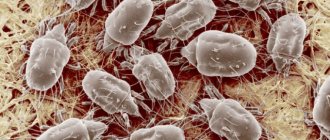
Characteristic features of development
The barn mite goes through the following stages of development:
- egg;
- larva with three pairs of limbs;
- nymph of the first age - already has 4 pairs of limbs and becomes similar to an adult;
- a second-instar nymph is an adult arthropod with 8 pairs of limbs and gender.
The transformation process from birth to adulthood takes about two weeks. In total, the life cycle of a barn mite is up to three months.
A feature of the life of the barn tick is the intermediate stage, which can occur between the nymphal stages of the first and second instars. Under unfavorable conditions, the tick goes into the hypopus state. This stage allows the tick to survive the lack of food and moisture. It is covered with a dense shell and does not feed. But it can spread, for example, to the fur of domestic animals or through their excrement. Hypopus is not afraid of any external influences:
- lack of food;
- drying;
- freezing;
- treatment with pesticides;
- ionizing radiation.
The tick experiences difficult times in this state, after which it emerges from this stage as a nymph of the second instar and continues its life, feeding and reproducing.
Variety of sizes
The sizes of ticks vary over a fairly wide range and depend on their lifestyle.
Dimensions of ticks on a background of graph paper
Here is the data on the sizes of the main groups of mites:
- Ixodidae. They can range in size from 3-4 mm in hungry people. In males who have drunk blood, up to 25 mm, and in females up to 36 mm.
- Argaceae. From 3 to 30 mm.
- Gamazovye. From 0.3 to 4 mm.
- Scabies. From 0.1 to 0.3 mm.
- Red heifers. From 0.5 to 0.8 mm.
- Feathers. About 1 mm.
- Demodexes. 0.2-0.4 mm.
- Ear. About 0.3 mm.
- Dust (or household). They have a size of 0.1-0.4 mm.
- Barn. 0.3-0.6 mm.
Within 3-5 days of feeding on a victim, female tick larvae can increase their weight by 10-20 times. Nymphs become 20-100 times larger in 3-8 days of feeding. A record increase in size is observed in adult female ixodids - within 6-12 days of active blood sucking, their size and weight can increase 10-20 times from the original.
Where do barn mites live?
Favorable conditions for granary mites are the presence of plant food, air and sufficiently high air humidity. Since they do not have a dense shell, direct sunlight poses a danger to them. Dry air harms them, since they do not have respiratory organs; they breathe with their whole body, therefore, when dried out, ticks turn into hypopus.
They live in a variety of places:
- rotting plant remains;
- soil and plant roots;
- rotting wood;
- mosses and lichens;
- mushrooms;
- plant bulbs;
- cheese and wine.
Granary mites can often be found in granaries, and at home - in packages with cereals and flour.
Principles of classification
Ticks are the oldest invertebrates with a primitive structure.
Their miniature body size helps them spread and survive everywhere. Their body is divided into two parts, the border is located closer to the front. Four pairs of legs consist of several segments, the final one is a tarsus, armed with claws and suckers. The first pair of appendages, chelicerae or jaws, are characteristic of all arachnids. They look like pincers and are used for piercing and cutting. The oral apparatus also includes pedipalps, limbs located on the side of the chelicerae. These processes grow together at the base and, together with other parts, form a movable head. There are some differences in the structure of the oral organ, depending on the type of nutrition. In saprophages that eat dead remains, it is gnawing, while in predators and parasites it is piercing-sucking.
Classification
Most species of mites are predators and saprophages. They live independently and do not need to parasitize other individuals to develop. Scientists divide the Acari subclass into three superorders:
- Harvester ticks (Opilioacaridae) are large terrestrial individuals measuring 1-3 mm in size. There are 25 known species inhabiting the tropics and subtropics. Their head and thoracic region merge into the cephalothorax, delimited from the abdomen. The oral apparatus consists of chelicerae, pedipalps and upper lip. On the back there are three pairs of eyes. Their long legs make them look like harvestmen. Representatives of the family live in the forest, under stones, and in the soil. They feed on solid food, including small arthropods, plant pollen and fungal spores.
- Parasitiformes are a superorder with 12.5 species. This group includes parasites of vertebrates, as well as predators and saprotrophs (individuals that destroy the remains of living beings). Among the most dangerous representatives of the superorder are ixodid and argasid ticks.
