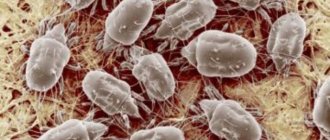
Spider mite
Spider mites are common everywhere except Antarctica. It affects crops both in open and protected ground.
This is a small arthropod sucking insect measuring no more than 1 mm. The pest has a soft, ellipsoidal body with a convex upper part and a flat lower part.
At different stages of development, the tick has its own coloration . Transparent larvae are light green or brown with dark spots on the sides. The body of an adult insect has an orange-red, bright red, yellow, and green tint. They, unlike six-legged larvae, always have 8 legs.
Types of spider mites
Spider mites belong to the arachnid family and have more than 1,300 species. Common types include:
- common spider mite. This species lives in colonies on the undersides of leaves. It is a polyphagous insect, which damages more than 200 species of plants. In different climates it reproduces from 8 to 18 times a year.
- hawthorn mite. This species prefers stone fruit and pome crops, and loves apple trees most of all. Females differ in appearance from males in body shape and coloring. During the growing season, the mite produces up to 8 generations.
- red greenhouse mite. A thermophilic species, in regions with cold climates it lives only indoors. Prolific - reproduces up to 18 times per year.
- Atlantic tick. Loves high humidity and can produce 5–6 generations. Inoculates both the upper and lower parts of the leaf.
- Turkestan spider mite. The pest is also a polyphage; it damages the leaves of more than 48 plant species. Gives up to 10 generations per year.
- cyclamen spider mite. It has an oval yellow body. Does not like light, settles on the upper side of the leaves. The accumulation of cyclamen mites resembles lumps of dust.
Sunburn of conifers
No less dangerous for conifers in winter is the sun, which, although it does not warm, can dry out and burn delicate needles, causing severe damage. Burns on conifers not only spoil their appearance and undermine their health, but also often lead to their death. To avoid this, we recommend covering the seedlings with burlap, special material or any available means.
Signs and Symptoms of Plant Infestation
A plant infected with spider mites
At the initial stage, the small pest does not manifest itself in any way. During this period, you can only notice a thin silvery cobweb on the shoots and on the bottom of the leaves.
As the population of the colony increases, other signs of its presence are already visible.
- Brown spots appear on the leaves where they are punctured by a thin proboscis . These are dead tissues devoid of plant juice. They grow and merge into large formations.
- their secretions on the underside . They look like small black or rusty specks and are easily removed.
- Injured leaves begin to turn yellow , curl and dry out.
- Wilting affects young shoots and buds.
- The plant slows down its growth and development. In the stage of severe damage, it dies completely.
Caring for conifers in spring
Also, in order to reduce the degree of desiccation and avoid burns of conifers in the spring, you can take care of the plants in the fall. Moisture-recharging watering of coniferous and deciduous plants will help with this. We have already discussed in detail the basics of moisture-recharging irrigation and you can familiarize yourself with its principles in our article “Important work in the garden in the fall for the safe wintering of plants
When spring finally comes into its own and the threat of the “dangerous” sun has passed, all shelters and strings (if any) need to be removed. After this, carefully inspect the plants for damage. Be sure to clean the needles - remove all dry needles that have accumulated during wintering. And remember that cleaning pine needles is an important preventative measure that must be carried out in the fall and spring. If you clean out the bulk of the needles in the fall, then in the spring this process will take much less time. And besides, cleaning pine needles in the fall will deprive any harmful insects and fungal diseases of the chance of survival.
Reasons for the appearance and reproduction of spider mites
Spider mites actively move in search of food. They enter the room:
- through open windows and doors;
- with clothes;
- with bouquets of flowers or potted plants, both purchased and brought into the house after being outside in the summer;
- when transplanted into soil contaminated with pest eggs.
Insects are carried into the garden by the wind from neighboring areas or when planting infected seedlings and seedlings. At an air temperature of 25–30°C, the larva grows into an adult in 8 days . At moderate temperatures this lasts a month.
