Keeping rabbits on a home farm or homestead is quite simple. It is important to provide the animals with the necessary conditions for this.
They require a room free from drafts, dampness, stuffiness and dirt. And not only standard cages and pits can be used as it. We should also not forget about the features of feeding and caring for animals and their fur, which determine the speed of development and survival of rabbits, as well as future income.
This article will tell you how to choose and arrange a room correctly, improve living conditions and provide proper care for rabbits.
Conditions of detention
The basic requirements for the conditions of keeping, caring for and feeding rabbits largely depend on the chosen breed, climate and some other nuances. However, there are some rules that must be followed under all circumstances.
Temperature and humidity
Many breeds and varieties of rabbits are able to withstand temperatures from minus twenty to plus thirty degrees. But heat and cold are permissible when keeping animals for no more than a few days. Both extreme cold and extreme heat are dangerous for them. A stable temperature of ten to eighteen degrees Celsius is considered optimal.
Too much dryness or humidity in indoor air can cause diseases in rabbits. The optimal figure is from sixty to seventy-five percent.
It is necessary to carefully monitor the temperature and humidity in the rabbits' cages.
Hygiene
Constant cleanliness in the premises is one of the prerequisites for maintaining the health of the livestock . In order to maintain it, it is necessary to clean it at least twice a week. It is also recommended to replace the bedding. Feeders and drinkers must be washed daily.
In order to prevent the occurrence of infections, once or twice a week it is useful to sanitize equipment, utensils and premises using slaked lime, caustic soda or a solution of potassium permanganate.
The size of the cell is also an important indicator. Rabbits know how to organize their space in such a way that their “latrine” has the least contact with the place of water and food. And if the size of the rabbit cages is not respected, it will be very difficult for the animal to do this. How to properly make a cage with your own hands, observing all proportions, read in this material.
The cage must be cleaned regularly, approximately every 4 days.
Nutrition
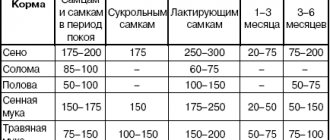
The diet of rabbits is compiled depending on the age and breed of animals. However, for almost all livestock, daily feeding includes:
- grain mixtures (corn, barley, oats);
- stern;
- feed and concentrates;
- hay and dried grass (depending on the season);
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- roots.
Most rabbit breeds include fermented milk products on their menu, but not all varieties tolerate them. The same applies to cabbage and carrots.
Much attention is also paid to drinking bowls for rabbits. This is due to the fact that when there is a lack of water, the animal begins to have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and the composition of the blood changes. If the hygiene of drinking bowls is not observed, then there will be infection with helminthiasis. And worms in rabbits can be fatal.
Natural thermoregulation in rabbits
When the air temperature reaches 24-26º C, all animal thermoregulation systems are activated.
- Since rabbits do not sweat - they do not have sweat glands - they simply breathe very often so that more water evaporates and the body cools.
- In the heat, the rabbit spreads its ears as far as it can to the sides, increasing their contact with the air. The fact is that the animal’s ears are pierced by large and small blood vessels, which expand at high temperatures. The blood cools, followed by the body. The method gives a noticeable result when a breeze blows over the rabbits or a fan is located next to the cage.
- Cooling through objects. The thinnest hair on a rabbit is on its belly. That's why in the heat he stretches out on the floor.
Animals can cool themselves without direct contact with surfaces. If the walls and ceiling are protected from the sun or made of cool-keeping materials, then the rabbit will feel cooler from them. But all of the above will not help rabbits at critically high temperatures. After +28º C they suffer from the heat, are depressed and susceptible to heat stroke, and can fall into a coma and die.
Disease Prevention
Prevention of rabbit diseases does not end with hygiene and sanitary procedures. There are other factors that need to be taken into account during the care and maintenance of rabbits.
