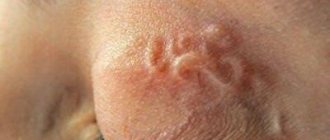
Signs of a pathological condition of an animal
Cats regularly look after their fur, licking themselves, scratching, and biting. But as the disease progresses, the pet’s behavior changes. If the following symptoms occur, you need to examine the animal and contact a veterinary clinic:
- Frequent scratching, the cat biting its fur and meowing pitifully.
- Constant biting of skin.
- Formation of bald patches, deterioration in the appearance of the coat.
- The appearance of dandruff and oily scales on the neck.
- The appearance of ulcers, red rashes, and spots on the neck.
- Detection of parasites and/or their metabolic products on the pet’s skin.
Frequent scratching of the neck is an alarming symptom
Ringworm and other skin lesions in cats caused by fungi
If an adult animal or kitten itches, but there are no fleas, the itching is often associated with the action of a fungus on the skin.
Trichophytosis, ringworm
Trichophytosis is a fungal disease that can be transmitted to people. This is especially dangerous for children, and it is much easier to cure a pet than a person. The disease manifests itself as hair loss in a local area and increased itching of the affected area. As a result of infection, since the pet is constantly itching, an abscess covered with a hard shell often forms under the skin of the bald spot. In this case, it is necessary to remove the pus, but the procedure must be performed by a veterinarian in a clinic setting.
You should not diagnose the disease yourself, since it is easy for an amateur to confuse ringworm (the popular name for trichophytosis) with other effects that have similar manifestations:
- sunburn, especially typical for representatives of short-haired breeds;
- damage from exposure to chemicals;
- hormonal alopecia.
If the diagnosis is established, special ointments offered by veterinary pharmacies are used.
Dermatomycoses
They arise from the infectious effects of fungi. Pets become infected from other animals, unwashed food, dirty objects, and unfavorable living conditions. The disease is often carried by mice.
Characteristic manifestations are scratches, wounds, scratches, reminiscent of those caused by fleas, covered with crusts, constantly itching, disturbing the cat and forcing it to itch.
Causes of itching
Traditionally, the search for causes begins with excluding fleas. The cat is examined by ruffling the fur so that the skin underneath is visible. If fleas are found, the animal is treated with a special flea remedy or bathed with an appropriate shampoo. Even after eliminating the parasites, a substance remains in the pet’s blood, which enters the body when a flea bites. Therefore, itching may persist for another 4-6 weeks after the cause has disappeared.
Hormonal and endocrine disorders
Failures in metabolic processes and changes in hormonal levels can cause itching. Only a veterinarian can identify the cause of the disorder and select effective treatment. It is recommended to go to a large clinic that offers hormone testing.
Allergic reactions
If an animal is hypersensitive to a particular food or food component, the pet begins to comb its face, paws, and ears. A food allergy can be detected through a diagnostic diet, which involves changing the diet to identify the trigger component.
Non-food allergies are characterized by itching as a reaction to anything other than food:
- Insect bites, fleas. Cats scratch bite sites. If there are fleas, there is itching on the back of the back, belly, and tail.
- Dust, flower pollen. In summer, this type of allergy gets worse.
- Individual intolerance. A rare type of allergy called contact allergy. The chest and stomach of the cat are affected. To find out exactly what substance the reaction occurred to, you need to conduct allergy tests.
Ringworm and other types of skin mycoses
Dermatomycosis is a fungal disease in which a cat scratches its neck, hair falls out at the scratch site, and clearly defined spots form. Only a veterinarian can identify the type of pathogen and select therapy.
You should not try to cure the cat yourself - this may worsen the disease. A person can get lichen after contracting it from a cat. The ringing type is especially dangerous. There is no need to waste time; it is important to get your pet to the clinic as soon as possible.
If your pet is found to have lichen, it should not be bathed. Otherwise, the pathology will worsen and the spots will spread throughout the purring body.
Dermatomycosis is a dangerous fungal disease
Infectious lesion
Infectious agents enter the house through the owners' shoes, then spread to the animal's fur and skin. If a cat has wounds or even small scratches, the infection gets into them and causes inflammation and suppuration. To eliminate pathology, ointments and powders are used. For humans, this pathology does not pose a threat.
Helminthiasis
Not all owners of purring dogs know that itching and scratching on the neck can be a consequence of helminthic infestation. Parasites disrupt metabolic processes in the body, and the pet does not receive the necessary nutrition. As a result, the skin dries out, dandruff and itching appear. Helminths also cause the development of an allergic reaction, manifested by a rash and itching. The pet suffers greatly and itches until it bleeds.
Infections can be caused by food or contact with contaminated objects:
- raw meat/fish;
- insect (flea) bites;
- sick animal;
- owner's shoes.
If you suspect a helminthic infestation, you need to have your pet's stool tested. The cat is prescribed a course of anthelmintics. For prevention, you should regularly give your animal anti-worm medications, such as Albentabs, according to a schedule.
Parasites pose a threat not only to cats, but also to people. The risks of infection are especially high among young children, as well as owners who let their pets into their beds.
