What do rats and mice have in common?
These mammals belong to the order of rodents of the mouse family. There are other common features. Because of them, these two species are often confused.
Mice and rats: general features of life
Both of them belong to cosmopolitan species. That is, these rodents inhabit all corners of the Earth except Antarctica and the Far North, and they are not found high in the mountains.
These rodents are considered synanthropic, that is, associated with humans. Wild subspecies live in human homes, utility rooms or those intended for keeping pets. Although in warm regions they can live far from human habitation.
Rodents are animals with a nocturnal and twilight lifestyle. They are most active at sunset. However, when kept in captivity, animals adapt to the rhythm of life of the owner, get used to staying awake in the light and reducing activity during human rest.
These types of rodents are very active. They climb, run, jump and swim beautifully. Possessing high plasticity of the body, the animals can “leak” into very small crevices.
In nature, mice prefer to live in colonies in which they maintain a hierarchy. Adult males can start fights among themselves. In families, aggression sometimes spreads to older offspring, which the parents expel from their territory.
Rodents are clean creatures. They keep their homes clean and tidy. The droppings and piles of dust held together by urine that they leave while moving are special marks for determining the route.
Both types of rodents not only live in nature, but also take root in captivity and are easily tamed. Today, breeders, which many fanciers are happy to keep as companion animals.
Similarity in appearance
The mouse really looks like a smaller copy of a rat:
- The house mouse and are covered with horny scales and sparse short hairs. Only the black rat stands out here. Her tail is covered with thick hair.
- Both species have round black eyes (in albinos they are red or dark ruby).
- The main characteristics of these two types of rodents are long, sharp incisors that grow throughout their lives and the absence of fangs. With their teeth, animals can gnaw through very hard materials, even concrete.
Gray rat: habitat
In nature, these rodents settle only where there are sources of water, without which they cannot survive even three days. They prefer lowlands overgrown with vegetation, but can also climb mountains. They don't bother people at all. Only rats that live near humans are harmful. Some are permanent tenants, others are temporary, leaving in the spring to live freely and returning in the fall. They live in boiler rooms, basements, barns, and can live in high-rise buildings, but they rarely rise above the 9-10th floor.
In cities, rats have chosen sewer systems and subways, port docks and store warehouses. In villages, they live on livestock farms, poultry houses, and fruit and vegetable processing factories. One rat family controls a territory of up to 2 thousand m2, which all its members regularly mark with urine. In case of food shortage, rodents can expand the boundaries of their kingdom.
What is the difference between a rat and a mouse
Despite the similarities between these rodents, they differ greatly from each other:
The main differences are due to the different number of chromosomes. In rats there are 22 of them, and in mice 20. Therefore, it is impossible to cross these mammals in order to produce offspring. Decorative rats reach 30 centimeters in length excluding the tail. Mice do not grow more than 9 and a half centimeters. Large rodents weigh up to 650 grams. A mouse cannot be heavier than 30 grams. Despite the fact that the number of newborn rat and mouse pups per female varies from 5 to 12, the number of nipples in rodents varies. A rat has 12 of them, while a mouse has fewer nipples - only 10. Due to their fast metabolism, the activity of mice differs from rats in being polyphasic. The animal falls asleep 15-20 times per day. Each activity phase lasts from 25 minutes to one and a half hours. The rat lives more “slowly”: it sleeps once a day if it is not disturbed. There is a difference between them in nutrition. Although both of these species are omnivores and can attack and eat other living creatures, the rat’s predatory instinct is more developed. Mice are seed eaters. Predatory instincts appear only when absolutely necessary, which is why they are even considered vegetarians.
Rodent hunters
A rat differs from a mouse in being more aggressive. When danger approaches, they show miracles of courage and can even attack a person in defense. In nature, rats often hunt in packs. Animals in groups can even attack mammals larger than themselves.
Mice prefer to hunt alone. Therefore, only insects and smaller animals become their victims. These animals are shy and extremely careful.
Due to such character traits, these animals are natural enemies. Large rodents attack small ones, kill them, and may even eat them. Therefore, the instinct of self-preservation dictates that mice beware of their larger relatives. Smelling the smell of a rat, small rodents leave their habitat.
For the same reason, individuals of these two species cannot be kept together. It is not even recommended to place cages with them in the same room.
Comparison of rodent intelligence
Rats are smarter and smarter than their smaller counterparts. Catching a wild specimen is a troublesome task. They are careful, attentive, cunning. If the loser suddenly falls into a trap, she lets the rest of the colony know about the danger. Never again will any animal appear here.
There are many stories about how these clever thieves opened bottles of wine, closed with plastic caps, one of them put the tail into the neck, pulled it out, and others licked the delicacy from it.
Or how rodents, climbing over a wide crevice, stuck together in a path, biting the tail of the animal in front with their teeth. Using such a living bridge, the entire colony easily crossed the obstacle.
Companion rats, living next to humans, also show their remarkable abilities. They are easy to train, respond to names, and even come up with their own games, inviting the owner to join.
There are no similar stories about mice. However, these sweetest creatures can give their owners a lot of pleasant moments of communication. They also become attached to a person and touch those who watch their lives with their habits.
Who grows faster: a mouse or a rat?
The metabolism of mice is higher than that of rats, so their lifespan is shorter. The average lifespan of small rodents when kept at home is 1.5-2 years, while their large relatives live up to 2-3 years.
