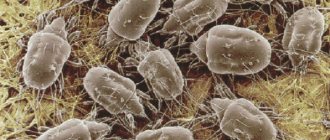
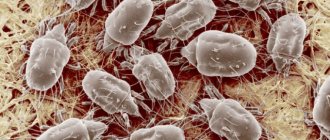
Demodicosis is a parasitic disease caused by demodex mites. Almost all animals have subcutaneous mites, and under a number of factors they become active and begin to multiply, causing inflammation of the skin, itching, and hair loss.
The disease is contagious, and therefore requires isolation of the infected individual from others, as well as sterilization due to the transmission of the disease by inheritance. To stop the disease, it is necessary to begin treatment as soon as possible using modern medicines.
By following the veterinarian's recommendations, it is possible to achieve complete recovery in almost 100% of cases.
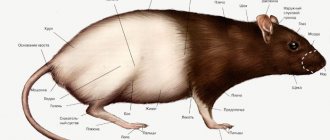
Rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti) – what it looks like, life cycle, habitat, features
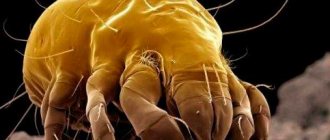
This is a small tick, the body length does not exceed 1.44 mm, but individuals with a length of 0.78 mm (females) and 0.53 mm (males) are more common. Offspring parameters:
- eggs – 0.34 mm;
- larvae – 0.3 mm.
Rat mites, like other representatives of the order, are covered with sensitive villi. They have 4 pairs of limbs, but the front 2 legs are longer. The outer covers are transparent light brown. After eating, the tick enlarges several times, and the color changes to dark red.
The parasite climbs onto the host when it needs to get a portion of food. It has a piercing-sucking type of mouthparts, which allows it to pierce the skin and suck out blood at a rapid pace, since the digestive system works on the principle of a pump. It is found in temperate and tropical climates, but does not live in cold regions. The main host is a rat (gray).
In the absence of a food source,
the parasite transfers to the mouse. Less often it bites other rodents.
If there is no suitable food nearby, rat ticks can bite a dog or cat, and sometimes a person. But at this stage of life the pest does not reproduce. For the birth of offspring, the blood of rodents is necessary. Moreover, the life expectancy of a person is 1.5 months. Life cycle of pests:
- egg;
- larva;
- protonymph;
- deutonymph;
- imago.
Moreover, the development cycle is short - about 16 days, sometimes less (from 7 to 12 days), which is determined by the ambient temperature. Most often, such pests live for 2.5 months, but the lifespan of males can be reduced to 45 days. Females, on the contrary, can survive for 9 months. They lay up to 100 eggs during this period, but they do this not at once, but in batches one at a time.
Rat ticks can carry serious diseases
Attack of rat ticks on adults and children - complications
Soon after a bite, people develop dermatitis of unknown etiology. Moreover, they are complicated by severe itching, the formation of papules, vesicles, and rashes over large areas of the skin. Bite marks are found where the fabric of clothing adheres more tightly to the outer skin. At the same time, a hyperemic area appears. Less frequently, the temperature rises and headache appears. This is caused by the body’s reaction to the substance introduced by the rat parasite (in saliva), as well as harmful microorganisms that the pest carries on its body.
Rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti)
What medications are used to make you feel better after bites?
When rat mites attack a person in an apartment, you need to use the most effective means with antiseptic, antimicrobial and antiparasitic properties:
- Benzyl benzoate ointment;
- Sulfuric ointment;
- Wilkinson's ointment;
- Bensocryl;
- Salicylic-zinc paste;
- Spregal.
What and with whom can the reaction to rat bites be confused?
When traces of contact with parasites appear, it is important to recognize who exactly attacked. If the tick has already crawled away, you need to be guided by the external signs of bites. A red spot remains with a dark dot in the center. These are nonspecific signs characteristic of most parasites. At the initial stage (during the first day), the bites of the rat parasite resemble traces of contact with mosquitoes and midges. But in the first case, the affected areas of the skin do not change much. In comparison, dermatosis caused by rat pests develops dermatitis later.
Midge bites
more painful, the affected tissues soon swell.
Rat tick bite on a human body
Rat mites can be a carrier of very dangerous diseases for humans.
