Only female wasps have a sting. It serves as a weapon of defense and attack. With its help, the wasp paralyzes the victim and takes it to the nest to feed its growing offspring.
To some people, the question of whether a wasp has a sting may seem obvious. However, this is not entirely true.
In fact, every female wasp has a sting, but males cannot boast of such a unique weapon. People's confidence in the presence of a sting in all wasps is due to the fact that most wasps belonging to the common paper species are females. That is why almost all wasps have a sting in their arsenal, which can be found on a plot, on an apartment balcony, in a house, or just on the street.
The presence of a sting on a wasp
It just so happened that in the process of evolution, the wasp ovipositor in females was somewhat reshaped, became much harder and connected to the poison gland. This is how the sting appeared, and as is now clear, it appeared only in females. Males cannot anatomically possess such an organ due to the lack of an ovipositor. But since in wasp families females predominate quantitatively (there are few males, and they become active only during certain periods), this is where the opinion was formed that wasps have a sting in principle.
A wasp's sting, unlike a bee's, does not have serrations, which gives wasps the opportunity to sting several times without injuring themselves when stung.
The wasp's sting is its main defense and “tool” for obtaining food. Since wasps are hunters and predators by nature, they kill their victims (beetles, spiders, etc.), but not always with a sting. The jaws of wasps are not equipped with teeth, but they are so strong that they can even bite through the hard chitinous covering of some insects. In this way, wasps sometimes “save” poison. The wasp needs the sting in order to poison and paralyze the victim, injecting a portion of poison into its body after the puncture. The composition of this poison may differ in its composition among different species of wasps, while the structure of the sting is approximately the same in all of them.
Features of behavior
A bumblebee and a wasp are much less similar than a bee and a bumblebee. The behavior of insects is explained by their instinctive skills and type of food. Bees and bumblebees collect nectar from plants, thereby ensuring complete pollination of crops. Honey plants have a special sac in their structure in which they collect nectar, and then convert it into bee or bumblebee honey. Bumblebees are unique in that they wake up much earlier than other pollinators. They warm up their body in a special way and go on a flight.
Bee, bumblebee and wasp
Representatives of the wasp family feed on fruit juices, nectar, and honey. But for the development of larvae, protein food is required. For this reason, predators attack other insects and their larvae. They chew their insides, form small balls, and feed them to the larvae. In return they receive saliva, which is secreted by their cubs. There is a mutual exchange of food.
Since wasps are omnivores, they can often be found in the garden, yard, summer cottage, even in an apartment or house. They are attracted to sweet, sour, rotten meat and fish. Wasps fly in small flocks and keep a certain distance. Bees cluster together, but bumblebees prefer to fly alone.
Anatomy of the sting and stinging mechanism
Externally, the sting of a wasp resembles a long thin needle. This is a very durable organ with a channel-duct inside, connected to a poisonous gland. Thanks to this connection, the poison enters the victim’s body through the duct.
Wasp sting under a microscope
In a calm state, the sting is “retracted” to the back of the wasp’s body and hidden there by special plates. In a state of aggression, before a bite, the plates open and the sting “moves out” from the inside along the so-called sled. In fact, the sting is two closed “stilettos”, its walls are smooth, and to the naked eye they appear dark, almost black, but in fact they are translucent. Through the channel-duct between the stylets and the sled, the poison is released into the body of the victim. The stilettos themselves do not have a channel, therefore, if the sting (stilettos) does not penetrate deep enough into the body, the poison may not get there.
Immediately after the bite, having quickly injected the poison, the wasp does not always remove the sting back inside: this allows it to sting several times in a row (on average up to 4-5 times). The wasp is capable of piercing the victim with its sting, provided that the body cover is softer than the sting; otherwise, instead of the sting, the wasp will have to use its powerful jaws.
A wasp only has one sting for its entire life. Even if she loses him, it’s not so scary for her. Loss of a sting is generally not typical for these insects (unlike bees). This is only possible if you slam the wasp at the exact moment of the bite.
Structural features
The main difference between a bee is the presence of a triangular head with the main part of the nervous system and brain concentrated in it. In the middle of the head, along the crown of the head, there is a suture, from which the compound (faceted) eyes of the insect are located on both sides.
From each individual hexagonal plate, a round tube extends into the depths, gradually narrowing downwards. The walls of the tube are covered with a membrane that allows light to pass through.
