A tick bite is a very unpleasant, although painless event. During the warm season, many of us refresh our knowledge on the topic of ticks: how dangerous they are and how to properly remove them. But many people do not know that a tick burrows into the skin primarily because of its blood. A tick is a blood-sucking insect, and if its meal is not interrupted immediately, it will change greatly in appearance and can be confused with another bloodsucker. In this article we will tell you what happens to a tick that has drunk blood and where it disappears after its dinner.
What does a tick that has sucked blood look like?
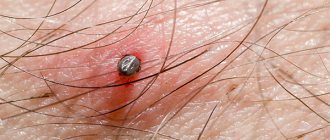
The appearance of a sucking tick is not the most aesthetic picture. But in this form it is easy to notice, which means taking timely measures to remove it and prevent it from becoming infected with various diseases. In order not to miss the moment of the bite, it is necessary to study what the tick looks like. The best way is to look at a photo of a tick that has drunk blood. Let's compare the appearance of a hungry and a well-fed insect. Hungry tick:
- It has a body length of no more than five millimeters.
- The shape of the insect is oval, the body is elongated along the axis, flat and oblong.
- Depending on the type of tick, the body may be red, brown or grayish.
- The tick is active, moves quickly, its legs are in chaotic motion.
As soon as the tick has chosen a convenient place for itself, it launches its proboscis from the head under the skin of a person or animal and attaches itself to a blood vessel.
Well-fed tick:
- It grows up to two centimeters in size.
- It becomes rounded and convex due to microfolds of the body, invisible to the ordinary eye, its body begins to hang over the head.
- After eating, the color of the animal darkens and becomes brown, dirty brown, dark gray.
- The tick becomes completely motionless.
After finishing eating, the tick literally swells from the inside, its body turns into a reservoir for storing the blood it drinks.
Types of ticks that can crawl under the skin of cats or dogs
Dogs and cats are affected by the following types of ticks:
- ear;
- subcutaneous;
- ixodid.
How to remove a tick from a cat or dog
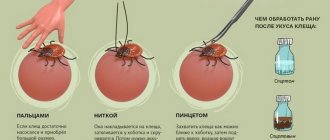
You can remove a tick from a dog or cat in the same way as from a person. You need to spread the fur, and using tweezers or thread, grab the parasite closer to the animal’s skin and pull it perpendicularly upward. If the head of the bloodsucker remains in the body, then you need to pull it out like a splinter. Do not forget to disinfect the needle and the bite site.
Ticks are removed from an animal as carefully as from a person.
What happens to a tick when it drinks blood?
The tick drinks blood for several reasons, usually to continue development, replenish reserves in the body, and procreation. After a bite, the animals do not die, but continue to exist.
For example, tick larvae wait for their prey in the soil. They need blood to transform into nymph, the next stage of a tick's life.
Adult males and females behave differently after being bitten and fed with blood. The male falls off and dies after several copulations. This completes his mission.
A sexually mature female has one goal - to lay eggs. A fertilized individual will not be able to do this if there is not enough blood in its body, so the insects go on a “hunt.” After replenishing blood reserves, the female’s task is to get to the soil and lay eggs, which will turn into larvae. Thus, the circle is closed and the life cycle of the tick with the participation of new individuals is resumed.
Where can you find ticks?
All districts of the Leningrad region and some districts of St. Petersburg, as well as 13 of the 18 territories of Karelia are infected with tick-borne encephalitis.
The North-Western region (in particular St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region, as well as the Vologda, Arkhangelsk, Novgorod, and Pskov regions) are endemic for tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. Tick-borne encephalitis is common in Siberia, Altai, Sayan Mountains, the Urals, and the Far East.
Lyme disease can be contracted through a tick bite in the forests of the Kaliningrad, Leningrad, Tver, Yaroslavl, Kostroma, Perm, Tyumen regions, and in the Komi Republic. In the Urals, Western Siberia and the Far East, ticks carrying borreliosis are found in pastures and forests along rivers.
You can see a complete list of endemic regions and areas on this website.
The probability that a tick in the Leningrad region is infected with encephalitis is about 1-2%, and borreliosis - 7-10%.
How long does a tick drink human blood?
The tick is not the pickiest insect to eat. He can drink the blood of any warm-blooded animal, it doesn’t matter to him - humans, birds or other mammals. The insect easily finds places where blood vessels are located close to the skin (places with a thin epidermis). For example, the groin area, armpits, neck, chest, sometimes stomach. The tick can fall off the skin on its own at any time. The duration of stay on the human or animal body usually varies from several hours to two weeks. On average, a tick feeds on blood from three to eight days, the maximum period being fourteen days. The timing is determined by the sex, age, and lifestyle of the insect.
As noted above in the article, a drunk tick disappears on its own. If this does not happen within the usual time frame, a person usually notices symptoms of parasitism. Even if the tick is not infected with dangerous viruses, a wound, redness, itching and other signs of allergy form on the skin.
The length of time a tick eats depends on how hungry the parasite is. If the last meal was several months or several years ago, the tick will tend to remain on the skin as long as possible. However, sooner or later it will disappear anyway.
What diseases do ticks carry?
- Tick-borne encephalitis
An acute viral disease that affects the brain and spinal cord. May cause death or paralysis. Infection with the virus occurs through tick bites or through the raw milk of tick-infected animals (cows, goats).
