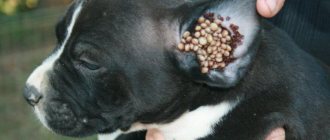
Psoroptosis is an invasive animal disease caused by skin parasites. Ear mites in rabbits can cause complications that can lead to very serious health problems.
Parasitic diseases are common in many animals, including rabbits
Read about how scabies manifests itself in pigs, measures to prevent it and methods of treatment in the article on our website.
In today’s article we’ll talk about how not to miss the appearance of such a parasite in your pet and consider the main ways to combat it.
Features of the disease
The causative agent of psoroptosis is an oval mite (0.2-0.8 mm in size) with a yellow color. It spreads quite quickly, especially if hygiene is not observed in places where animals are kept through carriers (mice, rats) and between individuals in contact with each other, so it is very important to identify the disease in time. Any breed of rabbit can suffer from psoroptosis.
Tick infestation quickly spreads among animals, regardless of their breed and age
Even minor signs of illness cannot be ignored. Animals attacked by parasites lose their appetite and lose weight, and changes in biological and physical processes begin to occur in their bodies. Males often lose the ability to mate, and females stop feeding their young.
Purpose
Acaromectin is used to treat parasitic diseases in rabbits. List of pathologies for which the drug helps.
- Sarcoptic mange is a contagious disease caused by itch mites.
- Notoedrosis is an invasive disease, the causative agent is the scabies mite.
- Otodectosis - ear scabies.
- Entomoses caused by fleas, lice or lice.
- Demodectic mange is an infection caused by ear, subcutaneous or fur mites.
Ivermectin in the composition changes the magnitude of the current of chlorine ions.
Because of this, the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted, and the functioning of the nervous and muscular systems malfunctions. The parasite becomes completely immobilized (paralysis), followed by death. ATTENTION! When applied to the skin, Acaromectin has a contact effect in places where parasites accumulate.
After absorption, a systemic insectoacaricidal effect begins - the substances enter the general bloodstream and tissues, killing parasites “from the inside.” According to the degree of danger, Acaromectin has class 4 - these are low-hazard substances. If the dosage is observed, it does not have an irritating, toxic or mutagenic effect. Well tolerated by adult rabbits. Not recommended for treating emaciated, pregnant, lactating animals, as well as animals under 1 month old.
Symptoms
This disease is very insidious because it is most often not detected immediately. However, if you are attentive to the animals on the farm, then ear scabies can be detected by some symptoms:
- the animal becomes more irritable and aggressive;
- Appetite is significantly reduced, so weight loss is observed;
- The rabbit often shakes its head from side to side.
If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to carefully examine the ears of the rabbits. If there are red blisters, this is a clear sign that the animal is suffering from tick bites.
Laboratory analysis of scraping the epidermis from the ear helps to accurately diagnose the disease.
Laboratory diagnostics can detect parasites and their eggs in scrapings taken from the animal’s ears. A similar study can be carried out without using a microscope: scrape a little skin from the surface of the inner part of the ear and stir it in warm (heated to 40 degrees) Vaseline oil - small arthropods will be visible under a magnifying glass.
You can learn about the main causes of psoroptosis and methods of its treatment from the following video:
The sooner the owner detects the disease in the rabbit, the faster and easier the treatment will be. In advanced cases, the process of ridding an animal of ear mites can take a long time. The lack of adequate treatment leads to the formation of a large number of scabs and hard crusts in the animal’s ears, which are an ideal environment for the development of harmful microorganisms.
The photo clearly shows what an advanced form of psoroptosis looks like in a rabbit
Is it only the scabies mite that lives in a rabbit's ears?
In rabbits, cutaneous parasites are localized and multiply directly in the ears, but sometimes they crawl onto the body and stay there for some time, and then move on to other animals.
Ticks are found on the skin of the neck and back, extremities with a strong spread, where they get due to scratching.
This is interesting! It is assumed that attachment to the habitat on the body of lagomorphs is associated with insignificant sweating in this area.
Drug treatment
The first stage of treatment for parasites is to rid the animal of hardened crusts and scabs that have formed on the inner surface of the ears.