A branched nerve approaches each tube from below. The eye of a working insect consists of 4-5 thousand facets, the uterus - up to 5 thousand, and the drone - up to 6-8 thousand. Simple eyes are located on the crown of the head, and the so-called third eye is on the line of the epicranial suture. The peculiarity of the structure of the visual organs lies in the form of transmission and processing of external information.
The wasp has 2 pairs of membranous wings, and its body measures 1.5 cm to 10 cm. On the sides of the wasp’s head there are 2 large and complex eyes, giving the insect the ability to see simultaneously in different directions.
Below on the front side there is a forehead, from which 2 movable segmented antennae (antennae) extend. They contain olfactory organs, designed for their orientation in a dark space. With its antennae, the insect perceives humidity, temperature, and the level of carbon dioxide in the nest.
The wasp has antennae on its head that perform the following functions:
- remote and direct perception;
- measuring cell sizes when building a nest;
- taste buds.
The insect has 3 pairs of legs attached to the lower part of the chest and consisting of 9 segments. The foot itself is formed from another 5 parts, connected to each other by a chitinous film. The wings of a bee consist of membranes and are supported by veins in a taut state, and during flight - perpendicular to the body.
Differences from a bee sting
As already mentioned, the wasp sting is smooth. In contrast, the bee’s sting is “equipped” with notches along its entire length, thanks to which the bee cannot pull out its “weapon” back after being stung. Therefore, if she manages to fly away, it is only by tearing off the back part of the body along with the sting, which remains in the body of the victim. After this, the severed part of the abdomen continues to pulsate, “pumping” more and more poison into the stung area (that’s why it needs to be removed as quickly as possible).
Of course, after a bite, leaving part of the internal organs along with part of the abdomen on the victim, the bee soon dies. In contrast, the wasp sting is absolutely smooth, can be freely and instantly pulled back out of the skin in the absence of any jagged edges. As already mentioned, a wasp can leave a sting in a victim only if it is swatted at the scene of the crime.
Stinging Aggressors
The wasp family belongs to the order Hymenoptera insects
The diversity of species in this family is simply enormous, and in this review we will pay attention to the behavioral characteristics, causes of aggression and consequences of attacks by two species such as the common wasp and the hornet. These species are most often found in our latitudes, so let’s take them as analyzed objects
Insects of this taxon are quite easily recognizable, especially when it comes to the large hornet. The wasp is clearly recognizable by its characteristic yellow-black body coloring. Like most poisonous insects, the wasp has a warning bright appearance; its striped abdomen eloquently makes it clear that you should not mess with this pitiful warrior.
Well, of course, each of us has heard such a popular comparison as “wasp waist.” This is another distinctive feature of all wasps, and many Hymenoptera in general. After all, the area of the body between the thoracic segment and the abdomen of these insects is really divided like a thin “corset”. It is not for nothing that wasps belong to the suborder of stalked bellies, which already speaks for itself.
If we talk about the size of the common wasp, then these insects usually do not exceed 1.5-2 cm in length. A hornet in our latitudes can easily reach 3.5-4 cm. There are also larger varieties, however, fortunately for us, they live in Asian countries.
How to remove a sting
Removing stings from skin is more about bee stings than wasp stings. However, if it so happens that the wasp sting remains inside, it must be removed in the same way as a bee sting:
- It’s best to take tweezers and disinfect them;
- you need to pull out the sting very carefully so that it comes out entirely (when stung by a bee, pull on the remaining part of the abdomen);
- to alleviate the condition after removing the sting, use traditional or folk methods (applying cold is good as first aid);
- treat the wound so that it does not get infected (you can use iodine);
- In case of complications, consult a doctor immediately.
What to do at home
It is not always possible for a person to immediately visit the hospital after being attacked by a stinging insect.
It is important not to panic, to act clearly and competently. Often, not only the well-being, but also the life of the victim depends on the correct behavior of others.
