Despite its small size, the bark beetle is capable of causing irreparable damage to forests and gardens in a short period of time, destroying huge tree stands. Its various species settle not only in living, but also in dead wood, turning it into dust and rendering building materials, wooden buildings, and furniture unusable. There are varieties of bark beetles that destroy food supplies.
- Where does he live?
- Characteristics and body structure Head
- Thoracic part
- Wings and elytra
- Limbs
- Abdomen
- Spruce beetle
- Larva
- Temperature method
To prevent a pest beetle invasion, you need to know what it looks like and what the danger of its appearance is. To combat the beetle and its offspring, the most effective methods should be used, as well as the necessary preventive measures.
Where does he live?
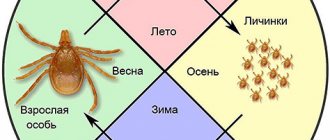
The main pests of forests - bark beetles - can be identified by their main feature - they feed on wood, raise offspring in it, overwinter and spend the main part of their life under the bark of a tree or in its nutritious part.
All types of bark beetles are herbivores. The main part of them are wood-eating insects, for which tree species are their habitat. These are mainly spruce, pine, birch, cedar, and larch trees, the bast tissue of which bark beetles feed on.
There are species of beetles of this subfamily that live in the fruits and seeds of tree species and herbaceous plants. They are usually representatives of tropical species.
The geographic distribution of bark beetles is directly related to the location of the tree species that feed them. Bark beetles live in different territorial zones, with climatic conditions characteristic of these zones. More often these are taiga areas, less often – steppes.
Why is it harmful?
Adult females and beetle larvae damage the bark of trees. When the female is ready to lay eggs, she gnaws through the wood to the bast (some species of the pest - to the sapwood). There, the female gnaws out a rather large (for her size) oval chamber, where she lays eggs. It is called the uterine.
When the larvae hatch, they begin to gnaw their way out, diverging in different directions from the camera. Since there are 20–40 eggs in one clutch, there will be the same number of “trenches” made by the pest.
Females and larvae of the bark beetle damage bast and sapwood. This has the most negative effect on garden trees and often leads to their death.
Basts are the “vessels” of plants. It is through it that water with inorganic substances dissolved in it flows from the roots to other parts of the tree. And then - organic compounds, including glucose, produced during the process of photosynthesis, disperse along the phloem from the leaves. Violation of the integrity of this tissue leads to the fact that some parts of the plant are left without nutrition. As a result, their death begins. As a result, the entire plant may die.
Sapwood is a tissue that stores stored nutrients. It helps plants survive the cold season. If the sapwood is damaged, the tree does not have enough resources for spring restoration, when the leaves have not yet blossomed, but nutrients are already needed. The plant may die.
Species of beetles that feed on conifers often lay eggs in houses and other buildings made of pine, spruce, and larch. The passages made by insects make the wood less durable and contribute to the onset of the rotting process.
Characteristics and body structure
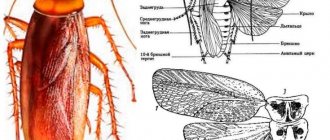
Externally, bark beetles are very diverse. The appearance of the tree pest, the bark beetle, corresponds to the image and conditions of its life. But beetles also have common characteristics by which they are classified and belong to this subfamily. Color can range from light brown to black. The smallest bark beetles living in Russia have a body size of less than 1 mm, and their larger relatives reach 9 mm.
Head
Although the bark beetle is considered a close relative of the weevil, its head does not have a rostrum, like that of an elephant. It is a continuation of the body with a blunt forehead. The front of the head varies between sexes of the same species. The eyes are round and flat. The antennae are geniculate and short. The head is usually darker in color than the rest of the insect.
Thoracic part
There are three segments on the chest - on the upper side they are called anterior, mid, and posterior. From the bottom - prothorax, mid-thorax, metathorax. The most important is the pronotum, which can be: spherical, quadrangular, oval, triangular. Its lateral edges are slightly rounded, and there is a narrowing at the very top.
Dotted grooves are applied across the entire surface. The tubercles and denticles located on the pronotum are of specific importance. The triangular shield is strongly recessed and also covered with dotted lines.