Rats and mice grow the same way. At the age of 1-1.5 months, young rodents are capable of reproducing their own offspring.
Rat tails are longer than mice's. They are equal in size to 70-110% of the body. Mouse tails are shorter. They can reach no more than 60% of the body; the tails of large rodents are thicker than those of mice and more powerful (with the exception of the tailless rat); rats' faces are sharper and more elongated. Mouse heads are rounder and less pointed; The body of small rodents is more round. The animals rarely straighten up, preferring to sit huddled together in a ball. And their species relatives can rest, lying on their tummy, with their hind legs stretched out, like cats; mouse fur is soft and silky, while rat hair resembles coarse hair; The hearing organs of rodents are structured differently. Mouse ears are thinner and rounded. They resemble petals rolled up into a ball. Rat ears are thicker, sharper, and not curled.
Intelligence
Rats are clearly superior to mice in terms of intelligence. Some scientific minds even put them on a par with dogs and cats. Before finding a home, the rat assesses the situation, studying the surrounding area from a safety point of view, ranging from the presence of predators to climatic conditions.
But the main difference between a mouse and a rat in terms of intelligence is the presence of their own community and a clear hierarchy among the latter. Mice rarely form flocks to perform specific tasks. They are much easier to deceive or outwit. While the rats act together, where each participant has their own role.
To understand the role distribution of animals in a closed system, and at the same time the level of intelligence, the French scientist Didier Desor conducted full-scale research in 1989, achieving significant results.
Didier Desor's experiment
Rats are smart and good swimmers. To test these theories in practice, scientists have equipped a special testing ground. On one side there was a platform where the individuals were located, and on the other there was a feeder with grains. A kind of pool was laid between them.
To get food, the rats had to cross a water barrier that was serious for them, while holding their breath for several seconds due to the great depth. All individuals, without exception, tried themselves as swimmers, getting to the coveted food.
But after a few swims they begin to break down into roles. The most revealing experiment was with six participants. Two rats become exploiters, two become workers, one becomes a scapegoat and one becomes independent.
Workers constantly swim for grains, and their owners immediately take away the spoils upon the first arrival. When the exploiters have fully satisfied their hunger, they allow the miners to eat. An independent individual swims for food itself, eats it itself, and fights for this right with both the former and the latter.
The scapegoat fulfills its assigned role. He is afraid to swim for grains, is unable to terrorize other rats, and has no choice but to be content with the crumbs left by other members of the group.
All rats beat the scapegoat, exploiters of their workers, and the independent individual fights with everyone. In this way, each reminds the other of their role. Moreover, once you have chosen your “position”, it is almost impossible to change it.
But the most interesting thing about this experiment is the mixing of classes. If you put 6 individuals in a cage with only exploiters, they will fight with each other all night. The vanquished are again assigned to their roles: independent, scapegoat, two workers and two masters.
The result will be the same in any case. From 6 individuals, only workers, independents or scapegoats, you will get a familiar, established community. But Didier Desor did not stop and decided to increase the number of rats to several hundred, where not a laboratory room, but part of a local gym was allocated for the experiment.
After a protracted battle of individuals, another class appeared - super-exploiters. After the victory, they no longer bothered themselves with controlling and urging other rats. This was done by ordinary exploiters. The last link of this community - the scapegoats - suffered more than usual. Workers and managers tore them to pieces, thereby reducing the number of mouths to feed and proving to others their class worth.
At the end of the experiment, the scientists decided to open the skulls of the experimental subjects, followed by dissection of the brains. After careful study, an interesting pattern was discovered. The stress molecules were overwhelmingly not in the scapegoats, as they thought, but in the exploiters. The latter were afraid of losing their status and experienced serious stress on this basis.
Such experiments with mice were unsuccessful. Small rodents relied only on chance and did not show aggression as such. No one forced anyone to run for food. If there were scapegoats, their relatives simply did not touch them. This status was expressed in congenital ugliness and the inability to provide oneself with food. They were simply dying of hunger, for lack of food from the rest of the mice.
Animal behavior
Mice in the house crawl out of their holes only when there is complete silence. If a slight rustle occurs, they try to move away unnoticed as much as possible. When a house is found, the whole family moves in there without first examining the territory. Due to the more primitive structure of the brain, they fall into simple mousetraps, and in many cases cannot recognize the poison used against them by humans. They move directly.
Rats always search the area first. Seeing a person, they are in no hurry to hide, they think over a safe route of retreat, and not finding him, they attack the enemy, biting the neck, and if such a bite is impossible, the limbs. The more adults die, the more babies are born to the remaining ones.
If you fail to catch a rodent, you should pay attention to the traces it leaves. The paw prints left by rats are quite clear and rare because they move by jumping
As for the tracks left by mice, they are more frequent. A careful inspection of the lower part of the walls will help you identify the uninvited guest.
When rats move, they press against the surface, leaving abrasions. Mice are more careful in this regard, so there are no characteristic marks left behind. Pasyuk is a rather aggressive creature that can attack a person if it feels that his life is in danger, which cannot be said about the practically harmless mouse, which often runs away at the sight of a person.
The house mouse is one of the most common species of mammals, whose life is closely related to humans.
In terms of mental development, a rat is significantly superior to a mouse. Some people even compare large rodents to dogs and cats. They are more careful and discerning. When choosing a new place to settle, Pasyuks first explore the territory to make sure it is safe. Because of this quality, it is quite difficult to get rid of rats using various poisons.
