An unremarkable butterfly - the cabbage cutworm - has long chosen human fields and vegetable gardens as a breeding ground, and agricultural crops as a source of food for voracious caterpillars. This pest is distributed throughout the European continent and is well known to people. Therefore, today there are effective ways to combat it.
What do cabbage cutworms look like and why are they dangerous?
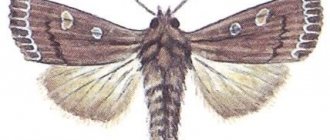
The butterfly belongs to the noctuid family and is included in the order Lepidoptera. The length of the body is 19-23 mm, and with the wings open, 40-50 mm. Externally, the insect is gray-brown in color with a pattern. The pattern on the wings looks like a double row of zigzags.
The lifespan of an adult cabbage moth is 2-3 weeks.
The mating period of butterflies begins 2-3 days after the insect emerges from the pupa. The female cabbage cutworm strives to lay eggs on the leaf blades, on their inner side, as quickly as possible. They are oblong in shape, white, 0.6-0.7 mm in diameter.
Important! The fertility of cabbage cutworm varies from 600 to 2700 eggs per life cycle.
The masonry on the underside of the sheet remains unchanged for 4-12 days. Then the larva appears. Before the pupation stage, it goes through 5-6 stages of development.
An adult caterpillar of the cabbage cutworm is light green or dark brown in color with black stripes on the back.
Insect larvae successfully feed on the plants around them: beets, lettuce, legumes. Their activity is hardly noticeable, since in the first stages of development they damage the leaves only from below. But as cabbage cutworms grow older, they gnaw holes in the shoots, and later are able to eat them entirely, leaving only the veins.
The pupal stage begins at the end of June, and the second generation appears in September-October. For the winter, the cabbage cutworm burrows into the ground, going to a depth of 10-25 cm. When the air temperature in spring reaches +16-17 °C, the butterfly is already emerging from the soil.
Description of the insect
The cabbage armyworm (Latin name - Mamestra brassicae) is a medium-sized butterfly, the wingspan of which reaches 5 cm. It belongs to the large family of cutworms (Latin Noctuidae), or “noctuids”, which includes almost 1890 genera.
The wings have a slightly jagged edge. The pigment is distributed unevenly over their surface: the closer to the edges, the more dark tones there are in the color. At the same time, there is no single standard of appearance for cabbage cutworm individuals: it can be variable not only in color, but also in the size and shape of the butterfly’s body
In the middle zone, the cabbage cutworm appears in the first ten days of June. In the southern regions it can be seen already in May.
Cabbage moth larvae develop into pupae within 50 days. Their color can be different: there are bright green, gray, brown, almost black specimens. The youngest caterpillar is always green. Adults have a frightening black pattern of stripes on their backs, designed to scare off potential enemies. Typically, the caterpillar, nearing the end of its development in this phase, reaches a length of 5 cm. It has 16 legs that help it move around plants.
Causes and signs of appearance
You can suspect the activity of cabbage cutworm when examining the plant. On seedlings, the insect actively gnaws the stems, so the crop falls. Cabbage cutworm larvae cause such damage.
During the day, the caterpillars gradually make their way to the base of the head of cabbage so that with the onset of autumn they can eat their way through. As a result of their harmful actions, the crop is contaminated with excrement. You may not see the cutworm from the outside, but if you cut a vegetable, there will be black spots and caterpillars inside it. This type of cabbage is not suitable for human consumption. There is no point in sending a vegetable damaged by scoops for winter storage: it will quickly rot.
Cutworm larvae gnaw holes on the leaves, leaving only thick veins
If no measures are taken, the insect completely destroys the plant, which, after losing its foliage, begins to rot from the inside. With minor damage, vegetables slow down their growth and become sick for a long time.
The main reason for the appearance of cutworms on cabbage is the availability of food. The butterfly's attention is attracted by the smell of hay, cereals and mixed feed. The pest can often be seen near grain warehouses.
Important! The abundance of weeds on the site provides the insect with a favorable environment for development and reproduction.
