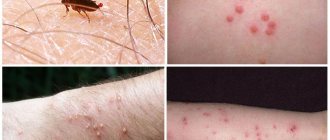
Rat poisoning in humans is rare. Typically, such poisonings occur in children or adults as a result of a suicide attempt.
Source: depositphotos.com
In the fight against a large population of rodents (rats, mice), biological methods are often ineffective, and there is a need to use chemicals, which include rat poison (rodenticide). It is widely used not only in agriculture, but also in everyday life. There are several groups of rodenticides that differ in the mechanism of toxic action on the rodent body. Currently, the most commonly used rat poisons are those based on zoocoumarins.
When is it possible for a person to be poisoned by rat poison?
Mouse poison is dangerous primarily for children, who may try it simply out of curiosity. In addition, they may play with the poison they find and then accidentally introduce it into their mouths through unwashed hands. The greatest danger for poisoning is represented by places where deratization is periodically carried out:
- Warehouses;
- Basements, attics, entrances of residential buildings;
- Country houses, garden plots;
- Preschool and educational institutions;
- Catering and food industry enterprises;
- Treatment and prevention institutions.
Poisons for rats and mice are used for suicidal purposes or as murder weapons quite rarely. This is due to the fact that the dose of the active component in the finished poison is minimal, because it is selected for small rodents, and not for people.
Peculiarities!
Typically, the concentration of poison in rodenticide does not exceed 2%. The rest comes from bait - grain, lard, cereals.
Mouse poison, as a rule, is sold ready-made - along with bait - in briquettes or in bulk. To receive a lethal dose, a person will have to eat about 150 g of this product. Highly toxic toxic substances like arsenic and ratsid, which pose a mortal danger to humans, are now practically not used.
Appearance of poison
This question can be easily answered by those who have often encountered and poisoned rodents. But for those who are faced with such a problem for the first time, this is quite difficult.
There are several types of poison:
- powder;
- briquette;
- powder;
- pills;
- granules.
Also, the difference between poison is that some have a smell that attracts pests, and some are simply odorless; the color palette of the poison is also different.
Also, the use of poisons can be in two variations:
- Just sprinkle the contents of the bag (everything is already packaged in it, and you don’t need to calculate the proportions).
- Scatter it on the floor, after mixing it with some kind of bait.
It is very important to be absolutely attentive in this matter. Poisons are very dangerous to human health and pets.
Types of rat poison and its effect on the human body
Rodenticides are produced in several versions containing active components with different mechanisms of action:
- Highly toxic poisons that are currently prohibited for use are arsenic, white and yellow phosphorus, thallium sulfide, lead. They cause rapid death of rodents, but are equally dangerous to humans. For serious intoxication, it is enough to receive a dose of poison through damaged skin or mucous membranes or by inhaling its particles.
- Preparations that are used to a limited extent for deratization due to an increased level of toxicity are zinc phosphide and naphthylthiourea (ratside). They are used only when zoocoumarins are ineffective.
- Zookoumarins are chemicals based on blood thinners that cause fatal bleeding in rodents. Depending on their chemical properties, they are divided into 2 groups:
- I generation of anticoagulant drugs (ethylphenacin, warfarin, isoindan, ratindan), which begin to act late and are quickly eliminated through the kidneys and digestive tract, and therefore are often ineffective. Moreover, many rodents have acquired resistance to such poisons over time.
- II generation of anticoagulant substances (brodifacoum, bromadiolone, flocumafen, difenacoum), which accumulate in the body, leading to the death of mice within 2-4 days. They exhibit an effect more slowly than the rodenticides of the first two groups, but are less dangerous to others and are quite effective. These products are easy to find on the market, and they are now most often used to bait rodents.
Release forms
Rodent control products are available in various versions. Rat poison looks different. It is produced in the form of aerosols, sprays, gels, creams, pastes, small granules, colored powder, tablets and briquettes.
