Troop Lice
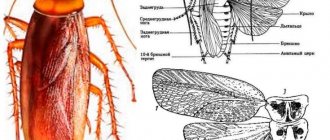
Represented exclusively by external parasites of mammals. The sucking mouthparts of lice are structured in a unique way, unlike, for example, the sucking mouthparts of bedbugs (Fig. 17).
Rice. 17. Squad Lice
The transformation of lice is incomplete. They don't have wings.
Lice should never be confused with fleas, which is often done due to their similar parasitic lifestyle. In fleas, the transformation is complete - these are completely different insects (Fig. 18).
Rice. 18. Louse and flea
Like other bloodsuckers, lice must somehow prevent blood from clotting in their digestive system.
To do this, substances that prevent blood clotting - anticoagulants - are released into the wound along with saliva.
The limbs of lice are tenacious, strong, and claw-shaped. With their help, they are attached to hair or clothing fibers.
About 250 species of these insects are known. Their body length ranges from 0.4 to 6 mm. Female lice lay eggs on hair or clothing. These eggs are called nits (Fig. 19). In total, a female can lay up to 300 eggs during her life.
Rice. 19. Nits
Lice are carriers of pathogens of various diseases. The most dangerous among them are chain fever and relapsing fever. The habitat of lice is hair-covered areas of the body and human clothing. Prevention of lice means keeping your body and clothes clean. The main measure to eliminate lice is the use of special products that are sold in pharmacies.
The thoracic region and the purpose of the paws
On the thoracic part of the cockroach's body there are wings with elytra, as well as insect legs. Cockroaches, like any representative of the “insect” class, have 6 legs, that is, 3 pairs. Each tarsus is located on one of the thoracic segments and represents:
- Prothoracic legs, which have the shortest length and serve as “brakes” if the insect moves too quickly.
- Medium-thoracic paws that can move in any direction, providing the insect with high maneuverability.
- The metathoracic legs are designed to move the insect only forward. They are the longest in size.
The cockroach's paw is a rather complex mechanism, which includes 5 segments. The thighs, flattened in shape, are armed with spines below. The first 4 segments are armed with pads, and the fifth with claws with a suction cup located in the center. This allows the insect to crawl on both horizontal and vertical surfaces.
Interesting fact! Having relatively long legs helps the cockroach not only run fast, but also jump high. In addition, with the help of all 3 pairs of limbs, the cockroach takes care of itself from the head to the abdomen.
In other words, the insect uses 3 pairs of its legs for its intended purpose. Cockroaches are able to move along the surface at a speed of about 4 kilometers per hour. If a cockroach grew to the size of a cheetah, it could easily outrun it. With the help of sensitive hairs located on the legs, the cockroach assesses the situation around itself. In 1 minute he is able to change his trajectory up to 30 times.
Here, on the thoracic region, the wings with more rigid elytra are attached. Using the length of the wings, you can determine the gender of individuals: females have much shorter wings. These insects use their wings during the mating season, as well as when moving or falling. By spreading their wings, individuals demonstrate their readiness to mate. Despite the presence of wings, cockroaches cannot fly, although there is one species that lives in South and Central America that can fly.
general information
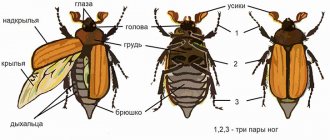
The structure of all beetles, of course, varies, but in general terms it can always be described. Most beetles have a separate head, which most likely contains antennae, eyes and mouthparts. Behind the head is the next part of the body - the chest. It is less mobile relative to the head. The first and second pairs of legs are located on the chest. The last body segment is the abdomen. The last pair of legs is located on it, the ducts of excretory glands and secretions open, with the help of which the beetle can mark the territory or leave a trace for communication with relatives, as well as spiracles.
Both wings are hidden under hard elytra
The entire body of the beetle is covered with a hard chitinous covering, which acts as an exoskeleton. This cover also protects the insides of the beetle from mechanical damage. The hard elytra are also made from the same material, which cover the beetle’s wings in a state of rest and protect them from damage.
Abdomen: structural features
A maximum of 9 abdominal segments can be distinguished, although it actually consists of 11 segments. The anus is located on the tenth segment, and the last segment is formed by paired outgrowths that have no purpose, but represent a separate sign of a certain type of cockroach. These growths have been preserved for millions of years, indicating their relict origin.