External parasites
In addition to fleas, the animal may have other external parasites that provoke scratching of the neck:
- Ear mite. The pet constantly twitches its ear and the area near it, tilts its head to one side. Often the result is severe bloody scratching.
- Sarcoptic mange (scabies mite). Accompanied by severe itching. It can appear on any part of the cat's body.
- Cheyletiellosis. Rarely seen. Appears as white moving dots located along the back. The disease is popularly called “pityriasis” scabies.
- Lice. Provoke itching. Parasites can be seen in your pet's fur.
Itching may be caused by external parasites
Psychological problems
Cats, like people, are susceptible to nervous tension. A purr may scratch its neck vigorously due to nervousness, having experienced stress from moving, or the appearance of a new person (child) or animal in the house. To normalize the condition, the pet is given a herbal-based sedative, for example, “Cat Bayun”.
Why does a cat scratch its neck?
There are many reasons that cause itching other than flea infestation. The problem may lie either in the activity of other parasites or in individual intolerance to certain substances.
Parasites
When the most obvious cause of neck scratching, namely fleas, has been ruled out, you should not immediately stop looking in this direction, because other types of parasites may also bother the animal. So, itching can be provoked by:
- Subcutaneous mites that cause demodicosis - a disease that affects the skin and coat of a pet. In the localized form of the disease, the lesion occurs in a separate area of the body, for example, on the neck. In this case, the skin turns red, pustular rashes appear, the integument peels off, and the hair on the head, ears and neck falls out. The animal is primarily concerned about severe itching and the appearance of bleeding wounds, which are further scratched with claws. Cat subcutaneous mites of any kind are not infectious to humans. Two types of such parasites can live on a cat’s body: Demodex cati, which is conditionally pathogenic (it is part of the normal flora, but under favorable conditions it can multiply and cause disease),
- gatoi, a scabies mite that belongs to a pathogenic species and can be transmitted from one individual to another.
The gatoi scabies mite causes severe itching in cats and can be transmitted to other pets, but not to humans.
Dermatological diseases
Skin diseases can be caused by both changes within the body and pathogenic microorganisms:
- Fungal dermatological diseases (dermatomycoses) are a common cause of problems in cats, caused by mold and yeast infections. The most common disease in this group is lichen, the causative agent of which is the fungus microsporum, epidermophyton or trichophyton. The disease affects the hair follicles and skin. Ringworm is contagious and can be easily transmitted from cat to person, so owners should be vigilant, especially if there are small children in the house. The disease manifests itself in symptoms: round redness appears on the body, which itches and bothers the animal;
- peeling of the skin and hair loss are observed, which most often affects the area of the head, neck and limbs;
- When a secondary infection occurs, scratching can transform into festering wounds.
Ringworm most often affects the head, neck and extremities, causing itching, flaking skin and hair loss.
- traumatic - due to mechanical damage to the skin on the neck, burn or frostbite;
Allergic reaction
A nonspecific immune reaction to an irritant can occur in animals as often as in humans. Possible allergens that can cause itching in the neck area:
- feed;
- flea drops on the withers and an anti-flea collar;
- medications;
- shampoo and other hair care products.
An allergic reaction can be limited to local itching and redness, which causes the animal to itch a lot, or cause additional, more dangerous symptoms, including life-threatening swelling of the airways (Quincke's edema).
Video: a cat has an allergic reaction to a flea collar
Effective Treatments
Itching and scratchy wounds are a consequence of the disease. Until the cause is eliminated, it is impossible to relieve the itching. But before the animal gets to the veterinarian, its condition can be alleviated. To do this, wounds need to be disinfected with hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. You cannot use any cosmetics, such as shampoo, cream, wool powder.
To prevent the cat from licking the medicine from the fur, you should wear a special collar.
A special collar protects the animal.
Treatment methods are selected individually based on test results:
| Type of disease | Treatment |
| Demodicosis | Lasts up to a year. It involves a number of measures:
|
| Helminthiasis | Antihelminthic drugs are prescribed (Febtal, Panacur, Prazitel, Kanikvantel). |
| Bacterial infection | Prescribed:
|
| Eczema | Therapy should be comprehensive:
|
| Allergy | Necessary:
|
| Dermatomycoses | Therapy lasts up to 2 months and involves:
|
For treatment to be effective, you need to provide your cat with a balanced diet. Nutrition should be adjusted, even if the cause of the pathology is not a food allergy. A lack of vitamins and microelements negatively affects the condition of the skin and coat, and the speed of wound healing.
Prices for appointments in our clinics
| Name of veterinary services | Unit | Price, rub |
| ⭐ Initial appointment | 1 animal | 400 |
| ⭐ Repeated appointment | 1 animal | 250 |
| Initial appointment with a specialist | 1 animal | 1100 |
| Consultation without an animal | — | 550 |
| Consultation with a doctor based on test results | 1 PC. | 400 |
| Weighing animals | 1 animal | For free |
| Additional fixation for aggressive animal behavior | 1 animal | 700 |