Read on topic:
Sulfur ointment: instructions for use, price and reviews
15.10.2019
Get Total - a modern means for effective control of insects
25.06.2019
Getting rid of cockroaches and bedbugs with Xulat Micro
25.06.2019
Xulat C25 - a powerful modern remedy for cockroaches and bedbugs
25.06.2019
The poison is odorless, but sometimes special flavorings are added to it to attract rodents. The deadly filling can be mixed with bait, placed on the surface of the ground and in places where mice live.
The most popular products are Inta-vir, Ratindan, Tsunami, Bromotsid. These drugs can be found in pet stores, construction hypermarkets, hardware stores and other specialized retail outlets.
When using rat poison, adhere to all sanitary standards, otherwise the risk of poisoning increases
Poisoning with rat poison occurs if sanitary and safety regulations are not followed. Deratization of institutions is carried out quite often, so people working in them should be notified about this procedure in advance. In addition, they must receive safety training. Most often, rodent extermination is carried out in such public places as:
- catering enterprises;
- educational institutions;
- health complexes;
- residential buildings, warehouses;
- premises related to production;
- enterprises processing agricultural products.
The first signs of intoxication
The initial signs of poisoning usually make themselves felt 3 days after contact with rat poison, but if the accepted concentration of the pesticide is too high, they may appear earlier. The main symptoms that attract attention:
- Dizziness, loss of coordination of movements, feeling of confusion in the head;
- Intense headaches, almost not relieved by analgesics;
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite;
- Nasal, gastrointestinal, uterine bleeding, increased bleeding of gums, bleeding in the urine;
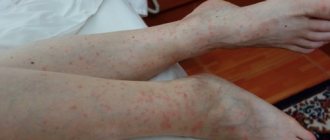
- The appearance of bruises on the skin for no apparent reason;
- Lethargy, drowsiness, lethargy;
- Joint and muscle pain, general weakness;
- Dilated pupils, blurred vision;
- Increased heart rate and shortness of breath;
- Hearing loss, tinnitus.
The severity of symptoms depends on the amount of poison eaten. If a small amount of poison enters the body, then all manifestations will be minimal and will go away spontaneously. At the same time, a person does not even always understand what causes the malaise.
Note!
Intoxication is most severe in patients with chronic pathology of the liver and kidneys, who cannot fully neutralize and remove toxins from the body.
Impact on humans
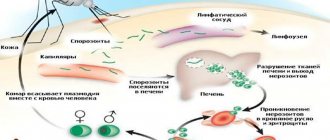
Substances contained in rat poisons also have a certain effect on humans. In most cases, these are anticoagulants, which cause the main symptoms of rat poison poisoning. Their effect is aimed at stopping vitamin K from being absorbed in the body. As a result, blood clotting is impaired and heavy spontaneous bleeding develops.
Without medical care, under the influence of rat poison, a person dies from blood loss.
Giving help
In most cases, you have to provide emergency assistance yourself if it becomes known that you have consumed rodenticide. In such a situation, after taking emergency measures, you must definitely seek medical help.
If several days have passed since the poisoning and the first signs of intoxication have already appeared, then you need to immediately call an ambulance or take the patient to the hospital. You will not be able to help in such a situation on your own, because the toxin has already been completely absorbed into the blood.
First aid
If 2-3 hours have passed since the moment of poisoning, then emergency measures should include:
- Flushing the upper gastrointestinal tract. The patient drinks at least 1 liter of boiled water and irritates the walls of the throat with his fingers to induce a gag reflex. Vomiting is induced until clear liquid is obtained from the stomach.
- Cleansing the intestines with enemas or laxatives (fortrans, magnesium sulfate). Microenemas (microlax) are also quite effective and easy to use. Together with the feces, the toxins “lingering” in it will be released from the intestines.
- Taking enterosorbents - polysorb, activated carbon, enterosgel. These drugs inactivate the poison remaining in the digestive tract.
- Rinse with running water the skin and mucous membranes that have received particles of poison. Most carefully, you need to wash the wounds on the skin.
