting branches and stones.
- Cover all open areas on your body.
If you are still bitten by a tick, then it is important to know exactly how to pull it out so as not to cause disastrous consequences. It is important to know that at the very moment the tick bites, it sticks its proboscis, which has many small spines, into your skin. Therefore, if you pull your proboscis along the axis, there is a high probability that the “spines” will dig into your skin even tighter. This can lead to the fact that the proboscis may remain forever in your skin, and you can simply separate and destroy the tick body itself. To prevent this from happening, you need to remove the tick from under your skin using circular movements. It turns out that the “pinches” on the proboscis will curl along the axis and the body will not be able to tear itself away from the proboscis.
Interesting facts about ticks:
- Ticks live wherever there is grass. Therefore, even on your summer cottage on the lawn you can find ticks.
- After a tick lands on a person’s body, it does not immediately attach itself, but searches for softer tissue. In total, the entire process can take about 15 minutes.
- Do not burn ticks or poison them with vegetable oil. The fact is that there is a myth that vegetable oil and cauterization will cause the tick to crawl out from under the skin - this is not true. The fact is that the vegetable oil will not suffocate the tick and if you burn it, it will not come back out. On the contrary, it can cause more active penetration into the skin, which will worsen the situation.
- A tick can infect several diseases at once.
- The drier the summer, the fewer ticks. Ticks love moisture, so their hunting season is autumn - spring.
The most active representatives of entomophages
Ladybug (coccinellidae)
The most effective enemy of any variety of aphids.
Moreover, the greatest damage is caused not by the adult beetle, but by its larva. If an adult destroys up to 50 aphids per day, then a larva destroys over 500. Great fertility is another advantage of this bright, cute bug. One female lays up to 300 eggs per season. In addition to aphids, it preys on whiteflies, mealybugs and Colorado potato beetle larvae.
Fast, predatory beetles, actively feed in the evening and at night. They are distinguished by an elongated body of dark colors with a metallic sheen. It is one of the most useful predators in the fight against plant pests.
One adult beetle can eat up to 350 caterpillars over the summer. Having found the victim, it releases a toxic liquid on it, which quickly dissolves the organs and tissues of the insect. The beetle eats the resulting liquidy homogeneous mass. The larva is even more voracious and destroys many more pests.
A spectacularly colored flying predator, often pretending to be something else, such as a wasp. Disguise is needed to escape from enemies. The adult fly feeds on flower nectar, while the larva benefits.
It eats spider mites, aphids and the eggs of many insects. While the larval stage lasts, the individual eats up to 2000 pests. Flies can be attracted by planting hogweed, carrots, dill and some other umbelliferae.
Lacewing
An insect with a long bright green body. Quite prolific, some species can produce up to 1500 eggs per season. The larvae are very voracious and happily destroy eggs of pests, aphids and herbivorous small mites. They are often used to kill insects not only in garden plots, but also in greenhouses.
After emerging from the eggs, the riders begin to feed on the internal organs of the victim, leading to their death.
Birds
To destroy pests, tits, swifts, flycatchers, pikas, starlings, wagtails, nuthatches, and redstarts should be attracted to the areas. All of them feed on numerous caterpillars, beetle larvae and adults, bringing very tangible benefits in the fight against harmful insects.
Birds are well attracted to hedges made of branching shrubs such as acacia, rose hips, and gooseberries. You can arrange feeders and bird houses (birdhouses and titmouses).
The tick (lat. Acari) is one of the oldest inhabitants inhabiting our planet. Contrary to erroneous belief, ticks are not insects, but are representatives of the arachnid order.
Causes of exacerbation of demodicosis
- various types of dermatitis;
- weakened immune system;
- acne;
- skin infections;
- HIV;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
To treat the disease, you must consult a doctor. Self-medication in this case is evil. The doctor will conduct an appropriate study and prescribe adequate therapy.
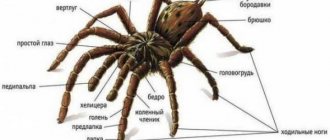
Who are ticks and what class do they belong to? What do they look like? Photo ????
Such pests belong to the animal kingdom, but they look and are structured like spiders, therefore they represent the class of arachnids (type - arthropods). Among these parasites there are herbivorous and blood-sucking individuals. They differ in appearance and eating habits. Main parameters of pliers:
- 4 pairs of legs, at the larval stage the parasites have 3 pairs of legs;
- oval shape, in some blood-sucking parasites, the body is narrower in the head region, representatives of other species have a wide body, microscopic parasites are often round or longer;
How dangerous is a bloodsucker?
There are more than 50 thousand species of ticks on earth. Of these, 713 are ixodid species. Of these, about 70 species are found in Russia. They are all vampires, or "temporary highly specialized obligate hematophages." All of them can be carriers of viruses, rickettsia, bacteria, spirochetes, trypanosomes, filariae and piroplasmids, which can cause more than 300 infectious and parasitic diseases in the donor. In addition, as a result of the suction of forest and taiga ixodid ticks, mixed infections often develop, which are characterized by a more severe course of the disease.
The most common disease transmitted through tick bites is borreliosis, or Lyme disease. In half of the cases, the bite site turns red, the spot expands, reaching a significant size in diameter. In some cases, borreliosis is initially asymptomatic or disguised as other diseases, for which it is called invisible. In later stages, the disease leads to damage to the joints, heart and nervous system. Borreliosis does not apply to pets.
The most dangerous tick-borne infections for humans are encephalitis (incidence in Russia has increased by 16 percent over the past year) and Crimean hemorrhagic fever (139 cases per year).
Well, our best friends - dogs, if they are small, old or weakened - easily die from babesiosis (pyroplasmosis), which destroys red blood cells. Unfortunately, there are no statistics on dogs dying from ticks.
All tick-borne infections can be treated in the early stages, but the only way to avoid catching borreliosis is to prevent tick bites.
Misconceptions and ignorance
I learned about ticks (forest ticks) at the age of 13 and began to be afraid, because they only scared me and no one had any useful information.
There are legends about them even today among the people. At least one of my friends found a tick on themselves every year. My father brought them to the dacha on birch brooms almost every summer and periodically on himself. I have never been their victim, I did not take any precautions, I carried flower bouquets from the forest, I had no idea what ticks looked like, and I only saw them 20 years later on the Internet. What I knew before: they live on birch trees, run fast, supposedly know how to jump and even fly. They jump from above (obviously, you can only jump from a birch tree). If the tick has already bitten you, you need to lubricate the bite with sunflower oil so that the tick begins to suffocate and crawl out on its own, and there you are, waiting with cotton wool. They are attracted to light-colored clothing. Encephalitis or paralysis is almost inevitable.
None of this is true. Some hospitals may still tell you to use oil. Almost any source of information is the word “no” without any explanation. And the biggest problem is the panic that happens when someone finds a tick on themselves, knowing only gossip about it.
Even if you think that you know everything, read this article.
Dogs and cats
Animals often pick up ticks unnoticed, especially long-haired ones. There are also repellents for dogs. There is no vaccine. If you notice that your dog has lost activity, lost its appetite, and is acting strange, it may have a tick. Unfortunately, manifestations of diseases appear late, after a week or three or later. If you find a tick on your pet, remove it according to the same rules as on a person. Secure the fur around the bite with something to make it easier to remove the tick.
Cats are very sensitive even to repellents, so consult your veterinarian.