The female has a special capsule (ootheca) at the end of her abdomen, which contains 12-16 eggs and subsequently develops into the hatched larvae. Under favorable conditions (availability of water and food), this capsule appears in the female every couple of days.
Interesting to know! During the process of growth and development, not only the size of individuals changes, but also their weight, which at the beginning of development is about 2 mg, and at the end of the process about 8 mg. The larvae, in comparison with the imago, do not have wings, cerci and spines on their legs, but have short antennae. After the fifth molt, the insects develop genitals and complete external resemblance to adult cockroaches.
According to University of Massachusetts professor J. Kunkel, cockroaches are endowed with basic driving instincts, such as hunger, thirst, survival and reproduction. In order to understand whether cockroaches have a brain, you should study its internal structure.
What kind of mouthparts do cockroaches have?
The device for grinding food includes a modified upper and lower lip, a pair of upper and lower strong jaws with palps.
Before anything edible enters the insect's digestive tract, it is tested for suitability using 2 pairs of olfactory palps attached to the branches of the lower jaw and lip.
The nutrient substrate is clamped between the protruding lips of the insect from above and below, falling into the hollow. For reliable fixation of a piece of food there is a pair of sickle-shaped lower jaws.
Chewing a bolus of food is carried out with the help of maxillae - the upper jaws, which have several sawtooth serrations that serve as teeth. In parallel with grinding in the oral cavity, the edible lump is moistened with saliva, rich in digestive juices.
The oral apparatus, adapted to breaking down coarse food particles with strong chewing organs, is called gnawing. This is exactly the type of mouthparts of a cockroach. It opens up the opportunity for the mustachioed to include in its diet almost everything that comes along the insect’s path.
Interesting! The insect's jaws are covered with a dense substance - chitin, which gives the insect's mouthparts greater strength. The complex structure is driven by the masticatory muscles.
Circulatory system
The circulatory system of the cockroach (Fig. 83), like that of all arthropods, is not closed. Blood directly washes the internal organs and tissues while in the body cavity, transferring nutrients to them and carrying harmful waste products to the excretory organs. Blood does not participate in the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide, that is, in respiration. Its movement is ensured by the work of the heart - a longitudinal muscular tube located in the dorsal part above the intestines.
The cockroach's heart, pulsating rhythmically, drives blood to the head end of the body. The backflow of blood is prevented by the heart valves. When the heart expands, blood enters it from the back of the body through its side openings, which are equipped with valves that prevent blood from flowing back. In the body cavity, unlike the heart, blood flows from the front end to the back, and then, entering the heart as a result of its pulsation, it is again directed to the head.
How many days do cockroaches live without food and water?
Cockroaches can go for a very long time without food. Harmful insects have a distinctive feature - low sensitivity of hunger receptors. Cockroaches can live for a long time without food also due to:
- Slow metabolism;
- Low energy consumption for the processes of thermoregulation, oxidation and respiration.
Red cockroaches can live without food for 40 to 45 days, and black pests - up to 75 days.
It is not surprising that cockroaches are very often found in apartments and houses, because there are all the conditions for their comfortable existence: warmth, water and a large amount of varied food. In addition to its speed and
endurance, cockroaches are known for their appetite. They easily adapt to different conditions and changes, and in the absence of food they can survive by eating various synthetic materials.
Experiment what cockroaches like more:
General information
Black cockroaches belong to the order Blattodea, which has approximately 4,600 species. These are one of the oldest arthropods that appeared on Earth approximately 300 million years ago. This is evidenced by fossils of dead ancestors preserved in amber millions of years ago.
Cockroaches have inherited the trait of photophobia from their distant ancestors. Insects prefer a nocturnal lifestyle. Large black cockroaches, of which there are about 1 thousand individuals, eat 9.5 kg of food in one year, but they simply dirty much more food. As soon as darkness falls, insects go in search of food: for crumbs of bread, pieces of vegetables, particles of granulated sugar. Cockroaches also love to feast on leather creams, laundry soap, shoe polish and ink.
Diet
Prussians are unpretentious about the nutritional value and taste of food: they are able to eat and process any organic substrate.