Wings and elytra
The body of the bark beetle is covered with strong, well-developed elytra, under which are membranous wings necessary for the insect to fly. The wings cover the main part of the abdomen. An important difference between adult individuals is the characteristic notch on the back of the elytra. It is called a “wheelbarrow” and serves as a device for clearing passages of wood flour. The elytra have pronounced points in several rows.
Limbs
Thin paws are covered with sparse, hard hairs or have none at all. The hip part of the forelimbs is round, the hind limbs are transverse. On the flattened shins, tubercles protrude from the outer side. The front legs are short, the hind legs are longer.
Abdomen
The abdomen is located horizontally, consists of five rings, and is covered from the upper part by elytra. Females usually have a wider abdomen than males. There are organs for oviposition.
Review of manufacturers
The best facade bark beetle plaster is produced by well-known construction brands:
- Ceresit . Advanced mixtures - ST 175 and ST 35. The first contains silicate resin and is very easy to apply and is frost-resistant. The second composition contains cement and minerals, has increased strength and a reduced price.
- Unis . The company produces a durable composition “Coarse-grained bark beetle” with cement and marble flour. The plaster is resistant to scratches, temperature changes and sunlight.
- Bergauf . The brand produces Decor plaster made from cement and mineral filler. Not afraid of humidity and frost.
Most of these brands produce bark beetle plasters for indoor use: Ceresit CT 64 made of acrylic, the “Starateli” brand, made in Russia. You can also select with the product “Bark beetle 1.5 mm” and “Osnovit Esterwell” with the mixture “Bark beetle 2 mm”. Alpina also produces universal compositions with a medium fraction.
Species and family of bark beetles
Previously, these numerous pest beetles belonged to the bark beetle family (Scolytidae). In the present systematization, this group is considered a subfamily included in the family Weevils (Curculionidae), order Coleoptera.
There are 140 species of bark beetles distributed on the European continent. In total, science knows more than 750 species belonging to this subfamily. Bark beetles are part of the 4-jointed group (Tetramera), which also makes them close relatives of the most numerous pest beetles, weevils.
Spruce beetle
Another name for this bark beetle is the great spruce beetle. This is the largest bark beetle that lives in Russia. Its length varies from 5 to 9 mm. Specimens measuring 18.5 mm have been described.
Dendrocton inhabits the lower part of trunks and protruding roots of trees. Resin flows out of the hole made in the trunk, which, mixed with drill flour sharpened by the beetle, hardens in the shape of a funnel. From this you can understand that the tree was attacked by the spruce beetle.
The female Dendrocton, unlike other bark beetles, lays eggs not in separate chambers, but in one pile. Therefore, the larvae live and feed together. Only before pupation does each bark beetle larva make an individual cradle for itself.
Grinder
People call the grinder a pretender because of his behavior in case of danger. If something threatens the life of a beetle, it falls and does not move, pretending to be dead. There are three groups of grinders:
- furniture;
- home;
- powder.
The borer is a real scourge for the home, because it is difficult to list everything that the insatiable bark beetle feeds on. He eats almost everything. Grinder larvae are especially indiscriminate in their feeding. Any wood and all its derivatives are used. Cereals, tobacco, and any chemicals are also destroyed. At the same time, the beetles are not afraid of being poisoned and remain alive and unharmed. In summer, grinders live actively, and in winter they are dormant.
Birch sapwood
Since birch sapwood is oligophagous, it harms only one type of plant - birch trees, and is distributed in areas where various types of birch trees grow. Pests settle on dried, weakened and old trees. Construction blanks and birch firewood also serve as a home for beetles.
The main damage is caused by the larvae, damaging the bark, sapwood, bast, as well as young beetles, eating the bark around the buds during additional feeding. You can find out if a tree is infested with a bark beetle by the round holes located along the uterine duct. The beetle makes these holes for ventilation inside the passages.
Generation takes place in one year. The larvae remaining for the winter tolerate frosts down to -30 0 C. They pupate in the spring, and in May-June the young beetles begin their years.
Shashel
The shachel bark beetle is also known under the name “woodworm”. It affects the wooden structures of the house and the wooden furniture in it. You can understand that there is a woodworm in the house by two main signs:
- a characteristic sound reminiscent of a grinding sound - this is how the shawl larvae gnaw their passages with their strong jaws;
- through piles of brown flour, which is formed as a result of grinding wood by beetle larvae and pours out through the holes they make.