We suggest you read: How to get rid of rats in a chicken coop forever
Development of baby rats by day
Newborn rodents grow very quickly, a defenseless blind lump becomes an adult after 4 weeks, males reach sexual maturity at 5, and females at 6 weeks. The development of rat pups day by day is as follows:
1st day
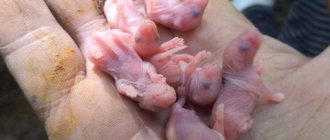
Immediately after birth, the pups are naked, pink, blind and deaf babies with underdeveloped limbs and a small tail, who can only squeak, suck and sleep.
3-4th day
The cubs' ears open, and now the pups can distinguish not only smells, but also sounds.
5-6th day
The bodies of newborns begin to be covered with the first soft hair, the skin has become flesh-colored with dark spots, the presence of which determines the color of rodents.
8-10th day
The baby rats are erupting their first teeth, the babies are already covered with short velor fur, the cubs are becoming very nimble, they start fights over the mother’s nipple, their movements are not yet fully coordinated.
12-13th day
The babies' eyes open, the pups explore the territory, actively try to get out of the nest, but the rat diligently returns the children to their original place.
14-16th day
At this time, secondary sexual characteristics are formed and the sex of the animals can be determined; in females, nipples are visible on the abdomen.
Intelligence of Rats and Mice: Key Differences
Rats have more developed intelligence than mice (this also applies to domesticated rats and mice). But this does not mean at all that a mouse is a bad pet. Decorative rats are very smart animals that quickly make contact, and they also quickly become attached to their owner. They are trainable and can express their affection and love. In addition, the decorative domesticated rat knows and responds to its name when it is called to itself, especially if the owner offers some kind of delicacy or fun activity.
Essentially, the intelligence of a pet rat can be compared to that of other pets (cats and dogs). Rats are sociable animals that respond well to people, as evidenced by their love of games. According to many owners of pet rodents, the latter can even come up with their own entertainment and games, subsequently willingly demonstrating them to their owners, inviting them to join in the fun.
Features of birth
After the baby is 3–3.5 weeks old, the owner can pick him up. Rodent breeders note that the more often you hold them in your arms, the more affectionate and obedient they will become. The key is to not overdo it. You need to know when to stop everything. Excessive affection is a factor in the development of stress in a pet. You should not separate the mother from the babies for a month. The immune system of newborn rat pups is directly dependent on how long they will be around it.
The total growth period for rat pups is one year. As for nutritional features, after a month you can add cottage cheese, boiled chicken bones, apples, milk corn, and bananas to their diet. There are also a number of foods that should not be included in the diet of baby rats. These are yolk, broccoli, salads, cucumber, liver, tomatoes.
Experts in breeding animals of the rodent family advise adhering to the above recommendations at least until the baby rats reach three months.
The small animal is a defenseless creature that needs special careful care and maternal attention. The attitude of owners towards an animal should be the same as towards their child.
Varieties of pet animals
Any species of rat differs in certain signs and characteristics: color, markings, body type and coat type. Therefore, rats are classified differently, and among them you can see completely different and unusual species. And many colors and types of coat were borrowed from dogs and cats.
After identifying the pasyuks, scientists still had a lot of time to search for other rats and breed new ones. Therefore, today there are many different colors, and eye color wins the hearts of many pet rodent lovers. The most unusual colors are considered to be the Himalayan and Siamese.
The eyes of rats can also surprise you, as can their color. Eye color can be: red, black, ruby. The most interesting are the different eyes, for example, one is black and the other is red. Such rats are not so rare. An interesting fact is that owners of black eyes see much better than their relatives with other eye colors.
A striking example of borrowing names from cats are sphinx rats, but it is rare that some animals are born with a color very close to that of a cat. All sources mention only 2 rats born with a tricolor color. The first was named Solaris, she was born in Alaska in 2002, and the second appeared in 2006 and was named Dusty Mouse.
How to determine the sex of baby rats
Unlike adults, it is not easy to distinguish the sex of newborn rat pups and this can be done when the babies are at least four to five days old. Since small rodents are devoid of fur, you can determine the sex of a baby rat by the nipples on the tummy, which resemble tiny pimples. The presence of mammary glands indicates that this is a girl, because boys, both in adolescence and in adulthood, do not have nipples.
Also, in male babies, you can see small dark spots located between the genitals and the anus, in the place of which testicles will form as the animal grows older.
House mouse - appearance and behavior
The house mouse is the most common rodent living in human housing. Over many years of coexistence, its diet has changed significantly; the animal switched from cereals and nuts to plant and animal products that people eat. In the summer, mice can live in the fields, picking up grains, but by mid-autumn they will certainly move closer to humans and a warm home.
The intelligence of house mice is quite low, they are also not very careful, so they easily fall into even the simplest mousetraps. The population of these rodents is maintained only due to their rapid reproduction - females give birth to offspring every month, up to 100 mice per year
Their body length is 7-8 cm, in rare cases with good nutrition - up to 10 cm, weight - 25-40 grams. Thanks to such miniature dimensions, the mouse is able to squeeze through even a centimeter gap.
Interestingly, the colors of mice depend on the geographic location of their residence. In southern and central Russia, rodents with light silvery skin are common; in Siberia, their fur is more brown than gray. The line between colors is becoming increasingly blurred over time - animals travel on all types of transport, so sometimes you can see an animal of an unusual color.
