23 January77736various animalsinsectivores
The common hedgehog or European hedgehog is an animal from the Hedgehog family, which is a representative of the order Insectivores. The common hedgehog has been familiar to us since childhood. The pages of children's books introduced us to this sweet and kind animal. In this article you will find a description and photo of the common hedgehog and learn a lot about this brave little guy.
Description of an ordinary hedgehog
The ordinary hedgehog is small in size: body length 20-30 cm, tail length up to 3 cm, weight 700-800 g. Ears are small, up to 3.5 cm (larger in the subspecies that lives in Cyprus). The muzzle is elongated. The nose is pointed and constantly wet. There are 20 small sharp teeth on the upper jaw, and 16 on the lower jaw. The head is large, wedge-shaped, slightly elongated. Paws with five fingers and sharp claws. The hind legs are longer than the front legs. The needles are short, up to 3 cm in length, smooth. A “parting” separates them on the head. The color is striped, brown and light. Inside the needles are hollow, with air. Between them are thin, long, sparse hairs. They are dark on the head and belly. An adult hedgehog usually has 5000-6000 spines, and juveniles have up to 3000. The color of the face, belly and paws is yellowish-white or dark brown. The breast and throat are plain, without spots.
Feeding features of the common hedgehog
— Advertising —
The common hedgehog is an omnivore. It feeds on adult insects, including harmful ones (chafer beetle, hairy ground beetle, nun caterpillar, gypsy moth), caterpillars, slugs, earthworms, and mice. He also eats fruits and berries. It can feast on the eggs and chicks of small birds whose nests are located on the ground.
In captivity, hedgehogs eat vipers without harm to themselves. In wild conditions this is also possible. Poisons (arsenic, sublimate, opium, hydrocyanic acid) have a weak effect on the hedgehog. Their dose, lethal to a person or other animal, does not kill a hedgehog.
What does a hedgehog eat?
Answering the question of what hedgehogs eat, scientists classify them as omnivores. The little hedgehog is a nocturnal hunter, actively eating any insects, small rodents, lizards, toads, frogs and even small snakes.
Lack of sensitivity to the venom of insects and snakes allows hedgehogs to successfully hunt dangerous prey. However, hedgehogs can also eat mushrooms, berries, acorns, vegetables and fruits.
Like bears, hedgehogs strive to accumulate a certain fat reserve in the fall so as not to die from lack of food and cold weather during hibernation.
Distribution of the common hedgehog
The common hedgehog lives in Western and Central Europe, Great Britain, southern Scandinavia, northwestern Russia, Western Siberia and Kazakhstan.
The species was introduced to New Zealand. The animal is found in a wide variety of habitats, avoiding only swamps and solid coniferous areas. The hedgehog loves to live on the edges, in copses, in small clearings, in floodplains, often next to people. Nowadays the hedgehog can easily be found in urban areas, where it has no natural enemies.
Hedgehog's enemies in the wild
Despite the ability to curl up into a spiny ball for protection, the hedgehog often becomes prey to larger forest predators. Hedgehogs are hunted by foxes, wolves, badgers, hyenas, jackals, large owls, mongooses, badgers, and ferrets.
In recent years, a large number of animals have died under the wheels of cars when trying to cross the road at night.
Common types of hedgehog
— Advertising —
The hedgehog family consists of two subfamilies: true hedgehogs (Erinaceinae) and rat hedgehogs (Galericinae), which number 7 genera and 23 species. The most interesting of them:
- The Eastern European hedgehog (Erinaceus concolor) is similar in appearance to the European hedgehog, but its throat and belly are lighter in color than its head and sides. The length of adult individuals is 35 cm, weight in summer is about 1.2 kg. It lives in countries such as Austria, Germany, Slovenia, Kazakhstan, the Mediterranean and Asia Minor.
- African pygmy hedgehog (white-bellied hedgehog) (Atelerix albiventris). Body length 15-22 cm. Weight from 350 to 700 g. Body color brown or gray, needles with white tips. The tail is 2.5 cm long. The eyes are small, the ears are round, females are larger than males. The species is distributed south of the Sahara, in Nigeria, Sudan, Ethiopia, Senegal, and Mauritania. It feeds on spiders, insects, scorpions, snakes, snails, and worms.
