lice
— blood-sucking insects of the order Anoplura;
parasites of mammals and humans. More than 150 species of lice are known. There are 3 families: Haematopinidae (blind lice) - parasites of terrestrial mammals (except primates); Echinophthiridae (spiny lice) are parasites of marine mammals; Pediculidae (pediculids) are parasites of monkeys and humans. V. are strictly specialized parasites that live on certain types of animals. Thus, Haematopinus macrocephalus lives on horses, H. eurysternus - on cattle, H. suis - on pigs, Linognathus piliferus - on dogs. Lice (body length 1-5 mm): 1 - head;
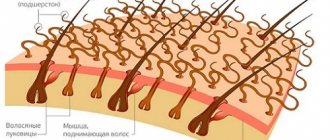
2 - clothes; 3 - pubic. On the right are nits. Humans are parasitized by the cephalic V. - Pediculus humanus capitis, the body V. - P. humanus vestimenti and the pubic V., or plateau - Phthirus pubis (Fig.). The body structure of V. is adapted to a parasitic lifestyle: it is flattened in the dorsoventral direction and covered with a chitinous cuticle. Body length 1-5 mm. Males are smaller than females. There are two simple eyes on the head. Many species are blind. The oral apparatus is of the piercing-sucking type (when sucking blood, the anterior section of the esophagus expands, acting as a pump). The thoracic region is not divided and bears three pairs of strong prehensile legs. The tarsus is single-jointed and ends in a claw. The claw, connecting to the protrusion of the shin, forms a “claw”, with the help of the V. cut it is firmly held on the hair. The abdomen is large, consists of 10 segments, in the female it is forked at the end; in the male the posterior edge of the abdomen is smooth. The entire life cycle of V. occurs on the host.
Outside the host, V. are found by chance and do not live long. V. eat often, in small portions (they cannot starve for a long time). If V. eats once or twice a day, then she can immediately drink 0.7-1.1 ml of blood. Males drink slightly less than females.
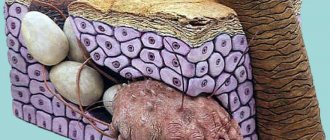
V. are insects with incomplete metamorphosis. Their development cycle consists of an egg, a larva that goes through three instars, and an imago (a sexually mature individual). The complete life cycle of V. of the genus Pediculus consists of periods: a) embryonic - from 4 days to 6 weeks; b) larvae of three stages of development - from 3 to 5 weeks for each stage; c) sexually mature form; the maximum life for a female dress V. is 46 days, for a male - 32 days, for a female head V. - up to 38 days, for a male - up to 27 days. The eggs (nits - Fig.) are elongated oval in shape, white-yellow in color, and are glued by the female using the secretion of the adhesive glands to the hair or fibers of the fabric.
During her life, the female lays up to 300 eggs (from 5 to 14 eggs per day). The optimal temperature for laying is 28-30°. The timing of hatching from eggs and further development also depends on temperature. The larvae differ from adult V. in their smaller size and the absence of the external genitalia. Within half an hour after hatching, they begin to suck blood. After the third molt, the larva turns into an adult V. The complete life cycle of the V. (from the moment the egg is laid until the female that develops from this egg begins to lay eggs) lasts at least 15 days.
V.'s bites cause severe itching, leading to scratching and skin irritation. The bite of the flathead is accompanied by the appearance of blue spots on the skin.
V. genus Pediculus, ch. arr. body clothes, infect a person with epidemic typhus (see Typhus, epidemic) and Volyn (five-day) fever (see Trench fever), as well as lice-borne relapsing fever (see Relapsing fever, epidemic).
Rickettsia typhus (Rickettsia prowazeki) V. becomes infected by sucking blood on a patient. Rickettsia multiply in the epithelium of the stomach of V., the epithelium is destroyed, and the pathogen, being released, enters the lumen of the intestine of V. and is excreted together with excrement. In V.'s excrement, rickettsiae appear on the 5th-9th day after infecting bloodsucking. V. die due to intensive reproduction of rickettsia in their body. The life expectancy of infected V. (3-31 days) depends on temperature and the infecting dose. Transovarial transmission of rickettsiae has not been established for V. V.'s bite is not contagious, because rickettsia does not penetrate the salivary glands. A person becomes infected when the feces of infected V. get on his damaged skin (scratching), as well as on the mucous membranes.
Infection with typhus can occur by crushing an infected V., or by inhaling dust that contains contaminated material, since rickettsiae in the feces of infected V. tolerate drying well.
The causative agents of relapsing fever - spirochetes (Spirochaeta recurrentis) enter the insect's stomach with the blood, then quickly disappear from there, but by the 6-7th day they appear in the insect's body cavity in large quantities and accumulate in the abdominal fluid. V. are contagious starting from the 6th day after blood sucking on a patient.