Life expectancy difference
Mice live very little in the wild and at home - their average lifespan is 1.5–2 years. Despite this, the colonies of these animals grow quite quickly, since rodents are able to give birth to offspring already at the age of 8–9 weeks. Moreover, additions to the family can occur up to 10 times a year.
You will be interested to know how many years decorative house mice live.
The lifespan of rats is longer - up to 3 years. They also become “parents” quite early, reproducing up to 12 members of the offspring at a time.
External differences
The main signs of differences between rats and mice can be observed in external characteristics. First of all, they are clearly visible in the mass of animals, as well as in the structure of the body. Based on them, you can easily determine which representative of the rodent family is in front of you.
Dimensions
The most significant difference between rodents is determined by size. Rats have significantly larger dimensions and a stocky body. The length of an adult can reach 30 cm, not counting the tail. At the same time, weight indicators fluctuate between 600–700 g. A mouse is a smaller rodent. It rarely grows more than 10 cm in length, and its weight does not exceed 30 g.
Tail
It is also not difficult to distinguish animals by the characteristics of the tail. In rats, it looks more massive, thick, has an impressive length, which is sometimes not inferior to the length of the main body, and sometimes exceeds it, reaching up to 35 cm. The tail is bald or bristly, depending on the species. In small rodents, the length of the tail ranges from 4 to 6 cm, almost all over it is covered with small hairs.
Find out also what to feed and how to care for a decorative rat.
Head
The shape of the head of a rat and a mouse also has significant differences. The former has a more elongated, pointed muzzle. The organs of vision are poorly developed. Small black or red eyes are deep-set and have a small viewing angle, so the animals have to constantly turn their heads to examine their surroundings. It is interesting that they see it in gray tones, and red objects are transformed into black.
In mice, the shape of the head is more rounded, flattened, and its size is much smaller. But the eyes, compared to the size of the muzzle, are large, convex, and expressive. The animal has developed farsightedness.
Important! Both types of rodents have teeth that grow throughout their lives, so they need to be given hard objects to chew on that can grind down their incisors.
Paws
There are practically no calluses on the rat's paws, which are necessary for climbing. But there are movable fingers with sharp claws. Thanks to this property, rodents can move freely through trees. Sometimes they make homes for themselves in abandoned hollows. The excellent muscularity of the paws allows rodents to jump long distances. Another advantage of the limbs is the presence of membranes between the fingers, which are similar in appearance to folds of skin.
They make rats excellent swimmers, capable of obtaining food in a body of water. When moving along a horizontal surface, the paws of rodents are widely spread. If you manage to examine the footprint, you will notice that the angle between the outer phalanges is about 180°. Since the predator often moves by jumping, the distance between the tracks can also be impressive.
You may find it useful to know what types of domestic rodents there are.
The legs of mice are short. Each of them has 5 tenacious fingers, so these small rodents are able to move through trees. However, their limbs are not as powerful as those of rats. They move mainly in mincing steps, with the toes spread minimally, and the distance between the tracks is about 1 cm.
Wool
Mice have softer, more delicate fur. In nature, its predominant color is brownish-gray or ash-gray, but it can vary depending on the environment. For example, desert mice have a yellow-sandy coat color, and among decorative species there are white, black, gray-blue, and variegated tones.
Did you know? Mice keep their homes clean and tidy, and with droppings they mark routes to food sources.
Rats have thicker, longer, and coarser fur. The most common colors are gray and dark brown. In individuals bred as decorative domesticated animals, many other shades are found: white, gray, reddish, spotted, etc.
Ears
The rat's ears are straight, even, pointed towards the top.] Hearing is very well developed - the animal perceives sounds with a frequency of up to 40 kHz, while humans - up to 20 kHz. In mice, this figure is even higher - animals perceive sounds with a frequency of up to 100 kHz, although the hearing organs themselves are small, rounded, rolled up.
Growth and development of babies
Little rats grow very quickly. In the first week of life, they gain 3 g of weight every day. Babies actively suck mother's milk, which has high nutritional value. It contains almost 9% protein, the same amount of fat and 4% lactose.
In the first days of their lives, rat pups are constantly near their mother. She moves them from place to place to warm everyone with her body. Small animals do nothing but eat and sleep. On the second day, hungry babies may begin to make a barely audible squeak. Approximately 4 days after birth, the ears of rat pups rise. Now they can hear.
Already on the 4-5th day of life, you can determine what color the little rat pups will have. In light-colored rat pups, the skin remains pink, while in dark-colored pups, it acquires a grayish tint. During this period, the first soft fluff appears on the body.
At the age of one week, baby rats' incisors begin to emerge. The molars will appear no earlier than in 3 weeks. In some individuals they grow only on the 35-40th day of life.
The rate of tooth growth depends on the individual characteristics of the animal and diet.
One of the most significant periods in the life of little rats is the time when their eyes open. This occurs 14-17 days after birth. At first a small gap appears between the eyelids, but after a couple of days the babies begin to see.
From this moment on, the little rats become more active and begin to crawl out of the nest. They look around with great curiosity, go around every corner of the cage, learn to wash themselves and clean their fur. By the way, by this time it has already completely grown back. Between the 15th and 20th days of life, females develop nipples.
