Pediculosis is a parasitic disease in which the louse gets on the hairy part of the host's body and begins active development. The insect lives only on humans, feeding on their blood.
The pest multiplies quickly, going through the nit, larva, and nymph phase. Under normal conditions, the ectoparasite becomes an adult within 16 days. Because the number of lice is rapidly increasing, it is important to study the stages of their development and take appropriate measures to prevent the progression of lice.
Symptoms of lice
The first few lice live in the hair almost unnoticed. But as soon as their number begins to grow, it becomes difficult not to notice the colony. The presence of parasites is indicated by:
- • active itching on the skin;
- • appearance of small scratch wounds;
- • blue-gray spots on the skin.
Pediculosis is not only uncomfortable in itself, but also dangerous for two reasons:
- • addition of a secondary infection;
- • infection with diseases carried by lice (typhus and relapsing fever).
Children most often experience head lice. This is due to close communication in teams. That is why outbreaks of this skin disease usually occur in schools, kindergartens, and holiday camps. You can protect yourself from the disease by following the rules of personal hygiene. To do this, it is important to refuse to use other people’s combs, towels, bed linen, and hats. It is advisable to wear long hair in a hairstyle without loose strands.
Today, treatment of head lice is neither difficult nor dangerous. Modern drugs are easy to apply, do not have an unpleasant odor and do not harm the hair. It is important to choose products that are suitable for age and shape. “Paranit” is available in the form of shampoo, spray, lotion, which means that everyone can find the most convenient format for themselves.
In addition, “Paranit” is not only a safe and effective treatment, but also a convenient prevention of head lice. “Paranit Repellent Protection against Lice” is suitable for adults and children from 3 years of age and will help protect themselves from lice. With “Paranit” lice and nits are not scary!
What are comfortable and uncomfortable living conditions for nits?
- Under normal conditions, from the beginning of development until the larva emerges from the egg, 5 to 8 days pass. Factors that make further reproduction possible are considered favorable: the temperature is about +33 degrees. It is close to the warm-blooded human body. This is the reason why the parasites are so prolific: no other type of bloodsucker leaves as many offspring as the number of eggs the louse lays.
- Fluctuations in temperature, both in one direction and in the other, entail a stop in the development of the larva in the egg or its complete death. This explains why when disinfesting nits, it is recommended to boil laundry (already +60°C is fatal for nits) or keeping things in the cold (freezing at -15°C).
- The protective capsule protects the undeveloped larva from damage by many insecticides. When wondering how to kill lice eggs, you need to carefully read the instructions for the drug. There is a limited number of insecticides that can destroy the shell and kill its contents. However, you need to be prepared for the fact that a number of side effects may occur.
Combing
This is one of the most affordable and safest ways to get rid of lice. For combing, use a special comb with fine teeth. The shoulders are covered with a towel, and the comb is soaked in vinegar. Combing should be done very carefully, strand by strand. This is necessary to eliminate nits, which are very well attached.
After the procedure, the comb is treated with boiling water, the towel and clothes the person was wearing must be washed, since lice remain viable for some time outside the human body.
Among more than 150 species of lice, only 3 parasitize humans. The head, body and pubic louse are small blood-sucking parasites that choose only humans as their host and feed on his blood. They live on different hairy areas of the body: from the head, eyebrows and eyelashes to the intimate area
Lice affect both adults and children equally. Pediculosis is a skin disease common to people from different social classes. Therefore, infection with it is not considered shameful and carries with it discomfort due to severe symptoms and the possible addition of infection.
Life cycle of a head louse
Once on a person, the louse continues to reproduce and feed. To get enough, adults drink blood once every 4 hours, and nymphs drink blood every 2 hours.
The life cycle of lice has its own characteristics. But for the active progression of pediculosis, it is enough for just one adult ectoparasite to land on the head. Next, the female lays eggs.
There are different stages of lice development::
- nit;
- larva;
- nymph;
- adult sexually mature individual.
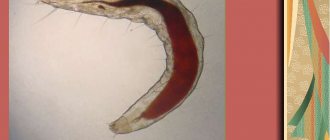
Nits phase
After mating with a male, the female's eggs are inseminated. Next comes the process of louse development. A couple of hours after fertilization, the first laying of nits begins.
Once on the head, the female attaches itself to the hair closer to the roots . A sticky fluid is secreted from her genitals, and subsequently the first egg is released.
A viscous lubricant envelops the nit, and it hardens, thereby forming a protective cocoon. The eggs cannot be washed off with shampoo or combed out with a comb. Moreover, most insecticides are not able to penetrate inside the egg. When the larva emerges from the cocoon, the latter remains attached to the hair.
The development of lice from nits lasts about 8-10 days. During this period, the parasite organism is formed. When the larva is hungry, it chews the cocoon to find food.
The nit phase and other stages of louse development are determined by environmental factors. At normal humidity and elevated air temperatures, the eggs come out of the shell after a day.