A person becomes infected by crushing insects and rubbing V.'s cavity fluid with spirochetes into wounds, scratches, and mucous membranes.
Clothes V. is also a carrier of Volyn fever rickettsia (R. quintana). Rickettsia of Volyn fever multiply extracellularly in V.'s intestines and are excreted in her feces. Human infection occurs when infected feces are rubbed into abrasions, scratched by V., or when insects are crushed.
The spread of lice is observed in unfavorable hygiene conditions. conditions, low material level, especially during periods of wars and other disasters. Lice bites cause skin rashes accompanied by itching and scratching.
There are lice in the scalp, trunk skin and pubic skin.
Lice on the scalp (pediculosis capitis)
caused by head lice. The occipital and temporal areas are predominantly affected, especially in the presence of long hair (more often in women and children). Head lice glue their testicles (nits) to the hair shaft through a special chitinous framework near the hair exit. At the sites of lice bites, vulgar impetigo and impetiginous eczema develop as a result of scratching; in this case, an increase in the cervical, occipital and postauricular lymph nodes is often observed.
In advanced cases, copious serous-purulent discharge sticks the hair together; in this case, the so-called tangle (plica polonica, trichoma) - gluing of hair like felt. Diagnosis is determined by the presence of lice and nits.
To treat uncomplicated head lice, one of the following methods is used: 1) rub kerosene (pure or half with sunflower or some other vegetable oil) into the scalp (preferably after a haircut), cover the head with compress paper and tie it with a scarf; after 1-2 such procedures, wash your hair with warm water and soap; 2) for three days in a row, generously moisten the hair with sabadilla vinegar, after which they wash their hair; 3) rub 50% soap-solvent paste or emulsion into the skin and hair, then tie the head with a scarf for 15-20 minutes, after which the hair is washed. After using all the products, you need to wash your hair frequently; to completely remove nits, you need to frequently moisten your hair with warm table vinegar, which dissolves chitin, and comb your hair with a fine-toothed comb. For complications of impetigo, after removing lice and nits, 2-5% white mercury ointment is prescribed.
Lice on the skin of the body (pediculosis corporis)
are caused by body lice, which live and lay eggs mainly in the folds of linen, from where they move to the skin only to suck blood, so the lumbar region and neck are affected mainly, where clothing fits the body most tightly. With lice on the body, scratching and often pyoderma are observed (see); Hyperpigmentation usually remains in these areas.
When lice has existed for years, a change in the skin develops, so-called. and French doctors suggested calling it “tramp disease”; the skin becomes thick, rough, hyperpigmented, especially in the lower back and shoulder blades, shoulders, and inner thighs.
Treatment requires frequent soap baths; Linen is disinfested before washing; When complicated by pyoderma, appropriate therapy is used.
Pubic skin lice (pediculosis pubis; synonym: phthiriasis)
cause pubic lice (plice), which parasitize primarily on the skin of the pubis and lower abdomen, thighs, from where they can spread to other parts of the body covered with hair (chest, limbs, armpits, mustache, beard, eyelashes, eyebrows, and in children and on the scalp). The plates are firmly attached by the proboscis to the mouth of the hair follicles, and by the front spoons to the hair. At the sites of their bites, peculiar round spots up to 1 cm in size from pale blue to pale gray remain - the so-called. blue spots (maculae caeruleae), reminiscent of fading syphilitic or typhoid roseola. These spots are caused by the parasite's saliva interacting with the host's blood hemoglobin. Scratching, pustules and crusts are very rare. Infection usually occurs through sexual intercourse, but sometimes through bedding.
Life of lice and dependence on humans
The lifespan of insects largely depends on the ambient temperature. For example, if the temperature is about 23 C, the louse will be able to survive for up to 2 days, but if the air is much warmer, for example, about 27-28 C, the parasite can survive without a host for only 24 hours. But when the ambient temperature drops to 10-15 C, the louse goes into hibernation and can survive without blood longer. But at negative temperatures it dies faster. Lice can live in water for up to 24 hours.
• using a comb, hat or scarf that contains adult insects or nits;
• swimming in a pool or pond without a swimming cap;
• using bedding on which an infected person has previously slept.
The most common route of transmission of parasites is direct contact. Less commonly, you can get them through other people's hygiene items and other things, in a pool or body of water.
When faced with unusual itching, small wounds on the scalp and unpleasant sensations, it is important to react quickly and make sure there are uninvited “tenants”
Today you can get rid of them effectively and safely. There are many ways to do this - from old grandfather’s methods to modern pharmaceutical ones. And the latter have a lot of advantages.
The full life cycle of an insect lasts no more than a month. In comfortable conditions, it can live up to 46 days. The head and pubic louse feeds exclusively on blood.