Such parasites are carriers of pathogenic microorganisms, and they also pose a danger to humans. Diseases spread by such pests:
- rat typhus;
- Q fever;
- Lyme disease;
- icteric leptospirosis;
- smallpox or vesicular rickettsiosis;
- tick-borne encephalitis;
- West Nile fever;
- tularemia;
- plague.
Bed bugs on rodents
Bedbugs are very rarely found on pet rats. Like fleas, a rat will only have bedbugs if another pet (such as a dog or cat) has them.
Make sure all your non-rat animals are on a high-quality flea (and bedbug, if necessary) preventative. Over-the-counter products are not always effective or safe. The best flea and bedbug treatments are recommended by your veterinarian. If your dogs and cats don't have fleas and ticks, then your rats shouldn't have them either.
Where do parasites come from in decorative rats? Precautionary measures
training rats - perhaps at the right time, thanks to training, the rat will not eat what it does not need.
How and where do they come from? Most often - from the filler that you use in the cage (we are talking about natural fillers - hay and sawdust). Inexperienced owners, in order to save money, purchase them not in special stores, but at sawmills. The result is infection of animals, since such material is not disinfected in any way. It is also easy to bring dangerous animals on your own body from the street. So the main ways to prevent misfortune are to use a safe litter and wash your hands thoroughly before each contact with the animal.
Causes
The disease is provoked by weakened immunity, stress, hormonal imbalances, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and oncology. The disease is transmitted in the following ways:
- from the mother in utero or after birth,
- contact from a sick individual,
- through food, bedding, care items.
Often, owners acquire already sick animals, which may not show symptoms, but they become a source of spreading demodicosis to others.
Description and photo of rat and mouse mites
Everyone knows about ixodid ticks. Instructions on what to do if you are bitten by an ixodid tick can be found at any medical facility. Few people have heard of Gamasidae. Even fewer people have thought about how dangerous these ticks are to humans. They are so small. Gamasid bloodsuckers usually do not tolerate tick-borne encephalitis, but they can also cause a lot of trouble. The rat mite is especially dangerous. It was he who previously carried typhus from rats to humans. Today his main “specialization” is tick-borne dermatitis.
Rat mite (Ornithonyssus bacoti)
An obligate temporary ectoparasite of rats, capable of feeding on the blood of other mammals. It was first discovered in Australia. But rats are not endemic to Australia. It’s just that some diseases were not previously associated with this type of tick. The rat mite was later identified in the United States as a source of dermatitis in humans. A few years later, it caused people to become ill in Hamburg.
The parasite was first discovered in 1913 due to its size. The length of its body is only 0.75-1.44 mm. If you look at the photo of a rat tick, it turns out that it is very similar to the common ixodid tick. There are also differences:
- there is no segmentation between the body and chelicerae;
- oval genital shield;
- cranial anus;
- pointed tail apex.
Rat mite
The color of sucked ticks is not light gray, but dark red in females or yellow in males. Hungry parasites are gray in color. After feeding, they are unable to move; when hungry, they are very active.
Diseases
The parasite's bites cause an itchy skin irritation in humans called rat mite dermatitis. Children may have an eczematous or vesicular reaction to the sting. Rat mite attacks must be differentiated from other insect bites or skin irritations caused by the body's reaction to an allergen.
Treatment of rat tick-borne dermatitis is symptomatic. To alleviate the condition of the victim, use:
- oral antihistamines;
- topical corticosteroids;
- benzyl benzoate;
- gamma-benzene hexachloride;
- Crotamiton.
But often the irritation goes away on its own or people simply do not react to the saliva of rat bloodsuckers.
Rat mite
The reaction to rat parasites must be separated from the symptoms:
Laboratory studies have also shown that rat mites can carry dangerous diseases:
In unfavorable times, rat ticks, along with fleas, were the main carriers of typhoid and plague from rodents to people.
Major rat parasites
In decorative rats you can find different types of ectoparasites, all of which cause unbearable itching and anxiety to the animal.
lice eaters
Red wingless small insects no larger than 1 mm in size with an oblong elongated body covered with bristles, shaped like cat fleas. In light-colored rodents, adult insects can easily be detected in the fur. Rat pests feed on particles of the epidermis and blood of the rodent.
Infection of domestic rats with lice eaters is accompanied by severe debilitating itching in the rodent; the domestic rat becomes very restless, twitchy, often itches intensely, refuses to eat, and progressive exhaustion is observed. There are numerous wounds, scratches, and bruises on the pet’s body, accompanied by severe swelling and inflammatory processes.
