The question of whether lice jump from one person’s head to another’s hair is of particular interest to parents who send their children to kindergarten: after all, children bring most diseases from there. Pediculosis is a serious disease that can be very difficult to get rid of. The situation is further complicated by the fact that the disease spreads very quickly: after a sick child appears in a group, within a few days symptoms can appear in everyone around them.
But this is not because lice are able to jump or fly. They can do neither one nor the other. They lack wings and usually move quite slowly. But if desired, a louse can cover a distance of 10 cm in 30 seconds.
Lice are the causative agent of pediculosis
There are several varieties of human lice. They differ in their habitat. Headworms live only on the scalp and in the human hair growing on the head. This is how they differ from pubic and wardrobe hair.
Parasites have a well-developed oral apparatus, with which they pierce the skin and suck out blood. When they bite, they inject saliva, which prevents the blood from clotting and causes severe itching. The louse feeds every 3-4 hours.
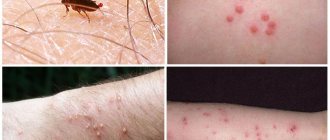
Lice infestation is called pediculosis. Signs of lice:
- severe itching;
- if there are a lot of bites, they constantly itch, scratches appear on the scalp that do not heal well;
- wounds become infected, skin lesions can be significant;
- with severe infection and a large number of parasites, many traces of their vital activity remain on the hair and skin, the hair becomes sticky, tangled, and tangles form;
- a person with lice becomes irritable and nervous due to constant itching.
Lice can be detected visually. They are clearly visible on light hair. Dark ones require more attention. You can see nits at the roots of the hair; these are lice eggs.
Lice carry typhus and other serious diseases
Head lice are indeed carriers of a serious disease - relapsing fever.
The infection enters the human bloodstream when lice are crushed and their hemolymph is rubbed into damaged skin when scratching the head. That is why it is important to get rid of lice early and quickly.
But there is no need to panic! Currently, relapsing fever is rare, can be treated well with antibiotics and is rarely fatal, especially if the person eats normally and sees a doctor promptly.
Just be sure to take your child to the pediatrician after you have been treated for head lice.
Life cycle of lice
The life cycle of this parasite averages 35 days. First, the female lays eggs. Translucent oval nits are attached to the hair at the very base. They are very small and can be difficult to see. After 7 days, nymphs emerge from the eggs. They survive several moults and after 7 days they turn into an adult capable of reproduction. The female lays 4-5 eggs every day; in total, she lays about 120 eggs in her life. If you don't fight lice, they multiply very quickly.
Lice eggs are laid at temperatures above 32 degrees, that is, the temperature of the human body is optimal for their reproduction. When the temperature drops, lice do not reproduce, but their life cycle also takes longer. When the temperature drops to +10 degrees, the louse can live up to 10 days, hibernating. A nit can also survive difficult times even outside the human body, and then, when optimal conditions occur, hatch and continue to parasitize.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Can toxoplasmosis be transmitted sexually?
Dog worms: can they be transmitted to humans, what do they look like in feces and what tablets to treat
What lice and nits look like on human hair, in adults and children
Horsehair parasite: structure and description, life cycle and routes of infection
Thiabendazole: instructions for use, active ingredient, price and analogues
Long worms in cats: main types, description and methods of treating parasites in cats
Methods of transmission of the disease
How is pediculosis transmitted?
The spread of the disease occurs through direct contact: through handshakes, hugs, kisses.
This is why children are most often infected: in kindergarten there are enough opportunities for such contacts.
You can also become infected through another person's belongings. The fact is that there are 3 types of lice: head, pubic and body lice. The latter prefer to live in the folds of textiles. They can be found not only in everyday clothes, but also in bedding. Therefore, when going on an overnight stay, you are not immune to the risk of catching lice.
Pubic lice are transmitted primarily during sexual intercourse. From intimate places they are able to move to other parts of the body (but usually do not settle in the hair on the head).
The disease can also be transmitted through household items, such as towels and underwear. Therefore, everyone should have their own personal belongings.
You can catch head lice mainly through contact with your hair, and also if you use someone else's combs, elastic bands or hairpins. Lice can live without food for up to 7 days. Therefore, simply by combing your hair with someone else’s comb, which a sick person has not used for a week, you can catch lice. In addition, lice are able to swim and survive in water for a long time. So the risk of infection in a pool or open body of water is also quite high.
Ways to spread head lice
The spread of lice always occurs in places where people live, and especially often when their settlement is dense. Head and body lice spread especially quickly in communal apartments, barracks, and refugee camps. During the war years, parasites plagued soldiers in barracks and trenches - lice feel completely at ease in crowded areas.
Lice-borne epidemic typhus is even called “trench fever” because it decimated soldiers during the Crimean Campaign, the Napoleonic Wars, and World War I in the trenches on the battlefield. In unsanitary conditions, lice spread between soldiers very quickly and infected almost everyone.