It is almost impossible to cure wood infected with the disease. You can find out about the damage too late, when the wood is literally crumbling before your eyes. It should be separated from the healthy part and burned along with the insects.
Longhorn beetle
The numerous species of longhorned beetle cannot be confused with other insects due to its main distinguishing feature - long segmented antennae, which can be 2-4 times longer than the body.
Longhorned beetles are found in all corners of the globe. This is due to their food supply, primarily tree species. That's why these beetles are called lumberjacks.
Representatives of longhorned beetles are very diverse in shape, color, size, and sculpture of the elytra. The beetle that poses a danger to the home can reach a length of up to 15-20 mm. Its female is capable of laying up to 400 eggs. To do this, she chooses the highest place to protect her offspring.
And after two weeks, larvae emerge from the eggs, capable of turning the tree into dust. During the day, the larva makes a burrow 15-30 mm long. After another 20 days, the larva pupates, and then a young woodcutter beetle appears.
wood beetle
The wood-boring beetle differs from other bark beetles in that it lays eggs exclusively in dead wood - building materials and wooden furniture. The woodworm looks like a small black or dark brown beetle, no larger than a match head, with thin wings.
The insect reproduces very quickly. With the onset of spring warmth, after mating, the female begins to lay eggs in all the cracks and crevices of the wood or makes passages herself, to a depth of several centimeters.
The wood-boring beetle gets into the house along with the affected wood. More often these are building materials or wooden furniture infested with a beetle. You can see the beetle itself at night - sometimes it flies out into the light. Or detect signs and traces of its vital activity - creaking in silence and wood dust near furniture.
Bark beetle typographer
It is also called the “large spruce bark beetle” - one of the most dangerous forest pests. He prefers different types of spruce to all conifers: Siberian, common, oriental, and Ayan. The main habitat of the bark beetle is considered to be coniferous plantations in Europe, Kazakhstan, Turkey, Siberia, the Far East, Sakhalin and Kamchatka.
It mainly affects trees that are weakened, diseased, broken, or already attacked by another beetle from the bark beetle subfamily, the chalcograph. Healthy spruce trees are able to independently resist the stem pest, producing the necessary amount of resin.
The typograph bark beetle has a brown-black, cylindrical body covered with small hairs. An adult beetle grows to 4.5-5.5 mm in length. It lives under the bark of the spruce tree, in the bast layer, on which it and its younger generation feed.
Ordinary engraver
The small-sized common engraver is found in mixed or coniferous forests. Prefers spruce and pine. Can settle on fir or larch. It affects young trees or the tops and young stems of old ones, as it can only gnaw through thin bark. Actively colonizes freshly prepared building materials.
The common engraver is easily recognized by its description:
- the body is 1.5-2 mm long, cylindrical in shape, dark brown or black in color with a glossy sheen;
- The wheelbarrow in males is edged with three spines on each side, in females - with small tubercles in the same number.
In addition to mechanical damage to wood, the engraver beetle causes damage by spreading fungus on trees - this can be seen by the blue color of the bark.
Errors during construction
Construction logs must be cleared of bark and subjected to special treatment. PROSEPT 42 or Prosept Ultra can serve as protection against bark beetle.
Propset concentrated products
Timely processing of wood will prevent the appearance and development of beetles.
When constructing a structure, it is necessary to ensure the continued safety of all wooden elements of the structure. Traditionally, the process of building a wooden house looks like this: the first layer is a vapor barrier, then insulation and wind protection, the construction is completed by a ventilation gap and finishing material (siding). Moisture rushing from inside the house to the outside encounters a vapor barrier, a dew point appears, and condensation occurs. Thus, good conditions have been created for the proliferation of bark beetles in a wooden house and the germination of fungal spores, although the destruction of the wood that has begun will not be visible for a long time.
The point of view of specialists in building physics and technologists working in wooden house construction is that a vapor barrier is not needed when insulating a wooden house. For a house that is constantly in use, vapor barrier is detrimental. Internal sources of moisture: people's breath, steam from cooking, moisture from watering house plants, and the bathroom increase humidity.
Beetles may settle in after construction is completed
When ventilation shafts, door and window openings are open, the structure becomes accessible to beetles. If insects are found, it is necessary to urgently take all measures to destroy them. And the most important condition for success is timeliness.