In hot climates, insects breed all year round. In our latitudes, outdoor pests go into hibernation for the winter and therefore look for shelter in the fall. They hide in plant debris and fallen leaves, in the top layer of soil, and in greenhouse structures. This does not apply to indoor pests. There is no respite for them here and they are dangerous to plants all year round.
Spider mite infestations pose additional threats to plants. Perhaps the appearance and spread of gray rot and various viruses . Yield losses can be up to 70%
For what
To do everything correctly, you need to understand why processing of conifers is necessary:
- wake up from winter sleep and activate growth;
- facilitate planting, reduce stress, increase survival rate and resistance to external negative factors;
- improve decorative properties, make the needles even brighter and more beautiful so that they do not fall off;
- protect from too intense rays - help avoid sunburn;
- reduce the risk of disease and exposure to pests - as a preventive measure;
- cure a disease;
- eliminate insect pests.
At each stage of development of a coniferous plant, general strengthening, preventive or therapeutic treatment is carried out. It allows you to keep the tree healthy and helps it cope with various diseases, pests and unfavorable external conditions.
What plants does the pest attack?
Among vegetables, spider mites often attack cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, legumes, and pumpkin crops .
Strawberries, gooseberries, currants, raspberries, and grapes are damaged by insects .
Spider mites harm fruit trees: apple trees, pears, apricots, cherries, plums, cherry plums .
The parasite loves flowers and ornamental plants: roses, asters, palm trees, fuchsias, callas, citrus fruits, orchids, impatiens, abutilons, ficuses, saintpaulias, cyclamen, pelargoniums, azaleas .
Disguised "infiltrators"
In addition to external enemies of coniferous trees, there are stem pests of spruce. They penetrate the bark of young seedlings, destroying the tree from the inside. The topographer bark beetle settles in the trunk of a coniferous tree. It releases an aromatic substance that attracts insects within a radius of 11 km. This is the main sign of the pest. Plant damage manifests itself in slow growth of shoots and massive falling off of old needles. Dried branches usually remain on the tree, as a result it loses its decorative effect.
The beetle must be destroyed before the offspring are born.
Dangerous stem pests of spruce trees are large pine beetles and black longhorned beetles, which make many passages inside the wood. As a result, the development of the plant is disrupted and it becomes sick.
Means of struggle
For pest control, it is preferable to use special anti-tick preparations - acaricides . Before use, you need to study the instructions - whether the product can be used together with other drugs or not, whether it is suitable for treating plants indoors or only outdoors.
No matter how effective the drug is, eggs and larvae cannot be completely destroyed in one procedure. To stop their reproduction, 2-4 treatments will be required .
The first spraying kills 70–80% of active adults, leaving larvae and nymphs behind. They are targeted for a second treatment after 5–6 days. After the same period, the following control sprayings are carried out.
All treatments are effective only on dry leaves, the best time is the morning until noon at an optimal air temperature of 20-25°C.
Spider mites adapt to chemicals, so they need to be changed. Spraying indoor flowers with preparations alternates with a hot shower. If you wash the leaves in the shower regularly - once every 2-3 weeks - then you will need chemicals less often . The use of green, laundry soap or shampoo will enhance the effect. Soap foam is applied to the leaves for 5 minutes, then washed off with hot water.
This method is not suitable for indoor plants with pubescent leaves that cannot be washed, otherwise rotting will begin, as well as large plants in large pots and tubs.
Chemical and biological drugs
Apollo
Pome and stone fruit crops are sprayed during the formation of buds before they turn pink. The grapes are harvested for the first time during the period of swelling and bud opening, and again during the budding period. To prepare a solution, 4 ml of the drug is diluted in 10 liters of water.
Akarin
This powerful insectoacaricide is often called “first aid” in pest control. It can be used in hot weather. The effect is reduced when used in foggy and rainy weather. Please note that the product is dangerous for bees.
The dosage of the anti-tick drug is 2 ml per 1 liter of water. For stickiness, add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of liquid soap or washing powder in a bucket of water.
Fitoverm
To spray fruit trees during the growing season, prepare a solution with a concentration of 0.15% (1.5 ml of the drug per 1 liter of water). A young tree will require 2–4 liters, an adult tree – 5–8 liters.