Rapeseed sawfly
Damages cabbage, less often radish, and mustard. Lives on wild cruciferous plants.
The adult sawfly is an insect with two pairs of transparent membranous wings. The sawfly's body is orange-yellow, with black spots on the back, 7-8 mm long. The female has an ovipositor at the top of her abdomen, retracted inward and consisting of four plates, two of which are jagged, like a saw (hence the name “sawfly”). The larva is grayish-green, with a black head, wrinkled, up to 20 mm long, with 11 pairs of legs.
The sawfly reproduces in large numbers, in patches. The larvae overwinter in the soil at a depth of 7-12 cm in a dense, water-impermeable silky cocoon. They pupate in the spring, and adult sawflies emerge from the soil in mid-May. First, they actively feed on the nectar of flowers of plants from the umbelliferous and cruciferous families, then the females begin laying eggs on the lower surface of the leaves. The female cuts through the skin of the leaf with her ovipositor and lays one or several eggs in the wound. The eggs are usually located along the veins.
The larvae eat leaves from the edges, often leaving only rough veins. Having completed development, the larvae go into the soil and pupate there. In July, a new generation of sawflies emerge. Their larvae cause damage in August. The sawfly develops in 2-3 generations.
Control measures. Destruction of cruciferous weeds on which sawfly larvae feed. If the number of larvae is high, spray the cabbage with sumi-alpha or kinmiks before tying the head of cabbage. Deep digging of the soil immediately after harvesting in areas where plants were damaged by sawflies in order to destroy the larvae.
How to fight with folk remedies
And although the cabbage cutworm caterpillar in the photo does not cause concern, getting rid of it is not so easy. To achieve maximum effect, it is recommended to use several methods, combining them with each other.
Folk remedies are popular not only because of their effectiveness, but also their harmlessness. Ready-made solutions are safe for human health and plants on the site. The advantage of traditional methods is their accessibility: most components are free or have a low cost.
To catch cabbage cutworms, you can use not only infusions, but also traps. To make them, just stock up on disposable cups or bottles that need to be trimmed, leaving sides 3 cm high. Fill the resulting containers with sweet liquid and hang them 1 m from the ground.
To prepare cabbage scoop syrup, mix 50 g of yeast with 1 liter of water. When the solution has fermented, add 1000 ml of flow and another 3 liters of water. Distribute the finished substance into containers. You can use compote or jam as a sweet liquid.
Important! Insect traps should be refilled with solution periodically. Once every two weeks, the contents of the container must be completely changed.
To prevent insects from escaping from the trap, the cut part of the bottle can be placed back into the container with the neck down.
Hot pepper solution
To use this product, you need to take 100 g of pods, fill them with 1 liter of water and put on fire. Boil the solution for 60 minutes. Cool the resulting remedy for cabbage cutworms, strain, and leave to infuse under the lid for two days.
It is convenient to spray plants against insects using a spray bottle, diluting the liquid in a ratio of 1:10 with water.
Liquid soap with wormwood from cabbage scoop
To obtain a solution, flowering wormwood must be crushed. Fill it with a bucket of hot water. Boil the raw material for 15-20 minutes, and then let it cool for six hours. Add 1 tbsp to the prepared remedy for cabbage cutworms. l. liquid soap. Shake the container with the mixture thoroughly before use.
Ash solution
Mix 200 g of nitrogen fertilizer and tobacco waste with 30 g of melted soap and 15 g of mustard. Pour boiling water over all components of the product, bringing it to 10 liters, and then leave the pan with the contents for one day. The ready-made preparation for cabbage cutworm can be used to treat vegetable crops.
Herbal infusion
Fill the bucket halfway with burdock leaves and compact them tightly. Fill the container to the brim with water. Leave the infusion in this position for 72 hours, and then strain it. It does not need to be diluted with water to use. To prevent the product from rolling off the leaves, it is best to add laundry soap to it.
As a substitute for burdock, you can use chamomile, datura or spurge
Cabbage scoop soda
The emulsion consists of only two components. To obtain it, you need to dissolve a glass of soda in a bucket of water. Spray the plant with the prepared cabbage cutworm remedy.