Lice eaters in rats multiply rapidly; an adult female lays more than a hundred nit eggs, which stick to the animal’s fur. The owner can detect light shiny inclusions on the lower back and near the tail, fixed in the pet's hair and reminiscent of ordinary dandruff. It is almost impossible to remove nits from a rat's fur, only by completely removing the animal's hair. A huge number of larvae emerge from the eggs, which within a month become adult, sexually mature individuals.
The parasitism of lice eaters in rats is dangerous due to the death of the pet, so treatment should begin at the first characteristic symptoms of infection.
Lice
Lice in rats cause severe itching and anxiety; these parasitic insects feed only on the blood of a domestic rat; per day, one louse attaches itself more than 10 times to the animal’s skin. Adults can only be seen under a microscope; the body size of the parasites is no more than 0.5 mm.
Rat lice are small red insects with an elongated body, at the head end of which there are hooks for holding on the animal’s body and two sharp stilettos for piercing the skin. The louse cuts through the skin, injects substances that prevent the rodent's blood from clotting, and attaches itself to the animal's body.
Reproduction of lice occurs in the same way as in lice, with the deposition of nit eggs and the hatching of nymphs, which turn into sexually mature individuals. White shiny nits of lice can be found on the fur of a rat; parasitism is accompanied by severe nervousness of the animal, active itching, lethargy and apathy of the pet; the development of anemia, typhus and hemobartonellosis in the rat is possible.
Fleas
Rat fleas are unpleasant blood-sucking insects of a red-brown color with a characteristic body flattened on both sides, the size of the insect is 2-5 mm. The flea is capable of jumping long distances and clinging to the host's fur with tenacious claws, and is capable of migrating between cats, dogs and rats.
When infected, pets constantly scratch itchy areas, become restless, and may develop anemia. Dried burgundy crusts can be found on the animal's body - flea secretions; when bathing a rat, they turn the water pink.
Mites are very common in rats; there are several types of parasites that live on the skin and in the epidermal layer. The rat tick is red-brown in color, 0.1-1 mm in size, has an oblong flat body, feeds on the blood of an animal and carries various serious diseases. With a lack of nutrition, the tick is capable of attacking humans.
IMPORTANT!!! Rat mites are dangerous to humans! People, especially children, have a hard time with eczematous dermatitis, which develops as a result of parasitism by these insects. Ticks infect people with typhus and murine typhus, tularemia, plague, rickettsial infections and Q fever.
Subcutaneous mites live in the upper layer of the epidermis under the skin of a rodent. It is impossible to visually detect these mites; the diagnosis is made only on the basis of examination of skin scrapings under a microscope.
Parasitism of ticks on the body of a rat is manifested by characteristic symptoms: hair loss and the formation of multiple swollen red wounds on the neck, head, spine and shoulders of the rodent.
Ear mites primarily attack the delicate skin of the ear, pinna and nose, which is manifested by the appearance of yellow or red growths on the ears, nose, limbs and genitals.
Bedbugs
Ordinary bed bugs can also drink blood from decorative rats, causing severe itching, scratching, anemia, and infection with blood parasites. Bedbugs attack domestic rodents during periods of food shortage or the absence of a person nearby as a food source.
Parasitic diseases of rats
In decorative rats, parasitic diseases caused by fleas, lice, and lice are most often diagnosed. The reason for this is the lack of regular treatment of cells and household items, and unbalanced nutrition.
Fleas on rats
The causative agent of flea infestation in decorative rats is ectoparasites from the order Siphonaptera. This disease is diagnosed as aphanipterosis. It is accompanied by dermatitis, since flea saliva contains toxic substances that cause allergies in the rodent.
The danger of flea infestation is that one flea can drink up to 11–16 μl of blood per day. And with mass reproduction, this can cause anemia in a decorative rat.
Aphanipterosis is accompanied by itching, which leads to scratching on the skin. When bacteria and infections get into open wounds, they begin to fester. This leads to a chronic relapsing course of the disease.
Lice and lice in rats
Infection of a decorative rat with lice and lice-eaters is diagnosed as pediculosis. The incubation period of the disease can last about a month.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- constant itching;
- red dots, scratches in the muzzle, neck, shoulders;
- anemia, causing weakness, drowsiness;
- refusal to eat;
- sudden weight loss.
