Experienced gardeners know that the more earthworms in the soil, the more fertile the soil. Even in the old days, peasants judged the fertility of the land by the number of earthworms living on the plot, and believed that the more of them, the richer the harvest, and the tastier the vegetables. Unfortunately, now earthworms are in great danger and this is due to the use of chemical fertilizers and modern plant care technologies. Earthworms are a factory for the production of fertile soil. But is this really so?
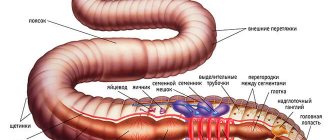
Reproduction
Earthworms are asexual hermaphrodites, capable of producing offspring within six months. They reproduce by cross-fertilization and find each other by smell on warm, humid evenings. In a wide belt on the body, fertilization and development of eggs occur, which are then laid in cocoons in the soil. Depending on weather conditions, up to 20 larvae hatch from the eggs within 1-5 months. And after another 3-4 months, the larvae become adults.
With good nutrition, earthworms reproduce very quickly. Over the course of a year, they can give birth to up to a thousand of their own kind.
How to restore the number of worms in our areas
Deep tillage is the number one enemy of earthworms. By digging and turning over the soil, we destroy the burrows of invertebrates and kill them themselves. Contrary to childhood misconception, a worm cut in half with a shovel dies; it does not produce two individuals.
Scientists have found that earthworms are animals intelligent enough to leave a place where they are in danger. Therefore, in order for these useful animals to populate your garden, you need to abandon the shovel and cultivate the soil with a flat cutter.
In addition to digging, the use of mineral fertilizers negatively affects the well-being of worms. To prevent animals from dying, the concentration of soluble salts in the soil should not exceed 0.5%. With the constant addition of chemicals, this figure increases several times.
An earthworm will never settle in an area where it has nothing to eat. These animals are vegetarians and use decaying plant debris and microorganisms as food. We are used to completely removing weeds and “putting things in order” in the garden. In the fall, we remove all fruit-bearing and flowering annuals, tops, and fallen leaves. And we also burn it all! With this useless work we deprive earthworms of food and they leave our land.
In order to restore the population of earthworms in your areas, you need to give up the shovel. There is no need to poison animals with chemicals. It is necessary to leave a sufficient amount of organic matter in the ground for their proper nutrition - the worm will never settle on bare soil. In addition, there is another simple way to restore the population of these invertebrates - you can simply breed earthworms on the site.
The role of vermicompost for soil fertility
American farmers were the first to draw attention to the possibility of using earthworms for processing organic matter. They used them to obtain biomass and expand the diet of domestic animals and birds.
It has been proven that when using vermicompost, the yield of vegetables increases several times. The ripening of the crop is also accelerated by 10-15 days. All thanks to the soil that passes through the esophagus and then contains all the mineral elements and complex compounds necessary for plants. In addition, vermicompost is useful because
- reduces the number of pests in the garden,
- binds heavy metal residues and removes residual radiation,
- increases yield without the use of chemical fertilizers.
What work do worms do in our gardens?
The invertebrate soft worm can break through even the driest and hardest soil. He tears off a piece of earth with his lips and swallows it. If very dense and dry soil comes across on the way, the worm moistens it with saliva. Having eaten to its fullest, it crawls to the surface, where it throws out the soil that has passed through the intestines. Thus, the worm passes through its intestines both the soil and dead plant particles, which are finally destroyed, crushed and mixed with the soil.
In the process of feeding and vital activity, earthworms enrich the earth with their own intestinal microflora, which contains various biologically active substances (antibiotics, vitamins, amino acids and other enzymes). During the digestion of organic matter, humic acids are formed in the intestines of invertebrates, which, when combined with the mineral components of the soil, form a valuable environmentally friendly fertilizer - vermicompost.
Earthworms are capable of digesting various bacteria, fungi, and protozoa (including nematodes). The activity of worms disinfects and heals the soil. This is especially important for compost heaps, where we put not only plant debris, but also manure and food waste.
High acidity is currently a problem for many vegetable gardens and garden plots. The main causes of acidification are considered to be the application of mineral fertilizers and the leaching of calcium due to soil destruction. Every year, farmers engage in liming (plowing lime and dolomite flour into the ground); this activity requires a lot of effort and time. Earthworms will help solve the problem of high acidity. During the metabolic process, worms secrete large amounts of calcium carbonate, which can significantly change the acidity of soils, bringing it closer to neutral.