For berry bushes, 2 ml are diluted in 1 liter of water. This volume is spent on one large bush. To spray vegetables, dissolve 1 ml of product in 1 liter of water. The break between treatments is 20 days.
For indoor and garden flowers, the dosage of the drug is 2 ml per 1 liter of water. Houseplants are treated at intervals of 14 days, in open ground more often - once a week.
Vermitek
Biological non-toxic insectoacaricide, it does not leave stains or burns on the leaves. Used for prevention and at the first sign of a pest. When spraying, completely wet the leaves, avoiding dripping. Consumption rates for the product are 2.5–3 ml per 10 liters of water.
Traditional methods
If there are few pests, use herbal decoctions and infusions.
- 1 kg of dry chamomile (leaves and flowers) is poured into 10 liters of hot water and left for 12 hours. The infusion is filtered and diluted with water in a ratio of 1:3. Then add laundry soap and spray it on vegetable and flower crops, trees and berry bushes.
- Half a bucket is filled with onion peels and finely chopped onions, then 10 liters of hot water are poured. Leave for 24 hours, filter and dilute with water 1:2 before use.
- The horseradish leaves along with the petioles are crushed, the bucket is filled 2/3 and water is added to the brim. Instead of leaves, you can take crushed horseradish roots. In this case, 2 times less raw materials will be required. The mixture is infused for 1 hour.
- 1 kg of tansy stems along with plant flowers are poured into 10 liters of water and brought to a boil. The broth is cooled and filtered before use.
- The pest is successfully destroyed by solutions of medications. For ticks, plants are sprayed with a solution of hydrogen peroxide – 2 tbsp – once a week. l per 1 liter of water.
- Ammonia (ammonia) not only removes pests, but also serves as a nitrogen fertilizer. 30 ml of ammonia is dissolved in 10 liters. water.
- Plants are protected by joint plantings with crops that are not afraid of spider mites. Onions, garlic, mustard, basil, parsley, and calendula repel the pest.
Watering conifers
When the temperature outside the window is above 0°C for several days, the snow begins to melt and the spring sun becomes a frequent guest in the garden, it is necessary to reduce the risk of drying out the needles, because under the influence of direct rays moisture begins to evaporate from it. Due to the fact that the ground is still frozen, plants have nowhere to take water supplies. The needles and shoots can dry out, increasing the risk of death of the entire seedling. To prevent this, it is necessary to irrigate the needles. To do this, you need to arm yourself with a spray bottle (a simple one is enough) and pour water at room temperature into it. It is recommended to spray the crowns of plants on a cloudy, windless day. Using these recommendations, you will restore the water balance of your plants. And remember that irrigating the shoots is mandatory for dry areas. If in your region there is an abundance of rain, snow, and even groundwater lies close to the surface of the earth, then this may not be done.
Gray mold
This is also a fairly common disease that develops in conditions of high humidity, in places where moisture accumulates and in shady areas.
Gray mold on coniferous trees
If the disease has already affected the tree, then all affected areas must be removed and destroyed. And treat the ephedra with Bordeaux mixture (1%) twice with an interval of 10 days.
Fusarium
Seedlings and young coniferous plants are subject to Fusarium drying out, which is provoked by fungi of the genus Fusarium. Sometimes you can find such a name as tracheomycosis wilt . The main danger of fusarium is that it first affects the root system, which turns brown and rots, and then passes into the vascular system, filling it with fungus and preventing the access of nutrients. The needles turn yellow, red, become coarse and fall off, the tree weakens and gradually dries out. The main sources of infection are contaminated soil and planting material, as well as plant debris.
Measures for the prevention and control of fusarium
|
Rust diseases
Rust affects most conifers, and its subspecies differ slightly from each other. Yellow-orange spots appear on trees and shrubs affected by the fungus, then spore-bearing bags are formed from the mycelium, and brown growths appear on the needles. Typically, rust appears on conifers after it has formed on grass crops. The needles gradually turn yellow, dry out and fall off, the plant looks thinned out and even slows down in growth over time.
Rust prevention and control measures
|