Lice are transmitted from person to person in several ways:
- crawl from one person's head to another. Most often this happens among those who share the same bed, as well as between children when playing together. This is the main method of transmission of lice.
- Head lice can be transferred through hygiene and household items - combs, towels, hair ties, hoops, and from there they get onto the head of another person when sharing these things. This method is relatively rare, but can occur.
- Lice are also spread through shared clothing. For head lice, hats, scarves and jackets with a hood are most relevant, and body louse can be transmitted through any clothing that contains nits, nymphs and adult insects.
- In very rare cases, parasites fall onto bedding and pillows, and from there they climb onto the head of another person who lies down on the same bed.
It is important to understand that carriers of lice are all people with any number of these insects on their heads. However, the more heavily a particular person is infested with lice, the greater the likelihood that they will fall from his head onto furniture or household items, and therefore the greater the risk of infection from him.
Lice can be transmitted through water in public bathing areas. It is known that in India, in poor areas, lice are carried directly in rivers, in the shallows of which children, adults, and old people swim. Pubic lice are most often transmitted in this way, however, head lice can also spread in the same way: scientists know their high resistance to hypoxia and their ability to survive in water for up to two days.
Nits (lice eggs) due to the inability to move are transmitted only by the forces of the person himself. This could be the use of shared combs, which leave hair with eggs attached, towels, shared clothing or bedding, which leave infected hair.
In general, nits are rarely transmitted and are not the main infecting agents. In other words, nits are not transmitted in quantities capable of causing an epidemic and infecting a large number of people.
How does lice infestation occur?
Lice can live off the human head for a limited time, up to 2 days. That is, you can catch lice, for example, on long-distance trains, on the headrests of seats in transport, and in other public places. You can become infected even in a swimming pool or bathhouse in the water, and at elevated air temperatures, lice can live for some time.
The main ways of becoming infected with lice:
- in very close contact with an infected person;
- when using his personal belongings;
- in common areas.
It is believed that lice appear in people who do not maintain personal hygiene. This is wrong. Lice are attracted to blood, and not other human secretions, so they live on both clean and dirty hair and skin. People with an antisocial lifestyle do not have the opportunity to fight parasites, so they are more likely to become infected from them. You don't need to wear their hats or use their combs (if they exist) to do this. It's enough just to walk or stand nearby.
Types of disease
We will talk about whether lice jump in a separate section of the article. And now we propose to consider the types of the disease. There are three types of parasites:
Head lice are more often found in people with long hair. There are a lot of possibilities for infection. The most common:
- Close contact with someone who has lice.
- Using one headdress.
- Shared hairpins, bows, comb with a person with lice.
Lice are noticed by the itching caused by the bites. Some people develop rashes, papules, or blisters.
Body lice live on human clothing and move to the body only to feed. There is a high probability of infection among those people who do not have the opportunity to wash themselves and change clothes (socially disadvantaged population, homeless people).
Pubic lice live on the hairy parts of the body:
- Itching.
- Rashes (papules).
- bluish spots 2-3 mm in diameter (pubic lice are capable of destroying hemoglobin in blood vessels).
What happens after infection
Like any other organisms, these parasites instinctively try to preserve their species. Therefore, they begin to actively reproduce. At first, not everyone can feel the presence of lice on their body. After all, they bite weakly, and there is no need to actively move around the body.
Only after 2 weeks will new parasites appear from the eggs laid by the adults.
During this period, the larvae actively grow and feed. Therefore, a person begins to itch constantly. Unbearable itching for some time causes a variety of assumptions in people: from stress to an allergic reaction to food or cosmetics. But very soon the real cause of the itching becomes clear.
During this period, young individuals move very quickly and it seems that the whole head and body are itching. This is why it is assumed that lice jump or fly.
In fact, there can be many of them, and they spread freely throughout the body, where they can easily reach the blood vessels.
One female can lay 200-300 larvae in a month, so if the treatment process is delayed, the number of lice on the body of one person can increase very quickly.
Can lice appear on their own?
There are still so-called myths about how these parasites can be acquired. So, some still believe that lice can appear when a person is nervous a lot, or that they are inherited. This is absurd, because lice is not some kind of genetic disease, but a disease caused by parasites living on humans. Also, stress has no effect on insects, so if a person often worries, he will not get lice.
Some people also believe that the appearance of parasites is influenced by a person’s level of cleanliness. In principle, this is only partly true, since head lice, for example, will prefer clean hair to dirty hair, because in this case it is easier for them to attach nits and feed.
What to do first
The first thing you need to do is try to protect your loved ones. Even if you still suspect the presence of the disease, you should immediately change your bed linen (wash dirty ones at high temperature), wash your combs, hairpins, etc. After this, you can try looking for parasites.
It is quite difficult to detect pubic lice: due to their color, they practically merge with human skin.
