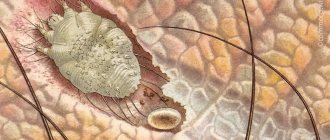
Among all cat problems, a contagious disease that is caused by a group of scabies mites stands out. Parasites penetrate the skin, causing a lot of anxiety to the animal. Unpleasant symptoms accompanied by itching are only the visible part of the iceberg. Scabies in cats can have serious consequences. To eliminate the disease, it is necessary to diagnose the type of pathogen in time and treat the pet with prescribed medications.
Signs of the disease
global $ads_google; //data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?>
$ads_google = true; ?> } ?>
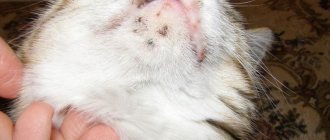
Scabies in cats manifests itself with a whole range of symptoms. They begin to appear as the tick spreads across the animal's skin. As a rule, infection begins from the cat's head. Signs become apparent 5-7 days after infection. Thickened formations covered with crusts appear at the site of parasite penetration. Such plaques can be seen on the center line of the nose, at the base of the ears, along the eyebrows.
Further, the symptoms expand. The changes concern mainly the skin, but since they affect the pet’s well-being, behavior changes. The animal becomes irritable and even aggressive. The cat may refuse food, sleep poorly, and not participate in games. Common signs of scabies are:
- frequent scratching of the body and head;
- deterioration in wool quality and hair loss;
- formation of bald spots on the body;
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- the appearance of white pustules;
- redness and suppuration of scratches;
- covering of the opened papules with scales.
The appearance of even one of the signs of scabies in a cat is a reason to consult a veterinarian.
Methods of infection
The main route of infection is contact. Outside the host, the tick can live for a very short time; all processes of feeding, growth and reproduction take place only in the skin of the animal. However, notoedres cati is highly contagious between cats. If someone in a group of animals develops this disease, it is highly likely that all of them will soon become infected. In the environment, a tick can live up to a week and still remain infectious. That is, even cats that live only in an apartment without access to the street have a small chance of becoming infected with a tick that the owners brought from a walk on clothes or shoes.
Since the body’s own immunity also plays a role in the development of clinical symptoms, it is quite rare to see notoedrosis in street cats. However, such cats can be hidden carriers, meaning that they themselves do not get sick, but can infect others - for example, your pet cats.
Types and causes of the disease
Not all cats are susceptible to infection. This may be due to direct and indirect reasons. They relate to the physiological state of the animal, its care and a number of other circumstances. The development of scabies in cats is promoted by:
- decreased immunity;
- unsanitary conditions;
- lack of insecticidal treatment;
- kitten age up to two years;
- genetic predisposition.
Scabies mites are microscopic organisms; their sizes are measured in fractions of a millimeter. The shape, body length, and structural features depend on the biological species. This determines the type of disease. Various mites cause demodicosis, otodectosis, notoedrosis, and sarcoptic mange. In each case, its own specific symptoms are observed and adequate drug treatment is prescribed.
Demodicosis
The causative agent is the light gray Demodex canis mite. The parasite settles in hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Infection sometimes occurs in the newborn period. Affected areas may be small - up to 2.5 cm (localized form) or spread over most of the body (generalized form). The first one often goes away on its own.
Demodicosis manifests itself in the form of scaly redness or in the form of ulcers and ulcers. The generalized form of the disease often combines both symptoms. In this case, it is very difficult to treat the cat, as complications often arise.
global $ads_google; //data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?>
$ads_google = true; ?> } ?>
Otodectosis
The ear mite Otodectes cynotis parasitizes the external and internal parts of the auricle. This type of disease is accompanied by the formation of scabs and scales on the surface of the auditory organ.
A strong putrid odor emanates from the affected area. Ear mange causes your cat to constantly scratch his head and especially his ears.
Notoedrosis
The disease, often called scabies, is caused by the Notoedres scabies mite. It has a round shape and gray color. This type of disease in cats affects the outer side of the ear. A gray liquid with an unpleasant odor accumulates in the affected areas.
Due to the discharge, the fur sticks together, later it begins to fall out and the pet’s head goes bald. In exposed areas, scales accumulate, forming scabs.
