Experienced gardeners know that the more earthworms in the soil, the more fertile the soil. Even in the old days, peasants judged the fertility of the land by the number of earthworms living on the plot, and believed that the more of them, the richer the harvest, and the tastier the vegetables. Unfortunately, now earthworms are in great danger and this is due to the use of chemical fertilizers and modern plant care technologies. Earthworms are a factory for the production of fertile soil. But is this really so?
Reproduction
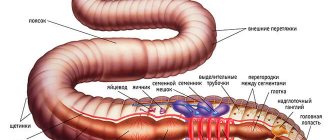
Earthworms are asexual hermaphrodites, capable of producing offspring within six months. They reproduce by cross-fertilization and find each other by smell on warm, humid evenings. In a wide belt on the body, fertilization and development of eggs occur, which are then laid in cocoons in the soil. Depending on weather conditions, up to 20 larvae hatch from the eggs within 1-5 months. And after another 3-4 months, the larvae become adults.
With good nutrition, earthworms reproduce very quickly. Over the course of a year, they can give birth to up to a thousand of their own kind.
The importance of earthworms in the biosphere, nature and human life
Earthworms have the following significance in nature and human life:
- improve soil quality;
- participate in the processing of organic waste;
- loosen the soil for better ventilation and moisture saturation;
- act as an intermediate host for avian parasites and helminths that infect the lung tissue of pigs.
In the Middle Ages, powdered dried animal worms were used to treat infectious wounds caused by tuberculosis. In Russian folk medicine, a liquid obtained from salted earthworms was used. This substance was dripped into the eyes of people with cataracts.
The role of vermicompost for soil fertility
American farmers were the first to draw attention to the possibility of using earthworms for processing organic matter. They used them to obtain biomass and expand the diet of domestic animals and birds.
It has been proven that when using vermicompost, the yield of vegetables increases several times. The ripening of the crop is also accelerated by 10-15 days. All thanks to the soil that passes through the esophagus and then contains all the mineral elements and complex compounds necessary for plants. In addition, vermicompost is useful because
- reduces the number of pests in the garden,
- binds heavy metal residues and removes residual radiation,
- increases yield without the use of chemical fertilizers.
TOP 7 benefits of earthworms in the garden?
- Earthworms normalize the natural balance of the soil, loosen and plow, significantly improving fertility and structure, and increase the amount of magnesium, phosphorus and calcium.
- When moving underground, they create tunnels through which air and moisture pass to the roots of the plants.
- They saturate the earth with oxygen and qualitatively update the chemical composition.
- They create natural organic fertilizer - bio-humus. A substance that has a beneficial effect on the development of a plant at any period of life, considered natural nutrition and protection of the plant from fungal diseases and insect pests.
- They destroy and process the remains of animals and plants, and prevent the proliferation of spores of fungal diseases.
- They are food for nocturnal inhabitants of garden plots.
- Earthworms are a good bait for swimming fish. A person uses worms strung on a fishing rod hook to catch fish in water bodies.
Having studied the features of the life of an earthworm, you need to create the proper conditions for its existence and reproduction. Earthworms are completely harmless to plants and humans, they only bring benefits to your garden plot, and if they are found in the garden, it is necessary to create all the conditions for the life and reproduction of these individuals - build compost pits and often moisten them with warm water.
Read: Why should you be friends with hedgehogs?
Join our Facebook group
The benefits and harms of earthworms
Charles Darwin was one of the first to point out the role of earthworms in soil formation in 1882.
He even suggested that they have intelligence, noting that pulling a piece of leaf into a hole occurs from the narrow end, and a bunch of pine needles pulls at the base to make it easier to get into. He observed them almost all his life and wrote the scientific work “The Formation of the Vegetative Layer of the Earth by the Activity of Earthworms and Observations on Their Lifestyle” (1881).
Benefit
Earthworms are also called soil formers, because by making tunnels in the ground, they loosen the soil and contribute to its saturation with oxygen. In wet weather, you can see how the worms crawl to the surface, and in dry weather they go up to half a meter deep and fall into an unconscious state.