Body lice are larger than their counterparts, so they can be seen on things or skin in places where itching is felt. More details in this video:
The most common type of parasite, hair lice, is the most difficult to detect. To do this, you will need a fine-toothed comb. You can look for lice on both dry and wet hair. Comb them with a regular comb, and then run a fine comb from root to tip along each strand and carefully watch what remains on the comb. Particular attention should be paid to the areas behind the ears and on the neck (the place where hair begins to grow). It is not always possible to see the lice themselves on a comb, but you will find nits (white larvae) very quickly.
You need to try to find and destroy as many larvae as possible.
Some may confuse nits with dandruff. The latter is characterized by flaking of the scalp. Scales can be easily removed from hair, but nits, on the contrary, are tightly glued to them thanks to a special liquid secreted by lice when they lay eggs. Dandruff particles are different in size, but nits have the same oval shape.
The larvae can have different shades: from milky to dark brown, while the dandruff flakes are much whiter. In addition, dandruff does not cause such severe itching: if there are lice, a person literally cannot take his hands off his head, constantly scratching the skin. This is not recommended: vigorous scratching can lead to even greater development of the disease, as lice stick more strongly to the affected areas.
How to distinguish living nits from dead ones?
There are several ways to determine whether there is a parasite embryo inside the shell. External signs of live nits:
- light shade (white, milky, beige);
- there is shine;
- the shape is correct - oval, there are no dents;
- If you try to crush the shell with your nails, you can hear a fairly loud click.
When studying the question of how to distinguish live nits from dead formations, you should pay attention to a number of features that characterize dry parasite eggs:
- lack of shine, the nit looks faded;
- color changes from light to gray-yellow;
- on one side you can see a hole - when the larvae appear, the lid opens;
- you can see dents on the surface;
- When you try to crush dead nits with your fingernails, there is no characteristic sound.
Photo of dead nits Live nits on hair
Ways to combat pediculosis
You can get rid of lice yourself. Buy a remedy for head lice at the pharmacy. Usually this is a lotion or shampoo, the main active ingredient in which is permethrin. The product is applied for 8-12 hours and then washed off.
In order for it to work effectively, you need to wrap your head with plastic wrap or wear a special shower cap.
There are also more convenient means to use, for example, an aerosol. Just spray it on your hair and rinse with water after 10-15 minutes.
Some try to get rid of lice using folk remedies, believing that the body does not need additional chemicals. One of the common treatment methods is treating hair with kerosene mixed with vegetable oil. This method is quite effective. But at the same time, there is a high probability of getting burns and severely weakening your hair.
Other folk remedies include tar soap, geranium oil, pomegranate juice, etc. But if soap somehow helps to cope with an unpleasant illness, then other means are ineffective. Whatever method of struggle you choose, you need to keep in mind that treatment should not be a one-time treatment. In most cases, a course of drugs is required. And the point here is not that the products cannot get rid of lice in one go: an adult is capable of laying eggs every 8 days. And the offspring themselves reach sexual maturity very quickly. To prevent the rapid spread of parasites, you need to use the products for several weeks.
Combing can also be one of the methods of getting rid of an unpleasant disease. This especially applies to children: after all, except for tar soap, not a single drug can be called completely safe for a growing organism.
It is best to carry out the procedure in the evening, when the child’s activity is minimal. You will have to comb out nits for a long time: to completely get rid of lice, you will have to spend evenings with a comb for several weeks.
When carrying out treatment, you need to regularly wash bed linen, towels and other personal items, and then be sure to iron them. It is better to carry out cleaning daily, and blankets, outerwear, and soft toys should be taken out into the cold more often (if treatment is carried out in winter). By following these simple rules, you can completely get rid of lice in a few weeks. In order not to become infected with them, you must always remember that using other people’s things is strictly prohibited.
Some features of lice transmission
There are also some details in the transmission of lice that may seem unusual and even curious.
For example, information has been statistically confirmed that head lice more actively infect nervous people who are prone to worry and anxiety. It is believed that nervous people have a more active blood pulsation and sweat more often, which makes their body odor more attractive to parasites.
In addition, sexual contact can transmit two types of lice at once - head and pubic. Such double infestation is one of the most unpleasant consequences of promiscuous sex life.
In any case, for reliable protection against lice, you should remember all the ways of their transmission and avoid:
- close contact with unknown people or those with obvious signs of lice infestation
- using other people's hygiene products
- swimming in places with a lot of marginalized social elements.
And if suddenly a case of lice infestation of one of the children was discovered in kindergarten, then it is better to keep your child at home for a week or two. This will save parents from serious hassle.
Despite the abundance of hygiene products that store shelves are littered with, lice still remains an acute problem. Basically, lice are observed in children attending preschool institutions, camps, and schools. Many parents who are faced with a problem are interested in whether lice jump? In this article we will talk about lice and tell you how you can get infected with it. In addition, we will look at the types of parasites and discuss methods of treatment and prevention.