For this you will need:
- gloves;
- cotton swabs;
- hydrogen peroxide.
To begin with, the rabbit must be well secured so that it cannot resist the procedure. Remember that these animals have quite strong hind legs - with them they can cause injury to a person. Then you need to take a cotton swab, soak it generously in hydrogen peroxide and treat the affected areas of the ears. When the crusts become softer, they can be carefully removed. Removed scabs must be disposed of using bleach or incineration.
Regularly cleaning your ears from dry crusts will increase the effectiveness of using medications
The second stage of ridding an animal of ear mites is to use special medications or various folk remedies. Recommendations for the use of some medications are given in the table:
| Name | Release form | Features of application |
| Dekta | Drops | Before using the drug, the external auditory canal must be thoroughly cleaned of surface crusts and scabs using a cotton-gauze swab soaked in camphor alcohol or hydrogen peroxide. The medicine is instilled into the animal’s ears, 3-5 drops. Treatment is carried out 2-3 times with an interval of 3-5 days. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated until complete recovery. |
| Butox-50 | Ampoules | The contents of 1 ampoule are diluted in 1 liter of warm water. The resulting solution is applied to the inside of the rabbits' ears by irrigation from a spray bottle. The treatment is repeated 3-4 times at intervals of 5-6 days. |
| Acaromectin | Spray | The drug is sprayed onto the inner surface of the ear (previously cleaned of scabs), holding the bottle at a distance of 10-12 cm, 2-3 times a day. Repeated treatment is carried out after 7 days |
| Ivermectin | Ampoules | The drug is used for subcutaneous injections in the treatment of psoroptosis in the later stages in combination with external treatments |
Treatment should begin when the first signs of the disease appear
Description and composition of the drug
The dosage form of the drug Acaromectin is a clear solution with a mild odor. Packaging varies: from 10 ml to 500 ml. Available in polyethylene bottles equipped with an aerosol spray. Large volumes are sold in glass or polymer bottles. Sold without a veterinarian's prescription.
The main active ingredient in the composition is ivermectin. This is a natural substance (a product of fermentation of soil fungi Streptomyces). It is a natural antibiotic, insecticide and acaricide. Auxiliary elements in the composition are isopropyl alcohol and mineral oil extract.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies also work well in the fight against ear mites in rabbits when treated at home. However, it should be understood that they are effective only at the initial stage of the disease.
We offer several proven and most popular alternative medicine recipes:
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs. You can use eucalyptus, chamomile, etc. as raw materials for preparing the decoction. It is best to purchase the mixture at the pharmacy and prepare it according to the attached instructions. The decoction, cooled to room temperature, is drawn into a syringe without a needle and irrigated on the inner surface of the ears.
- A solution of turpentine and vegetable oil (1:2). A cotton swab is moistened in the resulting product and the external auditory canal and skin lesions are treated.
- Camphor oil. Use in pure, undiluted form to clean the ears. The procedure is repeated 3-4 times a day.
In the following video, an experienced rabbit breeder explains how to fight ear mites using folk remedies:
How do rabbits become infected with ear mites and how does it develop?
The source of infection is a rabbit infected with scabies; mites fall out of its ears along with peeled flakes of skin and scabs and move onto healthy animals.
Ear mites on a rabbit
Infection occurs:
- in close contact;
- through objects, bedding, feeders, owner’s clothes, equipment;
- when transplanting healthy rabbits into a room where sick individuals were kept.
In rare cases, cats or dogs that were accidentally infected in a dysfunctional household can carry insects.
Favorable factors for the development of the disease:
- cramped conditions in the cage;
- humidity;
- regrouping of animals;
- malnutrition.
Important! Latent carriage plays a significant role in the spread of infection, when adults and nymphs live in the outer ear of apparently healthy rabbits.
When an optimal environment arises for the continuation of the cycle, arthropod parasites are activated, which causes an outbreak of disease in the herd.
Phases of development
When they penetrate the skin of the ear, mites begin to actively reproduce; one female reproduces up to 60 eggs, which are glued to the skin scales with uterine secretions.