Sarcoptic mange
The causative agent of the disease is the yellowish or completely white mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The parasites first settle on the cat's face and then spread to the entire body. The diagnostic sign is the formation of red spots with thin gray lines with a nodule at the end. An inexperienced person may confuse sarcoptic mange with an allergy, since their symptoms are similar in appearance
Sarcoptic mange is dangerous due to bacterial infection and general sepsis.
Is scabies contagious to humans?
The question of whether scabies is transmitted to humans or not worries every owner of a fluffy cat. The disease is considered contagious and can spread to other animals and humans. These parasites cannot live outside a living organism; they definitely need a host. However, scabies mites, having penetrated the epidermis of human skin, cannot exist in it for a long time. Symptoms of infection with sarcoptic mange or notoedrosis look like an allergy. In rare cases, otodectosis can cause otitis externa.
global $ads_google; //data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?>
$ads_google = true; ?> } ?>
Human skin is too dense for scabies mites; they cannot lay eggs in it or move around. This feature saves a person from cat scabies. In the short period while the ectoparasite is in the upper layers of the dermis, it causes itching and discomfort. After spontaneous healing, the symptoms disappear. Despite these features, when treating a sick cat, the owner must observe personal hygiene measures:
- use gloves when handling your pet;
- wash your hands with soap after treatment procedures;
- boil things that the cat has come into contact with;
- Regularly vacuum carpets and wash floors in the house.
Scabies mites disappear from the human body in less than a month.
What you should know about scabies mites
The cause of scabies, which is dangerous for both animals and humans, is acariform mites (type arthropods, class arachnids). These are microscopic parasites no more than 0.3–0.4 mm long. Cats are affected by different types of scabies mites that cause diseases (most often notoedrosis, cheyletiellosis, otodectosis, rarely demodicosis, sarcoptic mange). Sarcoptis, cheyletiella and notoedrus can be transmitted to the owner from the animal, but the parasites do not multiply in human skin.
| Pathogen | |||||
| Disease | notoedrosis | cheyletiellosis | otodectosis | demodicosis | sarcoptic mange |
- The first symptoms of sarcoptic mange in animals are small nodules and fluid-filled blisters, and then scratching, which first appears in the area of the nose, eyebrows and ears, and then on other parts of the body. Gnawing tunnels in the layers of the epidermis, females lay up to 60 eggs. The full development cycle of ticks is 2–3 weeks.
- Notoedrosis is characterized by the location of parasites in the form of peculiar “nests” on the head, tail and paws.
- The cheyletella mite is a cutaneous parasite that causes dermatitis with the formation of keratinized scales, most often on the skin of the back. Signs of damage include not only visible dandruff, but also itching, hair loss, and hardening of the skin.
- The demodex mite lives in the deep layers of the skin, so itching with demodicosis is not very pronounced. There are cats with a genetic predisposition to the disease. Demodicosis is accompanied by hair loss, roughening of the skin and an unpleasant odor. Fortunately, feline demodicosis is rare.
- The causative agent of otodectosis lives in the external auditory canal. When infected, a cat often shakes its head and scratches behind its ear. With prolonged parasitosis, the disease develops into a purulent form and can lead to perforation of the eardrum.
We suggest you read: Traces and signs of bedbugs in an apartment
Diagnosis of scabies
If you suspect your cat has scabies, it is important to seek veterinary help promptly. The clinic will help make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. Diagnostics includes an external examination of the animal and taking skin scrapings for microscopic analysis. This procedure is repeated two or three times to confirm the output. Based on the results, the doctor makes a conclusion about the cause of the problem. Often, a mite infestation can be confused with dermatitis, an allergic reaction, ringworm, or eczema. Therefore, a laboratory test is mandatory in the diagnostic system.
The duration of therapy is determined by the severity of the disease and the condition of the pet itself. The average treatment period for scabies ranges from one to four weeks. Medical care for a pet consists of injections, ointments, solutions, drops, and hygiene products with a therapeutic effect (shampoos, soaps). To eliminate scabies in cats, acaricides, antibiotics, antihistamines, antiseptics, and immunomodulators are used. To prevent the cat from licking the ointment applied to the surface of the skin, it is necessary to use a protective cap.
