general characteristics
The word "arachnid" comes from the Greek word "Arachne", which in mythology was the name of a skilled weaver who challenged Athena, the goddess of wisdom, arts and crafts. This impudence led to her turning into a spider. The classification of arachnids, of which there are approximately 100,000 species, covers a significant range of subgroups. There are currently about 11 orders and 3 extinct.
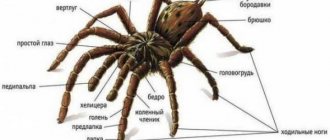
Almost all adult arachnids have eight legs, although the front pair may be modified in some species. In addition, all have two additional pairs of appendages - pedipalps (which look a bit like hands) and chelicerae, adapted for nutrition, protection and sensory perception. Their body consists of two parts : the cephalothorax and the abdominal cavity. In addition to having an exoskeleton, arachnids have an internal structure of cartilaginous tissue to which certain muscle groups are attached.
Ticks, like spiders, have bodies divided into two parts. Unlike other arachnids, the first go through four stages of development: egg, larva, nymph and adult. Their size varies from 0.08 to 20 mm.
Ticks are known to be external parasites that feed on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. They are found throughout the world, but tend to thrive in warm, humid climates because they require a certain amount of moisture to metamorphose.
Arachnids are primarily terrestrial, although some are aquatic, and can be found everywhere except in extremely cold places such as the Far North and Antarctica. They range in size from the mite (about 0.08 mm in length) to the black scorpion of Africa (about 21 cm in length). As arachnids grow, they molt several times. Arachnids are primarily carnivores, but since most are unable to digest food internally, they inject digestive fluids into their prey and then suck out the liquefied remains. Number of known species:
- 40,000 - spiders;
- 32,000 - ticks;
- 6300 - haymakers;
- 2000 - Scorpios;
- just over 3000 are false scorpions.
Most arachnids are harmless and only hunt insects. However, there are several species that are potentially dangerous to humans. Globally, 47 arachnid species are assessed as critically endangered.
Methods of protection
To protect yourself from ticks when going for a walk, you need to cover your body with thick clothing and a hat. Returning home, look through all things, remove and destroy dangerous arachnids.
If the parasite has already attached itself, you need to act carefully. It is necessary to treat the place where the tick is attached with vegetable oil or petroleum jelly. The essence of this action is that oxygen stops flowing into the spiracles of their trachea, located on the ventral side of the body. As a result, the tick falls off on its own. If you try to tear it off by force, the head of the parasite will remain under the skin. This can lead to the wound rotting. And in this case, it is impossible to do without surgical intervention. If you did everything correctly, do not throw away the tick. It is better to take him to a specialized laboratory in order to find out whether he is a carrier of a dangerous disease.
In order to prevent the barn mite from developing, it is necessary to monitor hygiene in the house, periodically change bed linen, dry pillows and mattresses in the sun, and carry out wet cleaning of the room more often.
Classification of arachnids
Arachnids (arachnids) belong to the phylum arthropods along with crustaceans. Their diversity of species is surprising - approximately 90,000, classified in 13 orders, are found almost throughout the world. Chelicerate arthropods with a body consisting of 18 segments organized into 2 main structures: the prosoma or cephalothorax and the posterior opisthosoma or abdominal cavity. Highly developed instinctive behavior. Prosoma has 6 pairs of appendages, 4 of which are used for walking.
Orders of the arachnid class:
- Araneae (Spiders);
- Opiliones (Haymaker);
- Pseudoscorpiones (False scorpions);
- Scorpiones (Scorpions);
- Solifugae (Solpugs);
- Schizomida (Schizomids);
- Uropygi (Telephones);
- Amblypygi (Phrynes);
- Palpigradi (Palpigradi);
- Ricinulei (Ricinulei);
- Acari (Ticks).
When classifying arachnids, taxonomists rely primarily on external structures, including features such as overall body shape, degree of visible segmentation, structural changes in the prosoma and opisthosoma, characteristics of the appendages, and specialized systems involved in sperm transport. Internal anatomical features, developmental features and serological reactions are taken into account to a limited extent. However, as more information becomes available about the molecular level, these characters play a more important role in the classification of arachnids.
Internal structure
There is no complete circulatory system. Blood too. It is replaced by lymph. There are 3-4 holes in the heart, called ostia. Through the ostia, lymph from the animal's body enters the heart, and from there, through the arteries, the heart drives lymph into the spaces between the internal organs. From the spaces, lymph enters the pericardial region of the body and returns again to the heart. Lymph has a mechanism that additionally supplies the spider with oxygen.
Spider structure
The respiratory system has a peculiar appearance. The lung sacs have plates and look like books. The breathing holes that open the lungs are equipped with protective covers. There are also long tracheal tubes that transport oxygen from the openings to the organs of the spider's body.
Being a predator, the spider has a well-developed central nervous system and a significant brain volume. In the cephalothorax of the arthropod there are 2 nerve ganglia, from which many nerves diverge, leading to the organs of the spider. These nodes are the brain of the animal.
Spider Squad
Spiders are the largest group of Arachnids. They occupy seventh place in overall species diversity among all categories of organisms. They have 2 body parts, 8 legs, no mouth parts for chewing, and no wings. Many species have a spinneret that produces webs used to catch insects in a web, form burrow walls, create egg sacs, etc. Most spiders can inject venom to protect themselves or to kill and reduce their prey to a semi-liquid mush.