It is important to know that lice are sedentary and quite vulnerable creatures. They are unable to travel long distances and cannot fly. And they are not able to reproduce quickly. A very interesting fact is that the female parasite is capable of reproducing only a few dozen nits (eggs) during its entire life cycle.
We suggest talking about whether head lice jump, consider the causes and types of lice.
The disease, which we know as pediculosis, has been tormenting people for many hundreds of years. In Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, the most common preventive measure was shaving the head. The cause of the disease is parasitism of one type of lice (head, body or pubic). In the latter case, the disease has a slightly different name - phthiriasis.
Now briefly about what lice are. The average length of an insect is only 5-6 mm. At the same time, you can see a very small head and a fairly voluminous abdomen. As you know, lice feed on human blood. This becomes possible thanks to the structure of the oral apparatus, which is represented by a tube, hooks and stylets. Can lice jump from person to person, and how do they stay in place? The insect's paws, which have curved claws that resemble claws in appearance, help the insect to firmly attach itself to hair or things.
Briefly about reproduction. Female lice are capable of laying eggs (nits) from which they hatch into almost sexually mature individuals (slightly smaller in size than adults). After just a few months, they also become capable of reproducing offspring.
Can head lice live on people other than humans?
Yes, head louse can exist outside of human skin and hair. For example, they can live for some time in a pillow, blanket, bedding, clothing and hats, upholstered furniture, combs and hair accessories. They can live and move on any surface, even in water. You can catch lice, for example, on the beach they can move on sand or pebbles.
The louse crawls quite quickly and can run about 50 cm in a minute.
The head louse is a human parasite. That is, it does not feed on the blood of dogs, cats, other animals and birds. They have their own parasites. But the louse can live temporarily on animals. For example, a dog can bring back a louse that has fallen on it from a walk, and an insect can pass from a dog to a person.
Adults can live outside humans for no more than two days. They usually die earlier within 24 hours, since they are left without food, and they need food every 3-4 hours. Nits can remain outside the human body for up to 4 days.
Lice live in a wide range of temperatures. When the temperature drops below 10 degrees, they hibernate. At temperatures below 8 degrees they die. At high temperatures they can survive if the heating is short-lived. If cooked for a long time, they die.
Ways of infection with pediculosis
There are several ways in which lice are transmitted from person to person:
- contact;
- through clothing and care items;
- through water;
- through surfaces.
The most common method is through direct contact with a lice-infested person. The least likely, but at the same time real, is through surfaces. It is worth understanding that a louse cannot jump or fly. But she crawls quite quickly, although her legs are not designed to move on smooth surfaces. The structure of lice is such that three pairs of legs help it cling to hairs. In half an hour, an insect can cover about 50 cm, which means it takes time to become infected. With instant contact, you may not become infected with lice. But an infected person can throw off the parasite if he violently shakes his head or his personal belongings near the new host. This is why you need to be careful when entering a new room with a large concentration of strangers.
How dangerous are lice?
Head lice cause lice. This disease is unpleasant in itself. The bite sites itch, the person scratches the wounds. They can become infected and take a long time to heal. Crusts appear on the head. Bites can also cause allergic reactions. Without treatment, lice will multiply endlessly. With severe damage, many traces of lice on their body, empty shells of nits, excrement, and saliva remain on the scalp and hair. All this covers the hair, tangles it, tangles form, and an unpleasant odor appears.
Unlike body lice, which carry typhus, for example, or pubic lice, which carry sexually transmitted diseases, head lice are less dangerous. But you can’t help but fight them.
Main causes of head lice
When thinking about where you can pick up lice, do not forget that they are transmitted only from person to person; You cannot get lice from domestic or stray animals.
Here are the main causes of head lice:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- close contact of a healthy person with a head lice infection;
- living in conditions of complete unsanitary conditions, and this is simply an ideal environment for the rapid proliferation of parasites;
- sharing hats and other headgear, as well as combs, hairpins, etc. with the infected person;
- use in public saunas, bathhouses of towels and other items that have not been carefully processed.
Factors that will increase the risk of infection:
- visiting beauty salons and hairdressers where the craftsmen do not follow hygiene rules and do not disinfect their tools;
- accommodation in a hostel, hotels (without regular treatment);
- constant use of crowded public transport;
- use of cloakrooms in public places;
- Swimming in public pools and ponds with standing water without a swimming cap.
The female louse lays up to ten eggs per day, and they attach to the hair with the help of a secretion secreted by the insects, which hardens quickly, which, in turn, allows the eggs to be fixed on the hair. That is why they are difficult to shake off, unlike dandruff.
Nits are attached closer to the scalp at a distance of up to one centimeter, where it is warm enough. The nits take seven to ten days to mature, and then the young louse hatches. It is similar to an adult, only smaller, and in about a week the parasites become adult, sexually mature insects.