Considering the incredible ability of this species to survive, it is logical to wonder how long lice can live outside of humans. Left without a food source, they will die on day 3
If the ambient temperature is 10°C, the insect will enter a state of suspended animation and remain viable for up to 10-12 days.
Lice survive only at the expense of their host, on whom they parasitize. Can lice live outside humans and for how long? Each type of insect can only live on a specific mammal.
The human head louse will never infest horses. Just like those insects that live on animals will never pass on to humans.
Blood-sucking insects feed frequently and in small portions, and females bite more often than males, but how long can lice live without humans?
A head louse deprived of food in the environment can exist without a person for about 2 days, or more precisely, about 55 hours - that’s the entire length of time that lice live without a person.
This type of insect needs permanent housing, namely human hair. But despite this, the louse can live on its own, but in such conditions its life is significantly reduced to a duration of four days. This will be facilitated by external factors; the air temperature should be no less and no more than 23 degrees, otherwise it will not survive at all.
An adult louse reproduces and develops quite quickly and is capable of producing about 140 eggs in its life. She begins to multiply after the first meal. Development under optimal conditions takes 1-2 weeks. If the conditions are not suitable, the temperature is too high or low, then the louse can develop for a whole month. The life cycle of the parasite lasts 16 weeks.
For prevention purposes, it is necessary to observe personal hygiene standards, wear only your own hat, comb, elastic bands, and also carefully monitor your sensations. It is recommended to wash your hair with lice shampoo, using it in small quantities once a month to avoid infestation.
Prevention methods
Preventing head lice is quite simple. It comes down to observing basic rules of personal hygiene. Those with long hair are advised to wear a ponytail or tuck their hair under a hat when using public transport. You should also not use extraneous hats, towels, hygiene items, or combs.
If infection cannot be avoided, it is necessary to prevent the further spread of head lice. Bed linen, towels, and hats should be boiled and ironed. How to treat an apartment for head lice? To do this you need to use special tools. They are sold in hardware stores.
After infection, it is important to undergo examination by a dermatologist, who will prescribe therapy, and notify contact persons in the garden, school, and relatives about the disease. The recovery process should be regularly monitored by a specialist.
Life outside of man
Lice survive only at the expense of their host, on whom they parasitize. Can lice live outside humans and for how long? Each type of insect can only live on a specific mammal.
The opinion that lice are transmitted from pets is completely erroneous.
Blood-sucking insects feed frequently and in small portions, and females bite more often than males, but how long can lice live without humans?
A head louse deprived of food in the environment can exist without a person for about 2 days, or more precisely, about 55 hours - that’s the entire length of time that lice live without a person.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O2MQtcvx9j8
How long lice live without food is a controversial issue. According to various sources, from 1 to 3 days. At room temperature, the insect can live for three days; once outside, it dies almost instantly in frost, within several hours at temperatures below 10 degrees Celsius.
Louse without food
How long a nit lives is much easier to answer. The durable shell protects the larva from the negative effects of surrounding factors and does not even penetrate toxic substances. But for the full development of lice, special conditions and a certain temperature regime are necessary. At high and low temperatures, parasites die.
The body temperature is about 37 degrees Celsius. If a nit with a torn hair falls to the floor, its development will stop
It is not so important how long she lives, the main thing is that she will not be born alive
Types of lice
The insect is divided into three types, depending on the place of life:
- Cootie. She is attracted by the human smell and is unable to live on a body. The parasite lives in folds of clothing and bedding.
- Pubic louse. Can live where coarse hair grows - eyelashes, mustache, pubis, armpits.
- Head lice and nits. They live only on the human head.
Those who are faced with a disease such as lice begin to wonder how long lice live without food. Each species differs from each other in this regard:
- The head dies after 2 days without human blood. The nit will go through its life cycle completely, but the hatched larva, without finding food, can live only for an hour.
- The pubic look won't last more than four hours. The egg will develop until it is the turn of the nymph to hatch, which will immediately die.
The human body is not suitable for permanent residence. Then the question arises: can lice live in pillows and blankets? This type of insect is able to take a liking to bedding, but only if it has access to a food source. No matter what type of lice they are, they do not live without humans.
People are concerned about approximately the same questions regarding the life of these insects. Here are the most common:
- How long do lice live on a person’s head? They usually die a month after their appearance. If a living parasite finds itself without a person at room temperature, it must find another victim within 24 hours. If the temperature is low, the pest goes into hibernation.
- Do lice live in bed linen? This can happen to an unscrupulous person. The clothing species prefers to live in the folds of clothing adjacent to the body, but the insect can move onto the bed and bedding. It’s not for nothing that the parasite is popularly called a linen louse. If you change the bedding, it won't stay there.
- Can lice live on a sofa - the answer to this question will not differ from the previous one. Furniture is not the place where an insect will build a “home.” It needs a constant power source.