At 3 weeks of age, the pups look like their adult counterparts. Their body length reaches 14-15 cm, but the tail is still short. At 25 days the animals become completely independent. Females are already capable of becoming pregnant, but this is undesirable, since the body is not yet fully formed and strengthened. The development of rat pups continues until they are one year old.
Differences in nutrition
In the warm spring-summer period in the natural environment, the mouse prefers to eat plant seeds and cereals. Field animals feast on wheat, buckwheat, and oats. Rodents living in forests prefer hazel nuts, acorns, and can even feed on small insects. Near reservoirs they find roots and stems of plants, berries, and larvae.
With the arrival of autumn cold weather, the mouse begins to actively look for warm places to eat, moving closer to humans. Penetrating into a home, it becomes omnivorous. In addition to any edible food, she will not disdain such products as soap or candles. Animals cause particular harm to stocks of vegetables stored in the basement, to cereals in bags, they can chew wires, and inhabit shelves with linen and clothes.
Important! Ornamental rodents should not be given raw meat, lard and smoked meats.
Rats bring even more trouble. These rodents are capable of causing damage to anything in their path, including wires and structures. Everything that humans eat suits them perfectly. Under natural conditions, rats need food high in protein, feeding on fish, amphibians, and insectivores. By nature they are predators, they destroy bird nests, and can eat small rodents, including mice.
At home, a large rodent eats any food products and waste, and does not disdain feed intended for livestock and poultry. The rat does not store supplies, but without food it dies quite quickly, after 3–4 days. Her diet must contain water or food containing a lot of moisture. Without receiving it, the rats die within a few days. As for domesticated ornamental species of rodents, it is recommended to feed them with grain feed and vegetables. Protein foods are served in the form of boiled chicken, egg whites, and cottage cheese.
Read how to properly bathe a rat at home.
How to feed baby rats
During the first 14-16 days, rat cubs feed only on mother's milk. Then they begin to become more active, crawling around the nest and even trying the food that their mother brings. 3 weeks after birth, the pups eat vegetables, grain mixtures, lean meat, eggs, cottage cheese, and fresh herbs.
There are often situations when small rats are left without maternal care. This happens for various reasons:
- Mom doesn't have enough milk;
- the female died after giving birth;
- someone touched the little rat with their hands, and the mother abandoned him.
In each case, the babies will have to be artificially fed, otherwise they will die.
Orphaned cubs must be kept warm. A lot of paper napkins are placed in the nest. They are replaced as they become dirty. To warm little rats, you can use a rubber heating pad or a plastic bottle with warm water.
To feed the litter, a cat or dog milk substitute, which is sold at a veterinary pharmacy, is suitable. If you can't find it, you can use baby formula. To increase the nutritional value, add a little condensed milk with a fat content of about 12% or glucose, as well as a little calcium gluconate.
It is convenient to feed small rats from an insulin syringe without a needle. The animal is carefully taken vertically in the left hand, and the head is held with the thumb and forefinger. The tip of the syringe is inserted into the mouth. The piston is moved very slowly so that the little rat does not choke.
Attention! If milk flows from the spout during feeding, it must be removed with a napkin. To clear the nasal passages of liquid, you should pinch the little rat's butt. When it beeps, the milk will completely leave the respiratory tract.
In the first week of life, rat pups are fed every 1.5 hours, then every 2.5-3 hours. At this age, they eat no more than 0.3 ml of formula at a time. It is quite simple to determine that the baby is full - his stomach is clearly visible through the thin skin on his stomach. It looks like a white transverse stripe. If its length is two-thirds the width of the body, then the stomach is full. Week-old rat pups eat about 0.5 ml of milk at a time, and at the age of 10-12 days - 1 ml.
Attention! Before each feeding, the baby rats receive a abdominal massage. This is necessary to improve intestinal motility. Gently move the fingertip clockwise for about a minute. Usually, after such stroking, the animals empty their bowels.
Types of mice
There are about 300 of their representatives. Some of them are decorative and are specially selected for home maintenance. These, for example, include tiny mice with a body length of about 7 cm. These rodents are brightly colored. At the same time, the juveniles have brownish, dull fur. After the first molt occurs, the rodents become bright red. They are kept in spacious cages and must be fed invertebrates, grains and greens.
The largest mouse is the Asia Minor mouse, reaching 13 cm. It is mainly found in Asia, Georgia in mountainous areas.
In the central regions, the field mouse is mainly widespread, which rarely settles in human buildings. Her tail is a quarter less than her body length. The color is reddish-brown on the sides, with a black stripe running down the center of the back. However, coloration for rodents is not one of the main characteristics by which they can be distinguished, since it differs somewhat by region, and due to their migration, it can change beyond recognition.
The most common taxonomic unit that inhabits homes is the house mouse. This type of mouse is characterized by the fact that their length reaches 10 cm, the tail can be the same length as the body length, or be half of it. During its existence with humans, it has adapted to its food, eating plant and partly animal products that humans consume. In the summer they can go to the fields, where they feed on grain, and with the arrival of autumn they move to human habitation.
Also, wood mice can settle in houses during autumn migration.
Litter
When solving the problem of how to distinguish a house mouse from a rat, you need to pay attention to the products of their vital activity, since this is often the only thing that reminds you of rodents. The differences between rat and mouse droppings are the shape, size and location. Rodents of different species leave waste products that differ in color and size. Thus, black rat droppings are large formations up to 12 mm in length, dark in color.
