Ticks appear at the end of March and disappear in October with the onset of persistent cold weather. They live in grass and lower branches of bushes. The location of the victim is determined by smell. They crawl onto clothes made of grass or fall from bush branches. It takes a few minutes to get used to it, choose the most favorable place, and attach itself. One of the most asked questions is whether a tick can fall off on its own.
How a tick bites and where
The pest looks around for a while, looking for a favorable place to bite. This process takes approximately half an hour. It penetrates into places where the skin is thin and blood vessels are located closer to the surface.
- armpits;
- groin;
- stomach;
- small of the back;
- breast;
- behind the ears;
- neck;
- scalp.
On a note!
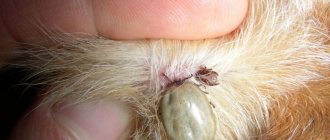
The tick bite itself is painless. The head penetrates the skin, the abdomen remains outside. A hungry tick is no more than 3 mm in size, so it often goes unnoticed. During feeding, the abdomen increases in size to 10 mm in diameter or more.
Can a parasite burst?
Despite the fact that in the process of eating blood, the tick swells to enormous sizes, it cannot burst. The integrity of the insect can only be damaged by physical force.
When removing the parasite yourself, you should be careful not to damage it. It is extremely difficult to pull out an insect piece by piece. If part of the pest remains in the body, suppuration will begin in this place.
Is it possible to miss a tick bite?
The arachnid bites with powerful jaws, but since they are miniature, the bite itself is not felt. The head quickly penetrates the skin, the parasite slowly sucks blood. Initially, the size of the tick is so small that even with an accidental touch you may not notice its existence.
After some time, the abdomen enlarges, becomes convex, oval, sticks out on the surface of the skin, resembling a wart or papilloma. If the parasite has attached itself to the back of the head, back, or groin, you may not notice it.
The body reacts to a tick bite in different ways. Depends on the sensitivity of the skin, the strength of the immune system, and the tendency to allergies. At the site of the bite appears:
- swelling;
- slight redness;
- slight itching;
- in the center, at the site where the parasite is attached, there is a dark spot with dried blood.
The tick bite
of the epidermis recovers on its own within a few days. With such a reaction of the body, you may not notice the bite and not know about its existence. If you have an allergy, the symptoms are more pronounced:
- swelling;
- large-scale redness;
- inflammation;
- incessant itching;
- additional rash.
Manifestations of allergies cannot be ignored, but you may not know the cause if the parasite is no longer present at the scene of the “crime”.
How long does a tick stay on the body?
Females and males attack humans. Females are more voracious, since they need blood to form new offspring. The male can bite and fall off in a matter of minutes. A few milliliters of blood is enough to saturate it. Further stay on the body is advisable only if the female remains there. In other situations, the male unnoticedly unhooks and climbs out.
On a note!
The female can also bite and fall off, but this takes longer. To saturate females, up to 20 ml of blood is required. The parasite replenishes these reserves gradually. The time spent on the human body depends on the initial degree of saturation. If the female was not too hungry, she latches on for only a few minutes. In other cases it lasts up to 3 days.
When the tick falls off on its own, it means that it has completely quenched its thirst, and further stay on the body loses its meaning. If the attempt is unsuccessful, the parasite bites a second time and starts eating.
Can a tick bite and crawl away?
This situation happens if the arachnid has attached itself to the skin and remained unnoticed until it was completely saturated. The pest carefully extends its head and falls away. Under natural conditions, the female lays eggs on the surface of the soil. At home, if this happens, the offspring will not be able to be born. The likelihood that a tick can bite again and leave remains minimal.
Tick bite
When the tick has sucked and fallen off, redness, slight swelling, and slight itching remain at the site of the bite. The skin is restored within a few days. In the presence of an allergic reaction, special treatment is required - the use of local, systemic antihistamines, antiallergic drugs. If the tick has been infected, manifestations of the disease appear after 14-60 days.
What to do after deletion
A tick removed alive must be burned or, after pouring alcohol or boiling water, flushed down the toilet. You can’t throw him away; he will continue to look for an owner.
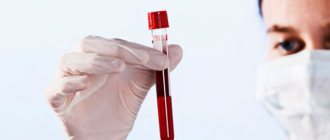
Mite for analysis in the laboratory
For your own peace of mind, the live tick can be taken to a laboratory to be tested for infections. This must be done within two days. During this period, store it in a jar with a damp cloth or paper (can be in the refrigerator).
The presence of encephalitis in the blood can only be determined ten days after being bitten by an infected tick. An analysis for antibodies to encephalitis is carried out after 14 days, to borreliosis - after 30 days. All this time you need to carefully monitor your well-being, skin condition and body temperature.
