- Garden bugs: harm and benefit
- Useful garden bugs for the vegetable garden Macrolophus
- Perillus
- Podizus
- Green forest shieldweed
- Do garden bugs bite or not?
Proper planting and proper care of garden crops does not yet guarantee a good harvest, because throughout the entire season, each plant is a potential “victim” of various diseases, rodents and parasites, such as the stink bug and other representatives of this suborder. Let's figure out what kind of garden bugs the family of stink bugs are, why they are harmful and useful.
Garden bugs: harm and benefit
Gardens and vegetable gardens are home to a large number of garden bugs, some of which are not only harmful, but also those that can be beneficial. All of them belong to the Shield family, which has more than 4 thousand subspecies, which differ in color, shape and body size. The insect species got its name due to the presence on its body of a hard, massive shield with elytra.
But among these creatures there are also beneficial species - predatory bugs that feed on pests such as Colorado potato beetles, aphids, caterpillars and other pests. They are an effective means of combating agricultural parasites, which is why they are specially bred.
Famous soldiers or common red bugs
This type of garden bugs does not require any special introduction, since there is probably no one who has never encountered them. A distinctive feature of this type of bedbugs from others is their coloniality, thanks to which they are deliberately noticeable due to their bright color. As a rule, these individuals are harmless to humans and the economy, but sometimes they can cause harm to plants due to their dominance.
Soldiers feed on plant and animal food, for example, rotting remains of fruits and plants, dead insects, etc. Only in the absence of food can such bugs move to the shoots of young trees and grapes, thereby damaging them.
Video fragments from the life of soldier bugs are educational for everyone to watch:
Useful garden bugs for the vegetable garden
Breeding predatory bugs on an industrial scale and using them as a harmless alternative to toxic pesticides to kill various pests is now actively practiced in the agricultural sector.
On the territory of Russia, only a few subspecies of useful Shield insects have taken root, which were able to adapt to our harsh climate.
Macrolophus
A polyphagous bug from the horsefly family. The adult individual has an elongated body (2.7-3.7 mm) with a light green color. Most often, this insect is used on closed ground (in greenhouses) to protect tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, sweet peppers and ornamental crops from aphids, thrips, spider mites, tomato leafminer moths and whiteflies.
Every day, one Macrolophus individual destroys 30 adult whitefly larvae or about 40 aphid adults. During its life, this predator is capable of eating 2.5 thousand whitefly larvae or 3.5 thousand whitefly eggs.
Perillus
A predatory bug from the order of secretive bugs of the Shield family. The length of an adult is 8-12 mm. These insects are distinguished by their bright appearance: their black shell is decorated with red or orange spots, and on their head they have a proboscis that resembles a sharp beak, with which they pierce the flesh of the victim and suck the juices from it.
The favorite food of adult bedbugs and their larvae are the eggs and larvae of the Colorado potato beetle. Perillus is most active in hot weather. During its development, the larva of the predator eats 250 eggs of the beetle, and the adult destroys 3.5 thousand eggs of the potato pest during its life.
These insects also feed on aphids, thrips, spider mites, butterfly eggs and whitefly larvae.
Podizus
A polyphagous bug from the Scutellidae family. Its homeland is North America, but in Russia it is bred for pest control. The body of adult individuals is brown and reaches a length of 14 mm.
These predators are unable to tolerate cold, so every spring new crop defenders have to be released into the sown fields. The Podizus menu includes over nine dozen species of coleopteran and lepidopteran insects, including the Colorado potato beetle, potato moth, white American butterfly, etc.
Variety of colors
Shield insects differ from their counterparts by a characteristic feature - bright coloring. The Italian stink bug has a striking, stylish “outfit” – a deep orange body with black stripes and specks. The boy stink bug, which parasitizes plants, has an intricate coloring.
The red-legged stink bug is a two-faced beauty capable of destroying both pests and plants. The top is dark brown with a green and bronze sheen, the abdomen, paws and mustache are reddish. The body of the earth shield is painted in a luxurious black color with a silver tint.
Garden bugs pests
As for Shield insects, which pose a threat to garden and vegetable crops, there are a great many of them living on the territory of Russia. Entomologists conditionally divide them into two subgroups:
- summer cottages are parasites that feed only on the juices of fruit and berry plants;
- forest bugs - bugs that live in forests and feed on wild vegetation, but easily switch to garden crops.
Green forest shieldweed
The main distinguishing feature of the pest is its bright green color. The length of adults is 1.5 cm.
These garden bugs live on trees in forested areas, but they can often be found in the garden or vegetable garden at the dacha. The forest green shield bug reproduces in those places where it feeds, so that the hatched larvae can immediately find food. Their favorite delicacy among garden crops are raspberry and currant bushes and herbaceous plants.