If at least one lice is noticed on the head, the hair should be carefully checked and treated. The parasite is small in size and difficult to detect. Having found a mate, one individual will quickly breed.
Although insects are not characterized by a long life cycle, they cause a lot of problems for humans. Because of them, you have to limit yourself in communication and endure many inconveniences. Fortunately, getting rid of lice is quite simple. To do this, use pharmaceutical pediculicidal preparations or folk remedies.
Stories from our readers
Anna: “The hair was falling out terribly, and at the same time there was flakes of dandruff and terrible itching... in general, the complete set. For a long time I went to a trichologist, checked my thyroid gland, took tests, bought special shampoos, ampoules...whatever happened! But it was all to no avail. Perhaps now I would be left with three hairs on my head if I had not come across this article. Anyone who is concerned about hair loss, itching, dandruff should read it!” Read the full article >>
(function(w, d, n, s, t) { w = w || []; w.push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: 'RA-268462-2', renderTo : 'yandex_rtb_R-A-268462-2', async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName('script'); s = d.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript '; s.src = '//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js'; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this, this.document, 'yandexContextAsyncCallbacks ');”+”ipt>
Sources
- Martínez de Murguía Fernández L., Puig Algora G., Bajona Roig M., Bacchini G. Effectiveness and tolerance of a squalane and dimethicone-based treatment for head lice. // Parasitol Res - 2021 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33797611
- Arserim SK., Cetin H., Yildirim A., Limoncu ME., Cinbilgel I., Kaya T., Ozbel Y., Balcioglu IC. The Toxicity of Essential Oils From Three Origanum Species Against Head Louse, Pediculus humanus capitis. // Acta Parasitol - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33770342
- Palma RL., Galloway TD. Menopon picicola: a new junior synonym of Menacanthus pici (Insecta: Phthiraptera: Menoponidae). // Zootaxa - 2022 - Vol4915 - N1 - p.zootaxa.4915.1.11; PMID:33756591
- St-Hilaire S., Cheng TH., Chan SCH., Leung CF., Chan KM., Lim KZ., Furtado W., Bastos Gomes G. Emamectin Benzoate Treatment of Hybrid Grouper Infected With Sea Lice in Hong Kong. // Front Vet Sci - 2022 - Vol8 - NNULL - p.646652; PMID:33644159
- Lamassiaude N., Toubate B., Neveu C., Charnet P., Dupuy C., Debierre-Grockiego F., Dimier-Poisson I., Charvet CL. The molecular targets of ivermectin and lotilaner in the human louse Pediculus humanus humanus: New prospects for the treatment of pediculosis. // PLoS Pathog - 2022 - Vol17 - N2 - p.e1008863; PMID:33600484
- Fölster-Holst R. . // Hautarzt - 2022 - Vol72 - N3 - p.232-242; PMID:33599802
- Alberfkani MI., Mero WMS. The Incidence of Scabies and Head Lice and Their Associated Risk Factors among Displaced People in Cham Mishko Camp, Zakho City, Duhok Province, Iraq. // Pol J Microbiol - 2022 - Vol69 - N4 - p.463-469; PMID:33574874
- Durden LA., Kessler SE., Radespiel U., Hasiniaina AF., Stekolnikov AA., Chalkowski K., Zohdy S. Host Associations of Ectoparasites of the Gray Mouse Lemur, Microcebus murinus, in Northwestern Madagascar. // J Parasitol - 2022 - Vol107 - N1 - p.108-114; PMID:33567091
- Waindok P., Raue K., Grilo ML., Siebert U., Strube C. Predators in northern Germany are reservoirs for parasites of One Health concern. // Parasitol Res - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33547507
- Cruz-Bacab LE., Perez-De la Cruz MC., Zaragoza-Vera CV., Zaragoza-Vera M., Arjona-Jimenez G., Lesher-Gordillo JM., Baak-Baak CM., Cigarroa-Toledo N., Machain-Williams CI., Garcia-Rejon JE., Gonzalez-Garduño R., Torres-Chable OM. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Ectoparasite Infestations in Dogs from the State of Tabasco, Mexico. // J Parasitol - 2022 - Vol107 - N1 - p.29-38; PMID:33535232
Can lice survive without food?
Lice feed exclusively on blood or skin. Their lifespan on the head lasts up to 42 days. Sometimes they move onto the beard, eyelashes or eyebrows, but an adult is not comfortable living there, so this happens extremely rarely.
Parasites are completely dependent on body temperature. Their home is the head of a person or the body of an animal. And if they are deprived of this home, then within 2 days they die.
If the larva is without food, that is, human blood, it dies so quickly. That is, a nit can survive longer without a person; its life activity is directly affected by temperature.
There are several types of lice in animals:
- Sucking louse - feeds exclusively on blood;
- Biting louse - feeds on skin particles.