Passing the soil through the intestines, the earthworm fills it with coprolites. Coprolites are the so-called dung of these invertebrates. Unlike the manure of other animals, it does not have an unpleasant odor and contains various biologically active substances in an easily digestible form. Some animals even use it as medicine. Coprolites cannot burn plants and infect the soil. Earthworm manure contains a complex of bacteria that are capable of converting organic matter into a form accessible to crops, as well as fixing nitrogen from the air. Coprolites contain the natural enzyme chitinase, which protects plants from insect pests, as well as various fungicides that prevent the development of dangerous diseases. In a word, coprolites are both fertilizer, protection, and growth stimulator.
From all of the above, it is clear that earthworms are excellent helpers for the gardener. They help improve the structure and fertility of the soil; during their life processes, environmentally friendly fertilizer is produced, as well as biologically active substances that protect crops from pests and diseases. Let's figure out how to increase the population of these useful animals, how to attract them to our gardens.
The benefits and harms of earthworms
Charles Darwin was one of the first to point out the role of earthworms in soil formation in 1882.
He even suggested that they have intelligence, noting that pulling a piece of leaf into a hole occurs from the narrow end, and a bunch of pine needles pulls at the base to make it easier to get into. He observed them almost all his life and wrote the scientific work “The Formation of the Vegetative Layer of the Earth by the Activity of Earthworms and Observations on Their Lifestyle” (1881).
Benefit
Earthworms are also called soil formers, because by making tunnels in the ground, they loosen the soil and contribute to its saturation with oxygen. In wet weather, you can see how the worms crawl to the surface, and in dry weather they go up to half a meter deep and fall into an unconscious state.
Over the course of a year, worms process a large amount of soil, equal to almost their weight, several kilograms of fallen leaves and other parts of plants. In one day, the worm easily processes about 25 g of soil. The soil is plowed by worms and becomes more fertile. Number of worms per 1 sq. m reaches up to a hundred specimens, and in wet meadows up to six hundred. Among the beneficial qualities of the life of worms in the garden include:
- loosening the top layer of soil, promotes its aeration;
- restoration of soil fertility;
- saturation of the soil with oxygen, and this has a positive effect on plant nutrition;
- enriching the soil with useful microelements - phosphorus, calcium, magnesium;
- maintaining the growth of bacterial populations;
- regulation of soil acidity.
During the digestion of plant residues, humic substances are formed in the intestines of worms, which, entering the soil, slow down the leaching of mobile compounds from it and prevent water and wind erosion of the soil.
Harm
Among gardeners, there is an opinion about the dangers of worms, which allegedly gnaw the roots of young plants. However, this is nothing more than a myth. There is no need to be afraid of worms; they cannot cause harm simply because of their feeding habits.
But they still cause harm. Earthworms are intermediate hosts of dangerous parasites for pigs - metastrogylids. The infestation causes respiratory distress in pigs and poisons them with toxic products of their vital activity. Animals that catch such an invasion die. They are also intermediate hosts of parasites - syngamids in birds, especially in domestic birds - chickens, turkeys, ducks.
Louis Pasteur, a French microbiologist and chemist, once pointed out the possibility of anthrax spores being spread by earthworms from the burial grounds of animals that died from this disease. However, he was wrong and this has already been recognized, since this is simply impossible due to the biological characteristics of worms.
Worms are the most useful pets
People have long appreciated the influence of worms on the fertility of the earth, so they began to breed them at home to obtain vermicompost. Unpretentious pets do not need excessive care; they provide their owners with free fertilizer all year round and help solve the problem of waste disposal .
In favorable conditions and with sufficient food, any worms increase productivity and reproduction rate. However, specially bred hybrids have unique qualities. They are ideal for cultivation under artificial conditions, and the humus they produce is not inferior in characteristics to that produced by their wild relatives.
Agricultural land has been depleted due to continuous long-term use. The use of pesticides has reduced populations of worms and other soil-forming organisms. Industrial cultivation of vermicultures makes it possible to increase the fertility of the land over vast areas. Environmentally friendly fertilizer is much cheaper, healthier and more effective than its chemical counterparts. At the same time, the problem of recycling a large volume of human and agricultural waste disappears.
Vermiculture
Currently, due to the frequent use of mineral fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, the population of earthworms has decreased significantly.
Some people are specifically engaged in vermicultivation, that is, the artificial propagation of earthworms. Vermiculture is a business that does not require large start-up capital. The demand for both earthworms themselves and the organic fertilizer they produce has been increasing recently.
You can breed worms yourself. Liming the soil will help increase the number of earthworms. Or they are bred in the following way. Place leaves, food waste, humus, manure in a dug hole and throw in worms. After a while, you will notice that there are much more worms in the soil. For faster reproduction, worms are fed with a three-day tincture of cut grass, nettles, dandelions, and food waste.