What do cockroaches eat in an apartment? Their daily menu successfully includes the following products:
- bakery;
- pasta, confectionery;
- vegetables fruits;
- meat and sausages, cheese;
- seasonings;
- jam, sweet drinks;
- human-prepared dishes, leftover food, crumbs.
The main requirement for food is its availability, so their diet often consists of expired food debris that has fallen on the floor and then remains after poor-quality cleaning of the premises and has been affected by mold fungi.
Aroma enhancers and sugar speed up the discovery of food using the olfactory receptors of cockroaches, shaping their taste preferences. In the absence of access to human food, insects do not disdain:
- newspaper, book glue, paper;
- clothing fabric or book bindings;
- leather goods;
- paste with starch;
- wallpaper.
As we can see, the variety of types of food cockroaches have is very wide.
Interesting! The male is able to eat about 25 grams of food per day, the female – up to 50.
Reproduction
The life cycle is divided into three forms of development: egg, nymph, adult. In the summer, cockroaches begin to mate. Females lay eggs in a chitinous cocoon, which holds 16 eggs. A female expecting offspring has a slightly enlarged belly. After a few days, she hides the eggs in a place hidden from view. The incubation period lasts 44 days, and then the larvae - small cockroaches - are born. Black insects live from several months to 4-5 years.
How does food search happen?
Since cockroaches are very shy pests, the process of searching for food occurs at night. A small group of pests crawls out of the shelter for reconnaissance.
After the scouting team finds a place with food, it immediately returns to the nest. The insects mark their return route with special secretions.
IMPORTANT: A female cockroach needs 40 grams of food per day, and a male needs half as much.
Insects cause the greatest harm by biting food. After this, food should not be eaten, because insects are carriers of bacteria, allergy agents, worms, and infectious diseases.
Sinanthropus animals
According to popular belief, if cockroaches have settled in a house, this is a sign of wealth and prosperity. It is unlikely that those who have ever tried to get rid of these annoying insects will agree with this. Since ancient times, cockroaches have settled in human dwellings. After all, it provides these animals with everything they need: constant temperature, moisture and food. Animals that live with humans are called synanthropes. In addition to this species, these include ticks, flies, mosquitoes, mice, pigeons, and ants.
Dangerous roommates
We must not forget that mustachioed animals are capable of bringing pathogenic bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and parasite eggs into the apartment from unsanitary places and delivering them to pieces of food. Neighborhood with these insects is dangerous due to helminth infections, intestinal infections, allergies, and bronchial asthma. There are also known cases of cockroaches biting people.
Therefore, at the first sign of an invasion of these insects, measures should be taken to combat them. Measures must be taken very quickly, as mustachioed animals reproduce even faster. Fortunately, there are now many effective anti-cockroach products on the market.
Well proven:
- powders: FAS and Clean House;
- gels: Dohlox, Global, Forsyth, Combat;
- aerosols: Raid and Raptor.
Etymology
The name of this insect appears in several languages. At the moment, scientists have not been able to establish the exact origin of this word. Translated from Chuvash it is translated as “running away.” And this is no coincidence. Cockroaches hold the record for the fastest movement among all land insects.
And it is very difficult to catch him. The fact is that in a second, cockroaches can change the trajectory of their movement more than two dozen times. Perhaps that is why, translated from the Turkic language, its name means “to diverge.”
Other types of mouthparts
The mouthparts of beetles are of the gnawing type. It is believed that it was from the gnawing mouthparts that the remaining types developed as a result of evolution:
- Sucking;
- Licking;
- Stitching-sucking;
- Gnawing-licking;
These types are also widely found among the insects around us. Lepidoptera have the sucking type: butterflies, moths. These insects feed on flower nectar and their long, hollow proboscis helps them extract nutrients from deep flowers. Flies are of the licking type. The main structure of this type is a hypertrophied lower lip, modified into a proboscis, with which the fly captures particles of liquid food (jam or honey) and delivers them to the esophagus.
have piercing-sucking mouthparts
In fact, there are many types of mouthparts, but they all evolved from gnawing ones. However, it is often very difficult to determine how certain parts of a new type developed. Therefore, the study of beetles and their mutations continues to this day and the number of species is increasing every day.
Classification
The structural features of cockroaches determine their systematic position. These animals are representatives of the Arthropoda phylum, the Tracheinobreathing subtype, the Insect class, and the Cockroach order.