Treatment of demodicosis
To help an adult cat or kitten, complex therapy is needed, including several drugs with different effects. You can treat your pet at home, but a treatment plan is developed by a veterinarian. If the disease is mild, then bathing with tar soap is sufficient to treat the animal. After this, sulfur ointment is applied to the affected areas or wiped with an infusion of medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects (chamomile, calendula, string).
For a localized form, liquid medicine Tsipam, Ivermek, Amide, Ectodes, Perol is used. The product is applied to the lesion 1-2 times a week. These drugs are not used during pregnancy. When treating a generalized form of scabies, the cat's hair is first shaved off. Then the skin is treated with acaricidal preparations. At the same time, subcutaneous injections of Cydectin and antibiotics (Betamox, Amoxicillin or Camacidin) are given. Drops against fleas and ticks are applied to the withers (for example, Amit Forte).
Treatment at home with folk remedies
There are several proven recipes that help treat scabies:
- In a ratio of 1:3, dilute black gunpowder or sulfur powder in kefir. Stir thoroughly and leave in a dark place for 3 hours. Treat the affected areas of the skin once a day. Residues are washed off with water and wiped with napkins, since the product dries out the skin greatly.
- Rub the skin of a sick cat with sulfur ointment and ash. Cover with film for 15 minutes. Repeat the procedure 3 times a day. After 5 days, treatment is continued if there are signs of scabies.
- Lard, laundry soap, and birch tar are mixed in equal proportions. Add a double portion of sulfur. Apply the mixture to the cat’s body and wipe it off with napkins after half an hour. The course of therapy is about a week.
How is otodectosis treated?
For ear scabies, the pet is prescribed medications with amitraz (Amitrazin, Tsipam), hexachlorane (Aurikan), as well as acaricides and insecticides (Neostomozan, Surolan, Ectodes, Aurikan, Dana). First, the surface of the auricle is cleaned with a cotton pad soaked in antiseptic. Then the liquid medicine is instilled. After this, the base of the ear is gently massaged so that the medicine is evenly distributed over the surface. For hygienic sanitation before treatment, you can use lotions and solutions:
- Otifri
- Otoklin
- Fitolar
- Furacilin
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Potassium permangantsovka
- Chlorhexidine
When treating scabies in cats, the medicine is instilled into both ears, regardless of the lesion.
Prevention
The best preventive measure is the regular use of antiparasitic drugs, in cats this is usually drops on the withers. If you pick up a stray cat on the street, you need to show it to a doctor before bringing it home. If there are already cats at home, it is recommended to isolate them from the new resident for a period of quarantine, observation and, if necessary, treatment. Typically, domestic cats are left in their usual quarters, and the new pet is given a separate small room.
Treatment of notohedrosis
Before using medications, it is necessary to remove hair from the outer part of the ears in the affected area. The second step is to bathe the cat with shampoo that contains acaricidal components. In the early stages, you can treat your pet with local remedies. Aversectin or novertine ointment is suitable for this; they are applied twice a week. An alternative may be Demos gel, the frequency of its use is once every four days.
global $ads_google; //data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?>
$ads_google = true; ?> } ?>
For systemic treatment of feline scabies, injections of drugs based on ivermectin (1%) are prescribed - five injections every five days. The therapy includes Stronghold drops with selamectin or Advocate, they are used every three weeks.
How is sarcoptic mange treated?
This type of disease requires treatment of the cat's entire body, so treatment at home is a labor-intensive but necessary process. As in other cases, it is necessary to remove hair so that ointments and solutions are more effectively distributed over the skin. Next, the cat is washed with tar soap or shampoo (Nizoral, TM Doctor).
For injections, acaricidal agents Ivermectin, Doramectin, Aversect are prescribed. For the treatment of sarcoptic mange, Sayfli tablets and local ointments Aversectin, Novertin, and Sulfur are intended. Preparations in solutions are also suitable for external use: Stomazan, Amit Forte, Amitrazine Plus. A choice of drops of coffee is dropped onto the withers of a sick cat: Lawyer, Stronghold, Fighter, Frontline.