Injuries
Large breeds of rabbits are not recommended to be kept in cages with mesh bottoms, as the bars can damage their limbs. In addition, it is important to pay attention to the integrity of the walls and floor, and the absence of potential danger. The volume of the premises must correspond to the size of the individuals so that they can move freely. Cages must be made without sharp corners.
The most common disease in rabbits is paw injuries, among which pododermatitis occupies a leading place.
Vaccination
It is necessary to start giving vaccinations after the rabbits are weaned from their mother. By this time they reach the age of one to one and a half months. Revaccination is usually carried out every six months to a year.
Approximate vaccination scheme for rabbits
Signs of illness
There is no need to start taking your pet’s temperature for no reason. However, you should be wary if a warm body is combined with other signs of illness. These include:
- decreased activity;
- excited state;
- loss of appetite;
- decreased thirst;
- various changes in the mucous membrane, skin and coat;
- wet nose;
- sneezing;
- cough;
- wet dirt around the anus;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- purulent discharge from the eyes and nose.
You should be wary if signs of the disease are found in nearby rabbits.
Methods
The choice of maintenance method should be based on the characteristics of the rabbit breed, weather conditions and the availability of available resources.
In winter
In warm regions, rabbits can also be kept in cages in winter. However, the best option would be an insulated shed without drafts or dampness. In such a room it is necessary to make bedding from hay, sawdust or straw. You can also use garages and greenhouses for this purpose.
In winter, it is recommended to keep rabbits in insulated sheds
During the cold period, it is necessary to place cages and sheds for rabbits on the south or southeast side so that they warm up evenly in the sun.
In the pits
A pit is a method of keeping rabbits that is as close to natural as possible. In such a room it is necessary to have an insulated floor and reinforced walls. The method is suitable for warm regions of Russia. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the fact that in pits it is more difficult to monitor the quality of wool, mating of individuals and the spread of infections in the population. It is recommended to clean the pits at least once a month.
In the barn and garage
An insulated barn or garage is great for keeping rabbits during the cold season. It is also possible to make an extension to the premises for free range for the summer. Large garages and sheds can also accommodate cages. For additional heating, it is recommended to use heaters and stoves.
In the sheds
Sheds are an improved way of keeping rabbits in cages. Such structures consist of individual wooden cages installed in rows in cascades or tiers. Passages are made between the shads for free movement and transfer of food.
Keeping rabbits in sheds can be done in both cold and warm regions. Most often, this method is used with a large number of animals and on large farms.
Shadow keeping of rabbits
In cells
Caging is the most common method among owners of farms and homesteads. Rabbit cages are made of both metal and wood. You can also build them yourself at home.
The cage method of keeping rabbits is suitable for almost any breed of rabbit. It is important to take into account the size of the individuals so that the cell volumes correspond to them. The minimum length should be eighty centimeters, width – sixty, and height – forty centimeters. Cages can be placed outdoors or indoors.
Approximate diagram of building a cage for rabbits
In polycarbonate greenhouses
A polycarbonate greenhouse is a non-standard maintenance method. It can be used instead of an aviary, and it is not necessary to heat it. To avoid undermining, it is recommended to place a net around such a greenhouse, burying it in the soil half a meter deep. The advantage of this method is the possibility of natural soil fertilization for further planting. For example, growing cucumbers in polycarbonate greenhouses.
One of the unusual ways to keep rabbits is to build a polycarbonate greenhouse.
Polycarbonate conducts and releases heat well. In order to preserve it better, it is recommended to paint the walls of the greenhouse with lime or water-based paint.
In the enclosure
The aviary method is one of the most convenient for keeping. An additional mesh fence to the main room allows you to take walks in the fresh air at any time of the year. It is also necessary to install feeders and drinking bowls in the enclosure. In addition, it is recommended to make an additional canopy to provide rabbits with protection from direct sunlight and moisture.
Aviary keeping of rabbits
Other effects of high temperature
- Decreased immunity, high susceptibility to disease.