Over the course of a year, worms process a large amount of soil, equal to almost their weight, several kilograms of fallen leaves and other parts of plants. In one day, the worm easily processes about 25 g of soil. The soil is plowed by worms and becomes more fertile. Number of worms per 1 sq. m reaches up to a hundred specimens, and in wet meadows up to six hundred. Among the beneficial qualities of the life of worms in the garden include:
- loosening the top layer of soil, promotes its aeration;
- restoration of soil fertility;
- saturation of the soil with oxygen, and this has a positive effect on plant nutrition;
- enriching the soil with useful microelements - phosphorus, calcium, magnesium;
- maintaining the growth of bacterial populations;
- regulation of soil acidity.
During the digestion of plant residues, humic substances are formed in the intestines of worms, which, entering the soil, slow down the leaching of mobile compounds from it and prevent water and wind erosion of the soil.
Harm
Among gardeners, there is an opinion about the dangers of worms, which allegedly gnaw the roots of young plants. However, this is nothing more than a myth. There is no need to be afraid of worms; they cannot cause harm simply because of their feeding habits.
But they still cause harm. Earthworms are intermediate hosts of dangerous parasites for pigs - metastrogylids. The infestation causes respiratory distress in pigs and poisons them with toxic products of their vital activity. Animals that catch such an invasion die. They are also intermediate hosts of parasites - syngamids in birds, especially in domestic birds - chickens, turkeys, ducks.
Louis Pasteur, a French microbiologist and chemist, once pointed out the possibility of anthrax spores being spread by earthworms from the burial grounds of animals that died from this disease. However, he was wrong and this has already been recognized, since this is simply impossible due to the biological characteristics of worms.
Interesting Facts
The table below contains answers to the most frequently asked questions.
| Question | Answer |
| What do earthworms eat? | The diet of these animals consists of organic plant matter and soil fragments. |
| How long does this individual live? | No more than 10 years. |
| How many hearts does an earthworm have? | The heart, as an independent organ, is absent. Its function is performed by ring channels that contract to ensure blood circulation. |
| Is the earthworm hermaphrodite or dioecious? | These individuals are hermaphrodites. |
| Does an earthworm develop with metamorphosis or direct? | In animals of this species, development is direct. |
| Is the earthworm a decomposer or a consumer? | They belong to the category of decomposers. |
| Is the earthworm autotrophic or heterotrophic? | These animals belong to a separate group - saprotrophs. |
Earthworms are part of the first tier of the food pyramid of the biosphere. Sexually mature individuals participate in the decomposition of plant waste, loosen the soil, and eat rotting products with a high concentration of nitrogen. The body of these animals is covered with a layer of thick mucus, which consists of enzymes with pronounced antiseptic properties.
Vermiculture
Currently, due to the frequent use of mineral fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, the population of earthworms has decreased significantly.
Some people are specifically engaged in vermicultivation, that is, the artificial propagation of earthworms. Vermiculture is a business that does not require large start-up capital. The demand for both earthworms themselves and the organic fertilizer they produce has been increasing recently.
You can breed worms yourself. Liming the soil will help increase the number of earthworms. Or they are bred in the following way. Place leaves, food waste, humus, manure in a dug hole and throw in worms. After a while, you will notice that there are much more worms in the soil. For faster reproduction, worms are fed with a three-day tincture of cut grass, nettles, dandelions, and food waste.
Summarizing what has been said, I want to say that, after all, the benefits for people from earthworms are much greater than the harm.
To prove it, watch this video “The Amazing Inhabitants of the Garden.” I wish you good harvests!
The benefits of worms for humans
Until now, no more effective way of restoring eroded, depleted or contaminated soils has been invented than breeding earthworms. Vermicultivation (growing invertebrates in captivity) makes it possible to produce vermicompost on an industrial scale and enrich large areas of land with it.