- Acarimorphic mites (Acariformes) are the largest group, which includes more than 30 thousand species. Individuals of the family are characterized by the addition of segments throughout life. About half of the group consists of sarcoptiform mites, which parasitize vertebrate animals. They feed on feathers, skin, and hair. Thrombidyphoid mites (almost 22 thousand species) include plant pests and carriers of infectious diseases.
Variety of tick species
Tick species have different feeding preferences. Some feed on plant sap, others on rotting organic matter, others on blood, and others on dead parts of the epidermis and fur. But there are no highly specialized species among them. If it's sap, it's the sap of many plants. If blood, then from all warm-blooded organisms living in the area.
Damage caused by barn mites
The barn mite is a pest. It affects food and causes the development of various diseases and conditions in humans.
Pests eat grain and spoil it with their flaking scales and secretions. As a result, sticky lumps form and the process of rotting begins. Flour or cereals infected with mites should not be consumed. The germination capacity of grain in which mites have settled decreases.
If for some reason a person eats contaminated food, he may develop:
- allergic reactions;
- catarrh of the respiratory tract;
- poisoning;
- asthmatic manifestations;
- intestinal disorders.
Argaceae
The family consists of 12 species. They have a characteristic ovoid shape. Sometimes you can even say oval. There is no point to the head. The legs are often hidden under the shell.
In some ways, these individuals resemble bedbugs. The Persian tick is constantly confused with them. How can you tell them apart? The bug has a hard chitinous cover, while argasids have a soft, leathery shell.
Their color changes due to blood. Those who are full are purple in color, while those who are hungry are gray. They can infect cats, birds, and humans. The resilience of these parasites is amazing. Some of them are capable of fasting for up to 11 years. They are waiting for the right moment.
These animals are dangerous not only because they carry tick-borne fever, relapsing fever, and borelliosis, but also because of their bite. The saliva of these arachnids is toxic, so the consequences of a bite are rash, itching, and redness. Some species are as feared by Mexicans as rattlesnakes. The toxins cause paralysis and some animals die from their bite. Mammals that are infected with Argasidae often behave restlessly. The animal becomes depressed.
Let's look at the main photos of tick types and names to understand the differences:
- Caucasian. Distribution area: Caucasus, southern Ukraine. He carries a dangerous disease - endemic relapsing fever.
- Shell-type. It often infects pigeons, and there are cases of human infection.
- Poselkovy. Carries spirochetes that cause borelliosis. Such an individual is dangerous due to the method of transmission of the disease. The arachnid can transmit the virus to its offspring. Thus, not only the tick, but also the virus multiplies.
Habitats
The barn mite has a large distribution area; it can be found on all continents of the globe. Pests live in finished food products or in raw materials for their production. Parasites prefer high humidity, average air temperature, good access to oxygen and as little sunlight as possible.
Harm from barn mites
The tick chooses as housing:
- barns with cereals or flour;
- warehouses with finished products;
- vegetable warehouses;
- home grocery cabinets.
Barn mites harm people; they spoil their food and make it unusable.
Important!
Eating foods with mites is strictly prohibited, even after heat treatment. If a parasite enters the body, it can cause digestive upset, allergic reactions, and other diseases.
How to get rid of dust mites in your home
First, you need to take care to eliminate places in the apartment where they may accumulate, such as down pillows, old mattresses, carpets and woolen blankets. This reduces contact with the allergen to a minimum.
Ventilation is an affordable remedy for dust mites, and if it is combined with traditional wet cleaning of the room, the amount of inhaled waste from their activity will be significantly reduced. You should definitely consult a doctor on how to reduce the body’s sensitivity to their waste products.
If there are severe symptoms of the disease, the doctor will prescribe medications that can help eliminate the manifestation of allergies.
Allergy treatment can be carried out in various ways that exist to eliminate this problem:
- Drug treatment can quickly help cope with the symptoms of the disease and bring the patient’s body back to normal. In addition to antihistamines prescribed by the attending physician, there is a desensitization technique. Its effect is that a dose of allergen is introduced into the patient’s body, which gradually increases. This leads to the body becoming accustomed to it and making it less sensitive to the allergen.
- The traditional method of treatment includes irrigating the nasal cavity with a solution of salt and soda, which should be done every 3 hours. Inhalation of water steam effectively relieves swelling. People with this problem benefit from visiting a bathhouse with deep inhalation of steam. You can use decoctions of medicinal plants, after making sure that you are not allergic to them, because they can aggravate the situation. If there is an air conditioner in the house, then air ionization, as one of its functions, will be very useful. Eliminating harmful foods from your diet, such as coffee and chocolate, will help bring your body back to normal. Applying knowledge of how to get rid of dust mites will significantly speed up the solution to the problem.