The danger of pediculosis is that its pathogens are also carriers of diseases such as typhus and hemobartonellosis.
Weight loss
Signs of rat tick bites
The favorite localization of bites is in places with the most delicate and thin skin. Most often, bites can be found in the following areas:
- under clothing that fits tightly to the body: belt area, collar area, cuffs;
- depressions on the body: armpits, navel area, ears;
- in skin folds: inguinal folds, on the abdomen, under the mammary glands.
Symptoms of a tick bite include the following:
- sensation of something crawling across the body, moving;
- itching of the skin in the area of the bite;
- skin hyperemia;
- a black or brown dot if the parasite has attached itself to the body;
- a red dot if the tick has fallen off;
- rashes on the skin;
- rise in body temperature to individually high numbers.
What are the consequences of being bitten by rat ticks?
After a bite, the tick attaches itself to the skin, or more precisely to the blood capillaries located in it. It may well turn out that the insect itself is infected with certain microorganisms, because rats are unclean animals, they walk and sleep anywhere, and eat whatever they can find. Therefore, after a tick bite, the victim has a high probability of contracting the following diseases:
- typhus;
- plague;
- smallpox types of sores;
- coli;
- tsutsugamushi, which means “river fever” in Japanese;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- high degree of intoxication of the human body;
- Q fever, which causes severe kidney syndrome and other diseases.
Infection is transmitted through bloodstreams to other organs. Some of the diseases caused by tick bites are extremely dangerous. For example, the development of Japanese river fever in a person if treated incorrectly or delayed, can be fatal.
Pet pathologies
Rats and mice living at home do not like drafts and are susceptible to respiratory diseases. Initial grunting, snoring, and wheezing quickly develop into pneumonia with a high risk of death.
Decorative mice suffer from a viral infection - mousepox, which ends in death in 80-90% of cases.
Infectious diseases of rats and mice:
- Tuberculosis.
- Arachnoses (parasites).
- Pneumonia, ARVI.
- Mycoplasmosis.
The constant companions of wild rodents are skin parasites (ticks, fleas, lice eaters) and ringworm. Pets are also sensitive to them, but diseases appear if they are poorly maintained.
Tumors of various origins, problems with teeth, gums, and urolithiasis are diagnosed as non-infectious diseases. Older rats suffer from cardio-renal failure and obesity, which is not surprising given a sedentary, well-fed lifestyle. This manifests itself in dysfunction of the respiratory system, water retention and swelling. You need to pay attention to the gastrointestinal tract, especially with improper feeding.
What symptoms do the bitten areas show?
Ticks love to bite most of all where a person's skin is thinnest and most delicate. If anyone is wondering where to look for such a tick on the body. Where he likes to go most of all, we can say with confidence that these bloodsuckers really like to suckle in places such as:
- under clothes that fit tightly to the body - under the belt, for example, where the collar, cuffs are, under the straps on the wrist, and so on;
- in the depressions on the body - armpits, navel, ears, etc.;
- inside folds of skin - in the groin, on the abdomen, under the mammary glands.
The symptoms of a tick attack and the appearance of the bitten areas can be represented by the following manifestations:
- There is a feeling as if someone is crawling over the body or moving in one place.
- The affected area is constantly itching.
- Redness of the skin at the site of the bite.
- A black or brown dot if the insect has attached itself to the skin.
- A red dot on the skin if the insect fell off on its own after drinking blood.
- A rash if enough time has passed after the bite for an infection reaction to occur through the blood.
- An increase in temperature already indicates infection of the body.
General symptoms persist for about two weeks, and the bite mark can still last 20 days. After this, the disease caused by the infection enters into an active phase if you do not rush to treat the bitten area in time.
Gamas mite in the apartment
Predatory gamasid mites, which attack people and pets, most often end up in apartments for one of the following reasons:
- Parasites entered you on their own from the street through windows, cracks in window frames, and ventilation.
- We arrived with pet hair, shoes, clothes, and shopping.
- They crawled from the basement, attic or cavities in the structure of a building or house where birds nest, rodents, amphibians and other insects live.