Most anti-scab drugs are strong poisons that place increased stress on the liver. To support it, the cat needs hepatoprotectors.
What are the possible consequences of scabies?
Areas affected by subcutaneous mites cause unbearable irritation in the cat. She combs the areas that bother her. Wounds and scratches are open gates for viral, bacterial and fungal infections. Pathogenic microorganisms cause inflammation. In severe situations, the outbreak festeres. In the absence of timely treatment of scabies and secondary infection, the cat may develop general sepsis.
Ticks, which lead an active lifestyle in the layers of the skin, secrete toxins. Toxic substances enter the blood and cause disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, heart, and lungs. With cat scabies, oxygen starvation is possible at the cellular level, which occurs due to metabolic disorders under the influence of harmful compounds.
Scabies (microscopic) mites.
These parasites are able to live and reproduce only in the host’s body, in different layers of its skin. Diseases caused by ticks are called arachnoses (from the Greek arachne - spider).
A cat becomes infected with mite scabies either through direct contact with a patient, or through contaminated (contaminated) care items, bedding, or a carrier. A person can become infected with some of the feline arachnoses, but the parasites will not be able to reproduce in their skin.
Otodecosis (ear scabies). The pathogen parasitizes in the ear canal. Dogs, cats, rabbits, and some other animals get sick. The first symptoms of infection are itching and hyperemia. Further development of the disease is accompanied by the release of exudate, which, after drying, forms brownish scabs that resemble ground coffee in appearance.
With tick-borne otitis media, ear discharge produces a specific, “mouse” odor. By scratching the ears, the cat damages the skin and introduces additional microflora into the inflammation. Otodectosis is often accompanied by bacterial and fungal infections, as well as surgical pathologies such as auricular hematoma. Uncomplicated otodectosis can be treated well, but in especially severe cases, mites in cats can cause hearing loss and even death of animals.
We suggest you read: How to remove fleas from cats and dogs using tar soap
Cheyletiellosis. May affect cats, dogs and rabbits. This parasite is often called “walking dandruff.” On the skin of an infected cat, movement of keratinized skin scales is observed. It is caused by the movement of ticks moving underneath them. The favorite location of the parasite is the back of the animal. The main signs of the presence of a mite in cats: slight hair loss, itching, hardening of the skin and an increase in the amount of dandruff.
Notoedrosis. The causative agent is Notoedres cati. This parasite is typical of cats, but also affects dogs and rodents. The disease begins in the scalp, causing moderate itching, scratching and hair loss, and later spreads in “nests” throughout the body. The released exudate glues the fur together, giving it the appearance of a “felt boot” in long-haired animals. Notoedrosis in cats often takes a chronic form, forming folds, cracks and numerous papules and pustules on the skin.
Sarcoptic mange. Foci of the disease are most often localized in the head, at the base of the ears, on the back of the nose and in the superciliary arches of the animal. Accompanied by intense itching, hair loss and hyperpigmentation. Fluid-filled nodules appear at the affected sites. It flows brightly, causing a lot of inconvenience to the animal. Cats rarely become infected with sarcoptic mange; it is mainly a canine parasite.
Demodecosis. Cats rarely suffer from this disease. It is believed that the disease most often manifests itself in animals with weak immunity. Demodex parasitizes in the deep layers of the skin, affecting the areas of the lips, eyes, ears and limbs. May spread throughout the body. Itching is mild or absent.
Preventive measures
To prevent infection with skin mites, it is necessary to remember and apply the rules of prevention. Firstly, if possible, it is advisable to protect your pet from contact with street animals. They often suffer from this contagious disease. Secondly, during routine insecticidal treatment it is periodically necessary to use selamectin-based products. It is enough to use such drugs once every six months. Thirdly, for hygiene procedures it is useful to use shampoos with insecticidal additives (for example, with tar).
At home, it is important to regularly carry out wet cleaning. A balanced cat diet also provides additional support. When you have enough minerals and vitamins in your diet, it is easier to keep your immune system healthy. It is also important to protect your pet from stress and hypothermia. A healthy, well-groomed cat is much less likely to be affected by subcutaneous mites and does not even pose a temporary threat to humans.
global $ads_google; //data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?> $ads_google = true; ?> } ?>