Shield berry
The habitat of parasites is gardens where there are berry bushes, and they eat not only the foliage of plants, but also the fruits, thereby completely destroying the crop. One female lays about 400 eggs.
The garden bug, the berry bug, is also called the stink bug because of the strong, unpleasant odor that it emits upon contact or if it is crushed. The hatched larvae go through five stages of development. Adults have a burgundy shell and a yellow belly. Stink berry bugs overwinter as adults and emerge in April.
Harmful turtle
This representative of the family poses the greatest danger to cereal crops, because they constitute its main diet. In the absence of usual food, the harmful turtle feasts on garden plants.
The insect got its name due to its external resemblance to a turtle. Thanks to their well-developed wings, these bugs can easily travel long distances. Turtles are characterized by high fertility (the female lays 15 eggs in one season), so it is difficult to get rid of them.
Eurydema northern
Cruciferous Shield with a variegated pattern on the body (bright spots of yellow, red or white are located on a black background). The length of an adult is 5.5-8 mm.
Externally, the pest resembles a soldier bug. Intensive growth of the population of this dangerous pest occurs with the onset of heat, so planted seedlings of various vegetable crops can be completely destroyed within just a few days. Eurydema northern feeds on leaves of cabbage, radish, radish, etc.
Pear lacemaker
This garden bug got its name because of the translucent beige cells covering its body, which resemble openwork weaving. The maximum body length of an adult insect is 3.3 mm.
The favorite habitats and feeding places of the pear laceweed are fruit trees (pears, plums, apple trees, apricots, etc.). Pests overwinter under tree bark, fallen leaves, and in hollows. They awaken with the appearance of the first leaves, and when warm weather sets in, they can fly 5 km from their wintering place.
Cucumber bug
A small (up to 3 mm) black parasite, endowed with the ability to jump well. Occupies the back side of cucumber leaves.
The cucumber bug feeds on the leaves of cucumbers, tomatoes, sweet peppers and eggplants. The parasite feels comfortable in the shade and dampness, so it settles down on the back side of the leaf, which does not always allow gardeners to detect it in time.
This subspecies of Shield insects is one of the most dangerous enemies of cucumbers, such as whiteflies, spider mites and melon aphids.
Italian bug
A representative of the Shield family with a flattened wide body up to 11 mm long, painted bright red with black longitudinal stripes. Under the shield there are two pairs of wings, which provide the bug with the ability to fly well.
The diet of adults and larvae consists of the juice of the tissues of umbrella garden plants (dill, carrots, etc.). The parasite feeds on plant seeds and young parts (tops, bases of leaf blades).
A large amount of damage leads to the death of the plant. The Italian bug has odorous glands, like the stink bug, from which an unpleasant odor is released in case of danger.
Soldier bug
The insect belongs to the red bug family. The length of an adult is 10 mm. There is a red and black ornament on the front back and elytra. In warm, clear weather, bedbugs gather in colonies near stumps, trees, and fences to bask in the sun.
Garden soldier bugs are omnivorous pests. They feed on all types of garden plants, fruits and seeds of some fruit bushes and trees, the remains of small insects, and in some cases even resort to cannibalism.
Life cycle
Garden bugs lead a similar lifestyle. Differs somewhat in nutrition. Insects are active in the warm season. In winter they hibernate. Shelter is found under leaves, stumps, in old trees, cracks in agricultural buildings, and under fences.
In early spring they wake up, gather in pairs, and the mating season begins. It lasts about 10 days. After this, the females begin laying eggs. For these purposes, each species chooses its own culture. One garden bug chooses shrubs, another chooses trees, and the third chooses garden crops.
Interesting!
The garden bug attaches its eggs to the back of the leaf. There are several pieces in the pile. Eggs of different colors with a lid on top. After 14 days, the larvae crawl out, gnawing through this lid. They begin to parasitize.
Bedbug larvae resemble adults. They differ in size. During the period of maturation - 20 days, 5 moults pass. At the last stage, the genital organs are formed. Young individuals of country bugs begin to mate.
How to recognize bedbugs on your property
The choice of settlement sites for garden bugs is determined by the availability of familiar food in sufficient quantities. Considering that the vast majority of pests feed on garden plants, garden plots and summer cottages planted with different crops are optimal places for them.
The main task of owners of suburban areas is the timely detection of parasites in order to prevent their further spread. A systematic and careful inspection of the plantings will help to cope with this task.
The danger threatening the future harvest is indicated by the appearance of larvae or adults on the back of the leaves, small holes and brown spots on them. To choose the right method of pest control, you need to know what a particular subspecies looks like.