The red counterparts leave behind droppings that resemble oat grains in shape and are brown in color. Mouse feces are small, outwardly similar to pointed granules no larger than 6 mm in size. In addition, mice defecate chaotically, and rats usually leave droppings in one place.
Interesting video: Smart Rats
Determining the type of rodent by the type of spoiled food
Preferred foods are affected first. For mice these are cereals. Moreover, they leave behind a large amount of litter and husks, but the rat eats the whole grain. In addition, large rodents do not feed in one place for several days, so the damage they cause is always greater. If the mouse returns to the same place every time to eat (for example, a bag or bag of cereal), then traces of the rat’s teeth remain everywhere: on furniture, food: cereals, fruits, etc.
Related posts:
How are rodents harmful?
Rats are pests. The very rapid reproduction of rats causes serious damage to both farmers and villagers, and residents of the metropolis. Here's why rats are dangerous in the country:
- carry severe infectious diseases: plague, tuberculosis, brucellosis, leprosy, rabies, typhus, hepatitis, etc.;
- these animals destroy food products in warehouses and factories;
- eat feed from farm animals and birds;
- chew floors and walls of premises;
- damage electrical cables and various devices;
- contaminate food products with helminths and salmonella.
Rats adapt well to any conditions, and they are very tenacious. These animals cause a lot of inconvenience to people and carry dangerous diseases, so it is necessary to get rid of them without pity in all possible ways.
Who-who lives in our house?
It is clear that it is unrealistic to conduct a comparative assessment of absolutely all species of mice and rats living on the planet in one material, so we should focus only on frequently occurring individuals in our climate zone.
Populated areas are mainly inhabited by gray rats and house mice; sometimes voles come to visit, but they are not particularly different from “domuses”. There are also black Sinanthropus rats, but they can only be found on the Pacific coast and in Eastern Siberia. Their second name is ship pests, since pests are regulars at seaports and water vessels.
What is the difference between a baby rat and a mouse?
Rodent breeders claim that it is not difficult to distinguish a mouse from a baby rat. Babies are different sizes and look different. But for a person who does not see newborn animals every day, it can be difficult to figure out which species is in front of him.
Baby mice and baby rats have the following differences:
- Mice have a pointed muzzle. Baby rats have a blunt nose.
- The mice's ears are large and round. Rats have a triangular ear that is pressed to the skull.
- The tail of a newborn minnow is long, but in rat pups it is thick and short.
- Small mice do not have skin folds between their fingers.
A baby rat reaches the size of an adult mouse in a month. At this point, it becomes difficult for many to distinguish a mouse from a baby rat. If the animals cannot be seen closely, then you need to navigate along the ground they leave:
- The print of mouse limbs does not show webbing between the toes.
- Rat tracks are located at a distance from each other. Fingers stuck out. The paw print is wide.
If you compare what baby rats and mice look like in the photo, it’s not difficult to distinguish the babies.
If it is difficult to recognize the difference between a mouse and a rat, then you should look into a pet store. Decorative animals behave in the same way as their wild relatives. The appearance of the animals also does not differ much from those of “free” rodents.
Rats and mice belong to the order Rodents. If you don’t know the difference between them, it’s easy to confuse the animals. This will lead to an erroneous choice of means of destruction. Adults are characterized by different sizes: a rat is larger than a mouse. At the initial stage of development, young animals are more difficult to distinguish. To understand who is found in the house, they first study the features of the rodent’s body structure.
Small animals of several species are found in residential buildings. A house mouse lives near a person, as well as a gray, black or red rat.
The difference between rodents becomes noticeable if we evaluate each body parameter separately:
Dimensions. When thinking about what ordinary rats look like, the image of a large-bodied animal immediately comes to mind. The body length of this rodent reaches 30 cm. The mouse is smaller in size, the average individual is characterized by a length of up to 10 cm. Weight. Given the difference in size, it is logical to assume that the mass of animals also differs. For example, a mouse weighs between 30 and 50 g, while a fellow rat family reaches 900 g. Tail. Differs in length and thickness. This part of the mouse's body is shorter
You should also pay attention to the thickness. The mouse has a thin tail, while large rodents have a thick tail, which is more noticeable at the base
In addition, it is not covered with fur. The mouse tail is also different: it is hairy, and the color matches the color of the body. The eyes of the mouse are larger. Rodent ears also vary in size, shape and location. For example, in a mouse they are round, wide, and directed to the sides. Rat ears are flattened and distinguished by a small base. The shape of the head is also different. The muzzle of a rat is elongated, while that of a mouse is triangular in shape.
Relative to the head, the rat's eyes are small. Mice have more expressive and slightly convex black eyes.
In addition, pay attention to the wool. There are other differences besides color.
The rat is characterized by hard hair, and the mouse has softer hair.
Rats, unlike mice, are able to jump high - up to 2 meters in extreme situations. They are highly intelligent
Differences between a mouse and a rat
The main feature of a newborn rat pup is its larger body size. This is noticeable upon birth. The mouse is always smaller. The main characteristic differences between rodents are the same as in adults: the shape of the ears, the color of the emerging fur, etc. Sometimes a baby rat is confused with an adult mouse.
To avoid this mistake, you should find out how they differ:
- A rat at an early stage of development is characterized by a blunt snout, while a mouse has a pointed head shape.
- The baby rat's tail has not yet developed enough, which means it is shorter than that of an adult mouse.
