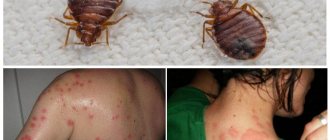
Scabies in dogs is a skin disease caused by scabies mites. Depending on the type, they cause the following diseases:
- Sarcoptosis (pruritic scabies) is a skin lesion caused by mites of the genus Sarcoptes canis. If treated in a timely manner, it can be easily treated.
- Otodectes, in other words, is an ear mite caused by a parasite of the genus Otodectes cynotis.
- Cheyletiosis (pityriasis scabies, wandering dandruff) is caused by the genus Cheyletiella mites.
- Notoedrosis is caused by a mite of the genus Notoedres and is more common in cats, but can also occur in dogs. It is dangerous because people become infected with true scabies from animals.
- Demodicosis, infects Demodex canis. The main feature is that demodexes live on all dogs, but the disease only manifests itself when the immune system is weakened or there are hormonal imbalances.
These are the main diseases of dogs, caused by scabies mites and characterized by itching, which is what unites them in one word: “scabies”. An exception to the rule is Demodex - if the disease is not complicated by microbes or fungi, then the disease can occur without itching.
Sarcoptic mange
Ticks of this genus are negligibly small, only 0.2 - 0.3 millimeters, so they can only be examined under a microscope. They live in the inner layers of the epidermis (the top layer of the skin). The greatest activity is observed at night - females gnaw passages deep and parallel to the surface of the skin, into which they lay eggs. Consequently, the greatest manifestation of symptoms occurs at night, but during the day, of course, you can notice the manifestation of the disease.
Main clinical symptoms
- signs of the disease first appear on the head, then on the paws and belly, and only then on the sides and back;
- the dog begins to itch within a few hours after the parasite gets on the skin;
- nodules form, which subsequently develop into small bubbles filled with liquid;
- as the disease progresses, scratches and crusts from the fluid that comes out of the papules when they rupture appear on the animal’s body;
- the skin thickens;
- due to trauma to the skin, as a result of constant scratching, hair falls out on the affected areas of the body and bald patches form;
- skin reddened, inflamed;
- If bacteria penetrate through wounds on the skin, then you can observe the active formation of pus.
Stages of development
After the female lays eggs in passages drilled inside the skin, the larva hatches within three to four days. Then it goes through a certain development cycle, which takes about three weeks. Adult ticks live for approximately two months.
However, do not expect that your pet will recover on its own after a couple of months, since during this time only one female will lay about 50 eggs, so the cycle will repeat again and again.
Treatment
Before you start treating an animal, it is necessary to reliably make a diagnosis, at least in order to know what we are dealing with and how dangerous it is for you, for the owner. That is why do not neglect going to the clinic.
Any treatment must be comprehensive, which will be aimed, first of all, at stopping the vital activity of the ticks themselves, restoring the skin and strengthening the dog’s immunity.
Simply washing your dog is not enough; on the contrary, both ticks and larvae thrive in a damp environment.
For bathing and treatment, acaricide solutions are used, as well as specialized shampoos and aerosols from a pet store or veterinarian. pharmacies.
They resort to treatments with special preparations (for example, Demos) and ointments. In this case, it is necessary to put a collar or muzzle on the dog so that it cannot lick the medicine off itself, otherwise it may be poisoned.
In some cases, it is necessary to use intradermal injections of a 1% solution of ivomec.
ATTENTION!!! These injections cannot be used on dog breeds such as Shar Pei, Collie, Bobtail!
Treatment options
It is very difficult to treat dog scabies, so only an integrated approach will help solve the problem. Getting rid of ticks will take a lot of time and expensive medications. A sick pet will have to endure several unpleasant procedures that may affect its mental state. Because of this, veterinarians advise surrounding a sick dog with care and passing on your love to it.
All diseases caused by various ticks can be cured using the following measures:
- Maintaining hygiene rules. An important step in getting rid of scabies mites is maintaining ideal conditions for your pet. Every day you should wash your pet's rug in hot water and dry it thoroughly in the open air.