In the cold, development slows down and lasts up to 10 days. When kept for at least 2 hours at a temperature of -20 degrees, the larvae die, and the nymph ceases to live at -10 °C.
High temperature also affects the development of the ectoparasite. Thus, at +40 °C, adults stop reproducing and feeding; at +50 °C, an adult louse loses its viability. And nits die at a temperature of about +60 degrees.
Larval transformations
The development of lice at the larval stage is considered incomplete metamorphosis. The nymph, in comparison with the sexually mature region, does not reproduce and is small in size. But in terms of feeding method and appearance, the larva is similar to an adult insect.
Over the course of three days after being released from the cocoon, the nymph’s body slowly develops, but its chitinous shell does not change. When an insect sheds its hard shell, the unprotected body gradually hardens under the influence of oxygen. The grown individual is similar in appearance to the imago, but differs in size.
After molting, the incubation period for the development of head lice at the nymph stage (first generation) lasts up to 2 days. Then a second molt occurs and the nymph moves to the next stage, which lasts up to three days. During this period, the reproductive organs are formed and the insect becomes an adult.
Adults can mate and the next developmental cycle begins. Several weeks after infection (up to 15-30 days), a new generation of lice parasitizes a person.
Adult
The life cycle of the head louse stops when the nymph becomes an adult after its second moult. After consuming blood for the first time, the insect can mate. At this stage of development, lice lay eggs two days after fertilization.
With a large accumulation of ectoparasites on the head, a person feels severe discomfort, and his skin is constantly itchy. No matter how quickly lice develop, their life span takes up to 40 days. Every day the female lays up to 4 nits. Accordingly, the parasite produces up to 160 eggs over its entire life.
For the life of the imago, food is necessary. Therefore, the individual dies after just 1 day of fasting.
For a female to produce offspring throughout her life, one mating is enough. This is what allows the parasite to continue its development and actively reproduce over a short life, even in the presence of negative factors.
Traditional methods of treatment
There are a huge number of ways to get rid of head lice using traditional methods:
- • treatment with vinegar diluted in water;
- • applying a mixture of garlic and onion to the hair;
- • use of cranberries or cranberry juice;
- • treatment of the head with kerosene
- • washing your hair with laundry or tar soap;
- • applying hair dye to hair;
- • treatment with alcohol.
Folk remedies have a number of disadvantages. Most of them cannot get rid of lice completely, so they require repeating the procedure several times. Some of them (for example, kerosene) can be dangerous and cause poisoning or scalp burns.
Mechanical removal of lice
In addition to pharmaceutical and folk remedies for the treatment of pediculosis, there is also a mechanical method.
Just a few decades ago, it meant manually removing nits and lice from hair. However, today this method is practically not used. It was replaced by a special comb. It is equipped with fine teeth, the structure of which allows hair to pass through and trap parasites, their larvae and eggs. The scalp is not damaged. The use of such a comb in conjunction with pharmaceutical shampoos or folk remedies only enhances the effectiveness of the therapy.
You can also purchase an electric version. The action of such a comb is based on electrical impulses. They are harmless to humans, but deadly to insects. An electric comb is best used to remove lice from a child. It has much fewer teeth than the classic version. However, this is compensated by high efficiency. Under the influence of impulses, the parasites die, after which they can be safely washed away with water.
Main methods of infection
These parasites cannot fly or jump, so they can only crawl very quickly. They have powerful, tenacious legs, so they can easily move along horizontal and vertical surfaces. However, outside the human body and food, lice live up to a day, so most often their transmission occurs through direct contact. In addition, you can become infected with pediculosis through
- • comb;
- • towel or bed linen;
- • hats.
Insects remain viable in water for some time, so in open water there is a low risk of them getting on the body
Distribution routes
Head lice are predominantly found in children and adults with long hair. They are transmitted through personal hygiene products, such as combs or hair ties.
Parasites can appear even in clean people who live in good conditions. They are caused by close contact with an infected person. Parasites pass from the “host” during games, sexual intercourse, wrestling, and accidental touching of the head.
Where do head lice in children come from? In children's groups, the spread of these insects occurs at lightning speed. They can be transmitted to healthy babies through shared towels or pillows, when bathing in the bathtub or wearing other people's hats. Therefore, a high risk of infection is observed in gardens and schools, swimming pools, hotels, and trains.
To summarize
In the struggle for survival, any organism tries as much as possible during its short (or long) life to reproduce its own kind. Lice are no exception. Adapting to the strong poisons used and mechanical extermination, insects strive to replenish their numerous offspring. This explains why a female lays so many eggs during her life, and why lice is still a pressing problem in our civilized world. Ignoring preventive measures to identify lice-infested hospital patients, conscripts, children in school and preschool institutions, etc., leads to rapid infection of healthy society. High effectiveness of parasite control is expected where it begins at the stage of nit appearance.
Source