Dogs are also susceptible to this disease. Parasites cling to hairs and attach to the skin. They feed on the blood, sebaceous glands and skin of the victim. The pet suffers from itching and loses its fur.
Pediculosis can cause more serious illnesses. Such as wasting or tapeworm. Therefore, animals need urgent treatment.
Can you get lice from contact with animals? No! The lifestyle of these parasites is significantly different. They are adapted to higher body temperatures than humans.
Without food, the insect will live no more than 3 days. At the nit stage, the parasite can remain viable until it transforms into a larva within 7 days. If after this period no food source appears, the insect will die.
Each biological species has its own types of parasites. Lice that parasitize humans are not able to live on animals. In humans, thinner skin and blood vessels are located closer to the surface. The insect does not have a long proboscis for deep penetration and cannot bite through the dense skin of the animal.
What do they eat?
Lice feed exclusively on blood (mainly human), their oral apparatus is adapted specifically to pierce the skin and pump out blood. Other power sources are not available to them. They cannot feed on hair, skin or dandruff as some people believe.
Lice feed about 5 times a day every 2-3 hours. In one suction, a louse can drink approximately 0.5 mg of human blood. Saturation with blood allows parasites to reproduce and lead an active life.
How long does a lice live without a person and what does it depend on?
An interesting fact: it was evolution that gave these parasites a unique chance to fully adapt to life exclusively on the human body. Another habitat is not suitable for them, and they simply die. The paws are only capable of clinging to hairs, the mouthparts are adapted exclusively for sucking blood.
Lice have developed a unique mechanism for reproducing on human hair - the adult lice lays eggs in a special sticky sac. Moving along the hair, the female deposits nits. As soon as the nit hatches, it will fall onto the skin and begin to suck blood.
So can lice live outside the head?
Only body lice lay eggs on clothing, but crawl onto the skin to feed. Their nits develop at the seams and only then cling to the hair. Such parasites have slightly different legs that are adapted to cling to textiles. How long do body lice live without humans? Parasites also cannot boast of longevity - 40 days. If there is no food, they will last only 4 days.
Do lice live on pillows and bedding?
We have already found out that the louse cannot tolerate hunger. So there is no need to say that the parasite can settle on your pillow, blanket or mattress for a long time. Lice simply have nothing to eat and they will look for a new owner; there is no way to lay nits. True, lice can still be found in a bed if an infected person slept there before - the parasite fell from his body, and is patiently waiting for a chance to get there again.
But clothes bloodsuckers may well take a liking to folds in blankets, but they do not form their own colonies here.
Please note that a lice cannot live for a long time without blood, but it may well get caught on a towel, comb or hair tie and infect another person. Be careful when using other people's personal items
Pets and lice - are they dangerous to humans?
Many people believe that lice easily change their host in search of food. It's a delusion. Some lice live outside the human head and body, but this is a completely different subspecies of the parasite. For example, so-called specialized canine parasites (lice eaters) live on dogs.
But this type of lice is absolutely not adapted for life on the human body. They have a different structure of their paws, which capture the animal’s fur. Bloodsuckers have a more developed oral apparatus for piercing dense dog skin, and an elongated body. Even if it lands on a human body, the lice beetle can live only a few days, and then it dies, unable to adapt to its new habitat.
Conclusion - dog bloodsuckers are not dangerous to humans.
Cat louse is also a subtype of lice that parasitizes exclusively on cats. These parasites also do not pose any danger to us - they simply cannot attach to human hair. But they cause significant harm to the animal: severe itching, skin lesions, and transmit helminth eggs.
Note that both human lice and nits cannot adapt to living on the bodies of animals, except for some species of monkeys. There is no need to worry that our pets will infect us, and we will infect them. But if you find lice on cats or dogs, it is necessary to destroy them, because they can be infected with helminths and other associated parasites that are dangerous to humans.
If you are faced with the problem of lice infesting you or your home, you need to solve this problem immediately. After all, you yourself can become a source of spread of this unpleasant parasite. Even if you try to destroy them mechanically, they can last for several hours without food and again get on your skin. Contact experienced specialists and exterminators will quickly and safely destroy lice.
Preparation for disinfection
Before carrying out actions to destroy lice, a number of preparatory work should be performed:
- Carry out wet cleaning of the premises.
- Close all food items.
- Protect dogs and cats with anti-flea collars, and remove other pets, in particular cold-blooded ones, from the treated area for a while.
- Upon completion of disinfection, the apartment must be ventilated.
It is also important to remember that you should not forget about preventive measures. It is always easier to prevent a problem than to correct its consequences later.