An adult wood-boring beetle lives for several weeks. His goal is to find a pair for reproduction and lay eggs. The insect summer lasts from April to July. At this time they are most vulnerable. To lay eggs, they make depressions in wood or use ready-made cracks. Some pests live in symbiosis with mold. They use damp wood to breed fungus. The best place for parasites is old boards, so it is necessary to treat all boards with a special agent against the bark beetle, which will not allow the beetle to lay eggs.
Eggs
Every year, the bark beetle larva eats 50 mm of 150x150 mm wooden beams. The little bug multiplies quickly. Tens of thousands are born from a hatched bug. The typograph bark beetle lives in wood at a depth of 1 millimeter, where female insects lay larvae. Two months later, new beetles emerge from the larvae, and the cycle of life of the parasites continues.
Reproduction
With the arrival of spring, when the air temperature reaches +10 0 C, the beetles begin to leave their wintering places. Males are the first to come to the surface, in search of a suitable tree for future offspring. The male penetrates under the bark of a tree and there builds a fairly spacious mating burrow. When everything is ready, the beetle begins to emit a special smell - a pheromone, to attract females. From 2 to 4 females fly to the smell.
After mating, the female goes to lay eggs, making her uterine passage in the bark, 8 to 16 cm long and 2-3 mm wide. On the way, she makes a side depression and places an egg in it. Seals the entrance with sawdust and continues working further. In total, the female is capable of laying, on average, up to 80 eggs.
The life cycle of the bark beetle includes 4 stages of development:
- egg – up to 2 weeks;
- larva – up to 3 weeks;
- pupa – a little more than 10 days;
- adult.
From the moment the egg is formed until the young beetle appears, about 60 days pass. It happens that the female has not yet finished laying the uterine duct, and the laid eggs are already moving into the larval stage.
Larva
Having been born, the larva begins to gnaw its individual path, directed strictly at an angle of 90 0 to the maternal passage. The fleshy body of the larva is light, with a yellowish tint and a brownish head, and has a concavity towards the ventral side. There is a noticeable large number of callus-like checkers on it, with the help of which the larva moves, gnawing its way.
At this stage of development, the beetle causes the most damage, because the larvae actively devour the phloem and de-energize the tree, destroying the part through which the sap moves. The larval passages end in a cradle, in which the insect turns into a pupa.
Doll
In appearance, the pupa resembles a beetle. It does not have a cocoon, its body is short, compressed, light in color and soft. The pupal stage lasts up to 2 weeks. If she did not have time to turn into a young beetle before the onset of cold weather, then she remains to hibernate under the bark of a tree until next summer.
The young beetle does not immediately come to the surface. It remains under the bark to receive additional nutrition. Over the summer, one or two generations of young bark beetles may appear.
Over the winter, the newly emerged pest remains near the tree, digging a hole in the ground to a depth of 10 cm within a radius of 3 m. The larvae and pupae remaining under the bark can live at temperatures not lower than -17 0 C.
Are there bugs in the house: what to look for
Although the appearance of pests that feed on wood is usually accompanied by characteristic sounds - ticking, clicking, rustling and other unpleasant noises, no one usually pays attention to these first “symptoms”. And in vain.
Such insidious insects as bark beetles, longhorned beetles, grinders and wood borers are capable of invading a building and “undermining” it to its very foundation. Of course, one, ten or even a hundred beetles are unlikely to somehow affect the stability of the structure. But in cases where the number of pests increases to many thousands (and sometimes tens of thousands), it becomes simply impossible to ignore the problem.
Among the signs of the appearance of your future “opponents”, in addition to the noises already noted above, the following can be highlighted: drill flour (shavings, wood dust) appears, which can usually be seen on various surfaces - walls, floors, and sometimes even on the ceiling.
Wood-boring beetles can target all wooden objects in the house, including furniture, walls, and supporting structures. If chair legs or closet shelves break over time, it's not so bad. But if the beetles get to the ceiling beams and ceilings, the entire house comes under attack, which imperceptibly loses stability and can collapse at any moment. That’s why it’s so important to detect traces of the beetles’ “work” in time.
Grinder beetles can damage not only wood products, but also food, spices, herbariums, books, icons and painting collections!