In order for a gamas tick to feel comfortable in an apartment, it needs:
- Food sources - people or animals
- Darkness
- Air humidity above 50–60%
- Increased warmth
Gamasid mites do not live permanently on those they bite. In nature, attacking birds, animals, amphibians, reptiles and insects, they usually settle near or inside their burrows, nests or other shelters. In a person’s home, the insect will find a place similar to what it chooses in nature. It can be:
- Products made from down and feathers
- Products made from natural fabrics
- Houseplants
- Small and large household appliances
- Cracks, space behind peeled wallpaper
- Area under the window sill
- Interior items, especially from natural materials
Parasites are attracted to heat, movement and carbon dioxide. It is these criteria that they will be guided by both when choosing shelter and when choosing a food source. To avoid wasting time looking for food, ticks are likely to choose a place for nesting near a bed, sofa, armchair or chair where a person spends a lot of time. If there are pets in the house, this could be a bed, a scratching post, toys made of fleecy materials, bedding in a cage or a terrarium.
How to distinguish a healthy pet from a sick one?
A healthy pet always:
- well-groomed, shiny coat, without bald patches or tangles (if the rodent is not hairless)
- clear skin, no wounds, eczema or rashes
- clear, shiny eyes without discharge
- clean nose and ears
- clean area under the ponytail
- smooth breathing without wheezing or whistling
- moderately well-fed body, without protruding bones
- behavior is normal, without sudden changes, appetite is preserved
If you are already the owner of a small pet, then you need to adhere to the following rules to avoid diseases of your little friend.
Infection of residential premises
Unfortunately, situations are possible when rat and mouse parasites infect apartments. This is a truly serious problem that requires the help of specialists. The first thing you need to do is make sure that the room is infested with rat mites. This can be done by a disinfectant. In the event that infection is confirmed, disinsection is carried out.
When carrying out disinfestation, potent drugs are used that are aimed at getting rid of parasites. In this case, it is necessary to treat all possible locations of insects. In cases where pets live in the house, be sure to visit a veterinarian who will recommend a remedy for treatment.
It is very important in this situation to find the cause of the infection; if this happened due to the presence of mice and rats in the basement, then this room must also be treated, since the situation will repeat itself.
Vaccination of rabbits
- Associated vaccine against myxomatosis and viral hemorrhagic disease (VHD) of rabbits, dry . After vaccination, immunity occurs on the 5th-7th day and lasts for at least 12 months against VGBV and 9 months against myxomatosis. The vaccine is used from 1.5 months of age. Rabbits are vaccinated at any period of pregnancy. Revaccinate every 9 months. In areas unfavorable for myxomatosis and VGBV, young animals are revaccinated after 3 months. It is prohibited to vaccinate sick animals. Before administration, the vaccine is dissolved with saline or distilled water and administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly in a volume of 0.5 cm3.
- The Nobivak Myxo-RHD vaccine against myxomatosis and viral hemorrhagic disease of rabbits forms immunity after 3 weeks, which lasts for at least 12 months.
When using any of these vaccines, only clinically healthy animals are subject to vaccination. Vaccination is carried out by a doctor after a complete clinical examination of the animals. A mandatory rule when carrying out vaccination is regular deworming of rabbits or preliminary 10-14 days before vaccination. It is prohibited to vaccinate clinically sick or weakened rabbits.
If you have a small animal, then it has already become a member of your family, which has the right to attention, care and love.
Remember, contacting a veterinarian in a timely manner will help save your pet. Due to the rapid metabolism of a pet, any disease develops faster than in larger animals.
When writing the article, material from Yu.E. Malysheva was used. veterinary surgeon, leading specialist in the treatment of rodents and exotic animals (rodentologist), veterinary clinic "AmVet", Moscow
Health to you and your pets!
Treatment of decorative rats for parasites
The best thing to do would be to go to the vet immediately. But, unfortunately for rat lovers, veterinarians who specialize in rodents are not so easy to find. Therefore, we will try to do it on our own.
Parasites in decorative rats
An ordinary veterinarian, not a veterinarian, will most likely diagnose your rat with a food allergy and recommend eliminating protein foods from the animal's diet. But judging by your description, the animal suffers from parasites. These can be lice eaters, as well as ticks. The first type of parasites is easy to see if you part the animal’s fur - they are small, reddish in color, swarming in the fur. The nits of these insects are white particles; they hang, firmly glued to the hairs of the rat's fur coat. Especially many lice eaters can be seen on the withers of a rodent.
As for mites, due to their small size, they can only be seen with a microscope. The doctor at the veterinary hospital takes a scraping for this purpose. However, mites may not be included in this analysis, and then the result will not be indicative. Indirect signs are scratching, scabs, scabs, especially in the neck and muzzle.