First aid
Basic rules for providing first aid for a bee sting:
The first stage is to get the sting. The longer the poison acts, the higher the toxic damage to the body. To remove the sting, tweezers are suitable, which must be doused with vodka, cologne or alcohol. It is not advisable to remove the sting with your fingers: it is easy to press it down or cause an infection; the second stage is treating the wound with hydrogen peroxide, alcohol or a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate. This advice will be useful to anyone who does not know how to relieve swelling from a bee sting. After applying one of the products, you need to apply a cold compress. After cooling the problem area, the pain decreases slightly; the next stage is drinking unsweetened tea or still mineral water
It is important to replenish your fluid supply; taking an antihistamine. A must for allergy sufferers
To prevent dangerous complications, it is advisable for every person who has been stung by a bee to take an allergy pill. Patients suffering from negative symptoms when exposed to various irritants should carry a syringe and allergy medications with them. A prerequisite is a patient’s passport, which indicates the type of allergy, a list of negative reactions, medications suitable for a particular person; If acute reactions develop, the victim must be taken to the hospital. The best option is to call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, the medications Diphenhydramine and Cardiamine are needed. Warm heating pads will help lower blood pressure; If those around you have the skills to provide emergency care, they will be able to restore breathing and start the heart in case of dangerous complications. If no one knows what to do, you need to give an allergy pill as soon as possible and call an ambulance.
How to treat a wound
How to treat a bee sting? It is important not only to numb the bite site, relieve swelling and redness, but also to prevent infection from entering the wound. The sooner you can remove the negative symptoms, the less you will want to scratch the bite site.
The following drugs are suitable for treating wounds:
- Fenistil-gel.
- Psilo-balm.
Compositions with a gel-like consistency act in a complex manner:
- reduce the risk of allergic reactions;
- reduce swelling and redness;
- relieve itching and pain.
Important! Before applying any product to the bite area, you need to remove the sting, wipe the affected area with a solution of potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide or diluted ammonia. Preliminary disinfection is a prerequisite to prevent the penetration of pathogenic microbes
Folk remedies and recipes
There are not always medications on hand to treat the wound after a stinging insect bite. The main task is to remove the sting in time,
prevent infection of the affected area.
Herbal ingredients and natural remedies for topical use will help reduce negative symptoms:
- plantain leaves;
- aloe juice and pulp;
- an aqueous solution with Aspirin and activated carbon tablets;
- onion gruel;
- soda solution;
- freshly squeezed juice from mint leaves;
- olive oil.
Taking activated carbon will help prevent the spread of poison:
These tablets are often found in your home medicine cabinet. Vacationers often take the drug with them to prevent stomach problems. Activated charcoal is effective against insect bites to quickly bind and remove toxins.
Interesting Facts
Any type of wasp has a sting, its own terrible weapon. The difference is that the strength of the poison’s effect on the victim’s body may vary depending on the concentration, which is different for each species. And the intensity of pain after a bite is also different for the same reason.
For example, the hornet is the largest wasp, it stings very painfully, and the poison injected into the victim can be fatal even to a person, and even just one bite can kill an allergic person. Deaths from hornet attacks are not uncommon, for example in Japan, where these insects are mainly found. European hornets are not much less dangerous. It is encouraging that these insects are not overly aggressive by nature.
Scolia, on the contrary, do not sting much, and the worst thing that can happen after their bite is a slight numbness in the stung area. It's all about the concentration of scolius poison: for humans it is too small to cause serious damage to health.
Philants (a type of burrowing wasp) generally cannot pierce the skin of a human palm with their sting. Therefore, you can crush such insects directly with your hand, or even while holding them in your fist.
Pompylids (also known as road wasps) are famous for having almost the most painful bite among insects. Only bullet ants living in South America are ahead of them in this sense. The pain from their bite is truly unbearable, and this fact is somewhat alarming, especially considering that about 3 hundred species of road wasps live, including in our country.
Whatever the type of wasp, the first thing you should not do is provoke them to attack. To do this, you need to use an effort of will, despite the fear (and many people experience it in front of wasps), stop all sudden movements, do not scream, do not wave your arms or run, and also do not attract their attention with sweet perfume. And of course, you should not swat a wasp that has landed on your skin, much less climb to its nest without observing safety measures.
The main thing is to always remember that wasps almost never bite just like that. Any attack they make is self-defense.
Precautionary measures
Bee sting
The most dangerous period of time, when there are many female wasps, is the end of summer and the beginning of autumn. It is during this period that they collect pollen from flowers and store food for the winter. Large concentrations of these insects can be found in the forest. Aspen nests are located on large trees. A person will be warned of danger by a not loud, but noticeable buzzing.
Attention! You should not approach the nest, much less disturb it with a stick for fun. In this case, the wasps will protect their home and a person will not get away with just one bite.