Like other representatives of this systematic unit, their characteristic features are the presence of three parts of the body - the head, trunk and abdomen, a fat body in the cavity, striated muscles and an exoskeleton in the form of a cuticle.
American (Periplaneta americana)
In fact, the homeland of American cockroaches is hot Africa, and they came to America with the help of cargo ships. After some time, they began to be found on almost all continents.
Food remains in huge quantities that accumulated in trash cans near houses, as well as a high level of unsanitary conditions in public places, led to the appearance of this type of cockroach in our country. The American cockroach can be easily distinguished from other types of similar insects by its large size, as well as by the shape of its body, which is oval in shape. In addition, this insect has a brown shell that looks like folded wings.
There is another factor that helps distinguish this insect from other types of cockroaches - this is the fact that the American cockroach is afraid of the cold. Already when the temperature drops to 0 degrees, these insects die. In addition, the American cockroach is characterized by an increased level of aggression, so it can attack both humans and domestic animals, which cannot be said about other types of similar insects.
Where do white cockroaches live in the apartment?
During the next molting of a cockroach, several events occur:
- the pest loses its dense exoskeleton;
- its shell mainly consists of soft tissue;
- The cockroach turns white.
As a result of the processes that have occurred, the domestic pest becomes more noticeable to predators and humans. Therefore, during the molting period, until a new chitinous shell is formed, the cockroach often settles in secluded, inaccessible places.
The likelihood of finding a white insect on the walls or floor is extremely low. They usually crawl out of secluded places in cases where a person has treated his apartment with pesticides. Exposure to chemicals causes the cockroach to lose orientation in space, causing it to leave secluded places.
Under normal conditions, white pests are localized where predators cannot reach them. Insects hide until their body color takes on the traditional color.
Mostly people encounter white house pests while cleaning. Cockroaches hide under the bottom of furniture, under rugs, ventilation holes and other places.
During the molting period, pests become inactive. This is explained by the peculiarities of the processes occurring in their body. People should not be afraid of white cockroaches. They are not dangerous and differ from other representatives of their species only in the color of their shell. During molting, it is much easier to catch a white cockroach than other “relatives”.
Household pests live for about a year. During this period, molting takes up to three days. Due to the fact that the change in chitin forces cockroaches to look for secluded places, the likelihood of encountering a white insect even in the presence of a large colony is extremely small.
Species diversity
Like all insects, cockroaches are characterized by significant species diversity. A typical inhabitant of human dwellings is the Russian cockroach, or red cockroach. The structure of these insects is not very different from that discussed above. There is an opinion that the red cockroach was brought to our country by soldiers returning from Prussia. Hence the second name of this parasite.
The structure of the black cockroach is more impressive in size. Some individuals can reach 5 cm in length. They can be quite dangerous for humans. Getting into his home from garbage dumps and sewers, they carry eggs of other parasites and pathogens on their limbs.
White cockroaches are not a fiction. This kind actually exists. They acquire this unusual color for these insects as a result of molting. Over time they darken.
A special type of cockroach is the furniture cockroach. It has a bright red color. The wings of such an insect are transparent, with brown stripes on them. His favorite treat is starch and everything that contains it. These are mainly wallpaper paste and book bindings. Therefore, they settle not in kitchens, but in libraries and archives.
The most common species in the south is the Central Asian cockroach. It can be recognized by its yellow head and dark belly. They jump high and are able to fly short distances. It is practically omnivorous and feeds on leftover food, plants and waste.
So, the peculiarity of the structure of cockroaches is the presence of three parts of the body, a dense chitinous cover, six walking legs and a pair of wings. These insects are synanthropic animals. This means that cockroaches prefer to settle in human dwellings. Here they have all the comfortable conditions: warmth, moisture, darkness and a sufficient amount of food waste.
Legs
The legs of a cockroach are typically running legs. In other insects, legs are used for many purposes. Material from the site https://doklad-referat.ru
Running is the main type of movement of a cockroach. In this case, the front and rear legs of one side move simultaneously with the middle leg of the other side. In addition to running, cockroaches can jump, pushing off primarily with their hind legs. In the cockroach, the abdomen is attached to the metathorax with a wide base and is inactive in relation to it, but in other insects it can be attached with a narrow stalk (wasps, ants).
A little about the life of insects
How do these insects live?