- Taking into account safety tips. Protective gloves should be used during any contact with animals. This will not only protect the owner from becoming infected with ticks, but will also reduce the likelihood of additional problems for the pet. In addition, you should limit your dog's interaction with other people.
- Strengthening the immune system. The fight against parasites must be carried out in all directions, including activating the work of the animal’s body’s defense system. For this, highly qualified veterinarians advise using special tablets. They contain not only vitamins and minerals, but also substances that help cope with ticks. However, such drugs are expensive and can only be found in large veterinary pharmacies. You can replace them with Tetravit and Gamavit. These two medications are available as a solution for subcutaneous administration and help strengthen your pet's immune system.
- Regular bathing using special anti-tick shampoos. This option is the safest, as it practically does not harm the pet. Special products help quickly get rid of ticks and prevent their reproduction. The only contraindication is the presence of eczema on the pet’s body.
- Use of broad-spectrum acaricidal agents (Permanon, Breeze, Tsifoks and others). These medications come in drop form, making them easy to mix into your dog's food. They must be used at certain intervals and in strict dosages. Such products will help eliminate not only parasites, but also the eggs they lay.
- The use of hepatoprotective drugs (Karsil, Divopride, Ornitil and others). These medications must be given to the dog, as they will help reduce the negative effects of other medications used on the liver.
- Following a certain diet. During treatment for scabies mites, it is recommended to give your pet only those foods that will not cause an allergic reaction. It is best to feed the animal with special high-quality food. It should contain many vitamins and minerals, as well as special additives that prevent dysbacteriosis.
- Treatment with folk remedies. They can be used only at the initial stage of treatment, since in the future they will be ineffective. Lavender oil is considered the best folk medicine of natural origin. It will help little in the fight against mites, but will help reduce itching and quickly heal damaged areas.
Notoedrosis
The causative agent of notoedrosis is very similar to the culprit of sarcoptic mange. It also lives inside the skin, but mainly in the outer layer of the epidermis. Females also gnaw holes to lay eggs, but the life cycle of this mite is somewhat shorter - only 15-18 days.
This disease is more specific for cats, so in dogs the symptoms appear rarely and not so clearly, and more often they are simply carriers, and do not get sick themselves.
The parasite first affects the face, then the neck and paws; in advanced cases, the entire body is affected.
Main clinical symptoms
- itching and rashes;
- intensive scratching leads to the formation of bald areas that become covered with crusts due to bursting papules;
- thickening of the skin;
- as the disease becomes chronic, problems with the eyes appear (conjunctivitis, eyelids become swollen). It happens that the nostrils narrow, which leads to difficulty breathing.
Treatment
First, it is necessary to isolate the dog not only from other animals, but also to limit contact with humans.
Then you need to wash your pet using special products aimed at softening the crusts that have formed and affecting the parasite.
Specialized medications are applied to the skin, most often insecticidal preparations, sulfur-containing and aversectin ointments.
It is necessary to understand that only a qualified specialist can prescribe treatment, since the wrong dosage can harm the pet.
How are scabies mites spread?
Sarcoptes mites are infectious in the environment for about 36 hours. Dogs diagnosed or suspected of having sarcoptic mange should have their environment thoroughly disinfected, including bedding, collars and harnesses, using parasite-killing detergents or replacing them.
Dogs that are in close contact with infected dogs, such as while walking at dog parks or coming into contact with stray dogs or wild animals, can easily become infected with scabies mites.
Cheyletiosis
The causative agent of “wandering dandruff” or “pityriasis scabies” is somewhat different from the previous ones. It is also small in size, only 0.3-0.5 millimeters, therefore, it can only be seen under magnification.
Unlike previously described parasites, Heyletella live on the surface of the skin, and lay eggs, attaching them to the hair, at a distance of two to three millimeters above the skin. Their life cycle is about a month.