Dandelion infusion
Add 500 g of raw materials to 10 liters of water. You can use crushed leaves and shoots, roots and flowers. Add 1 tbsp to the resulting solution. l. liquid soap and leave it to sit overnight before use.
Tomato infusion
Chop green tomato stems. Mix them with bitter wormwood. To 10 liters of boiling water you need to add 350 g of the resulting mixture, and then leave all the components to infuse for six hours.
Bird droppings with wormwood
Boil 1 kg of herb in 3 liters of water. Two days before use, add 100 g of bird droppings to the infusion. Dilute the resulting remedy for cabbage cutworms with water to 10 liters, and then use it for its intended purpose.
Processing times
You can drive pests away from your garden beds or prevent their attacks with the right approach to the problem. In this case, the use of all methods is justified: biological, folk and chemical. Each method has different effectiveness.
Folk recipes and biological protection products are used when the problem first appears. In case of massive damage to seedlings or adult bushes, it is better to use chemicals. If you follow the basic rules, it is destructive to the pest and absolutely safe for the gardener.
Recommended timing of treatments with insecticidal and biological preparations:
- Early spring. Powerful insecticides are used, which are sprayed 2 weeks after planting young seedlings in open ground. The average daily temperature should be no higher than 14 degrees. Once the indicator exceeds this mark, the risk of rapid spread of cabbage and cruciferous flea beetles increases.
- Early - mid June. Treatment is carried out against the main pests of cabbage. Insecticides or broad-spectrum biological preparations are used.
- Consolidation of the result. Provided 10-14 days after the second treatment. The same remedy is used.
Meeting deadlines is not enough. In order for the treatment to give full results - to destroy all pests and protect the cabbage from them later, you must follow these recommendations:
- choose cloudy and almost windless weather;
- study the forecast of weather forecasters and exclude rain during the day;
- add regular soap or shampoo to the solution prepared for treatment (so that the drops linger on the surface of the sheet longer);
- treat all plants (not just infected ones);
- Prepare the products used according to the instructions.
It is not recommended to exceed the doses specified by the manufacturer, because such actions may cause damage to the plant itself. It will not be possible to increase efficiency, but the gardener may well destroy the crop.
Chemicals
To treat cabbage against pests, “radical” chemistry is rarely used. This is due to the fact that it is more difficult to wash off the remaining drug from the soil and from the leaves of the head than in the case of other crops.
Most often, such treatments are carried out before the head of cabbage is formed - in the first month after planting seedlings in open ground or a greenhouse.
Then proceed with caution, choosing biological and traditional methods
In spring, young shoots are treated with the following means:
- "Alatar";
- "Decis";
- "Aktara";
- "Spark";
- "Fury";
- "Bankol."
Traditional methods
Safe ingredients are used to prepare homemade insecticides. The solutions contain the following substances:
- tobacco;
- hot pepper;
- ammonia and vinegar;
- laundry and tar soap;
- roots and leaves of plants;
- mustard powder;
- table salt.
These repellents repel insects with their distinctive scent. They are completely safe for humans and plants, are not absorbed into the structure of the leaves, and do not change the taste of the vegetable. After use, the upper leaves may be slightly bitter, so they are advised to be removed. Repeated use is allowed.
Popular folk recipes that ensure the destruction of pests on cabbage:
- A solution of liquid soap and ammonia. Helps destroy aphids. Dissolve 100 ml of soap and 4 tbsp in 10 liters of water. ammonia. Mix the liquid and spray the beds.
- You can destroy the eggs of cabbage flies with a solution prepared from 250 g of salt and 10 liters of water. They water the plants separately in the holes, and then sprinkle the soil with wood ash.
- Spraying with vinegar solution. Helps in the fight against larvae and butterflies, protects against white moths and moths. Dilute 1 tbsp in 10 liters of water. vinegar essence. Mix and spray quickly, otherwise the active substance will evaporate.
- Treatment with a solution of dandelion and laundry soap. Together with the roots, 3-5 adult plants are pulled out, crushed and poured with boiling water. Leave until cooled, then add grated laundry soap (1 bar). Leave it for a day, and then spray the plants.