- The ears of baby rats are still small and smaller in size than the hearing organs of adult mice.
- There are still skin folds on the soles of the baby rats, while they are absent in the mice. This feature allows you to determine the difference from rodent tracks.
A distinctive feature of rat pups is their blunt-nosed, as if chopped off muzzle.
Baby rats and adult mice have similar paw sizes, but the placement of the toes is an additional characteristic that can be used to distinguish rodents.
Rat breeding
Determining the sex of a rat is quite simple: males are larger and heavier than females, and by the age of 1.5-2 months, large testicles grow at the base of the animal’s tail.
The age of a rat can be determined by weighing the animal:
- At 2 months, males weigh 160-220 g, females 150-200 g;
- At 3 months, males weigh 250-310 g, females 210-250 g;
- At 4 months, males weigh 350-410 g, females 250-290 g;
- At 5 months, males weigh 450-490 g, females 290-340 g.
When a rat is six months old, its weight remains unchanged
To understand that this is an old specimen, pay attention to the following signs:
- the animal's fur becomes sparse, dull, and sticks out in places;
- the skin on the tail becomes rough, rough, with many flaking keratinized particles;
- the incisors become significantly longer. Their back part is ground down, and the teeth take on the shape of a chisel.
Rodents living in their natural habitat breed mainly in the warm season, mainly in spring and autumn. Rats living close to human habitation, or decorative individuals, can reproduce regardless of the time of year.
The female's pregnancy lasts 22-24 days, after which 8-10 cubs are born. Rats are born naked, blind and helpless, so they need extra care. The problem is that babies cannot pass feces and urine on their own. The owner can help them along with the mother rat by massaging their bellies from time to time. This helps stimulate excretory processes.
Rules for assessing appearance
Deciding on the size
The average length of an adult house or field mouse, they are the ones who most often settle in a person’s home, is 5-6 cm. Weight no more than 30 g.
Gray and black rats are much longer - their size can reach 30 cm, and the maximum recorded weight is a kilogram! Among the rat species (and there are more than 60 of them), there are also smaller animals (from 8 cm), but they are not found in our country.
Comparing tails
The mouse tail is very thin, almost the same length as the body of the animal, in any case, it should be at least three quarters of it. Covered with scales (they are arranged in a ring) and small, barely noticeable hairs.
In rats, the tail is much shorter than the body (about half of the entire body length), it is massive, hairless or bristly. Black individuals have a longer “fifth limb” (270 rings) than gray ones (210 rings).
Ears
The ears of mice are round, spreading, hairless, wide at the base, and large.
Rat ears are small, have a more triangular shape, at the base they seem to be rolled into a tube and pressed to the head. In black individuals, the locators are translucent and have no hair, while in gray individuals, on the contrary, they are hairy and non-transparent.
Paws
Rats have powerful and muscular legs, adapted to run on a horizontal surface, as well as jump quite far. Between the phalanges there are rudimentary membranes - the so-called leathery folds.
Head and eyes
When comparing, more attention is paid to the shape: in rats, the muzzle is elongated and elongated forward (although in gray ones it is rather blunt), while in mice it is triangular and slightly flattened. Relative to the head, the rat's eyes are small, like beads. Whereas mice have more expressive and slightly convex black eyeballs.
Coat color and quality
If we are talking about representatives of wild fauna, not taking into account decorative individuals, then mice are often gray or even smoky with an ashen tint. While rats are brown or dirty gray in color, black rats are tan in color, which goes against the name of the species.
Mice have soft, short and silky hair, while pasyuks have thick, coarse and long hair.
When to transplant young animals
The development of baby rats occurs rapidly. At the age of 25 days, it is already possible to place the male rats separately from the girls. This recommendation applies more to males, as they can mate with sisters or their mother. After about a month, it is advisable to seat the males, otherwise they will start fighting with each other.
The young animals are provided with fully equipped cages, the same as those for adult rats. Each animal should have its own resting house. To increase physical activity, a running wheel, ladders and tunnels are placed inside.
The diet of the younger generation must include fresh greens, wheat sprouts, as well as animal foods, which contain a lot of protein. 1-2 times a week, rat pups are given fish oil.
At 5-6 weeks, the rats can be given to new owners. You shouldn’t delay this, because the younger the pet, the easier it will tolerate a change of environment.
What do the tracks look like?
What do rodent tracks look like?
The imprint of a rat's front paws on wet ground or snow is approximately 1.5 x 2 cm in size. You can see traces of 4 toes, which are widely spaced. The hind legs are larger (up to 4 cm), however, during movement, a small imprint remains - 2x2 cm, i.e. the mark is only partially visible. If the animal moves slowly, a thin chain of prints will remain on the surface. During the jump, the rat leaves rare traces - at a distance of up to 1.5 m.
The paw prints of mice during a jump are characterized by a smaller step (up to 30 cm). The tracks form a kind of trapezoid: when moving, the mouse places its hind legs wider, pushing off with its front, closely spaced legs. As a result, the tracks of the hind paws remain in front, and the tracks of the front paws remain behind. In addition, a thin line is visible behind - from the tail.
House mouse, how to choose the right one
Rodents are quite easy to keep at home. They do not require much attention from their owners and easily make contact with people, which makes decorative mice very popular pets.