Main clinical symptoms
- the main symptom is still unbearable itching, but it is localized on the surface of the dog’s neck and back;
- reddened skin;
- scales appear on the surface of the skin, resembling bran or dandruff;
- the quality of wool sharply decreases, which leads to its intensive loss;
- pustules and ulcers on the body, then the formation of crusts;
- Sometimes you can observe hyperpigmentation - a change in the color of the skin, becoming darker. Appears as dark spots on the surface.
Treatment
In most cases, treatment consists of external treatments. For this purpose, acaricidal preparations are used, for example spot-on drops. In the generalized form, that is, with a more severe course of the disease, injections, for example of the same Ivermak, may be needed.
Despite the fact that, at first glance, the treatment is not complicated, the disease is not at all harmless. If treatment is not started in time, cachexia may develop - an extreme degree of exhaustion of the body, which leads to death.
What will happen if left untreated?
Parasites found in a dog's ears pose a great danger. Unqualified assistance or its complete absence can lead to serious consequences - deafness, meningitis. These pathologies, in the absence of veterinarian help, in most cases lead to death.
The main danger of ear mites is that even after a course of therapy, relapse and deterioration of the pet’s condition are possible. This is due to the fact that not all medications are effective against mite eggs. Thus, after treatment, larvae appear from them, which begin to feed on the blood of the pet, while the dog experiences serious discomfort - constant itching, shaking its head, itching, any sudden movement causes pain.
Ticks can provoke the development of an infection that is dangerous to the dog’s health and life. According to statistics from veterinary practice, a third of all infectious diseases end in the death of a pet.
Demodicosis
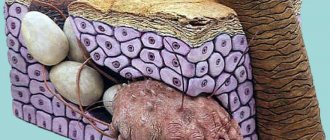
Other names are “red scabies” and “subcutaneous mite”. These parasites live under the skin, localized in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles (more than a hundred individuals can live in one).
Modern research confirms that about 85% of all dogs are carriers of Demodex, but the disease develops only under certain factors. The disease can be triggered by decreased immunity and hormonal imbalances.
There is an assumption that the predisposition to the disease is inherited, so sick animals are not allowed for breeding. The clinical picture depends on the form of the course. There are squamous - scaly form and pustular form.
Main clinical symptoms
- loss of appetite;
- skin redness;
- depressed state.
The scaly form is characterized by:
- Round hairless areas form on the face and limbs;
- there are a large number of pityriasis scales on the skin;
- itching appears if bacteria or fungi have penetrated through wounds on the skin;
- at a later stage, the skin turns pale and acquires a grayish-blue tint.
The pustular form is characterized by:
- the skin is swollen, wrinkled (similar to cellulite), hyperemic (reddened), weeping;
- thick dense nodules are felt;
- ulcers form from the nodules, yellow, brown, sometimes black in color;
- the pus can be squeezed out with your fingers, it may be mixed with blood, ulcers and abscesses form;
- unpleasant odor from the affected part of the skin;
- enlarged submandibular lymph nodes;
- the affected areas of the skin are hotter, relatively untouched.
Treatment
Compared to other types of scabies, demodicosis is the most difficult to treat. It is possible to completely get rid of the disease only if the dog became ill at a young age - up to two years.
If an adult animal becomes ill, it is possible to stop the disease and prevent the appearance of symptoms, but with a high probability the disease will return throughout its life. Therefore, such dogs require special care.
When treating Demodicosis, any external treatments are not enough. Intradermal and even intravenous injections are also used.
The disease is very serious and only a veterinarian can prescribe high-quality treatment in each individual case.
General methods in the fight against tick-borne parasites
The type of parasites does not affect the course of the treatment process, in the sense that there cannot be a quick recovery, since in order to completely cure a pet, an integrated approach is required. Today, the variety of medications has no limits; you can use a special cream, ointment or spray as prescribed by a veterinarian. The treatment process is most active if the dog is cut, washed properly and the whole body is treated with a medicinal product. The main thing is to get rid of parasites.