Be sure to read:
Infectious stomatitis in rabbits: treatment of a wet muzzle, why biting midge is dangerous
The further life cycle includes the following development phases:
- Larva. It has 6 legs and emerges after an average of 4 days. Molting occurs after 2-3 days.
- Protonymph. This is the nymph of the next stage.
- Teleonympha. Preparatory stage for puberty.
- Imago. Males become mature 2 days earlier than females.
At sufficient temperature and humidity, development time for males is limited to 14 days, females mature in 16. The parasite lives on the skin of a rabbit for 2 months.
It is best to contact a veterinarian to confirm the diagnosis Hrunya.ru - your indispensable assistant on the farm
Males create copulatory pairs with female nymphs of the second phase, holding the insect with their legs. Fertilization occurs when the female emerges from the teleonymph's shell.
Infested ticks pose a danger in the spread of the disease.
This is interesting! The duration of the transformation phases from egg to adult insect is determined by the temperature and humidity of the environment. At +35°C and low humidity, the life cycle is extended to 55 days.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance and spread of psoroptosis, farmers need to know and follow the following rules:
- places where animals are kept must be dry and clean;
- You should not place a large number of rabbits in one enclosure, as this can cause the rapid spread of parasitic infestation;
- It is necessary to promptly disinfect cells. Experienced farmers recommend doing this twice a year - in spring and autumn. As a disinfectant, use solutions of tea tree oil (2 drops per glass of water), quicklime or soda ash (1:1 with water, after the slaking process another 9 parts of water are added), bleach.
Compliance with animal husbandry rules helps reduce the risk of disease
To exclude the possibility of re-infection with psoroptosis after successful treatment, the following preventive measures must be taken:
- carry out unscheduled disinfection of places where rabbits were kept, not only sick ones, but also healthy ones;
- process the clothes that the farmer usually wears while farming;
- Inspect your animals' ears regularly to detect the disease in its early stages. Particular attention should be paid to pregnant females, since if they are not treated in time, the offspring will most likely be infected;
- Rabbits with suspected psoroptosis must be immediately quarantined, separated from other animals for the entire duration of treatment.
All procedures related to disinfection and treatment must be carried out using disposable gloves.
Efficiency
Acaromectin is a highly effective remedy. Efficiency has been confirmed in clinical studies and experiments. The tests were carried out in Moscow, the initiator was JSC Narvak.
Calculations were carried out empirically, type - critical test. The effectiveness was confirmed to be 85.7% with a single use and 100% with a double treatment according to the scheme. The test animals showed complete freedom from parasitic mites.
The substances in Acaromectin have a detrimental effect not only on adult individuals, but also on their larvae. Therefore, the use of Acaromectin will be effective at any stage of development of a parasitic disease. The effect of the drug begins immediately after contact with the skin of a sick animal.
Complications caused by psoroptosis
- As the disease progresses, the itching in the ears may almost stop. The next stage begins when small ulcers appear on the neck, behind the ears, which then move down to the front legs.
- If liquid exudate comes out of the ear, this means that the eardrum has begun to rupture. This in turn leads to otitis media followed by meningitis. A ruptured eardrum can cause the animal's head to tilt and the ear to droop on its own.
- Frequently shaking the head and ears of a sick rabbit can cause lymph nodes to rupture.
All these reasons, if not eliminated in time, will subsequently lead to the death of the animal.
How to understand that a rabbit has become infected with psoroptosis - ear mites
If a tick is detected, it is necessary to relieve the rabbit of itching, since scratching the ears not only promotes the spread of the tick, but also causes great discomfort to the animal.
Infection with the parasite causes discomfort, so the owner determines the infection by the following signs:
- pets often itch;
- rubs ears with front paws;
- shake their head;
- There is an increased accumulation of wax in the ears, which distinguishes the disease from frostbite.
Examination of the animal reveals scratching in the ear area, redness and nodules filled with fluid are noticeable in the ear canal.
Important! If the disease is asymptomatic, you can suspect the presence of a tick by looking at your pet's dirty ears.