- Replenishing fluid loss due to repeated vomiting. The victim needs to drink still mineral water or weak tea in small portions.
Hospital treatment
Hospitalization is indicated for severe intoxication. The following therapeutic measures are carried out in the hospital:
- Vitamin K injections for bleeding symptoms.
- Intravenous drip administration of detoxification solutions - rheopolyglucin, hydroxyethyl starches, saline, glucose.
- Lavage of the stomach and intestines, if this was not done immediately.
- The use of diuretics – furosemide, Lasix.
- Prescription of hepatoprotectors (heptral, essentiale, phosphogliv) - drugs that protect liver cells from damage.
- Hemodialysis (“artificial kidney”) for severe renal failure.
- Plasmapheresis is a hardware removal of toxins from the bloodstream.
- Transfusion of blood components in case of massive bleeding.
Enterosgel and treatment of poisoning
The ability of carbon (coal) and silicon (clay) sorbents to absorb harmful substances has been known for a long time. Our ancestors intuitively understood that wounds heal better if they are sprinkled with ashes or covered with clay. Ashes and clay were used for stomach pain, fever and other illnesses.
However, the low absorbency and tablet forms of enterosorbents limited their medicinal properties until recently. The invention of Enterosgel, a new generation gel-like sorbent, at the end of the 20th century opened up additional opportunities for saving lives and treating patients with poisoning.
Enterosgel is especially effective for oral poisoning. Often, its timely use relieves all symptoms of food poisoning, since it absorbs and removes not only toxins, but also pathogenic bacteria, without disturbing the normal intestinal flora. Toxins do not have time to be absorbed into the blood, and bacteria do not have time to multiply and show aggression. Enterosgel removes from the gastrointestinal tract the products of secondary inflammation and intoxication that accompany poisoning with caustic substances.
No matter how the poison enters the body, it enters the intestinal lumen through the intestinal mucosa and is then reabsorbed. Therefore, Enterosgel is used for almost all types of acute poisoning.
Enterosgel is also used to prevent chronic poisoning in people employed in hazardous work.
When is hospitalization needed?
Seeking qualified medical help in case of poisoning with toxic chemicals is necessary in any case. The patient is admitted to the hospital in life-threatening situations:
- Massive blood loss, ongoing bleeding of any location;
- Presence of signs of damage to the nervous system - lethargy, depression of consciousness, visual and auditory disorders;
- Incessant vomiting, dehydration;
- The appearance of symptoms of toxic hepatitis - pain in the right hypochondrium, jaundice;
- Anuria is the absence of urine for a long time.
Injured children and pregnant women must be hospitalized.
Possible complications
Severe consequences of rat poisoning develop in people if medical assistance is not provided in a timely manner. Complications may include:
- increased bleeding of gums,
- development of severe bleeding in response to even minor damage to the skin,
- development of internal bleeding of varying intensity,
- formation of chronic anemia.
All these consequences can be avoided if medical assistance to the victim was provided in a timely manner and in full. Otherwise, intoxication with a fatal outcome is possible.
Antidote for mouse poison for humans
Specific antidotes for drugs of the anticoagulant group include synthetic derivatives of vitamin K: phytomenadione, vikasol. Zoocoumarins increase bleeding by disrupting the synthesis of vitamin K, which ensures normal blood clotting. To compensate for its deficiency, vikasol or phytomenadione are administered by injection - intravenously, intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Tablet forms are not used to treat poisoning due to lack of effectiveness. Vikasol is only allowed to be injected into a muscle; phytomenadione is sometimes given into a vein.
Important!
Phytomenadione should be administered intravenously very slowly due to the high risk of developing an allergic reaction.
The course of treatment with antidotes continues for 2 weeks. During this time, the poison is completely removed from the body, and the natural synthesis of vitamins is restored. During outpatient follow-up treatment, it is sometimes recommended to take Vikasol tablets.