Danger of the bark beetle
It is believed that the main purpose of the bark beetle is sanitary cleaning of the forest from diseased, weak and old trees. However, during an outbreak of mass reproduction, healthy trees are attacked, which causes irreparable damage to coniferous forests. If we compare it with medical terms, bark beetles are for trees like the immunodeficiency virus is for humans.
It is not the beetle itself that causes the greatest harm to trees, but its worm-like larvae. They are very voracious, and feed on wood throughout their active life until they pupate. Several larvae can destroy a tree in one year.
In addition to eating the bast, damage to the tree is caused by fungal spores, which the beetle brings there to feed the larvae. As a result, the space under the bark becomes covered with fungus, and the plant weakens and dies faster.
A great danger to humans are bark beetles, which settle not in living trees, but in the wooden structures of the house. They can damage the wood so much that the building collapses. There are species of this subfamily, the larvae of which destroy everything in the house, including food and medicines.
Preparation for fumigation
- Close off all parts of the room where gas should not enter (chimney, ventilation).
- Cover the wooden window frames with masking tape.
- Sometimes the bark beetle settles not only inside, but also outside the house. In this case, the house needs to be wrapped in polyethylene, creating an airtight “dome”.
- At the time of the procedure, equipment, personal belongings, plants, and animals are removed from the house.
Fighting methods
There are many options for controlling bark beetles. The choice depends on what is infected - forest plantings or wood structures. Also, the choice of control method and its effectiveness depend on the degree of damage to trees by insects.
Temperature method
Temperature is considered one of the most effective methods of killing insects. It can only be used to clean wood structures, such as furniture or building materials, from pests.
Since some species survive at temperatures down to -30 0 C, liquid nitrogen can be used to destroy it. Or heat the wood to +65 0 C.
Pheromone traps
Installing traps that attract beetles with a special scent - the smell of pheromones - is an effective way to collect insects and get rid of them. It is recommended to use the trap over large areas, from April to August, when the beetle is most active.
The disadvantage of this method is that it only affects adult beetles that fly, and has no effect on beetle larvae. Therefore, the method is effective not for control, but for controlling the number of insects.
Chemical methods
A popular method currently is the use of insecticides and biological products. Both methods cannot be used simultaneously. Pollination with insecticides is carried out from April to August, using hand and motorized sprayers.
Trees are also given special injections, injecting poison against the beetle under the bark. In the fall, before wintering, a thorough inspection should be carried out and, if necessary, the tree should be treated again.
Fumigation gives a good result - treatment with poisonous gas using insecticidal bombs or fumigators. With this method, you cannot stay in the room for one to three days, and it is advisable to carry out subsequent degassing.
Folk remedies
The pest was fought when insecticides and fumigators did not yet exist. The methods were effective before, and they can be used now:
- kerosene or turpentine is poured into the holes using a syringe;
- boiling water is poured through cracks and holes in the bark;
- the steel wire is inserted as deep as possible into the passages and then the melted mass of paraffin with rosin, vegetable oil or fungicide is poured into it;
- They make trap trees from a special log suitable for colonization by beetles, and then burn it along with the insects, their larvae and pupae.
In any case, if the tree is severely affected, it is unlikely that it will be possible to completely get rid of the bark beetle. Therefore, the right solution would be to destroy the source of infection, be it a tree or construction wood, in order to prevent the pest from spreading further.
How to fight
Bark beetles have an excellent sense of smell, which is how they identify their prey. The plants they prefer are:
- with cracks in the bark;
Bark beetle larva.
- transplanted to a new location;
- with weakened roots;
- wounds.
The fight must be comprehensive; strengthening the health of the tree and fighting the pest will be required at the same time.
Mechanical method
Places where beetles have entered need to be cleared to assess the scale of the infestation. During the beetle's course, some people push a metal wire through to pierce the beetle.
Folk method
This includes cleaning affected areas and sealing wounds with garden pitch. A good way to make bait is to place split logs on the site, bark beetles will immediately settle on them, then it’s easier to burn the entire generation.
Chemicals
Insecticides are used for spraying, the beetles will be released into the wild and will come under the influence of the drugs. Treatments are carried out several times.
Biological products
These substances affect stem pests at any stage of development.
Follow the link to learn about 12 ways to fight bark beetles.