- Decreased appetite up to complete refusal of food. In the case of a nursing rabbit, not only she suffers, but also the rabbits.
- Reproduction disorder. Studies have shown that sperm quality (the number of live, active sperm) in males decreases. Both females and males are reluctant to mate.
- Often, mother rabbits abandon newly born rabbits. At the moment of giving birth, problems become more frequent. There are more dead rabbits in the litter.
All of the above is a serious threat to the livestock. Therefore, a caring owner will take measures to ensure that the rabbits do not suffer from the heat - they will hide them from direct sun, make screens, cover the roofs of the cages with hay and straw, and provide plenty of clean water. There is experience when owners freeze bottles of water and put them in cages: as soon as the water melts and warms up, the bottles are replaced. A great option is an enclosure with several dug holes, but this is suitable for very few people.
Conventionally, rabbit breeding can be divided into industrial, farm and amateur. We are interested in the features and general information about keeping rabbits in the conditions of farms and amateur farms only. By the way, in the countries that are leaders in the production of rabbit meat and skins, and these are Italy and France, amateur rabbit breeders account for up to 40% of the production. Selection and breeding of rare breeds with valuable fur properties is often carried out on small farms. Let's consider what the optimal conditions for keeping rabbits should be.
Breed selection
There are four main types of rabbit breeds:
- meat (Flandres, Risen);
- skin (Down rabbit);
- meat-skin (White and Gray giants, Vienna blue, Silver);
- decorative (Germelin, Angora).
The weight of meat rabbits reaches twenty kilograms, meat-skin rabbits - ten, the average weight of representatives of skin-bearing species is four to five kilograms, decorative ones - one to two kilograms.
The choice of breeds must be made based on the goals of the establishment. It may also be affected by climate conditions and possible costs. The purchase of young animals for breeding is recommended only in specialized large farms. Animals should also be purchased there for restocking.
Temperature and humidity conditions and lighting
The recommended maintenance temperature is 12-18 Cº, fluctuations within ±5°C are considered acceptable. Adult healthy animals, depending on the breed, are able to withstand temperatures from -30 Cº to +30 Cº for several days; beyond these values they become seriously ill and die. Rabbits do not tolerate sudden temperature fluctuations, high humidity or dry air (optimum 60-75%), and catch colds in strong drafts.
Animals feel better in the presence of sunlight within daylight hours. When kept open in hot weather, it is necessary to make sure that the animals do not get heatstroke; protect the cages from overheating from above with straw and hay. A small dose of ultraviolet light will be beneficial for animals. In closed rabbitries, it is recommended to provide windows with an area within 8-10% of the floor area. In some large farms, in addition to natural lighting, artificial lighting is used from 6 am to 9 pm.
conclusions
- To organize the keeping and breeding of rabbits at home, it is necessary to choose the right premises, breed, and feed.
- The choice of premises should be based on the characteristics of the breed and weather conditions, as well as the time of year.
- It is necessary to maintain cleanliness, optimal humidity and temperature in the holding areas.
- To prevent diseases, it is recommended to disinfect and vaccinate livestock.
Also read about the features of keeping California rabbits at this link.
Belarus, Kazakhstan
In nature, rabbits are not afraid of high air temperatures: they take refuge in burrows. In captivity, where the rabbit is completely dependent on humans and is deprived of freedom, temperatures above + 28ºC can lead to heat stroke, even death of the animal
.
In addition, during the heat, the reproductive functions of animals suffer. Simply put, if it’s above + 22ºC outside, rabbits don’t want to breed or multiply and often they simply can’t
.
Sterilization of animals
Sterilized rabbits gain weight faster, and their meat is more flavorful and tender. It is recommended to castrate eared cats no later than 4 months of age.
Sterilization is carried out in three ways:
- Closed (remove the testis without damaging the membrane).
- Open (the scrotum is dissected, the membranes of the testes are incised, the spermatic cords are crossed).