Interesting Facts
You should know some features of the behavior of parasites:
- when released into a liquid environment, a louse lives 2 times longer than in a normal environment;
- blood-sucking insects love warm places, such as the back of the head and the area behind the ears;
- the removed louse, if given the opportunity to choose, returns to the owner;
- parasites cannot fly, swim, jump, but they quickly run away as fast as they can and hide;
- the louse does not have eyes, but in the absence of organs for movement in water it does not die;
- infection occurs after direct contact with the carrier or his item.
It turns out to be difficult to cure pediculosis in practice. Constant combing and washing with special shampoos does not provide a 100% guarantee of cure. In addition, sprays and gels, in addition to destroying parasites, also affect the human scalp. They leave an unpleasant mark after use, causing skin irritation, dandruff or seborrhea.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=YhNfS7r7_Mg
Specifics of the method
Pediculosis is a disease characterized by the presence of blood-feeding parasites on the hair of the human body. Most often, this problem occurs in childhood. Can adults get lice? Of course they can. There is an opinion that hair dye can help adults get rid of pathology.
Features of the pathology
You can become infected with head lice from a carrier in several ways:
- With direct contact. Therefore, if a child has lice, then his parents may also have them.
- When using the wearer's personal belongings. For example, you cannot use another person’s combs, towels, or hats.
- When visiting public places. Infection often occurs in hairdressing salons, beauty salons, swimming pools, saunas and other places.
Therefore, it is quite easy to become infected with lice. It is enough to touch the host or use his personal item and the insect ends up on the hair of a healthy person. What kind of parasite is this - a louse? This is a small parasitic organism that settles in human hair and feeds on his blood. It has a short life cycle of about 6 weeks. During this period, the individual lays several hundred eggs (nits).
There are several types of lice depending on their location:
- cephalic - settle on the hair growing on the scalp;
- facial - live on the coarse hair of the face - mustache, eyebrows, eyelashes;
- pubic - live in the groin area;
- clothes - they settle on clothes and move onto a person’s skin to bite him.
If an infection has already occurred, then the question arises of how to kill the lice. One of the means to combat pathology is called hair dye. Is it so? Do lice die from hair coloring? The answers to these questions are ambiguous and depend on which product was chosen, because not every hair dye kills lice and nits.
Composition of the product
To kill lice with paint, it must contain aggressive toxic substances that kill the parasites. That is, gentle products are not suitable in this case; lice do not die from this type of paint. Each hair dye contains a dye and an oxidizing agent. The first contains coloring pigments that do not in any way affect the viability of lice. The second one can be quite toxic. If it was decided to remove lice with hair dye, then it should contain the following components (oxidizing agents):
- Ammonia. If hair dye for lice contains ammonia, then the parasitic organisms die from poisoning by chemical fumes. This oxidizing agent also has the ability to destroy the adhesive that attaches lice eggs to hairs.
- Hydrogen peroxide. This is an active chemical that has the ability to destroy complex organic molecules. If it comes into contact with a louse, penetrating through its shell, it affects the respiratory organs of the parasite with toxic fumes.
So, is it possible to remove lice using paint? Does it kill parasite eggs (nits)? The answer is simple - if you dye your hair with a dye containing ammonia or peroxide, the lice will die. But the nits will remain. Since these substances are not able to penetrate the egg shell. Therefore, they must be combed out using a special comb.
Many women are interested in whether lice grow on previously dyed hair? Immediately after the dyeing procedure, lice do not appear, since the ammonia smell repels them. After just a couple of days, when this unpleasant odor disappears, the parasite appears with the same probability as on ordinary ones. That is, if the hair is dyed, this does not fully protect against lice.
We fight with the help of professionals
The fog method is used today to kill all existing species of insects. Only the drugs loaded into the generator differ. The latter is a cannon that creates clouds of smoke. After covering an apartment or other room with them, the question of how to remove lice and nits disappears. There is simply no free space left at the facility in which predators could hide. At the moment, this method is the only one - it is used in the USA, Europe, and other countries. Our company will be happy to provide it to you.
Operating principle: sprayed substances consist of several components. They are based on 2 effects:
- Extermination - all larvae and adults are killed. The drug remains effective for 30-50 days. Therefore, the effect is guaranteed;
- Repellent - creatures passing by will feel uncomfortable near your home. Therefore they will prefer to leave it.
How long do ectoparasites live on a person’s head?
Since humans are the “host” for parasites thanks to the blood they feed on, lice can live on hair permanently. And only effective treatment will get rid of them.
Once on the hairy part of the body, within a few days the adult individuals begin to actively reproduce. They immediately lay 2 to 5 eggs, which are attached to the hair using a special adhesive substance. These eggs are nits, which are very difficult to remove mechanically.
The development of nits lasts about 8 days. Then insects appear, which are called nymphs. They are slightly similar to adults, but they are lighter in color. The nymph is smaller and has an underdeveloped reproductive system. Its development lasts 5 days. For development, nymphs need to go through 3 stages, which are expressed in a change in chitinous cover. The nymph grows, but the cover does not, so she changes it, since it no longer suits her in size. After 10-14 days, the nymph turns into an adult.