Most often have 6 to 8 eyes, although some have fewer or none at all. The bites of about 200 of the 40,000 species can cause health problems in humans . Some scientists are studying whether spider venom can be used as a medicine or as a non-toxic pesticide.
Spiders do not have extensor muscles. Instead, they expand their limbs using hemolymph pressure. The largest species of spider in Canada, which belongs to the Pisauridae family, can reach up to 15 cm, including legs, and can feed on fish and salamanders. Most of these creatures live no more than one or two years, although some, such as tarantulas, have been known to live up to 25 years in captivity.
Because of their fascinating physiology and behavior, spiders are of interest to scientists. In addition, because of their importance as predators and association with specific habitats, they are often used in North America for ecological research, including usefulness as biodiversity indicators.
The total global mass of spiders is enormous - about 25 billion kilograms! Collectively, these arachnids consume between 400 and 800 million tons of animals each year. On average, they consume about 10 percent of their body weight in food, which would be similar to a 90kg person eating 9kg of meat every day. It is estimated that one spider consumes up to 2,000 insects per year. By comparison, humans as a species (all 7 billion) and whales as a group eat about 400 million tons of other animals per year.
Lacquer bug
Relatives of cochineal scalebugs are varnish scalebugs. They produce shellac resin, which is used in the paint and varnish industry. Also, this connection does not conduct electricity, therefore it is used in electrical engineering as an insulating material. However, contrary to the name, real shellac is not currently used to cover nails.
Shellac in products is designated as food additive E-904
In addition, the substance is edible; it can be used to coat tablets and candies.
Insects are part of nature; without them, the Earth's ecosystem could not exist. But even on a smaller scale, some of these creatures bring benefits to humans, and quite tangible ones.
Meaning in nature
Spiders are an integral part of the ecosystem as they regulate the density of other invertebrate herbivores and predators . Many of the insects they eat are unpleasant or dangerous and fatal to humans, such as mosquitoes that bite people and carry diseases. They also help increase crop yields by eating pests. Unfortunately, farmers' use of pesticides also affects the abundance of spiders in their fields, making the pest problem worse rather than solving it.
Ticks carry and transmit a wide range of diseases to people and pets. Even those that can lead to death. There is a small consolation - ticks are food for other animals, which eat them in large numbers. For example: guinea fowl, chickens, wild turkeys and opossums. Although many tick bites do not have long-term effects, it is advisable to be very careful in general and to keep an eye on yourself, your pets and livestock. One must use remedies for these parasites and medications when necessary.
Scorpions, like spiders, have two body parts and eight legs, but they also have a six-segmented tail that contains the scorpion's anus and its stinger, which includes venom glands. Of the 2,000 known species, only 30 or 40 have venom strong enough to kill humans. In the adult stage of life, most are nocturnal, usually alone, remaining in the same territory.
The significance of scorpions in nature is no less important. Due to their predatory nature, they control potential pests . There is a possibility of turning their poison into pesticides and important medicines. Scorpions are also food for other animals such as centipedes, shrews, owls, bats, hornbills and coyotes.
Although not many species are endangered, anything that may contribute to pollution or loss of their natural habitat should be avoided. They need to be protected because the role of arachnids in nature is important in general, and especially in the control of unwanted insects, in providing food for animals higher in the food chain and in the decomposition of organic matter. Precautions must be taken to avoid or manage the harmful ones and treat others with the respect and appreciation they deserve.
What is a web
The predominant number of arachnids are capable of building trapping nets from a special substance found in special warts. They produce threads that can be compared even to steel wire in their strength. The web pattern is characteristic of each species. There are drops of sticky liquid on the spirally twisted threads. If an insect gets caught in it, it has little chance of getting out. In addition to the trapping net, dwellings and cocoons are made from this substance. The importance of arachnids in nature and human life is also determined by the way they feed.
Distribution and habitat
Spider in the forests of Russia Spiders live on all continents except Antarctica.
Being invertebrate animals, they cannot control their body temperature and are susceptible to cold, however, in northern Canada, Greenland and northern Russia they get along well. They are one of the few species of animals that get along well in the highlands. There are certain species that feel great even in an aquatic environment.
The main factor that limits their habitat is the availability of food.
Habitat
The great importance of arachnids in nature and human life is due to their wide distribution. These are not only forests, salt and fresh water bodies, soil, various plants, surfaces, as well as the body of animals and humans - all these environments are perfect for the feeding and activity of ticks.
The negative significance of arachnids in the lives of people and nature is that many types of ticks are the causative agents of very dangerous diseases. Feeding on the blood of humans and animals, they can transmit encephalitis, piroplasmosis of cattle and dogs, and relapsing fever.
Severe itching on the skin and the appearance of scabs (scabs) may be a manifestation of parasitism of scabies. This mite gnaws holes in the skin, laying its eggs there. From there, after a while, young sexually mature ticks emerge. It is not always possible to immediately notice the cause, because the size of the itch varies between 0.2-0.5 mm. The danger also lies in the fact that a person can become infected through everyday means: by using the same towel, comb, or shaking hands.
The sebaceous glands and hair follicles of the human body can be parasitized by the acne gland. This parasite causes the appearance of pustules on the skin and hair loss.
Barn mites and gall mites cause damage to agriculture and food supplies. Barn species do not parasitize humans. These mites live in mattresses, pillows, blankets, bed linen, floor cracks, and feed on dead organic matter. But the products of their vital activity, the integument that remains after molting, often enter the human respiratory tract, causing severe allergic reactions.