With several bites of these insects, a lethal dose of poison can be obtained even from small individuals. In this case, the person may not even be taken to the hospital, and it will no longer be so important whether the wasps left a sting or not.
Experts name several preventative measures:
- Clothes should be dark shades.
- The smell of perfumes and cosmetics repels these insects.
- You should not walk near aspen nests and it is better to avoid walking on the grass without shoes.
- It should be remembered that bees and other honey plants are attracted to sweets (spilled jam, open sweets, etc.)
If the operation at home was successful, then you should immediately treat the wounded area with hydrogen peroxide and go to the medical center. Removing the sting does not mean that the danger has passed. Most likely, the poison has already entered the bloodstream. Doctors will give directions for tests and prescribe the necessary medications.
In any case, a person should always be vigilant and closely monitor the activity of insects around. And then trouble can be avoided.
0 0 votes
Article rating
What do adults eat?
The diet of wasps is quite varied. Insects prefer fruit and berry juices and fruit pulp. Among their favorite fruits are raspberries, plums, apricots, strawberries, and grapes. Wasps try to avoid harder fruits whenever possible. Adults are very attracted to overripe fruits that have begun to ferment. Syrup, honey, jam and sugar are among the favorite products of winged sweet tooths. Wet sugar or fresh jam will inevitably attract many wasps into your apartment.
Some representatives of aspens at certain stages of their life cycle give preference to the young of various beetles, as well as some species of wasps. These predators are capable of exterminating even larger insects and can successfully hunt spiders of impressive size.
While feeding their larvae, adults hunt other insects and feed them chewed to their offspring. In the process of chewing the prey, the predator also consumes some of its hemolymph. Hemolymph is rich in protein and replenishes the energy reserves of the imago. Directly in the process of feeding and transferring food to the larva, the adult insect receives some of the saliva of the offspring, from where it takes the necessary substances for normal life. However, despite this, plant foods and sweets are preferable for imagoes. A danger to people is represented by wasps that appear out of nowhere in the apartment, flying to the aroma of food.
Nest arrangement
Bees build their hive from wax (they secrete it themselves), making strictly symmetrical honeycombs inside. Domestic bees live in special houses that beekeepers build for them. A hive of wild bees can be located in a hollow tree or in a crevice of a steep rock.
Wasps make their home from parchment, which is made by chewing wood or other plant cellulose. Their hive is round in shape, gray in color, and looks papery. Wasps attach the hive to the branches of a tree or the ceilings of rarely visited buildings, and sometimes they build it in the ground.
The nest of bumblebees is called a bombidarium; insects make it in burrows of small animals, hollows, and abandoned bird nests. Bumblebees, like bees, build the first cells of their nest with wax. To construct subsequent cells, they use capsules of already hatched larvae.
Allergic reaction
The action of immunoglobulins in a healthy body can neutralize the effect of poisons. Its production begins immediately after the foreign substance enters the body.
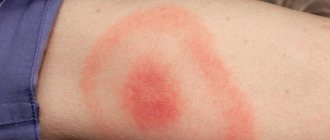
If the person bitten is allergic to wasp venom, the reaction to the bite may be unpredictable. You can distinguish an allergic reaction from a normal one by the location of the bite. The first thing that will confirm the guesses is large swelling, more than 1 cm in diameter. The further occurrence of reactions depends on the human body.
Allergy symptoms also:
- rash;
- strong pain;
- burning, itching;
- hives.
In addition to local reactions, the following may appear:
- headache, dizziness;
- nausea;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- difficulties with the breathing apparatus;
- elevated temperature;
- pale skin;
- muscle spasm.
Anaphylactic shock that develops within the first 5 minutes is a strong and dangerous reaction of the body. It begins with difficulty breathing and swelling of the larynx. If such a reaction occurs, immediate medical attention must be provided. Prednisolone and adrenaline are administered, and a tourniquet is applied above the wound. Further treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
What are they?
To date, there has not yet been a consensus on how to carry out an unambiguous and stable classification of wasps. At the moment, they are divided into several groups and families, the representatives of which, depending on the research conducted, can move between groups. At the first level of this classification, wasps (species) are divided into social and solitary. The latter include the following:
- sand;
- floral;
- burrowing;
- Germans;
- road;
- scolias;
- Typhia;
- sparkles.
The social ones include a single family - true wasps, but they are also complemented by sand species of wasps.