- Percutaneous (the scrotum and testis are pulled at the base - within a week they fall off due to the cessation of blood supply).
Hygiene and nutrition
Rabbits, unlike other domestic animals and birds, do not tolerate crowding well and are demanding of hygienic conditions. Animals are very sensitive to air purity. The cages or enclosures where they are kept must be cleaned regularly; when kept in enclosed spaces, high levels of ammonia, carbon dioxide, fluff and dust in the air should not be allowed; rabbit hutches must be well ventilated.
Drinkers and feeders must be cleaned daily, cages - when dirty, but at least twice a week when kept outdoors and daily indoors. If manure is removed well through holes in the floor, the frequency of cleaning can be reduced. Cages or enclosures should always have fresh bedding.
Step-by-step instruction
In fact, the procedure for measuring an animal's temperature is simple to perform. But there are some points that are worth paying attention to. Rabbits are shy animals, so sudden movements and screams should be avoided. Talk to the little rabbit in a gentle voice, stroke it and calm it down in every possible way.
If you cannot calm the rabbit and fix it in a suitable position, it is better to let it go and try again after a while. Temperature can only be measured when the animal is completely calm and does not struggle or twitch. Otherwise, injury may occur.
The procedure is performed according to the following scheme:
- Place the animal on a soft surface on its side or back;
- choose the position in which the little rabbit behaves more calmly;
- let the assistant firmly fix the chest and hind legs;
- Lubricate the end of an electronic or mercury thermometer with Vaseline or a special gel;
- the thermometer must be inserted into the rectum parallel to the spine; it is enough to insert the instrument 2-3 cm;
- After the required time has passed, carefully remove the thermometer and look at the measurement results.
If you need to exert effort to get the tip inside, it means that the angle of insertion is incorrect, or the rabbit is lying in the wrong position. If everything is done correctly, the thermometer will easily penetrate the rectum.
The tip of the thermometer must be disinfected after use with medical alcohol.
If the indicators differ from the norm
If your rabbit's body temperature is higher than normal, the spike may be due to stress. Manipulations with the thermometer could frighten the animal, and its body reacted to what was happening in such a unique way.
Or perhaps the reason lies in the hot air of the environment. A cool bath will not help normalize the animal's body temperature, and may only frighten it even more. Rubbing rabbit ears with cool water is more effective. It is this organ that is responsible for maintaining optimal thermal balance.
Read also: Vienna blue rabbit
If even after this the thermometer column is above 40.5 degrees, the rabbit is definitely sick. It is necessary to look for and eliminate factors that provoke fever.
Low temperature is much more dangerous for the life of an animal. If the thermometer shows 38 degrees or less, we are talking about hypothermia. To begin with, the rabbit must be moved to a warm room, you can warm it with a heating pad.
A temperature of 38.1 is already a good indicator. But it's best to take your pet to the vet, as hypothermia is a sign of toxic shock caused by certain types of infections.
If the body temperature is high or low, routine vaccination is strictly prohibited. In the article “When and what vaccinations to give rabbits” we talk about this in detail.
Please leave your like as a sign that you found the article useful.
Share in the comments what difficulties you encountered while measuring your rabbit's temperature.
Preparing winter queen liquor
Dog breeds (even short-haired ones) that can be kept outside all year round
The ability of rabbits to reproduce sharply decreases during the cold period. But if you take care in a timely manner about arranging a warm queen cell for the rabbits, you can achieve a replenishment of the rabbit family even in winter. For this purpose, a separate compartment is equipped inside the cage. It should be dry, warm and protected from drafts.
Most often, polystyrene foam and polycarbonate are used as insulation. Insulation constructed using these materials can last for many years. In addition to constant insulation, you can warm your rabbit family using a special film blanket equipped with heating elements. With the arrival of cold weather, it is placed at the bottom of the house, and a layer of straw is placed on top, and such a blanket must be securely fastened. With the arrival of warmth, it should be dismantled and stored until next winter.