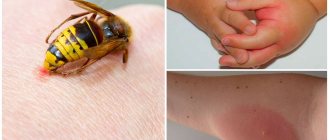
Are they dangerous for humans?
Unlike bed bugs, herbivorous and predatory species are safe for humans. The only trouble that awaits urban and rural residents is the smell that insects leave on plants or emit at the slightest danger.
Herbivorous insects are safe for humans.
Do they bite or not?
Garden pests cannot bite through human skin. Their soft proboscis is adapted for sucking juices from tender leaves and shoots. The digestive system of bedbugs is not able to digest human blood. Therefore, it is impossible to get a bite from a country or forest stink bug.
The exception is the predatory bug, which feeds on small invertebrate animals. Theoretically, its long proboscis could pierce the skin of an adult or child and cause pain. But before this happens, the person will have time to brush off the pest, which reaches a length of 1.5-2 cm.
How plants die from bugs
All varieties of garden bugs obtain food using proboscis, with which they pierce plant tissue and inject special enzymes into it that change the viscosity of the juice. In its transformed form, the plant juice is ready for consumption. Over time, damaged foliage withers and dies. With large-scale lesions, the plant dies.
By devouring green mass during the growing season, harmful insects are capable of destroying any cultivated plantings in the early stages of their development. By attacking garden plants, parasites not only destroy foliage, but also prevent the formation of ovaries, which can lead to complete loss of the crop.
Riders
These representatives of Hymenoptera insects are overwhelmingly parasitoids of other animals, mainly other arthropods. Many of the ichneumonids, such as Braconidae and Trichogramma, are beneficial to humans because... regulate the number of agricultural pests.
Trichogramma (egg-eaters) are miniature insects that feed on nectar. They “fight” pests at the stage of larvae, which parasitize in the eggs of other insects, most often lepidopterans and homoptera (cabbage white moth, apple moth, meadow and corn moth, winter and cabbage cutworm, gooseberry sawfly, etc.), gradually killing them , eating away from the inside. At the end of the development of the pupa, adult Trichogramma individuals emerge from the host egg.
These insects can be used to combat more than 70 types of garden pests! Mass reproduction of Trichogramma is on an industrial basis, and you can buy these little helpers in specialized laboratories. And there is no doubt that the help will be valuable - one female Trichogramma released onto the site can damage up to 1000 eggs of pests.
In small areas, parasites are purchased at the rate of 1 insect per 10 plants. For larger areas, the calculation will be as follows: adult Trichogramma are released at approximately 10-15 points on 25 acres of plantings. When fighting cabbage and winter armyworms, up to 10-15 thousand Trichogramma individuals are released onto 25 acres in two stages during the period when insect pests lay eggs.
In English-language literature and Russian-language tracing papers, many wasps are still commonly called parasitic wasps.
Braconids are larger riders. Depending on their species, they parasitize on various harmful beetles, aphids, bedbugs, flies, moths - both garden pests and those that spoil grain or dried fruit stocks in storage facilities.
Chemicals
It is worth fighting the invasion of parasites with the help of special pesticides only in advanced cases, when the problem has acquired a large scale. It should be remembered that the use of such drugs can harm beneficial insects, birds, and animals, so you should resort to their help in emergency situations.
Such chemicals contain insecticidal components of the pyrethroid and organophosphorus groups. According to the type of action on pests, they are divided into systemic, contact and intestinal.
Penny leafhopper (Slobber)
The body of an adult cicada is oblong-oval, up to 10 mm long; color - from light yellow to brown. Adult insects and larvae suck juice from the stems and leaves of strawberries, dill. Dill is a genus of annual herbs of the Apiaceae family, which includes everything..., parsley, parsnips, carrots, sorrel, tarragon, cucumbers, onions, garlic. Among flower plants, it damages asters, chrysanthemums, dahlias, phlox, etc.
The leafhopper is moisture-loving and is most often found in dense crops. Yellow-orange eggs overwinter in leaf petioles and in young stems of damaged plants. Larvae hatch from eggs in late April - early May. They live on the underside of leaves, on the petioles of leaves at their base, sucking out the juice.
Damaged leaves wrinkle and the ovaries become ugly. The larva secretes a foamy liquid similar to saliva, which, hugging the larva on all sides, protects it from drying out and enemies. The presence of leafhoppers on crops can be easily confirmed by the presence of salivary lumps of foam in the grass. Adult cicadas emerge in late June. After laying eggs, they gradually die off.
Control measures. Spraying strawberries and flower crops before flowering with karbofos or a solution of green soap.
Traditional methods for garden bugs
- Infusion of onion peels. It is necessary to prepare a solution of 10 liters of water and 250 g of husk. After it has been infused for 5 days, it is filtered. Plants are sprayed once every 4 days.