Otodectosis
Although the causative agent of otodectosis is larger than some of its relatives, it is still impossible to see it with the naked eye; its size is only up to 0.5 millimeters. They live inside the ear and feed on wax and epithelium.
This disease is widespread among dogs. If no measures are taken, then mites cause inflammation of the ear canal - otitis media, and this already has very serious complications.
Main clinical symptoms
- Severe itching, the dog constantly scratches its ears, sometimes tearing them into blood;
- shakes his head (actually due to itching);
- plaque forms in the ears. These clusters are dark brown or black in color and can be either dry or wet.
Treatment
It’s not at all difficult to get rid of ear mites if you don’t start the disease.
It is important not to stop halfway, for example, different drops need to be instilled again, after a certain number of days (this depends on the specific drug), it is not enough to drop once and that’s it.
The prescription of drugs depends on the stage of the disease, but there is a general algorithm of action:
- Clean the ears with a cotton pad or gauze soaked in chlorhexidine or a special lotion.
- Before visiting the veterinarian, do not clean your dog’s ears under any circumstances, this will complicate the diagnosis!
- A drug is injected into the cleaned ear, usually drops. Most often, Aurikan, Bars, and Tsipam are prescribed for otodectosis.
- After administration, the ear should be massaged for better distribution of the medicine.
Don't self-medicate! If the animal’s condition worsens, contact a specialist.
Forecast
Sarcoptic mange is debilitating for a dog and does not go away spontaneously, but is highly treatable. The prognosis is favorable.
It will take 4 to 8 weeks to completely eliminate itching and restore skin and fur. However, noticeable improvement occurs within the first 14 days. The rate of recovery depends on the size of the lesion, the severity of the lesion, and the animal’s immunity.
If after 6 weeks from the start of treatment there are no noticeable improvements, the itching does not go away, additional studies are prescribed to determine the real cause of the disease.
Infection with scabies can be avoided if you keep your pet away from dogs with obvious signs of sarcoptic mange and use anti-mite means: drops on the withers, collars or tablets.
Diagnostics
First of all, the veterinarian examines the dog and identifies the lesions.
By palpation, one feels thickening of the skin and dense tubercles/nodules in it.
The inflamed areas of the body are illuminated with an ultraviolet lamp (traces of tick activity are clearly visible under ultraviolet rays).
An accurate diagnosis can be established only by taking a scraping from the affected skin or a smear from the released pus (in it you can observe mites at all stages of development, both adults, larvae, and eggs) and ear discharge.
A scraping may not always be informative, since it is taken from the surface of the skin, and many of the mites live deeper. Therefore, several samples are taken from different parts of the body.
Cheyletiellosis (walking dandruff)
Dandruff that may be seen "walking" is actually Cheyletiella yasguri mites moving across your dog's skin. Walking dander is highly contagious, especially in kennels or households with multiple pets. Humans can also be infested with these types of ticks.
Symptoms: Peeling skin and infection along the back are common signs of walking dandruff. While some animals do not itch at all, others experience severe itching. Pets that don't show any signs can carry ticks and spread them to other pets and people.
Cheyletiellosis is diagnosed by examining the animal's skin and examining samples of the skin and hair using a microscope.
Call a veterinarian Moscow
+7(495)162-70-70
Prevention
It is unlikely that you will be able to completely protect your pet from ticks. To minimize the danger, follow these simple rules:
- do not walk your dog in places with large concentrations of stray animals, as they are more likely to catch all sorts of “evil spirits”;
- do not use grooming items for your pet from other dogs, this is one of the ways of infection;
- After each walk, wash your pet’s paws and belly;
- if in the area where you are walking your dog an animal with scabies is found, then change the place of walking;
- it is necessary to periodically treat the dog with antiparasitic drugs, for example “BlochNet”.