Summer residents do not have to propagate vermiculture artificially. Having assessed the importance of worms in agriculture, a farmer can attract worms to his plot in the following ways:
- avoid deep plowing (it is better to dig or loosen with a flat cutter);
- mulch the surface to avoid drying out of the soil and sudden temperature changes;
- leave a minimum area of the site without planting (vegetation prevents moisture evaporation);
- in the fall, leave some plant debris on the beds (worms need food);
- reduce the use of chemicals;
- annually add compost or humus as fertilizer;
- Do not burn plant waste, but compost it and subsequently add it to the soil (especially since worms do not like excess ash).
Breeding worms on the site also has a side effect - the abundance of invertebrates attracts moles. Vermicultivation in closed containers will help avoid this. As a useful product, the farmer will receive not only vermicompost , but also worm biomass for feeding livestock or selling.
How to breed worms in the garden
These animals are found everywhere.
Depending on the species, they inhabit soil layers at a depth of 10 cm to 1 meter. Since it is not difficult to breed worms in the garden, they are often grown in garden plots. In order for the worms to settle in the required territory, you need:
- Dig a small hole in the ground, approximately 30-40 cm on sides.
- Place leaves, waste paper, and old newspapers at the bottom. Water generously with water or any slop containing organic residues.
- After about a week, you need to place a few worms collected in a damp place (under leaves, stones) on the prepared surface.
- After a few days, the “pets” begin to be fed. Any organic matter is suitable for these purposes: animal manure, bird droppings, food waste, vegetable and fruit skins, wet paper, bread crumbs, drunk tea or ground coffee. Feeding is carried out at least once every 2 weeks, each time covering the nursery with a 5 cm layer of food.
- The soil is regularly moistened. It is better to use settled or rain water, watering the nursery with it from a watering can. The optimal humidity for keeping earthworms is 80%.
- Twice a week, the compost heap is carefully loosened to enrich it with oxygen.
Worms can be bred in special boxes in any technical premises (basements, sheds). They are not kept in residential areas due to their specific odor. The contents of the box turn into vermicompost within a few months. To remove worms, the easiest way is to spread bait on the surface. For example, paper soaked in sweet water. The collected worms are placed in a new portion of compost.
When breeding worms, you should protect them from moles, which are their main enemies in your summer cottage.
Habitat and lifestyle
Earthworms live on all continents except Antarctica, where it is always cold. Their spread was largely due to man. After all, one of the signs that there are earthworms on a site is fertile soil and high yields. This means that the wider the distribution area, the better for agriculture.
The mucus that covers the body of the worm is one of the adaptations to the environment. Thanks to it, the invertebrate can move even in the densest or hardest substrate.
But still, soil moisture can be called among the characteristics of the earthworms’ habitat. Animals prefer to live near bodies of water, in wetlands, damp forests, and in areas with a humid climate.
Worms spend most of their time in the soil, where they create many tunnels. The bristles covering the body of the worm also perform a protective function. They cling to the ground and prevent the animal from being forcibly removed from the hole.
When it rains, earthworms crawl to the surface en masse, as it becomes difficult for them to breathe the water that accumulates in their burrows.
It is noteworthy that the life of earthworms is inextricably linked with their relatives. Animals are social, they form numerous communities, and they can communicate through touch.
For example, decisions about migration are made jointly. In general, the behavior of the earthworm is quite complex, which promises scientists many more interesting discoveries.
What do they eat?
The type of food an earthworm eats depends on the species to which it belongs. Everything that earthworms eat can be called organic waste. This concept includes:
- rotting leaves, branches, grass;
- perishable fruits and vegetables;
- bird manure and droppings;
- drinking straw.
- sawdust.
Earthworms have a very interesting way of feeding. They ingest plant debris along with the soil, and the body absorbs only the necessary nutrients. Without having time to process the food, the worms drag it into their holes. In addition, many species store supplies in specially created storage facilities, and then visit them with the whole family.