The only method of protection is vaccination!
All scientists and doctors are of the opinion that the only method of protection against encephalitis is appropriate vaccination. Anti-bite medications do not provide a guarantee, but only reduce their likelihood and, of course, do not protect against the virus.
Consequences of bites from infected ticks
Even if the tick was able to get out on its own and went unnoticed, the virus, when it enters the blood, begins to develop and progress. The first symptoms appear within 1-2 months. Depends on the strength of the immune system and the type of disease. The infection is transmitted through saliva and blood.
- Tick-borne encephalitis. The virus enters the human body through the blood. If the infected creature gets enough and falls off, infection will not occur. If it is accidentally injured or removed incorrectly, its blood enters the wound and the virus begins to spread. Affects the spinal cord, brain, and nervous system. Leads to disability, paralysis, madness, death.
- Lyme disease or borreliosis. The infection is transmitted through saliva. Affects the central nervous system, heart, joints. If not treated in a timely manner, complications may lead to disability and death.
- Ehrlichiosis. Less common disease. The virus leads to respiratory and kidney failure.
Diseases from ticks
Other diseases transmitted through a tick bite are typhoid, anaplasmosis, babesiosis, tularemia, hemorrhagic fever.
Important!
The first signs of the disease resemble the flu. Fever, nausea, vomiting, muscle aches, weakness, headache, increased body temperature, etc. appear. The condition returns to normal after 5-7 days, but recovery does not occur. Within a month, the disease makes itself felt again, but with renewed vigor and different symptoms. Treatment is carried out in a hospital.
Danger to humans
These blood-sucking creatures pose a great threat to humans, as they can infect dangerous diseases. In this case, it does not matter at all whether it is found on the body, or whether it drank blood and fell off on its own; it is its bite that is dangerous. Therefore, it is very important to contact medical institutions when it is detected.
If you manage to save the insect, you can submit it for analysis, which will show whether this individual is infected. If you remove it from the body yourself, then you need to put it in a glass container along with a piece of damp cloth, which will not allow it to dry out. Analyzes are carried out with live insects, which allows you to obtain accurate results. If the parasite is dead, burst, or there is only a fragment of it, then research can be carried out, but the result will not be accurate.
In cases where you have not noticed the tick itself on your body, then symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately. These parasites can transmit diseases such as encephalitis and Lyme disease.
Lyme disease
This disease is manifested by such symptoms as fever, headache, body aches, weakness, and a cough and runny nose may also appear. These symptoms are similar to a cold or even the flu, so a person may not think about having a dangerous infectious disease. The main sign that you definitely need to pay attention to is the appearance of a large red spot on the body, which has a clear outline.
This disease affects the nervous and lymphatic systems. It is very important to start treatment at an early stage, since brain activity suffers, memory may deteriorate, and disturbances in thinking processes occur. The facial nerves are also affected as they are damaged.
If the correct treatment is applied, the disease can be completely cured. In situations where treatment is not applied, complications occur, which in severe forms are not always amenable to treatment.
Tick-borne encephalitis
This disease is very dangerous with complications. Encephalitis manifests itself with the same symptoms as the previous illness, only there is no reaction in the form of a circle on the skin.
If left untreated, the nervous system is affected; this process can occur as early as a week after infection. The person experiences severe headaches and epileptic attacks may occur. Next, internal organs are damaged, the liver, kidneys, etc. are destroyed.
Regarding children, the disease poses an even greater danger for them, since children cannot correctly describe their condition and talk about their feelings, which for parents does not allow them to create a complete picture and correctly respond to the situation. It is very important after each walk in nature to pay maximum attention to examinations and, at the slightest suspicion, consult a doctor.
In addition to the above diseases, ticks also carry other dangerous infections, which include typhoid, ehrlichiosis, fever, tularemia, etc. The diseases are treatable, the main thing is to seek medical help in time, then you can avoid serious consequences.
Prevention means
You can prevent a tick bite by following basic rules of behavior:
- Wear thick clothing with cuffs, elastic bands, socks, and hats. If the pest does not reach the skin, it falls from the clothing back to the ground and does not bite.
- Use tick repellents. They use aerosols and sprays - Gardex, Taiga, Raptor, Raid, Clean House, etc. The action lasts for a maximum of 2 hours, then you need to repeat the treatment of the clothes.
- Inspect the body every 2 hours. This will help remove parasites that have not yet attached themselves.
- Upon returning home, throw all your clothes in the wash and take a shower or bath. Inspect the body again, especially in places where ticks may be attached.
The main preventive measure against encephalitis and borelliosis is vaccination. After removing the parasite, it is recommended to send the tick to a laboratory for examination. If the virus is detected, the person is given drugs to prevent the progression of the disease.