When choosing a mouse, pay attention to the following nuances:
- teeth should be white and straight;
- the animal's eyes should be shiny and moist;
- the rodent must move actively and have a good appetite;
- there should be no bald spots on the skin;
- There is no unpleasant discharge from the eyes and nose.
The average lifespan of mice is 3-4 years, so choose an animal no older than 12 months. The mouse is a collective animal, and it is better to have several animals at once
This is especially important if the owner spends a lot of time at work. But you should not have several males in one cage, as this can lead to conflicts
Those who plan to breed mice on their own should know that until mating, males should be kept separate from females.
The main difference between wild animals and ornamental animals is safety. Wild rodents are carriers of various diseases, which makes them undesirable for domestication. When buying a mouse in a specialized store or at an exhibition, you can be sure that the animal has been vaccinated. In addition, when trying to tame a wild animal, you should remember that at first the mouse will be afraid and will not make contact with humans.
Types of house mice
House mice are popular pets, so breeders have created many subspecies of these rodents. The main differences between different breeds of mice are the quality of their fur, by which they are distinguished. The main characteristics are as follows:
- short-haired;
- medium-haired;
- long-haired;
- naked.
The following are added to these characteristics:
- Rex - wavy coat;
- Texel – thick long wool;
- Rosette mouse - the fur has different growth directions: from head to tail, and from tail to head. Where the hairs meet, a ridge or rosette is formed. The minimum number of such rosettes on an animal’s skin is 2, on each side of the body;
- Satin mouse - the fur of these rodents is very smooth and has a metallic tint.
In addition, breeds are divided according to color type:
- plain;
- broken marked - with dark spots;
- ribbon - white paws and dark skin, with one light spot;
- white rump - the main color is dark, and the back of the body, including the paws and tail, are light in color.
All types of these mice have the same life expectancy - 2-3 years. The animals weigh about 80-100 grams. and have a body length of 8-10 cm. In males, these figures are always greater. The breed does not in any way affect the character and habits of rodents.
Care and maintenance of mice at home
To keep domestic mice, you need to purchase a cage that must have:
- drinking bowl;
- feeder;
- house.
In addition, it is worth adding to the cage various ladders, wheels like for hamsters, and other devices that allow the pet to spend time actively. The size of the cage depends on the space in the apartment, but the larger it is, the better.
Mice are omnivores, but it is worth remembering that your pet’s diet must be balanced and meet the following requirements:
- grain is the basis of the diet;
- you should alternate between dry and juicy foods;
- use vitamins once every six months;
- Don't forget to give your mouse protein food.
Difference in tracks
Rats eat meat, cookies, bread, smoked meats, lard, and sausage. They sharpen their teeth on wood or other hard objects, including concrete. They can chew through electrical wires. The habitat is located near waste storage areas. They move with long strides and can jump up to 2 m in length and 1.5 m in height. The tracks are long. The angle between the extreme phalanges is almost turned around.
Mice prefer grain and flour products, sugar, and very rarely eat meat. They damage paper, polyethylene and leather products. They move in small steps, jumping is generally unusual, they are characterized by climbing on horizontal surfaces located above the floor. The tracks are round. The distance between them is about 1 cm.
Physiological features
It is important to first address the physiology aspect. Many have already read articles about mice and roughly understand the characteristic features of a rodent
The information obtained is not always enough to make a final verdict on the situation. In addition to photographs, we suggest studying several fundamental aspects for successful pest identification:
- Body length. Rats are significantly larger than mice and reach a body length of up to 30 cm. Such pests are more muscular and look especially massive compared to fragile mice. There are also individual specimens of mice where the differences are not particularly noticeable, but this happens extremely rarely;
- Muzzle. Rats have a more elongated skull, so their eyes stand out as much as possible. Mice are characterized by a somewhat flattened muzzle shape;
- Tail. This part of the body in rats is completely naked and significantly thickened at the base. The tail of mice is slightly smaller and matches the color of the fur on the body;
- Weight. The difference is especially noticeable when comparing weight, since female rats sometimes grow up to 900 g, and mice rarely exceed 50 g of both weights;
- Ears. Rats are endowed with much smaller ears, tightly pressed to the head, while mice have ears that are quite wide.
Pay attention to the structure of the coat, as in large rodents it is stiffer and denser. In general, there are a number of obvious signs that make it difficult to confuse two rodents
If you don’t know how to distinguish a mouse from a baby rat, then pay attention to the characteristic body structure in the proportional ratio of the sizes of the ears and tail.
What to feed a mouse
Ornamental mice feed mainly on grain mixtures, including seeds of herbaceous plants such as wheat, oats, peas, barley, cake, millet, sunflower seeds, and flax. Can be supplemented with nuts.
Oilseeds should be present in an amount of no more than twenty percent of the mixture in summer and thirty in winter, otherwise the risk of obesity is high. Too much legume seeds can also lead to obesity, although their presence in the diet is desirable. Mice can be pampered with berries, fruits, especially apples, dried fruits, carrots, cabbage, potatoes, beets and cucumbers. In addition to all of the above, feeding mice porridge is common. Oatmeal, rice and millet porridge are suitable
It is important that the porridge is cool and contains grains that have been previously cleared of impurities
It is vital for mice to have their incisors ground down from time to time. Small branches of trees and shrubs are well suited for this purpose, the main thing is that they contain bark. Almost all plants are suitable for this, except lilacs and conifers.
If preparing food yourself is difficult, then pet stores sell ready-made mixtures and other nutritional components for mice.