Symptoms
The disease often begins in the head. The pet scratches its ears, spots appear in areas where there is the least fur. There it is easier for mites to get to the skin. Peeling and a thin crust appear along the edges of the ears.
Gradually there are more spots. The infection spreads to the face. Next they are amazed:
- muzzle;
- elbows;
- hock joints;
- rib cage;
- belly, etc.
Red itchy dots gradually give way to nodules. They fill with liquid and burst, forming scabs, scabs, cracks, and erosions. Over time, the dog becomes bald, the skin thickens, and continues to itch. The pet itches a lot and gnaws the skin. Females rest during the day, so exacerbations occur at night.
Breeds prone to mange
Any animal can get sick, but most likely this will happen to those tails that have reduced immunity.
But there is also a breed predisposition, for example, for demodicosis:
- boxers;
- pugs;
- French Bulldog;
- Rottweiler;
- German Shepherd;
- Staffordshire Terrier;
- dachshunds;
- Dobermans;
- English and American cocker spaniel (the greatest tendency to damage the limbs is demodicosis of the paws).
Breeds with long, floppy ears are most susceptible to otodectosis.
FAQ
Is scabies transmitted to humans?
The answer is YES, but partially! There are nuances depending on the type of tick.
Thus, if your dog has sarcoptic mange or cheyletiosis, you run the risk of contracting pseudoscabies. It does not require treatment, everything will go away as soon as the source disappears, in other words, when you cure the dog.
Demodectic mange and ear mites have strict species specificity and are completely safe for humans.
But if your pet has notoedrosis, then you will soon become infected with true scabies. Although this type of tick is less likely to infect dogs than cats, they can carry it, so be careful.
How to distinguish scabies from other diseases?
Itching is a sign of many diseases, both life-threatening and harmless to your pet. The true cause of itching and other clinical signs can only be determined in a clinic by taking a scraping or smear. This is the only way to differentiate scabies from other diseases and determine the specific type of parasite.
Why is scabies dangerous?
First of all, the constant debilitating itching causes excruciating discomfort for the dog. Not only from the physical side - the dog scratches his skin until it bleeds, and this is a direct path for infection, which greatly complicates the situation and leads to other dermatitis. Constant itching can develop mental disorders in a pet, it becomes irritable, fearful, and aggressive.
Making an accurate diagnosis
Avoid taking anti-itch medications and grooming treatments before visiting the veterinarian. They distort the clinical picture, preventing the correct diagnosis.
During diagnosis, the veterinarian:
- examines the four-legged patient, checking the condition of his fur and skin;
- collects anamnesis, trying to determine possible causes of infection;
- takes a urine and blood test to study existing deviations in basic indicators;
- conducts X-rays and ultrasounds to help track internal pathologies with a latent course;
- takes a skin scraping necessary to determine the pathogen.
Treatment for scabies mites in dogs is selected based on the type of parasite, duration of infection and the degree of damage to the body. On average it takes from 4 to 8 weeks.
Briefly about the main thing
- Scabies is a skin disease caused by scabies mites.
- Depending on the type of pathogen, sarcoptic mange, cheyletiosis, notoedrosis, demodicosis and otodectosis are distinguished.
- Scabies can only be diagnosed in a clinical setting, since the mite is not visible to the naked eye, and external changes are similar to other dermatitis.
- For prevention, it is necessary to periodically treat your pet with antiparasitic sprays or lotions.
- Any animal can get sick, regardless of breed, age and gender.
- Scabies is a dangerous disease that is complicated by dermatitis, and in some cases leads to cachexia and death.
When to use
This drug is used for the prevention and treatment of dogs and cats. It is active against fleas, scabies mites, lice, lice, roundworms, heartworms (heartworms). If your dog has sarcoptic mange, you may also be prescribed Stronghold to treat it.
Stronghold drops are easy to use. Remove the pipette and, holding it vertically, press the cap. Apply the medicine to dry, intact skin in the area between the shoulder blades, spreading the fur. It is important that the entire volume of the drug is applied to the skin.