Summarizing what has been said, I want to say that, after all, the benefits for people from earthworms are much greater than the harm.
To prove it, watch this video “The Amazing Inhabitants of the Garden.” I wish you good harvests!
The invaluable work of earthworms
The activity of worms radically changes the chemical composition of the soil for the better:
- During the season, invertebrates form many kilometers of passages in the ground. Due to them, aeration, water permeability and looseness of the soil increase, its layers are mixed.
- Coprolites change the structure of the earth, increasing its clumping and moisture holding capacity. Tiny lumps measuring 1-5 millimeters in size have a stable shape that lasts for a long time. The beneficial substances from them are slowly released into the environment, and are not washed away with rain.
- Worm waste (vermicompost) enriches the soil with a full range of substances necessary for plant development (vitamins, minerals, natural antibiotics, humates, and so on).
- Along with waste, worms absorb and process pathogenic organisms, releasing digestive enzymes and microflora from their intestines into the soil. The content of beneficial microbes in vermicompost is hundreds of times higher than in their environment. Just a few coprolites can provide nutrition and the necessary microflora to one small plant for the entire season.
Worms not only influence the cycle of nutrients in the soil, but also regulate the number of microorganisms in it. Thanks to the activity of worms, favorable conditions are created in the soil for the proliferation of aerobic bacteria, which also utilize waste into compost. The symbiosis of decomposers significantly accelerates the process of decomposition of organic matter, while the fungi and bacteria themselves are useful protein food for worms.
With a sufficient number of soil-forming organisms on the site, agricultural producers can significantly reduce the use of chemical fertilizers (or even abandon them altogether). Pesticides and artificial mineral additives have a detrimental effect on the quality of the land and the environment in general. Harmful substances enter the body of people and animals along with agricultural products, while environmentally friendly vermicompost can neutralize the effect of nitrates.
To understand in more detail why earthworms increase soil fertility, and how this benefits humans, you can read the book by the pioneer of domestic vermicultivation, Anatoly Mikhailovich Igonin.
Download the book : “How to increase soil fertility tens of times with the help of earthworms” from our website using the links:
.pdf format
.epub format
Humus and soil: Earthworms
12. 2. 2022, biom.cz, Vladimir Vrba, Ludvik Huleš
Earthworms are the most important animal component of agricultural lands. About 50 species of earthworms are known in the Czech Republic, of which only one third can be found in agricultural systems.
The smallest number of earthworms can be found on arable land, where, according to a study conducted in 1994, several dozen individuals can be found per 1 m2. However, this number can be much higher on permanent pastures. The importance of earthworms for the soil lies primarily in their influence on the decomposition of primary organic matter and the formation of humus. Earthworms are involved in converting complex organic compounds into simple forms that can be used by plants. The conversion occurs in two ways:
Direct: by ingestion, digestion and excrement.
Indirectly : by influencing populations of microorganisms by eliminating their enemies or using their nutrients, influencing soil moisture and aeration, or by chopping and transporting plant material.
Earthworms have a positive effect on soil structure and microstructure and soil fertility, as has been demonstrated in many studies. This is primarily due to the production of excrement, in which mineral particles are mixed with decomposed remains of organic microflora. They promote soil aeration by creating tunnels. The importance of excrement in the soil is great as its production is also high and therefore it can significantly affect the quality of the soil. In our conditions, up to 40-50 tons per 1 hectare are formed annually on the soil surface, which is about 4-5 mm. Their production depends on how favorable living conditions are for earthworms. In soils with a large population of earthworms, plants produce much more powerful root systems, which is a prerequisite for an adequate supply of water and nutrients to the plants. The activity of earthworms prevents the formation of a crust on the soil surface, which promotes plant germination. The presence of earthworms leads to an increase in crop yields, as well as a decrease in the number of harmful factors (phytopathogenic fungi).
Important signs of earthworm activity:
- They improve soil structure and prevent the formation of crust on the soil surface
- Their tunnels help water reach plant roots and allow excess water to drain out, which also helps aerate the soil.
- Earthworm populations create up to 4,400 km of tunnels per hectare.
- Earthworms can reproduce in numbers in excess of 33 tonnes per hectare each year.
- They increase the availability of phosphorus in the soil.
- Each earthworm is capable of producing 20-40 cocoons filled with eggs per year.
- They reach maturity in less than a year and live up to 10 years.
- The population continues to grow throughout the year, so it is necessary to take this into account and change the soil cultivation method - no-till or minimizing tillage.
- The earthworm population is more numerous in soils with plant debris on its surface.