How to deal with head lice
Lice can be seen in good lighting and without additional equipment. Detecting nits is more difficult. They may look like hair product residue or dandruff. Nits are usually located behind the ears, along the hairline on the neck.
Combing hair is not only a way to detect parasites, but also one of the mechanical ways to combat them. It only works in one case, if there are very few insects and their eggs in the hair, that is, immediately after infection. Careful brushing can remove all adults and individual eggs. But if even one nit remains, in a few days everything will repeat itself, the insects will multiply.
Important: if the disease is detected in one family member, it is necessary to check all other household members for the presence of head lice and nits.
It is impossible to wash off lice with regular water. They are not afraid of water and can live in it for up to two days. Regular shampoos don't help either.
If the hair is short, the treatment will be faster and more effective. With a short hair length, there is little space left for laying eggs, so the rate of parasite reproduction decreases. And it's much easier to process short hair. Shaving your head has always been the most effective way to control lice. But this is not always possible for aesthetic reasons.
Diagnostics
Despite the high level of development of modern medicine, the only way to diagnose the disease is through examination. It is regularly held in all educational institutions (schools and preschools). The diagnosis is confirmed only when living individuals are detected, and not nits. Infected children are excluded from attending educational institutions and are sent for examination to a dermatologist.
The specialist conducts an examination using a Wood's lamp (for head lice) or a slit lamp (for clothing parasites). Sometimes microscopic examination of hair, nits, or live specimens is performed. A modern diagnostic method includes videodermatoscopy, which allows you to capture enlarged lice in a photo or video.
Traditional methods
There are many folk remedies to combat lice. They are preferred for use in cases of head lice infestation in children. It is believed that folk remedies are less harmful and cannot harm health.
To combat lice use:
- washing hair with kerosene;
- vinegar wrap;
- rinsing with tansy infusion or wormwood decoction;
- masks made from crushed cranberries;
- masks made from onion pulp.
Kerosene and vinegar are good because they not only kill insects, but also clean the hair roots and dissolve the substance that attaches nits to the hairs. After this treatment, it is easier to remove them from the hair.
The danger of these methods is that, firstly, you need to know the exact concentration and time of exposure, otherwise you can burn your scalp or get an allergic reaction. Secondly, kerosene and vinegar damage hair; it will take a long time to restore it after such treatment. Traditional methods require repeated use. The fight against lice can take a long time, and during this time new individuals will appear from the nits remaining on the hair.
Dust soap is effective against lice and nits. They wash their hair with it several times for several days in a row. It is necessary to rinse your hair well and comb out dead insects and eggs from your hair each time.
Effective treatment
An effective way to get rid of lice is to use special lotions or sprays. These pediculicides can get rid of lice in one application. If the infection is severe, it will take longer.
We offer medications for treatment: Medilis-BIO, Medilis-Malathion, Medilis-Permifen, Medilis-Super. Lotions are rubbed into the scalp, left on the hair for a certain time required for effect, after which the head is thoroughly washed. To remove nits and dead insects remaining in the hair, the hair must be combed thoroughly.
A spray differs from a lotion only in the form of application. Spraying the head is a more dangerous method, since with such application you can inhale a dangerous substance. It is not dangerous to humans in itself, but in high concentrations it can cause allergic reactions. Spray products are not recommended for use in the treatment of children, pregnant women, people suffering from asthma and respiratory diseases.
When using any means, you must follow safety precautions, in particular, protect your eyes from contact with toxic substances. Leave the product on your head for no more than the permitted time to prevent skin irritation and chemical burns. When processing, it is necessary to provide access to fresh air into the room; after processing, the room must be ventilated.
Each drug has instructions for use, which must be strictly followed.
These products are not suitable for treating pregnant and lactating women and children under 5 years of age. For them, it is better to use less dangerous folk remedies.
When using any professional or folk products, in addition to the head, you need to treat combs, towels, everything that can come into contact with the hair, and where lice can move.
We destroy lice: don’t panic!
Of course, you must first visit a doctor, but in fact, the number of people dealing with this problem is low. Many people immediately run to the pharmacy, because modern pharmacology is replete with drugs to combat lice.
Moreover, each manufacturer praises its product, publishing information that it is safe and promising to get rid of “uninvited guests” in one use. Is this so? After all, we are talking about the health of the baby. Let's figure it out.
Lice control products
For external use, two groups of drugs are used.
1. Insecticides - chemical compounds
- Permitin preparations: Medifox, Hygia, Nyx, Nittifor
- Phenothrin preparations: Aniti-bit, Veda
- Malathion preparations: Pedilin, Para-plus
They are produced in the form of shampoos, soaps, aerosols, emulsions, gels, creams.
How do they work?