- Using a mixture of ash, soda and red pepper. Recipe in this video:
How to get rid of a pest using drugs
Chemical methods involve treating plants with certain insect repellents. Such drugs include:
- Zeta;
- Sherpa;
- Pyrethrum;
- Inta-Vir;
- Bankol.
The effect of chemicals is usually to destroy the cabbage cutworm: its nerve endings are paralyzed, so it dies.
Treatment with solutions is not carried out if there are less than four weeks left before harvest.
There is a group of insecticides whose action is selective. Cabbage scoops do not get used to such remedies as Decis, Fury and Karate. Among the neonicotinoid preparations that are safe for people and animals, we can highlight such as Aktara, Tanrek and Confidor. These products quickly decompose in the soil.
Important! Neonicotinoids can not only destroy the cabbage cutworm, but also the bees on the site.
In the summer, it is recommended to spray vegetable crops with products that contain phosphorus: Danadim, Zolon
General principles of working with insecticides:
- It is recommended to irrigate beds with crops on a windless, sunny day;
- The optimal time for insect repellent treatment is sunset;
- Frequency of use of insecticides – no more than twice during the growing season.
A mandatory step in working with drugs is the use of protective equipment - goggles, mask and gloves. It is recommended to cover the rest of the body with clothing.
Important! The use of the chemical method implies strict adherence to the dosage of the drug.
Among the biological agents effective against cabbage cutworms are Lepidocide and Fitoverm. Their use is possible in accordance with the instructions. Five days before harvest, all work to combat the cabbage cutworm should be stopped.
Important! The advantage of biological insect repellents is their harmlessness to the human body.
Cabbage cutworms are destroyed by Trichogramma, which are hymenopteran insects that lay their eggs in other people’s clutches.
Damage caused
Due to the gluttony of caterpillars, cutworms are classified as pests. First they eat the leaves of weeds, and then move on to cultivated plants. They gnaw through the stems and petioles at the root collar, and eat away the upper part of root crops.
Gnawing armyworms are polyphagous and harm more than 145 plant species. The caterpillars feed on grains and melons, potatoes, beets, corn, sunflowers, tomatoes, grapes, carrots, lettuce, etc. The pest overwinters in the soil as an adult caterpillar.
Agrotechnical and mechanical measures to combat cabbage cutworm
For the winter, butterfly pupae are buried in the ground to a depth of 30 cm. Due to this feature, agronomists recommend annually plowing your plot in the fall.
This event allows you to raise to the surface of the soil all the cabbage cutworm pupae that will die during the frost period. As a result of plowing, the land is also cleared of weeds.
Other agrotechnical methods for combating cabbage cutworm:
- deep loosening of the soil in the beds during the period of egg laying;
- regular weed control;
- mowing grass around the perimeter of the site.
If you remove all excess vegetation from the garden and around it, the butterflies will not have enough food. Favorite delicacies of the cabbage cutworm are pigweed, nettle and quinoa.
Important! Optimal conditions for the development of caterpillars are humidity in the range of 50-80% and temperature +15-25 °C.
Mechanical control of cabbage cutworm involves manual collection of insects. Inspection should be carried out weekly. You need to pay attention to cabbage leaves. All discovered masonry must be destroyed.
The optimal time for the procedure is early twilight. During this period, the larvae are activated to search for food. But manual collection of cabbage scoops is considered to be an ineffective method. It does not completely destroy the pest. Without combination with other methods, the insect will successfully restore the population within a few weeks.
Cabbage pests: leaf beetle, cabbage fly
The cabbage fly is a flying insect that in appearance resembles an ordinary fly, but its body size is more compact and is about 5 mm. The fly begins its destructive activities in May, when it begins laying eggs. The laying is carried out directly into the ground, in close proximity to the cabbage seedlings. After about 10 days, the eggs hatch into voracious larvae that feed on tender roots.
It is not difficult to determine whether a plant is affected by cabbage fly. The plant begins to lag in growth and looks lethargic. As the root system deteriorates, symptoms become more obvious. Initially, the lower leaves acquire a lead color, and after a few days the plant dies completely.