- Long-spined hedgehog (dark-spined, bald hedgehog) (Paraechinus hypomelas) in length from 22 to 27 cm, weight 500-900 g. The name of the species is associated with a small bald spot on the crown and long, thick needles, about 4 cm long. The needles are colored differently : black with a white base or light, almost white. It is found on rocky and sandy plains and in the foothills. Its habitat includes the Arabian Peninsula, the Persian Gulf Islands, Iran, Pakistan, and Kazakhstan. The species is listed in the Red Book of Uzbekistan and is protected by Turkmenistan.
- The Ethiopian hedgehog (Paraechinus aethiopicus) has light brown quills, short, dark legs and a dark “mask” on its face. Other parts of the body are white. The body length is 15-25 cm, weight 400-700 g. A very voracious species that is found in the deserts and steppes of northern Africa.
- Daurian hedgehog (Mesechinus dauuricus). Distinctive features of the species are the absence of a strip of bare skin that divides the spines on the head. The needles are short, sandy or brown, the fur is coarse, gray or dark brown. A typical inhabitant of the forest-steppe and steppe from Transbaikalia to Mongolia and northern China.
- Common gymnura (Echinosorex gymnura). Body length 26-45 cm, weight from 500 g to 2 kg. The tail is covered with sparse hair and scales, 17-30 cm long, white at the back. The back and sides are black, the head and neck are white. The species is found in tropical rainforests in southeast Asia from Malacca to Borneo.
- Lesser gymnura (Hylomys suillus) is the smallest representative of the genus, with a body length of 10 to 14 cm. The tail is 2.5 cm long. Weight is 45-80 g. The species is distributed in the mountainous areas of the countries of south-east Asia (in Indonesia, Brunei, Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, China).
Behavior of an ordinary hedgehog
The common hedgehog is active at night, but does not leave the house for a long time.
Spends the day in nests and other shelters. The hedgehog builds a nest in bushes, a hole, a cave, an abandoned rodent burrow, or in the roots of a tree. Its average diameter is 15-20 cm; inside there is a bedding of dry grass, foliage, and moss. Males behave aggressively towards each other and protect their territory from intruders. The area of one plot of a male is from 7 to 39 hectares, that of a female is from 6 to 10 hectares. The animals lead a solitary lifestyle and do not come close to each other. After frost sets in, the hedgehog closes the entrance to its burrow and goes into hibernation, on average from October to April. During the summer, the hedgehog stores a lot of fat, since if it is less than 500 g, then in winter it can die of hunger. After hibernation, the animal leaves the nest after the temperature rises to 15 °C.
Shedding is slow and occurs in spring or autumn. During the year, one needle out of three changes and grows from 12 to 18 months. The hedgehog carefully takes care of the needles - licks and cleans.
The common hedgehog is a fairly fast animal for its size. It reaches speeds of up to 3 m/s, swims and jumps well. The hedgehog's eyesight is poor, but it has a keen sense of smell and hearing.
The lifespan of an ordinary hedgehog in nature is 3-5 years, in captivity up to 8-10 years.
Hedgehog lifestyle
Hedgehogs are predominantly nocturnal. They usually make burrows in bushes and tree roots. There are known cases when animals occupied ready-made burrows of other forest inhabitants.
The hedgehog leads a solitary lifestyle and does not stray far from its burrow. Males protect their territory from invasion by other males. Animals meet with representatives of the opposite sex only for the purpose of reproduction.
As a rule, animals sleep in their burrows during the day and go hunting at night. At the same time, it is not uncommon to see hedgehogs in nature during daylight hours.
Reproduction of the common hedgehog
When hibernation ends, the mating season begins for the hedgehog.