They paralyze the nervous system of lice, so they die. After all, all processes in their body stop: breathing, movement, cardiac activity, and so on. The instructions state that these drugs are practically safe. However, in reality this is not always the case. Since they often cause allergic reactions, dry the scalp, increase hair fragility, and lead to the formation of dandruff.
In addition, recently, lice are increasingly developing resistance to these drugs.
2. Preparations based on mineral oils - dimethicones. They are safer because they rarely cause allergic reactions. An additional advantage is that they do not irritate the scalp and lice do not develop an addiction to them.
This group includes Paranit, Pediculen Ultra, Nyuda and ROSH TOV Double Impact.
The drugs are available in the form of an aerosol, shampoo, and lotion. Some of them are equipped with a special fine-tooth comb and a magnifying glass.
How do they work?
Oils clog the respiratory corpuscles of lice, larvae and nits, which means they actually suffocate. In addition, under the influence of drugs, lice's water balance is disrupted and dehydration occurs.
However, no matter what product you choose - based on a chemical substance or natural oils - remember that they are not recommended for use by children under three years of age, pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers. In these cases, it is still better to consult a doctor.
Another important point: these drugs will not get rid of lice just in one go, because, alas, they do not completely destroy nits, because the eggs have a rather thick shell. But these preparations still dissolve the glue that attaches the nits, and after treatment they are easier to comb out.
Therefore, you will have to treat your head again after 7-10 days (remember the development cycle of lice). This approach gets rid of lice in 99.9% of cases, and three-time treatment at regular intervals completely cures them.
The exception is Paranit Sensitive. Manufacturers claim that it completely destroys nits and lice within 8 hours (that’s how long the treatment lasts).
How to process?
It's not that complicated. The main thing is to strictly adhere to the instructions of the drug: how to apply, cover your hair or not.
There is no need to overexpose it. Firstly, there is no point (living individuals will die within the time specified in the instructions, and the product will not have much effect on nits), and secondly, it can cause harm.
However, some general rules still exist:
* Before use, make sure that the child is not allergic to the drug you have chosen. Therefore, apply a little product to the skin of the inner surface of the forearm and leave it for 20 minutes. If after this time there is no itching or redness on the skin, then the product can be used.
*Before treatment, be sure to cover your face and cover your baby’s shoulders with a towel so that the product does not accidentally get on the skin or eyes. And only then apply it.
* After the allotted time has passed, wash off the drug with shampoo, but in such a way that water does not get on other parts of the body or in the eyes.
* Use a special fine-tooth comb to remove nits and dead lice from damp hair. After combing each strand from the end to the ends of the hair, do not forget to thoroughly clean the comb with a napkin or rinse it under running water.
* Wash and iron clothes, underwear, bedding with an iron and steamer. After all, lice die at high temperatures.
* For items that cannot be washed, arrange a two-day “quarantine”. Because lice do not live long without food.
Preventing lice infestation
As mentioned above, no one is immune from head lice. Most often, children are susceptible to it after being in a group. It is easy to pick up parasites at a health camp and even at school. One person can spread pests many times over. Children bring lice home from children's institutions and infect all family members with them. It is impossible to guarantee yourself protection from this, but some measures should be taken to get rid of pests immediately and prevent a severe infestation.
What you need to do to avoid getting lice:
- Do not under any circumstances wear other people’s hats;
- do not use other people’s combs and hair accessories;
- avoid direct contact with people who do not maintain personal hygiene and lead an antisocial lifestyle;
- regularly inspect children’s heads for nits and lice;
- If you suspect an infection, comb your hair, you can use weakly concentrated anti-parasitic shampoos.
You can use parasite repellents. It is believed that they do not like strong odors, for example, tea tree, geranium, caraway, mint, etc. You can use herbal decoctions to rinse and flavor your hair. This will not protect against infection 100 percent, but it may repel insects.
The main thing when you detect pests in your hair is not to turn a blind eye to the problem and start fighting immediately. This way you can get rid of them faster and without harm to your health.
Lice jump or fly
No, lice do not jump or fly. Unlike fleas, their tenacious legs are designed only to hold tightly to human hair, but they are not suitable for jumping. In addition, lice have a fairly massive body and no wings. All this would make them extremely vulnerable to parasites if they could not crawl. They do this masterfully quickly and deftly: they only need a few seconds to jump on someone’s head.
Is it true that head lice can get from dirt if you don't wash for a long time?
No: contrary to popular belief, these parasites do not appear spontaneously in humans, i.e. from dirt, they can only be transmitted from another infected person. But there are other types of human lice that are more capricious and are infested precisely because of poor personal hygiene: body lice and infrequent changes of underwear.
Can lice that have left the head breed again?
No, lice do not live long after they are removed from the head! The eggs require constant contact with a warm human head and die within a few hours of removal. Larvae and adults need blood for timely molting, maintenance of life and reproduction, so they will also die a maximum of 2 days after removal. So don’t go to extremes in your fears: lice can only survive on the head of the owner. They do not crawl on carpets, furniture or vehicles (like a bus) in search of a new owner, but simply die, leaving their heads.