The photo shows the cabbage leaf beetle and its larva
If you notice something is wrong, you need to water the beds with Thiophos solution or spray the cabbage with dust. Traditional methods help by watering the soil next to the bushes with vinegar essence at the rate of 1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water. It is quite effective to sprinkle the rows with tobacco dust, mothballs, mustard, and hot pepper.
Cabbage leaf d is a small green bug that itself is not dangerous to the plant. However, it lays eggs, from which larvae hatch and readily eat cabbage. As a result, the farmer notices the appearance of characteristic damage on the leaves, as shown in the photo.
Tobacco dust, ash, slaked lime - these are time-tested substances that can be sprayed on cabbage. It is possible to catch insects using glue traps placed on the garden bed. Using poisons is guaranteed to help get rid of the leaf beetle. The preparations “Karate” and “Aktara” will quickly destroy beetles and their larvae.
Cabbage pests: bugs and cutworms
Cabbage bugs are very prolific pests that feed on plant sap. A characteristic light spot forms at the site of the bite, as can be seen in the photo. Bacteria, viruses and fungi can penetrate through the wound, causing various cabbage diseases.
The photo shows a cabbage bug and a lightened area of the affected leaf.
Cabbage bugs are repelled by naphthalene, which is pre-mixed with sand and scattered between the beds. Spraying the leaves with tobacco, a decoction of potato tops with onion peels are safe but effective methods of control. Chemical preparations “Phosbecid” or “Belofos” will help get rid of insects even during massive attacks.
The moth moth is an insect that reproduces quickly, especially in the southern regions of Russia. The butterfly lays eggs, which it attaches to the bottom of the leaf. Soon voracious larvae emerge, actively feeding on cabbage leaves and gnawing holes in them. The pest is predominantly nocturnal, hiding during the day at the base of the cabbage stem. The use of traditional repellents and poisons allows you to get rid of cutworms on cabbage.
Pictured is a cabbage cutworm and its caterpillar
Caterpillars are a fairly common problem. Among various insects, the ones that most often cause damage to crops are:
- Cabbage white caterpillar. It has a yellow-green color, a body length of up to 6 cm. The caterpillar is generously covered with long hairs and has a good appetite.
- Turnip white. The caterpillar is green in color and eats only the tender flesh, but ignores the veins, leaving the leaf skeleton intact.
- Rapeseed sawfly larvae. They eat leaves, causing significant damage to the plant.
For effective prevention, it is worth inspecting the leaves every few days and mechanically destroying the pest eggs found on them. For chemical control, the drugs “Kemifos”, “Inta-vir”, “Creotsid” are used. Plantings are sprayed with solutions of these poisons. A positive result comes quite quickly.
Cabbage pests and how to deal with them using folk remedies
The photo shows pest eggs attached to the back of a cabbage leaf.
Farmers increasingly prefer to grow vegetables without the use of chemicals and potent products. This is correct, because even if all safety rules are followed, a small amount of hazardous substances still gets into the ground and can penetrate the human body. What folk remedies can be used to control cabbage pests? We invite you to familiarize yourself with the most popular of them, namely:
Video about cabbage pests and methods of controlling them:
Dangerous cabbage pests cause enormous damage to farms every year. Photos of insects and a description of effective methods of combating them will help the vegetable grower quickly recognize dangerous symptoms and destroy them. You can also preserve the harvest using folk methods, which will allow you to harvest cabbage without harmful substances and good for health.
Babanukha
Babanukha is a dark greenish insect with brownish legs. The insect eats almost all varieties of plants, including cabbage. The leaf beetle waits out the winter under fallen leaves, in manure granules.
In early June, this beetle leaves its wintering site and begins to eat cabbage leaves. Females are able to form depressions in cabbage leaves, in which eggs can later be found.
To escape from this type of pest, use the following:
- painstakingly destroy all traces of plants during the harvesting process;
- get rid of unnecessary plants;
- do not leave radishes and mustard to grow;
- plant seedlings early;
- in the autumn, dig up the ground in the area with seedlings.