Preventing and combating dust mite allergies includes measures that will not only help alleviate the symptoms of the disease, but also eliminate the causes of its occurrence.
To do this you need to do the following:
- Do frequent wet cleaning in your living space, especially carefully monitor the condition of upholstered furniture, bedding, pillows, mattresses and carpets. If you are prone to allergies, consider minimizing the presence of such items in your home. There are items made from alternative materials in which dust mites practically do not live. For sofas with soft upholstery, you can purchase or sew special covers that can be easily washed and ironed.
- Dryness in the room is detrimental to ticks; if the humidity is below 40%, they die, but do not forget that in bed the living conditions for them remain optimal.
- Washing floors with a salt solution will help deal with the individuals that live on their surface. There is usually no need to use special acaricidal agents, because ticks can be dealt with using safer methods.
- Ventilation and air ozonizers can reduce the amount of parasitic feces in the air. This is an excellent remedy for dust mites and will make the air much cleaner.
- In winter, you can take out objects in which ticks can accumulate in the cold. Low temperatures have a detrimental effect on parasites. This will help reduce their population in the home.
Take these available measures into service if you are interested in the question of how to get rid of dust mites. Cleanliness and safety of the living space will only be beneficial, even if none of the family members have allergies.
In most cases, ticks live next to humans without causing any concern. Under certain conditions, some people show signs of allergies to dust mites, but knowing how to minimize exposure to them, while reducing their number to acceptable levels, can cope with this problem.
It is impossible to completely get rid of these parasites, but it is possible to create conditions under which their rapid reproduction will be excluded.
Do not ignore the problem just because microscopic mites are not visible, this does not mean that they are not there
Since your attention is directed to this problem, you can do everything for yourself and your family to make your living conditions more comfortable. It is easier to keep your home clean and follow preventive measures than to look for a remedy for dust mites when there are too many of them. https://www.youtube.com/embed/TwuDc4NcybY
Fighting methods
The fight against flour mites is very difficult, since this pest belongs to the category of annoying ones. This means that if such a “guest” settled in food supplies, then here he found conditions acceptable to himself, and the development of the colony will occur incredibly rapidly. As a result, absolutely everything will have to be disposed of. How to destroy the flour mite and prevent it from spreading to shelves with other products?
- First of all, you should find the location of the parasite - the source of spread, and then immediately throw away the infected supplies.
- The remaining “clean” bags and other containers with products must be removed from the shelves and wiped dry. This technique will stop the migration of wandering pests.
- If there are cracks on the shelves and racks, they should be cleaned using a powerful vacuum cleaner with a narrow nozzle. Here, make sure that all remnants of food supplies are removed, as they will likely contain a large number of eggs and larvae of the pest.
- Next, wash all flat surfaces with a hot, thick soap solution. At this stage, the sponge should be rinsed as often as possible and kept constantly soapy!
- We carefully seal all products in containers and send them in this form for further storage.
At the same time, we increase ventilation in the room and monitor humidity.
General information
Ticks belong to the class of arachnids, combined into one large subclass. They are divided into several groups. It is believed that arthropods are dangerous to humans and domestic animals, as they are carriers of dangerous diseases. But their diversity is so great that most of them do not pose a threat. Some individuals are microscopic in size, others grow up to 10 mm. Body shape and color may vary. According to the method of feeding, arthropods from the subclass of mites are divided into:
- herbivorous (feed only on plants);
- parasites (parasitic on the body of warm-blooded creatures);
- predators (hunt other arthropods);
- homo-vampires (feed on the entrails of their fellows).
The habitat of ticks extends throughout the world from the tropics to dry steppes. They live in soil litter, home carpets, and under water. A large number of individuals can be found in the ground layer of the earth. Up to 100 arachnids live per 1 cm³. These invertebrates are even found in Antarctica. They settle on sea coasts in bird nests, feeding on their blood.
Classification by groups
Due to the huge diversity of species, classification of ticks is difficult. They are divided into groups according to their form of life activity, body structure and physiology. The formation of orders and families occurred on the basis of ordinal groups (taxa). Representatives of each of them have similar characteristics. Based on this, the entire subclass of mites is divided into 2 superorders:
- parasitiforms - includes over 12 thousand species;
- acariformes.
Acariform mite