Is it possible to get infected in transport, cinema or at work?
As for public places, you can also become infected in transport, during sports activities, as well as in the theater and other places where unfamiliar (barely familiar) people are forced to be nearby.
Police officers, doctors, social workers and other people who, due to their duties, are forced to come into contact with a large number of strangers, are also at particular risk. How can they protect themselves? For example, use tea tree oil as a lice repellent.
Is it possible to get lice at home?
Yes this is true. The most common places where adults can get lice are at home and in public places. And lice are usually brought home by small children from kindergartens and less often from school or brought from summer camp. Therefore, it is believed that lovers, families and even neighbors and hostel residents are at particular risk, since they spend a lot of time together while being close to each other.
Can you get lice while taking a selfie?
Yes, there is such a danger, because during selfies people are usually head to head and this is an ideal path for lice to travel. These parasites only need a few seconds to cover the small distance between the heads of two people. Therefore, it is better not to take pictures with just anyone!
How do you get lice?
There are several options for transmitting lice:
- Adult lice usually simply crawl from the hair of an infested person to another head and are transmitted through head-to-head contact. A louse can manage to crawl unnoticed even during a short kiss or hug with a person carrying lice.
- Lice eggs are rare, but can be transmitted through shared household and hygiene items: combs, elastic bands, towels, pillowcases
- Eggs may be in the folds of clothing. Do not wear other people's clothes and hats, this may result in infection!
You can get infected from any patient, but the more lice an infected person has, the more dangerous the contact with him. People are most infective when they have adult head lice because... newborn larvae do not leave the host territory. Try to stay away from such people if you are forced to be in the same room with him and notice that someone is crawling in their hair.
Is it true that lice appear more often on people with straight, long hair?
Yes, this is partly affected by hygiene, hair type and length. But, as we said above, lice do not start from dirt, the level of hygiene in this case affects in a completely unexpected way. Lice are not selective and can appear on anyone, but it is believed that they would rather prefer clean (!), long and straight hair, from the roots of which fat, dust and skin flakes have been washed away so it is easier to cling to them.
Why straight lines? Different hair (straight, curly or very curly) has a different section and number of hair shafts. So, straight hair has a round cross-section and one shaft is convenient for lice to grab onto. According to research, African Americans rarely get lice because they have very curly hair.
Why long? Often they are simply loose and not tied up, making it easy for lice to climb up them and settle at the roots. In addition, there is an opinion that nervous people are more likely to suffer from lice: supposedly they worry more, sweat more, and this attracts lice.
Is it true that only children get lice?
No, that's not entirely true. Lice are indeed common in children aged 3 to 12 years, since they usually spend a lot of time together in groups. And it costs lice nothing to crawl from one head to another. In kindergarten, children play together and sleep in adjacent beds, so if one child has lice, there is almost a 100% chance that all of them will soon have lice. In addition, young children often do not look for the causes of itching in the head and do not complain about it, but simply scratch their heads. Therefore, schools and kindergartens should conduct periodic medical examinations of children for head lice. But adults can also become infected: absolutely no one is immune.
Is it possible to clearly determine how long ago the infection occurred?
Almost impossible. If you come to your senses and see a lot of lice on your head, then it is obvious that you have been their carrier for a long time. As a reminder, it only takes about 3 weeks for a generation of lice to become adults and begin producing their next offspring. Also keep in mind: nits are usually white in color, but as they approach hatching time they turn brown. This color means that larvae are already sitting inside, ready to hatch.
Is it possible to get lice from pets - cats and dogs?
No: domestic animals have their own types of lice, but they are strictly species-specific and cannot be transmitted to humans or animals of other species. For example, cat lice will not feed on the blood of a person, dog, or other creature. Human head lice also cannot affect anyone except other humans and some very closely related species of monkeys.
Infection from animals
Now we will answer the question of whether lice jump like fleas. Is it possible to get them from pets? Remember: lice cannot jump, since their body and the structure of their paws are completely unsuited to this. But fleas are typical blood-sucking parasitic insects that live in apartments and can jump.
The so-called cat lice are the cat lice, and the dog lice are the dog lice. These insects are commonly called lice only because they have a similar appearance to the parasite we are considering. It is worth remembering that each type of lice eater is specific; it cannot live on other animals (including humans). For example, if a cat's hair eater gets on a person, he will soon die. The same fate awaits them if they fall on a dog or any other living creature.
How to get rid of lice in 5 steps
Knowing the mechanisms of the appearance and reproduction of lice, it becomes clear: it is dangerous to get rid of them somehow or not completely. Even a couple of eggs left in the head can again create a colony of blood-sucking lice. But you don't need to shave your head, especially if your hair is long. This is too radical a solution to the problem, and it is only suitable for brutal men or very young children. You don't have to sacrifice your hair to get rid of lice, just be consistent and patient and use the right products. We present you our step-by-step guide.