These are quite mobile creatures, they love warmth and moisture, and are nocturnal (they hide in a dark place during the day and crawl out at night in search of food). Winged birds can fly to the light at night. They feed on plant and animal remains. And, of course, they multiply quickly. These are the hardiest insects: certain subspecies and individuals can go without food for a very long time! The body of the insect is oval and flat. The length of an adult cockroach ranges from 1.7-2 cm to 9.5 cm or more. The structure of the body allows it to hide in any crevice.
Lifespan
How many years do these insects live? The lifespan of cockroaches depends on external conditions. If there is enough moisture, food and warmth, then an adult red locust can survive for 1 year. The lifespan of the black one is 2 years (the development of this species is slower), and the Madagascar one (in a terrarium) can live from 3 to 5 years, depending on care.
The life cycle of a cockroach can be divided into 3 stages of development: egg, larva, adult insect. The most important thing for this beetle is to be fruitful and multiply, giving life to new cockroaches. The female attracts the male with odorous substances secreted by special glands. Some individuals court females for a certain time, but the result is the same - fertilization.
Subkingdom multicellular (METAZOA)
Phylum ARTHROPODA
Subtype Gill-Breathing (BRANCHIATA)
Class Crustaceans (CRUSTACEA)
Subtype CHELICERATA
Class Arachnida (ARACHNIDA)
Task 1. Consider the structure of the opened crayfish. Indicate in the drawings the main elements of the external and internal structure.
| 1 — |
| 2 — |
| 3 — |
| 4 — |
| 5 — |
| 6 — |
| 7 — |
| 8 — |
| 9 — |
| 10 — |
| 11 — |
| 12 — |
| 13 — |
| 14 — |
| 15 — |
| 16 — |
| 17 — |
| 18 — |
| 19 — |
1.1. Limbs of crayfish.
| 1 — | |
| 2 — | |
| 3 — | |
| 4 — | |
| 5 — | |
| 6 — | |
| 7 — | |
| 8 — | |
| 9 — | |
| 10 — | |
| 11 — | |
| 12 — | |
| 13 — | |
| 14 — | |
| 15 — | |
| 16 — | |
| 17 — | |
| 18 — | |
| 19 — | |
| 20 — |
1.2. Opened crayfish.
Task 2. Examine microscopic specimens and drawings of cladocerans, copepods and barnacles.
| 1 — |
| 2 — |
| 3 — |
| 4 — |
| 5 — |
| 6 — |
| 7 — |
| 8 — |
| 9 — |
| 10 — |
| 11 — |
| 12 — |
| 13 — |
| 14 — |
| 15 — |
2.1. Daphnia. The body is enclosed in a shell. The head section is free. Antennas are branched. There is an eye formed by the fusion of two. The thoracic limbs do not perform the function of movement. They are covered with bristles. The abdomen is tucked under the chest. Does not carry limbs. The heart is located on the dorsal side. There are no vessels. Females are larger than males. Females have a brood chamber. In the development cycle, the appearance of a parthenogenetic generation of females is observed. The appearance of males occurs at the end of summer, beginning of autumn, when bisexual reproduction is observed.
| 1 — |
| 2 — |
| 3 — |
| 4 — |
| 5 — |
| 6 — |
| 7 — |
| 8 — |
| 9 — |
| 10 — |
2.2. Cyclops. The body is segmented and consists of a cephalothorax and abdomen, ending with a furca. The fork contains feathery bristles. There is no sink. Unpaired eye. The cephalothorax is ovoid and consists of five segments. All head segments merged together with the first chest segment. The male's abdomen also consists of five segments, while the female's has only four, since the first segment of her abdomen is fused with the second and is called the genital segment.
Task 3. Study the external structure of arachnids using a drawing and a textbook. Consider the location of the main organs. Make signatures.
| 1 — |
| 2 — |
| 3 — |
| 4 — |
| 5 — |
| 6 — |
| 7 — |
| 8 — |
| 9 — |
| 10 — |
3.1. External structure of a scorpion.
| 1 — |
| 2 — |
| 3 — |
| 4 — |
3.2. External structure of the spider.
| 1 — |
| 2 — |
| 3 — |
| 4 — |
| 5 — |
| 6 — |
3.3. Ixodes (dog) tick (Ixodes ricinus) hungry female from the ventral side.
Task 4. Draw the development cycle of a pasture tick.