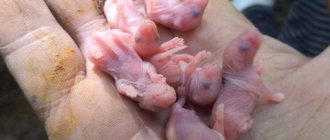
Males often fight over females, bite, push, use needles in fights, while sniffing and snorting. The one who emerged victorious from the battle circles around the female for a long time. After mating, the male and female separate. The hedgehog seeks shelter for itself or digs a hole, lining it with dry grass and leaves. The female raises only one brood per year. The duration of pregnancy is 49 days. There are 3-8 (on average 4) cubs in a litter. They are born naked, blind, with a body weight of about 12 g. After a few hours, the babies develop soft needles. The entire needle cover appears before the 15th day. The female feeds the cubs with milk for 1 month. After which the hedgehogs live independently. They reach sexual maturity at the age of 10-12 months.
Interesting facts about the common hedgehog
- The benefit of the common hedgehog for humans is the destruction of harmful insects; it eats cockchafers, nun caterpillars and gypsy moths. But it can also destroy chicks and eggs of birds. For example, in the Outer Hebrides, where hedgehogs were introduced, they became real pests, as they destroyed clutches of snipe, dunlin, snail and lapwing.
- Hedgehogs carry ringworm, yellow fever, salmonellosis, leptospirosis, and rabies. They are inhabited by ticks and fleas (carriers of tick-borne encephalitis and tularemia), which the hedgehog cannot get rid of.
- Hedgehogs are very often kept as pets. Residents of Ancient Rome back in the 4th century. BC e. Hedgehogs were raised for their meat: hedgehogs were baked together with their needles in clay. Today, fried urchins are a popular dish among gypsies. Hedgehog skin was used for leather tanning.
- Since ancient times, there has been a common misconception that hedgehogs prick food, such as apples and mushrooms, on their needles. Pliny the Elder described this in his writings, but in reality the hedgehog never tolerates its food, and practically does not eat apples and mushrooms.
How to properly organize the life of hedgehogs on your property and minimize harm from them
Hedgehogs bring more benefit to gardeners than harm, and therefore people specifically try to feed and attract hedgehogs to their plot so that they settle on it. To do this, they need to create conditions similar to those to which they are accustomed in the natural environment.
How can you attract hedgehogs to your site?
For this purpose, the hedgehog should be provided with a reliable home, temporary shelter, and objects that pose a danger to the hedgehog should be removed or fenced off.
Creating safe conditions for the animal
If there is an artificial pond on the site, then, once in it, the animal will not be able to climb up its slippery walls and will drown. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to place a board at the edge of the reservoir, along which the animal will climb to the ground.
Chain-link fences are also dangerous for hedgehogs. These animals can become entangled in this net and suffer serious injuries. Therefore, it is better to fence the area with other material. You can also raise the fence above the ground to a height of 20–25 cm, then the hedgehog can freely pass under it.
Chemicals intended for use against plant diseases, pest control, and products with strong odors (solvents, paint) should be kept out of reach. The animal can get into where they are and get poisoned.
You need to be careful and careful when using garden tools. Hedgehogs often settle in heaps of compost on plots. And before you stick a pitchfork (shovel) in there, it’s worth checking whether a hedgehog lives there. You should also not leave gardening tools unattended so that the hedgehog does not get hurt.
Garden tools should be placed out of reach of hedgehogs.
How to make a hedgehog shelter with your own hands
It’s easy to build a comfortable and safe home for a hedgehog yourself, using boards, a small wooden box (for vegetables), pallets, and bricks. Approximate dimensions of the house: its length is 30 cm, its width is 25 cm, its height is 25 cm. Then, from short boards, you need to make a narrow entrance, inaccessible to cats and dogs, into a tunnel-type dwelling.
The lower part of the home is lined with dry leaves. Brushwood, slate, leaves, and grass are used as top cover. The main requirement for housing is protection from natural precipitation and animals (foxes, owls, badgers) that harm hedgehogs. The house is placed in a quiet corner of the site.
A hedgehog house can be made from a box, boards, bricks
In natural conditions, hedgehogs usually choose dry forests and thickets as their habitat. To create a comfortable life for hedgehogs in a summer cottage, it is a good idea to build a hedge for them and plant dense bushes (hawthorn, rose hips). They will protect hedgehogs from sunlight and prying eyes.