Tree prevention
Timely measures taken to prevent the appearance of bark beetles will help protect the tree from infection by the pest. There are many such actions, and they depend on whether this needs to be done in forest plantations or in a house:
- Garden varnish is used to seal cracks, wounds, and holes in the bark.
- Coat the tree trunk with a mixture of humus and clay, thereby creating a barrier for beetles.
- Damaged leaves are burned and the tree trunk is dug deep.
- They care for the trees according to all the rules so that the plantings are healthy and strong.
- Trees are treated annually with chemicals or a mixture of manure and slaked lime.
- Wood material intended for building a house or making furniture is thoroughly dried, ventilated, and impregnated with a special composition against bark beetles.
Preventive measures against attacks by bark beetles are a necessary concern for protecting the environment and improving human living conditions.
Preventive measures
To prevent the beetle from taking a liking to garden trees and the house, it is important to take appropriate preventive measures.
The most effective is insecticide treatment. It is carried out at least once a year (ideally, at least 2 times). This is done using a spray bottle. Apply as much of the substance solution as is necessary for sufficient absorption into the bark.
In particularly advanced cases, fumigation with toxic gases is used. To do this, use phosphine or magtoxin. These compounds are dangerous to humans, so it is better to entrust the procedure to specialists.
In residential buildings, special ultrasonic devices can be used to repel beetles. They emit a high-frequency sound that female bark beetles and male borers cannot tolerate. The repeller is turned on from early spring to early summer. This is when most pest species have mating season.
Selecting a ready-mix
“Bark beetle” plaster is sold in the form of a dry mixture, to which just add water and stir before use. This mixture is packaged in paper bags of various sizes.
This packaging method allows you to prepare only the required amount of the working mixture, taking into account that the solution must be completely worked out within about an hour.
The remains of the unstirred dry mixture are well preserved in a dry place in a closed package.
The second type of packaging is ready-to-use solutions. They are sold in sealed plastic or metal buckets.
To get started, just mix the prepared solution using a drill with a mixing attachment. Such mixtures are more expensive than dry ones, but due to special additives they allow them to retain their working properties much longer. Even long breaks from work are allowed. In this case, it is enough to hermetically seal the container with the remaining solution.
High-quality and affordable dry mixes, which are in demand on a limited budget, are offered by German and Russian companies Bergauf, Knauf, Volma, Ptrfekta, Ceresit:
- Bergauf is a joint Russian-German manufacturer that supplies high-quality cement-based products at affordable prices;
- Knauf - products have well-balanced characteristics and are truly universal for interior and exterior work;
- Volma is attractive due to its affordable prices and the presence of reinforcing microfibers in its mixtures, which make it possible to obtain a crack-resistant coating;
- Perfekta is the lowest price category, however, the products, due to modified additives, have an extended operating temperature range and are therefore suitable for regions with cold climates;
- Ceresit produces both dry mixtures and ready-made solutions of good quality. Widespread distribution is hampered by increased cost.
In the category of enterprises producing ready-to-use mixtures, it is worth noting Dessa Dekor, VGT, Bayramix, Dufa:
- Dessa Dekor - a wide catalog of stylistic design options, the possibility of tinting in any colors, ease of application and increased quality of the result;
- VGT is a domestic enterprise that has a whole system of materials for finishing work;
- Bayramix is a Turkish company that produces a wide range of plasters with natural marble granules at reasonable prices;
- Dufa is a German company that pays special attention to the environmental friendliness of its products. The applied solutions look very stylish and have excellent performance characteristics.
Wall coloring
The final drying times for the mixtures are indicated on the packaging. Usually this process takes two days indoors; outdoors everything happens faster. The completely dry surface should be treated with fine sandpaper. If the walls were finished with colored acrylic compounds, then the work can be considered completed.
Cement, silicone or silicate plaster bark beetles are painted with various compositions. It is better to carry out the work using a construction roller with long pile to paint the grooves. Perform movements in horizontal and vertical directions. If, after drying, you treat the wall with a dye with a less saturated color using a velor roller, you can get tinted grooves. It looks impressive and gives the interior originality.
Using a new method of decorating walls instead of boring wallpaper will require a lot of time and effort. You will have to purchase tools and master the profession of plasterer. The original stylish interior, durability and practical properties of the new coating will justify all the efforts and additional costs.