Fleas are also ectoparasites, so you can get rid of them from a rat using the same drugs that are intended for the above-mentioned parasites.
Treatment of rats for lice, ticks, fleas
Please use any of the suggested medications to cure your pet.
Unoiled. This drug is inexpensive and can be found in almost all pharmacies. It is very effective in getting rid of any ectoparasites. But you have to tinker a little:
- You need to dilute a 2 ml ampoule of the drug with warm water (400 ml).
- Place the rat on the edge of the bathtub or sink, holding it with one hand.
- Gently soak a cotton pad in the solution and, without squeezing, wipe the animal over the fur. First, the back, then the tummy and chin, we wipe the shoulders very carefully and scratches and wounds are treated without fail.
- Be confident and calm.
- Avoid contact of the solution with the animal's eyes, nose and mouth.
- Soak the rodent generously in the solution, wring out the fur a little and wrap it in a warm cloth (towel).
- There is no need to wash off the drug!
- You need to wait for the skin to dry completely. Make sure that the animal does not lick the fur while it is wet!
- Keep your rat in your arms and warm. After the wool dries, the drug ceases to be toxic.
- After 10 days, repeat the treatment.
- The rodent's house, cage, dishes - everything also needs to be carefully processed.
You can use an aerosol for cats called “Bars”. A good remedy for lice. Be careful - only aerosol, not drops! Attention! The active ingredient must be fipronil! Read the composition! The drug may contain permethrin - this aerosol cannot be used to treat rats! To use, just point the bottle at the rodent’s withers and press once. Check the drying of the drug. Until the medicine has dried, you should not allow the rat to lick or wash itself! Where there is the most scratching on the skin, you can wipe it with a cotton pad soaked in the medicine. After 10 days, repeat the treatment.
Prazicide complex - use drops on the withers. Attention! Do not use the anti-worm suspension, the name is the same, but for oral administration. A good remedy for any subcutaneous mites. You need to part the fur at the withers and drop 1 drop of medicine onto the skin. In the same way as in the case of previous drugs, we hold the rat in our hands until the medication dries completely.
How to avoid re-infection of rats with parasites
Prevention of ticks, ticks and fleas in rats:
- Wash your hands before handling your rat. Otherwise, you can easily bring her parasites - from the street or from the dog you just petted.
- Do not buy random bedding on the market (sawdust, hay), because... she may be infected. Only in briquettes and a high-quality analogue from a pet store.
- Create optimal living conditions for your rat. Parasites most often affect weakened animals kept in an inappropriate environment.
- Nutrition should be complete and varied.
- Clean your pet's cage frequently.
Finally, I will say that rat lovers are convinced that specific rat parasites are not dangerous to humans.
Quarantine
- Preventive quarantine when introducing new animals into a group is 14 days. During these 14 days, animals are kept separately, regardless of where or from whom you purchased these (or one) animals, and regardless of the fact that these animals do not show any signs of illness. During these two weeks, the animals are monitored and hygiene measures are observed to prevent the transmission of possible infections through hands and animal care items. It should be remembered that hands are the main source of transmission of infections and infestations.
- Quarantine can be not only preventive, but also forced. The necessary measure is to keep clinically healthy animals isolated from clinically sick ones. Otherwise, the entire group of animals can become infected and fall ill. And then the scale of the “disaster” can become significant.
- Mycoplasma pulmonis and Streptococcus pneumoniae are pathogens that cause chronic respiratory syndrome in rodents and can be transmitted by direct contact and by airborne droplets. These pathogens infect the lungs, cause otitis media, and in females cause the development of endometritis. Mycoplasma and streptococcus are dangerous for rats, hamsters, gerbils, guinea pigs and chinchillas. Rats, often suffering from otitis media and systemic respiratory infections, become over-infected in a group and everyone gets sick.
- Chinchillas are re-infected with giardiasis and everyone in the group gets sick.
- Myxomatosis in rabbits is extremely contagious. To date, there is no effective treatment for myxomatosis. Vaccine prophylaxis is used.
Following simple quarantine rules will help keep your pets healthy and alive.
Remedies for rat tick bites
Before using any remedy for tick bites, you must directly remove the tick itself. To do this you need to do the following:
- steam the affected area, soften the skin with cream;
- disinfect the skin by treating it, for example, with alcohol, Chlorhexidine, Septocide;
- remove the tick using a special twister;
- consult a doctor.