- According to the study, there are 10-20 earthworms per 1 m2 of arable land together with permanently cultivated crops, and 1,300 earthworms per 1 m2 of fertilized pasture (according to our older sources, 100-800 earthworms per 1 m3 in the Czech Republic , and their weight reaches 5 t/ha), but recent studies show that the number of earthworms in our country is lower.
- Earthworms prefer alfalfa and clover residues to grasses or brome.
- Their populations grow in well-fertilized soils.
- Their population decreases when liquid fertilizer is reused.
- During plowing, gulls consume 6% of the earthworm population. However, plowing itself destroys up to 20% of the earthworm population. The plow also removes plant debris from the soil surface and makes it more difficult for worms to access it.
- Pesticides are toxic to earthworms.
- Many herbicides have a direct effect on earthworms.
- Ammonia is toxic to earthworms.
Depending on the species and lifestyle, earthworms affect the soil in the following ways:
Deep-burrowing earthworms create large, multi-meter, nearly vertical, permanent tunnel systems that open to the soil surface, where they feed on dead plant material. These types of soil tunnels significantly affect the water regime in the soil.
Surface earthworms live in waste on the surface of the soil. However, they are currently of little importance due to the limited accumulation of organic matter caused by current tillage practices.
Subsurface earthworms live below the surface of the soil and are part of cropland. Soils rich in earthworms absorb water better than soils without them because the vertical tunnels created by the earthworms speed up the flow of water into the soil. This makes the soil less susceptible to flooding in winter and spring, and more water flows to plant roots. Earthworms increase soil resistance to erosion. In heavy soils, earthworm tunnels are the main space into which plant roots penetrate (40 - 60% of plant roots are in these tunnels). Research has shown that 42% of aerobic nitrogen-fixing microorganisms are located near earthworm tunnels. The number of earthworms depends on the cultivation system. No-till farming systems provide more earthworms that are active at night. In general, the more plant debris you have on the surface, the better it is for earthworms. To increase earthworm numbers, farmers are not advised to immediately switch to a no-till system because there are tillage methods that leave 15-30% of crop residue on the soil surface during the growing season.
ESSEX CONSERVATION CLUB in Canada in the spring of 1996 received the following results:
| Cultivation method | Number of earthworms |
| No-till | 693 135 |
| Minimum | 203 602 |
| Traditional | 139 835 |
| Forest soil* | 722 395 |
* forest type not specified
Classic methods of soil formation, including deep plowing, reduce the number of earthworms in the soil due to mechanical damage, bringing them to the soil surface - prey to predators; destruction of earthworm tunnels during repeated plowing leads to a significant reduction in the earthworm population; Tilling changes soil temperature and moisture, as well as food availability. The loss of organic matter in the soil causes the most pronounced decline in earthworms. Shallow plowing does not reduce earthworm numbers as much as deep plowing. The no-till method is the most favorable for earthworms. The number of earthworms in the soil increases if straw remains on the surface of the unplowed soil after harvesting. When the no-till method is used for several years, the earthworm population increases up to thirtyfold, but this population may gradually decline as soil organic matter is the limiting factor. Higher nitrogen mineralization was found in soils where shallow tillage was used than in soils where conventional cultivation methods (deep tillage) were used. It has been found that earthworms and plant roots can cause decomposition of organic matter through increased microbial activity by releasing exudates into the environment. According to research conducted in Germany, earthworms can significantly reduce the incidence of scab in fruit trees. If there are enough earthworms in the soil, they can drag all the autumn leaves into the soil, so the fungus Venturia inqaequalis (the cause of apple scab) will not be able to reproduce on the fallen leaves, so it will be destroyed. Earthworm activity also improves soil structure. To encourage the spread of earthworms, it is recommended to constantly mulch the area surrounding the trees with grass clippings. It is also recommended to cut freshly cut branches as they are very suitable substrate for earthworms. Leaves that fall into lakes in the fall should be left in place so they are available to earthworms.
Vladimir Vrba, Ludvik Hules
Source: VRBA, Vladimír, HULEŠ, Ludvík: Humus - půda - rostlina (2) Humus a půda. Biom.cz
[online]. 2006-11-14 [cit. 2018-01-29]. Available at WWW: . ISSN: 1801-2655.
How to breed earthworms
The worms are hermaphrodites, that is, they mutually fertilize each other, after which they lay cocoons with eggs. In nature, this process proceeds quite slowly. Invertebrates awakening after hibernation enter the mating season and lay one cocoon per week for three months. The juveniles hatched from them reach maturity only in the fall, when the period of hibernation begins. Unfortunately, in winter, during severe frosts, most of the young worms may die.