The incubation period (the time from a tick bite to the appearance of the first symptoms) is from 2 to 25 days. The onset is acute, with an increase in temperature to 39-40 degrees. A sharp headache, nausea, vomiting, redness of the face, neck, upper chest, redness of the eyes, muscle pain, sometimes loss of consciousness, and convulsions appear.
Encephalitis can be fatal. Possible residual effects are paralysis, muscle atrophy, decreased intelligence, epilepsy. Recovery takes years. Full recovery may not occur.
- Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease)
From the bite to the first symptoms it takes from 2 to 30 days, on average two weeks. In 70% of cases, a characteristic round or oval red spot with a diameter of more than 10 cm appears around the bite, which then turns pale and turns into a “ring”.
Sometimes such a spot may not appear at the site of the bite or, after disappearing, reappear on another part of the body. After a month, the spot disappears, and after some time the disease affects the nervous system, heart or joints.
Chronic borreliosis leads to disability. At this stage, it is difficult to diagnose borreliosis, since it has to be distinguished from multiple sclerosis and other lesions of the nervous system.
The diagnosis of borreliosis can be confirmed using a special blood test at an infectious diseases hospital.
- In addition, ticks carry several rarer serious diseases. Of these, in Russia there is Congo-Crimean hemorrhagic fever, tularemia, ehrlichiosis, babesiosis and several more rickettsioses (diseases transmitted by ticks), from which vaccination cannot be protected.
What's next?
After the tick is saturated with blood and its body is completely filled with liquid, it detaches from the skin of a person or animal. The further life of the insect can develop according to two scenarios.
If a tick falls off on the street, it will continue its life cycle. The larva will turn into a nymph, the female will lay eggs. This will happen thanks to the soil and the natural habitat of these insects.
If a tick detaches itself in a person’s apartment, it most likely will not be able to continue its life. Of course, he will try to immediately hide in a secluded place, but even in the darkest corners of the apartment it is impossible for the female to lay eggs. If a tick drinks blood and is not in the right conditions, it will die. It must be remembered that when a tick is detected, it must be immediately placed in a test tube and sent for examination to the hospital.
Firstly, if the tick has not had time to get enough, it can bite again, and this increases the risk of contracting dangerous diseases.
Secondly, you need to immediately determine whether there are antibodies to the tick-borne encephalitis virus in the tick’s saliva. This disease can be very dangerous for a person, so with timely diagnosis, a person will avoid serious health problems.
What should I do if bitten by a tick?
We go to the nearest emergency room or infectious diseases hospital, where the tick will be removed, and then you can go with it to the laboratory, where the tick will be taken for analysis. Sometimes laboratories are located at hospitals.
We also remove ticks and conduct an analysis, so you can come to us if your child has been bitten by a tick!
If the arachnid fell off at home
In a situation where the parasite bites a person and falls off after a few hours, it often goes unnoticed. A red spot, slight inflammation, and slight itching remain on the body. The tick falls off if it has fully satisfied its need for food and replenished its nutritional reserves.
Tick drunk on blood
If a thick tick falls off at home, there is no future for it. The nymph will not be able to continue development because there is no soil. The female will not be able to lay eggs for the same reasons. After some time, the parasite dies. The tick is dangerous if it has not drunk blood, then it can bite again. There is no need to worry too much about where the tick goes in the apartment. Even if he is not discovered, he will soon die.
Symptoms of a tick bite in a dog
A tick bite in itself does not pose a serious threat to a dog’s body. The danger comes from diseases that are transmitted by a tick bite to a dog. Here are some common symptoms that a dog may experience after a tick bite: lethargy, low activity, the dog lies down more. Change in urine color (urine becomes dark, sometimes acquires a brown, brown or red tint). The visible mucous membranes and sclera of the eyes have an icteric tint. Body temperature rises to 40°C and above. Shortness of breath appears, the dog has difficulty breathing.
You can protect yourself from ticks using repellents
Repellents can actually protect you from ticks - otherwise why were they invented? However, you should not rely completely on these funds. The fact is that, even if you apply the anti-tick spray according to all the rules, after two to three hours it will completely disappear, so it will have to be applied again and again. But even in this case, you cannot count on 100% protection: repellents can only be applied to clothing, and if a tick gets on an open area of skin, alas, it is unlikely to be frightened by the scent of your jacket.
Bite sites
As already mentioned, they most often stick to areas with thin skin. Most often this is the head, where there is hair, the back of the head, behind the ears, armpits, groin, knee bends, and stomach.
If we talk about the bite itself, namely the sensations that a person experiences, then this process goes unnoticed for a person. Therefore, it is impossible to detect it before it suctions strongly. This happens for the reason that the parasite’s body produces a special anesthetic enzyme, which it injects when biting, so the person does not experience any pain or discomfort.
The very first symptom is itching, which most often allows you to detect a tick on your body. Less commonly, other symptoms may be observed, for example, drowsiness, general malaise, aching joints, etc.
Ticks are dangerous only in May and June
The first period of tick activity in Russia begins in early April and lasts until mid-June, and the largest number of bites is traditionally recorded in May. However, we should not forget about the second period of activity - it lasts from the beginning of August to the beginning of... October. And the chances of encountering a tick in the fall are especially high for residents of regions with warm climates. By the way, a tick can attach itself to its victim even in winter. So, in 2011, a five-year-old girl from Rostov-on-Don fell victim to a bloodsucker, and it happened on New Year’s holidays.