After removal of the parasite, antihistamines are prescribed (for example, Cetrin, Loratadine). Medications with antiparasitic and antiseptic effects are also used.
Benzyl benzoate ointment 10%
It is an antiparasitic drug used topically. Available as an ointment in metal tubes or glass jars.
The duration of treatment is about 4 days.
The first treatment with ointment is done in the evening before going to bed. The skin of the arms, torso, legs, including the soles and fingers are treated. Treatment is carried out on clean skin. After treatment, you should put on clean underwear and clothes. In the next 2 days, it is necessary to take a break from therapy, and it is forbidden to wash off any remaining medication from the skin. On the 4th day in the evening, repeated treatment is carried out, similar to that on the first day. On the 5th day the ointment is washed off.
Sulfuric ointment
It is an anti-itch agent and is used externally. The product is released in the form of an ointment in metal tubes.
The duration of treatment is from 7 to 10 days.
The drug is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 2-3 times a day for the specified duration of treatment. After completion of therapy, taking a bath is allowed; changing underwear and bed linen is necessary.
Wilkinson's ointment
It is a product for external use, which contains tar, sulfur, and naftalan oil. Has anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, antiparasitic effects. The product is produced in the form of an ointment in tubes and glass jars.
Used externally. Once a day, the ointment is rubbed into the skin of the entire body, excluding the face and scalp. Duration of treatment – 3 days.
Treatment for external and subcutaneous parasites (fleas, lice, lice)
- Although small decorative pets are neat animals, even under comfortable living conditions, external and subcutaneous parasites still occur
- If your pet has become restless, often itches and bites fur with its teeth, scratches, bloody crusts, and areas of baldness appear on the body, then it is quite possible that there are external or subcutaneous parasites.
- Be sure to consult a veterinarian to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, otherwise the parasites can cause exhaustion and death of the fluffy. Clarification of the type of parasite is necessary to select a drug, since they are different for external and subcutaneous parasites.
- Treat your pet with insectoacaricidal preparations. Green Fort drops , Deltsid, Dana spot-on, Green Fort bio spray , Fiprist spray, Leopard spray.
- In case of complications, the animal is prescribed anti-inflammatory ointments, immunostimulating drugs, a course of vitamins and antibiotics.
- When kept in groups, all animals need to be treated
- At the same time as treating your pet, you must: Throw away the bedding
- Treat the cage, all accessories and the entire room with insectoacaricidal preparations
- Change filler
- During treatment, your pet's nails should be trimmed short to prevent scratching.
- Parasites affect animals with low immunity, so strengthen your pet’s health with a balanced diet and the addition of vitamins.
Prevention measures
Preventing the occurrence of rat mites primarily involves timely getting rid of rodents that carry them. Includes the following measures:
- Control over the size of the rat population and constant measures for deratization in areas inhabited by rodents.
- Isolation of premises from rats. The sealing of manholes is carried out by residents.
- Maintaining premises in proper sanitary and technical condition.
You should know that rat mites reproduce in warm conditions and in the presence of food. It can develop all year round, but is especially active in the spring. Parasites are very easy to disinfest and die almost immediately. Most often, to get rid of them, a one-time treatment of the premises is enough. However, after a while they may appear again if preventive measures are not followed. If ticks reappear, acaricide treatment is carried out again.
Sources
- https://misterklop.ru/klesshi/krysinye-i-myshinye-kleshhi-kto-eto-kak-vyglyadyat-na-chyom-parazitiruyut-mogut-li-prichinit-vred-cheloveku-sposoby-borby-v-domashnih- usloviyah
- https://likehamster.ru/domashnie-krysy/o-zdorove/parazity-u-krys-kak-borotsja/
- https://parcenter.ru/myshi-i-krysy/kleshhi-u-dekorativnyh-krys.html
- https://homkin.ru/krysy/zdorovie-krys/blohi-vlasoedy-vshi.html
- https://hlopklop.com/zhiv/krysinye.html
- https://dezplan.ru/vopros/krysinye-kleshchi-foto-ukusov-i-lechenie
- https://TezarVape.ru/ektoparazity/kleshchi-u-krys.html
- https://sichovka.ru/parazity/gamazovye-kleshchi.html
[collapse]