For those worms that are hatched under artificial conditions, the reproduction process is much faster. To breed worms, it is absolutely not necessary to buy a Californian or any other artificially bred breed. You can use the “mutts” that already live on your plots. In a sense, this is even more correct, since they are well adapted to local climatic and other conditions. And, for example, Californian worms, although they are distinguished by increased fertility and rapid reproduction times, do not tolerate local frosts at all, and simply die in the cold season.
How to properly organize a worm house
It is better to breed worms in a container. This will protect them from animals for which they are natural food (moles, rooks and others). You can adapt anything for this - an old bathtub, a large trough, any drawer. If you don’t find anything suitable, you can organize a worm hutch right on the ground. However, in this case you will have to take additional protective measures. You can, for example, cover the ground with a mesh or concrete it with a slope (so that the water does not stagnate). This will protect your pets from moles. To protect against birds, you need to cover the top of the worm cage with a fine mesh.
The size of the house for invertebrates should not be very large, no more than 2 m2 in area, otherwise it will be difficult to care for. There is no need for more, unless, of course, you are going to breed worms for sale. Earthworms need moisture and relative coolness to live, so the worm house must be placed somewhere in the shade (under a canopy, under trees, in a barn or cellar).
Next, you need to prepare a nutritious bed of compost, which we place on the bottom of the container in a layer of 40–50 cm. If you organize a worm hutch on the ground, you should end up with something like a small bed.
The compost needs to be well watered with warm, settled water; it is best to use rainwater. After this, we cover the litter with burlap or straw and let it sit for 5–7 days. The home is ready to move in.
Where to find manufacturers
There are three possible answers to this question. Firstly, worms can be found on your own property. You can rummage through old manure heaps and piles of last year's leaves. For this purpose, you can dig up a small plot of land in the spring. Even in the most “dead” soil there will always be a certain number of earthworms. You can also dig up worms in the forest or collect them on paths after rain.
If you are unable to find a sufficient number of invertebrates using the methods described above, try luring them. To do this, in a quiet, damp place, for example, in a raspberry patch (or even in a forest one), you need to dig a small ditch, fill it with compost, thoroughly moisten it and cover it with burlap or paper. After 1.5–2 weeks, earthworms will definitely appear here. All that remains is to carefully collect them together with the compost with a pitchfork and bring them to the new home.
And finally, you can simply buy worms. For a good worm trap that will constantly supply you with vermicompost, you need from 500 to 1000 individuals per 1 square meter. m. You can purchase Californian ones, but it is more correct to give preference to local breeds that are better adapted to our conditions. It is important to note that you need to make a purchase from trusted sellers who have permission to sell. This will protect you from being deceived, since there have been cases when, under the guise of young worms, “cunning” entrepreneurs sold nematodes.
How to populate a worm house correctly
So, there are worms, and the house is ready for them - let's start moving in. You need to make a hole in the center of the worm bin and tip a bucket of worms into it. Next, level the surface and cover with burlap or straw. In hot weather, it is important to prevent drying out; the worm pit must be watered with warm, settled water quite often.
When populating worms, it is necessary to initially provide them with their usual food. To do this, they must be resettled with a certain amount of the substrate in which they lived previously. Gradually, they themselves will look for new sources of food and switch to the diet that you can offer them. It should be noted that worms collected outside after rain take root best - apparently, they are used to eating anything.
In a week you can already evaluate the first results. Observe whether your pets occupy the entire space of the worm house, and what they look like. If their surface is clean, the worms are mobile and hide from daylight, then everything is in order. You need to start feeding the worms 3-4 weeks after moving in, and before that, do not forget to regularly water their home with settled, warm water.
How and what to feed earthworms
It is best to organize a worm farm in the spring or early summer, so that invertebrates have the opportunity to reproduce and grow stronger before the onset of cold weather. Juveniles grow quite quickly, and over the summer the number of worms can increase 30–50 times, depending on the fertility of the breed.
To grow and reproduce, you need to provide your pets with enough food. Therefore, you should periodically add fresh food to the worm cage. This should be done every 2–3 weeks, adding 15–20 cm thick layers of organic matter on top.
Earthworms can eat almost any organic matter you have on your property. Suitable food for them:
- cattle manure stored for 6 months;
- pig manure aged for at least a year;
- rabbit or goat manure (can be given immediately);
- vegetable and fruit peelings and other kitchen waste (except citrus fruits and animal waste);
- used tea and coffee infusers;
- crusts of stale bread;
- soaked shredded newspapers or cardboard.
Any food should be fed to worms only in crushed form, since they do not have teeth. You should also maintain a constant feed composition, since if it changes, it will take some time for adaptation. It is important not to forget to maintain the necessary humidity by watering with well-settled warm water.