- Laundry soap solution. Prepare a solution of 10 liters of water and 300 g of soap. Treatment is carried out every week.
- Mustard solution. Dissolve 100 g of mustard powder in 10 liters of water. Repeat spraying every 3 days.
Ants
Ants often settle in the garden. They make nests in the soil with a system of complex passages. At the location of the colony, vegetable crops do not grow, they wither and quickly die, not without the participation of ants. The ants remove the remains of dead plants from the territory of the colony. Repeated digging of the soil at the site where a colony forms does not always lead to its disappearance.
Control measures. Ants can be exterminated or forced to move to another location in a variety of ways.
- Add 5 g of borax, 50 g of sugar, half a teaspoon of honey or jam to 1/4 cup of water. All this is mixed and placed in a small container on the soil, where the ants live. Ants willingly eat semolina themselves and, taking it to the nest, feed it to other ants and larvae. The dishes must be made of non-oxidizing metal and have no foreign odors. The amount of borax should not be increased; the working ants should not die immediately, but only after they bring the bait to the nest and feed it to the ants and larvae located in the nest underground.
- From ordinary yeast, mix a thick paste in water, add a little honey or jam to it, and place it on the ants’ nest.
- Ants are repelled by the smell of mint, garlic, wormwood (this feature can be used in the fight against them).
- Adding Thunder granules to the top layer of the anthill.
How to find bedbugs in a house or apartment
Garden bugs cannot exist in residential areas, because... deprived of their usual habitat and food opportunities. If an insect somehow ended up in the house, it will not be difficult to detect it, even if it is a specimen without bright coloring.
These parasites, finding themselves in conditions that are uncomfortable for them, try to immediately find a way out of the enclosed space. In addition, most varieties of bedbugs smell unpleasant (in case of danger, they secrete a secretion with a characteristic odor from special glands), which will indicate their presence in the room.
Natural enemies
Unfortunately, garden bugs do not have a natural killer. Birds do not peck this insect because of the disgusting, stinky odor that resembles a mixture of skunk and cilantro. Of all the birds, only ducks can tolerate the stinking smell of the beetle and peck at it. Chickens that eat stink bugs become inedible because their meat stinks.
INTERESTING The killer of stinking insects is the locust.
Wasps can also kill these pests. But there is no point in such helpers: locusts cause even more harm than stink bugs, and wasps parasitize on the eggs of stink bugs, preventing their intensive reproduction. But the next problem after stopping the garden bug infestation will be getting rid of the wasps.
If bedbugs appeared in kindergarten
The appearance of garden bugs on the territory of children's institutions is a common situation. The reason for this is the presence of conditions for their normal existence. Harmful insects can be attracted by flowering ornamental plants and thick lawn grass, fruit trees and berry bushes growing in the kindergarten yard.
Just like for adults, bedbugs do not pose a threat to the health of children. The only exception is considered to be allergy sufferers, whose body may react negatively to the secretion secreted by parasites with an unpleasant odor.
Another problem is that any small child is curious and often puts anything that interests him into his mouth. Considering the bright colors of many harmful creatures of the Scutellidae family, there is a high risk that he will want to taste a beautiful bug, and this is a direct path to food poisoning.
Thus, if a population of garden mites is found near a kindergarten playground, urgent measures must be taken to eliminate them.
Herbal aromas
According to numerous reviews from people familiar with this problem, grass is another sign of what house bugs are afraid of. The most famous herbal repellents are:
- Tansy. Fresh and dry flowers, as well as decoctions prepared from them, have repellent properties.
- Wormwood is recognized as the most effective plant in repelling bed bugs. Insects are afraid of the smell of both fresh and dried grass.
- Calamus is another plant that is completely safe for human health and has a pungent odor. Can be used in powder, decoction or infusion form.
- Bay leaf. This plant, or rather its leaves, is used to prepare various dishes. The pleasant aroma for humans is feared by parasitic insects. It is enough to put a few bay branches in your bed to prevent bloodsuckers from bothering you at night.
- Chamomile. Like other synanthropic insects, bedbugs do not like the smell of Pyrethrum, a drug based on chamomile.
- Marsh rosemary. The shoots cut in August have a particularly pungent odor, which parasites are afraid of.
Do garden bugs stink when crushed?
All varieties of bugs of the stink bug family have special glands that secrete a secretion with a specific odor, the intensity of which differs in different types of insects.
With the help of this bodily function, they scare away enemies and signal about approaching danger, attract partners for mating, find fellow tribesmen and navigate in space.
The unpleasant aroma is especially intensified when the bedbug is physically damaged, when the odorous secretion is squeezed out of the glands in which it is formed and stored.