Possible consequences
Poisoning with rodent poison rarely leads to death, since the dose of toxin entering the body is usually small. However, rodenticides often cause serious complications:
- Kidney failure;
- Toxic hepatitis with liver failure;
- Persistent hearing and vision impairment;
- Shock caused by blood loss;
- Inflammation of the upper digestive tract - pancreatitis, gastroduodenitis, cholecystitis.
Severe forms of liver and kidney failure lead to disability. The patient is forced to constantly take medications and periodically undergo hemodialysis courses.
How to avoid poisoning
To ensure that the advice in this article never comes in handy, follow these precautions when working with rat poison:
- Wear a change of clothes, rubber gloves, and a medical mask when laying out the bait.
- After the procedure, wash your hands and face thoroughly.
- Keep the poison out of reach of children.
- Warn household members or employees of the enterprise that deratization is being carried out, and inform them about the places where the poison lies.
- Keep a close eye on small children if they are playing near the bait.
- When processing a garden plot, make sure that the poison does not come into contact with vegetables and fruits. In any case, rinse food thoroughly before eating, because poison particles can reach them through animals.
If there are rats at home or in the country, then it is better to entrust deratization to trained and trained specialists. Then you will minimize contact with chemicals, and you will not have to store them at home. And in some cases, the best effect comes from biological methods of rodent control: just get a cat and the problem with mice will be solved.
Catching rats. What you should know
Rats are smart creatures and sometimes catching them in traps is quite problematic. Here you need to adhere to the following rules:
- Before setting traps, you need to get rid of all crumbs, food, and water in the house. Carefully check all cabinets where food is stored for holes and cracks. Maintain hygiene, ventilate the room and take out the trash to deprive rodents of their last opportunity to eat. Rats, in the absence of food, will be more willing to fall into your traps.
- Traps should not be placed in a random order, but where the approximate location of the rats is in your home. Find the entrances to the burrows along the walls, also pay attention to where there is a large accumulation of parasite feces and place them there. Here
- You need to understand that if you place a trap in the center of the room, it will not bring you success, since rats run along the walls and hide from people’s eyes.
- Rats have a very developed smelling apparatus, which is why do not touch traps with your hands, only with gloves. All traps must be clean and free of foreign odors. Before using the trap, you must rinse it well and only then use it. And this procedure needs to be done several times. After you catch a rat, it is necessary to wash the trap, because the next victim will not fall for it if the trap is not washed.
- Bait. It should be a product with a strong odor - smoked or fresh meat, slightly burnt lard, sausage, minced meat, fish, bread soaked in vegetable oil. Cheese is not always effective. The bait must be changed periodically to ensure it remains attractive to rats.
- It is necessary to select traps of appropriate quality. This is especially true in cases where a rat is caught alive - then products made from materials that it can easily chew through will be ineffective. If part of the trap is adjacent to a wall or floor, care must also be taken to ensure that the rodent does not damage them. When catching large rats, you should choose traps from which this rather large animal will not be able to escape and which it will not be able to throw.
It is worth remembering that when you remove a rodent from a trap, it is important to do this with gloves, since the slightest wound can lead to serious consequences and illnesses. After completing the procedure, be sure to wash your hands with soap and water.
Also pay special attention to children and pets. There are a lot of cases where small children fell into traps and traps. All traps are, of course, safe for human health, but some mechanisms are designed in such a way that they can cause injury to a cat, dog or child.
Now let's look at rat poison from rats.
There are several groups of toxic substances.
- Instantly toxic substances. If a rat swallows just such a bait, then death will occur after the poison enters the stomach, that is, immediately. As a rule, such poisons have a mummifying effect, which means that after the rat dies, it will not smell disgusting, but will immediately begin to dry out.
- Long-acting anti-inflammatory agent. If such bait gets into the rat's stomach, then death will occur within 1.5 -2 weeks, depending on how much poison got into the stomach. In any case, the toxic substance in the rat's body will slowly destroy the circulatory system.
Each type of poison is unique in its specificity. Some have a detrimental effect on the nervous system, some on the digestive tract, and some simply kill by causing paralysis.