Next, the male fertilizes the female, and she begins to lay eggs. The entire development cycle from larva to adult is approximately 2-4 weeks. The life of an insect is about a month
But the development of parasites continues, since an individual lays up to several hundred eggs during its life. Important! The female can lay eggs only when feeding on blood.
Adult parasites feed on blood every 3-4 hours. Nits do not feed on blood, but develop in their cocoon.
Getting rid of lice
Pediculosis can be cured in both humans and animals at any stage of its progression. To do this, you need to start active treatment immediately after detection of the disease. Use special shampoos and ointments; pharmacies and veterinary pharmacies offer a huge range. Or use traditional medicine.
A well-known method of treatment is also combing; it allows you to completely get rid of both lice and nits. An interesting fact is that nits can survive on a person’s head, even after being cut bald. They attach to the bulbs, are able to develop and subsequently reproduce productively.
Your benefits
In addition to quality medications, the sanitary and epidemiological station is pleased to offer experienced employees. We do not employ people without experience - this guarantees that there will be no errors during the facility cleaning procedure. Another reason was reliability - today there are an abundance of companies in the service market whose budget does not allow them to purchase good substances. Hence the resulting disadvantages. Protect yourself from this.
We do not force clients to waste time waiting. If you agreed on 13:00 on Sunday, you will receive the team right on time. Despite the quality, prices here remain average. Call, ask how to remove lice and how much it costs, and then order the service.
Other insects:
- Bedbugs
- Bark beetle
- Cockroach
- Mite
- Ant
- Flea
- Mole
- Mosquito
- Wasp
- Medvedka
- Fly
- Carpet beetle
- woodlouse
- Silverfish
- Hay beetle
- Midge
- Bug
- Woodworm
- Louse
How to get rid of lice?
Mechanical methods
Typically, mechanical methods mean hair cutting, shaving and combing out parasites with a comb, but they can also include thermal treatment with a hair straightener or tongs. Hair cutting at the root is the cheapest and most effective treatment method, but it is not suitable for everyone. Women and girls will not want to lose their hair, and not all men are ready to go bald.
Chemical and mechanical methods must be combined. Just treating with a drug from a pharmacy will not be enough; you need to comb out dead lice and their larvae from your hair. The fact is that most drugs are not capable of destroying nits; their shell reliably protects the offspring from chemical exposure.
Don't expect to get by with a regular comb. Nits must be combed out with a special comb with very frequent teeth located almost close to each other.
Chemicals
There are a large number of modern drugs for head lice; they differ in cost, consistency and method of application. The most common types of medicinal formulations can be distinguished:
- Shampoos are the most popular, inexpensive and quite effective products when used correctly and following all the procedures specified in the instructions. Here are some of them: Hygia, Paranit, Lavinal. Shampoos specifically designed for children are sold separately.
- Sprays are more effective than shampoos, but are more difficult to use, are difficult to wash off and can cause unwanted allergic reactions. Usually a comb is included. The most famous: Paranit, Lavinal, Nyuda, Para Plus.
- Aerosols used to treat contaminated clothing. Someone even uses Dichlorvos against lice.
- Creams are less common than shampoos and sprays, but they are not inferior to sprays in effectiveness. Among them: Nix, D-95.
- Combs - designed for combing out bloodsuckers. They differ from ordinary ones in that they have very frequent teeth that detach the nit from the hair using mechanical pressure. But this is an auxiliary product used in combination with chemicals, most often included with the product.
Linen lice are removed by thoroughly washing and ironing bedding or clothing. Temperatures above 60 and below -10 °C are destructive for parasites.
Traditional methods
Although folk remedies can be recommended by most representatives of the older generation, they cannot be called particularly effective. Their main advantage is accessibility, but they can cause harm or, at the very least, be useless. Here are some common folk remedies for lice and nits.
- Kerosene - smear it on your head, wrap it around your hair and leave it for 2 hours. After treatment, the substance must be washed out for a very long time, besides, it damages the hair and can leave a chemical burn on the scalp.
- Cranberry juice has a depressant effect on lice and detaches nits from the hair, as the acid dissolves the adhesive. All that remains is to comb them out with a fine comb.
- Vinegar 6 or 9% acts similar to cranberry juice. Take three tablespoons of vinegar per 300 ml of water and apply the mixture to the scalp. The composition dries out the scalp greatly.
- A mixture of pomegranate juice and mint decoction, in a ratio of 1 glass to 3 tablespoons, is boiled for more than 10 minutes. Moisten the hair with a warm decoction and rub it into the skin.