Step 1: Head Exam
Infestation in this case is the presence of living adult lice, young larvae and/or white (brown) eggs. Look for any possible signs of head lice by examining all areas of the scalp. Pay special attention to the back of the head and the area behind the ears. Not only the sick person, but also those who are in close contact with him are subject to examination. Therefore, keeping silent about lice is a very bad option! If you or your child has lice, it is not your fault, so it is better to inform those closest to you.
Step 2: Preparing Tools: What you will need to get rid of lice
To get rid of head lice, you will need a pediculicidal shampoo, a special comb for combing out eggs and adult lice, and oil (tea tree, olive) to make combing out easier. Simply washing your hair with regular shampoo will not solve the problem; you will just waste time! Lice are too tight in your hair! It is better to use these products in combination with each other to ensure that you get rid of all stages of lice: adults, larvae and eggs.
In addition to the main products, you may also need auxiliary tools: nail scissors, cloth, a bowl of water, a magnifying glass and a regular comb.
Step 3: Shampoo
Pediculicidal shampoo is the first stage of head lice treatment. Getting rid of adult lice (eggs, to a lesser extent) largely depends on the effectiveness of the shampoo. In this regard, the question arises about active substances with a proven pediculicidal effect. What to look for in a shampoo? Pyrmethrin and pyrethrin are the most active and effective pediculicides.
Step 4: Combing out nits with a comb
Step 5: Cleaning and washing
The two most important measures in the fight against head lice are shampooing and combing. Since lice do not live long after being removed from the head, cleaning the house will not have any effect on the development of head lice. It is needed more to maintain hygiene (removal of lice feces and dead nits) and your own peace of mind. This includes washing and vacuuming:
- Wash the bed linen, towels and clothing of the infected person in hot water (at least 60 C). Also pay special attention to hats and outerwear. It’s even better to dry all items in a hot dryer after washing and then iron them with a hot iron. If items cannot be washed at home, take them to the dry cleaner.
- Use a vacuum cleaner to clean the sleeping area, upholstery and carpets that may contain hair with glued nits. Don't forget about any objects that could come into contact with your head, such as car seats.
Do without fanaticism: the cleaning measures given are quite enough to live peacefully in your home after recovery. There is no need to douse furniture and household items with insecticides; it is better to spend more time brushing your hair daily.
Manifestation of symptoms
The signs and characteristic symptoms of the disease will help determine whether lice are present.
People often confuse symptoms. The scalp may itch in case of an allergic reaction to shampoo or dandruff. Before buying anti-lice products that are chemically harmful to the body, make sure that there are parasites.
The first and main symptom is itching around the ears, on the back of the head.
This burning sensation is especially felt before bedtime, when the body is as relaxed and immobilized as possible. When a bloodsucker bites, saliva is released under the skin, which, when concentrated, causes a reddish rash. Visually noticeable irritation indicates that the disease has been progressing for more than a week.
Signs of a lice infestation
What are the visual signs of lice? The main types of lice, pubic and head lice (underwear, clothes), differ visually. To ensure a correct diagnosis of the disease, arm yourself with knowledge of the main signs of the presence of insects.
Pediculus humanus is characterized by:
- The habitat of the bugs is exclusively the epithelium of the head.
- Nits on hairs. White cocoons are quite difficult to notice on light hair; they will shine in the light. A magnifying glass will help you accurately determine the origin of the transparent white ball.
- If the disease progresses for several weeks, the hairs will stick together in tufts. Long-term illness will affect local immunity
- The prolonged presence of parasites causes inflammatory processes in the body, which will affect the enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Are there any flat spots:
- The size is much smaller than that of head lice.
- Constant itching in the groin area.
- Visible wounds from bites begin to appear, which cannot be scratched so as not to leave scars.
Risk group
Why are children the most at risk group? Often, children do not choose friends based on social status; children do not care whether the family is prosperous. Children play together, in a group, constantly hugging and exchanging toys. The rapid spread of lice occurs in kindergartens and primary schools due to close contact with infected people.
Possible causes of lice infection and accompanying symptoms:
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules will be an excellent reason for infection. Kids happily exchange hairpins, elastic bands, and hats with friends. Parents need to convey to the child that they should not be allowed to use personal items of clothing or hair care.
- Playing in the sandbox and using one set of toys means that there is a fairly small distance between the kids, which allows the lice to move to a new victim.
- In a wide social circle of children, the likelihood of a “rot carrier” increases.
Important: preventative checks
Prevention will help get rid of the unpleasant consequences of the disease, which consists of constantly checking the hair on the baby’s head, because in order not to interfere with the process of socialization and comprehensive development, children need a team.