- Hair coloring will not prevent lice. Only very caustic and harmful paint can kill 40-80% of parasites. This method cannot be considered effective
All folk remedies involve wrapping the head in a towel for up to two hours. But in children it is necessary to check the condition of the skin every 30–40 minutes to avoid burns.
We do not recommend resorting to traditional recipes if it is possible to purchase a safe and effective medicine at the pharmacy.
If after one wash with an insecticidal agent and combing the insects survive, you should treat your hair again after a week. And comb out again, since initially some nits may not be combed, and larvae will hatch from them.
Prevention of lice is to follow the rules of hygiene: use only your own things, swim in the pool with a cap and avoid untidy people.
Stages of lice development
All varieties of parasites are perfectly adapted to the places where they live. They have their own way of reproducing on the human body. The female lays an egg on the hair, which is also called a nit. The formed larva immediately gets onto the skin of the human scalp. She immediately begins to suck blood.
The life cycle of each species is different. The development of lice on the human body occurs quickly. For active life, parasites require a lot of energy. Head lice feed 3 or 4 times a day, and pubic lice feed every 3-4 hours.
Nits develop from 7 to 10 days. Body lice eggs can take up to 2 months to develop, provided the nit develops at room temperature. At low temperatures, development can take up to a year.
When temperatures drop to -1°C or lower, nits can only survive for one week. As for the development of the nymph, or larva, the process also proceeds faster - under favorable conditions in 15-20 days. Adult lice live for 40-46 days. The lifespan of insects that live on clothing is about 40 days.
The above data is disappointing. 1.5-2 months after infection, a whole population will already live on the scalp. After 3 months, the parasites will begin to cause inconvenience to their owner. In humans, one can observe pronounced signs of pediculosis.
Despite the fact that the life of a louse is fleeting, it manages to go through several stages. An insect has only 3 molts. They begin every time the chitinous “clothing” for the nymph becomes small. When the third molt ends, the nymph becomes an adult insect. The female can lay 2–4 eggs per day. During its short life, a louse manages to lay 140 eggs.
Despite the fact that body louse and head louse have different structures, their individuals, placed in a limited space, begin to interbreed with each other. After a few generations, the differences disappear.
When the larva hatches from the egg, the insect can pierce the cap of the nit with its jaws, but is not able to get out of it on its own. The larva begins to actively breathe. In this case, air passes through the insect's digestive system and exits through the anus. When air accumulates at the bottom of the nit in large quantities, it pushes the larva out of the case, which lands on the skin of the scalp and begins to suck blood.
-t-swBokzNQ
How long can lice live outside the human body?
Head lice
Ectoparasites cannot live for a long time outside the head, they are completely unadapted and cannot live for a long time without humans and food, and lice feed almost continuously. In general, they are gluttonous, and some of them even die from overeating. Blood-sucking insects from the head will not survive even two days without food.
The parasites have adapted perfectly to this habitat. The insect's abdomen, the shape of the body and legs for capturing hairs are adapted to comfortable living on the human body. Their reproductive organs have also adapted to it: the female, moving along the hair, attaches the egg cocoon with an adhesive composition. As a result, immediately after its birth, the larva immediately falls onto the skin and begins to actively feed.
Nits living in their shell are not independent insects.
They develop in a strong chitinous shell, so without humans they can retain the ability to develop for a long time. Even dead nits that are firmly attached to the hair can remain on the head for several years until the hair is cut off.
If the lice have not been poisoned by insecticidal preparations and do not fall from the head by accident, then the nymph develops within 15-20 days, and the adult up to 40-45 days. Thus, the head can live for about 2 months. Although they die quickly, they manage to leave behind numerous offspring.
Pubic lice
Pubic parasites live less than head parasites - only six weeks, but during this time they also manage to reproduce. The determining factor is the ambient temperature. In hot conditions, the maturation cycle accelerates and the cooler it is, the longer the development of parasites takes. The pubic louse is less hardy, it feeds every 3-4 hours and after 8-9 hours without food it dies if it does not reach the human body. They can survive in water for 2 days, so they can be transmitted from person to person in bathhouses, swimming pools or on a river.
Clothes insects
Without a person's body or head, ectoparasites can only live on his clothing. Body lice cannot infest the head, but
adapted to life on linen. They have a different structure of their paws, with which they confidently hold on to any things made of fabric. Here they mate, lay nits, and crawl onto the human body to feed. They can be infected through clothing and underwear that have recently been used by an infected person.
Adults live about 40 days, and without a human body - up to 3-4 days. Parasites, although they live on clothing and not on the human body, still feed on his blood. If a person does not put on clothes, then they die, since they absolutely cannot tolerate hunger, which is how they differ from other parasitic insects.
All types of lice are not long-lived and cannot exist for long without humans.
To get rid of uninvited guests, they must first be weakened with anti-pediculosis drugs, and then combed out and preventive measures taken, more than once.