Bedbugs are found everywhere; species diversity has given them different body shapes and sizes. A distinctive feature of insects is semi-rigid wings, although some groups lack them. Not everyone knows what bugs look like, even if they have seen them on plants in the summer. They can be of different colors: brown, green, red. The most familiar species shown in the photo is bed bugs. The parasite feeds on human blood and settles in homes.
Some types
- Deciduous keelweedAcanthosomatidae
- Alcaeorrhynchus grandisPentatomidae
- Carpocoris mediterraneusPentatomidae
- Carpocoris fuscispinusPentatomidae
- Scutum berryPentatomidae
- Elasmostetus birchAcanthosomatidae
- Gray shieldbillAcanthosomatidae
- Eurydema ornatumPentatomidae
- Lined scale insectPentatomidae
- Halyomorpha halysPentatomidae
- Loxa viridisPentatomidae
- Green arboreal shieldweedPentatomidae
- Picromerus bidensPentatomidae
- Raphigaster nebulosaPentatomidae
- Troilus luridusPentatomidae
- Zicrona caeruleaPentatomidae
- Soldier bug
- Eurydema northernPentatomidae
- Enoplops sibirica
Harmless representatives
Soldier bug - in early spring, these representatives of hemipterans awaken and come out. The combat color and their numbers are the main strength of these insects. Scientific name: Red bug, wingless, widespread. It feeds on seeds, sap of young plants and dead insects.
The alder bug is a brood hen and lives on the leaves of alder and birch. The females lay eggs on the leaves and then carefully protect them until the larvae hatch and become stronger.
Description
Most bedbugs have scent glands, the openings of which are located in adult bedbugs on the underside of the chest between the first and second pair of legs. The secretions of these glands have a characteristic odor that is unpleasant to humans, it is believed that it repels enemies, and possibly acts as a pheromone. The secretion consists mainly of aldehydes, for example those close to CH3-(CH2)2-CH=CH-CHO, and is close in composition to pheromones.
Some species have developed developed care for offspring and signs of subsocial behavior. For example, females of the tree bug Parastrachia japonensis, which lives in Japan, daily bring fruits of the Schoepfia jasminodora tree from the olax family to their nest with their larvae[3]. At the same time, other females can steal fruits from the unattended nests of other females of this species. By the end of larval development, up to 150 fruit drupes can accumulate in the nest[3]. Some bugs, such as Phyllomorpha laciniata, lay eggs on the dorsal side of the male's body, where they remain until the larvae hatch.
Reproduction
The process of maturation, as well as the development of bedbugs, occurs as an incomplete transformation - an egg appears, then a larva (goes through 5 stages), then an adult (imago) appears. It is noteworthy that the larva is also similar in appearance to the adult, but smaller in size.
Every day the female lays from 1 to 15 eggs and adapts them with her gland secretions to the surface (wallpaper, furniture, cracks).
This secretion has a very unpleasant odor, which is why places where insects gather smell so bad. This special liquid repels other types of insects from the home of bedbugs. For an egg to mature, it will take 30 days under favorable conditions, and 50 days under unfavorable conditions. Adult bedbugs range in size from 0.5 mm to 1.5 cm.
Hemiptera Water bugs
During excursions to fresh water bodies in spring, summer or autumn, you can almost always encounter aquatic predatory bugs. They can serve as excellent examples of the influence of the secondary transition to life in an aquatic environment on the organization of these animals.
On the surface of fresh water bodies, various water striders and runners from the genera Hydrometra and Limnoporus are common, perfectly adapted to gliding along the surface of the water on thin, widely spaced limbs, the paws of which are not wetted by water. These are, in fact, land bugs that never dive into water and spend the winter on land. They glide along the surface of the water, finding food here. Among water striders, a small number of species live on the surface of the oceans, often far from the shores.
Of the bugs living in water, the one that attracts the most attention is the large predatory smooth bug (Notonecta glauca). The hind limbs of the smoothie have changed into rowing legs, with the help of which it quickly swims with its back down
This is also associated with the unusual distribution of coloration for aquatic animals, which has a protective value. However, the smoothie is capable of flying, and even over quite long distances. No less dexterous swimmers are swimmers (Ilyocoris).
All aquatic hemipterans, bugs breathe atmospheric air, and their spiracles are placed at the end of their abdomen, which from time to time is slightly exposed above the surface of the water for breathing. The water scorpion (Nepa cinerea) is very interesting for its adaptations to breathing atmospheric air with the help of a long tube at the end of the abdomen and for its grasping forelimbs. It stays in shallow places among fallen leaves.
Bed bug
A bedbug (fig.) is a parasite that inhabits human homes; the presence of the bug is an indicator of the unsanitary condition of the room. The participation of bed bugs in the transmission of infections and infestations has not been proven. When sucking blood, it injects saliva, as a result of which a blister and an itching sensation appear on the skin. A bedbug can go without food for six months or longer and is resistant to low temperatures, so “freezing out” beds and other things in order to free them from bedbugs is ineffective. In the fight against bed bugs, general sanitary and hygienic measures play an important role. When moving into new houses, furniture and belongings from old apartments where there were bedbugs must first be thoroughly disinfested (see). The interior decoration of apartments must meet sanitary and technical requirements (no gaps or cracks in the plaster and wooden walls and beams, well-pasted wallpaper, etc.).
Fighting bedbugs
The fight against bedbugs should be carried out everywhere and at the same time - not only in a separate room, apartment, but also in the whole house. To combat bedbugs, chlorinated hydrocarbons are usually used - dusts and emulsions of DDT (at a rate of 2-4 g/m2), lindane (at a rate of 0.2 g/m2). Organophosphorus compounds also have a high insecticidal effect - trichlorometaphos (or trichlorvos) in a concentration of 0.2-0.4% at a rate of 0.2-0.4 g/m2, melation (or karbofos) - 5% dust at a rate of 15- 25 g/m2. Chlorophos in a concentration of 2-3% at a rate of 2-4 g/m2 is also very effective.
DDVF aerosols can be used.
When working with these drugs, it is necessary to take measures to protect workers from their toxic effects; treatment is carried out in gowns, using a respirator or closing the airways with a gauze bandage with a cotton pad. In cases where insecticides cannot be used, areas where bedbugs accumulate are treated with boiling water (cracks in the walls, beds, mattresses, etc.).
How to get rid of bedbugs in an apartment?
Domestic bugs in an apartment are an unpleasant neighborhood. The destruction of these insects is a necessity, but the choice of method usually depends on the number of blood-sucking parasites. If you have a question about how to get rid of bed bugs yourself, pay attention to effective means in the form of modern insecticides: today they are produced taking into account almost absolute safety for humans, since the toxins present in them specifically act specifically on the bedbug population. Below we describe in more detail how to deal with bedbugs at home.
- Temperature methods of fighting bedbugs (freezing and heat treatment) have their drawbacks: cold kills parasites, but the heating system may suffer, and renting a heat gun can be much more expensive than calling a pest control service.
- Collecting insects by hand or with a vacuum cleaner is a labor-intensive and ineffective method, so the best method of combating bedbugs is the use of various insecticides.
- Sprays, concentrates and powders against bedbugs work effectively, regardless of the region and time of year, and allow you to completely destroy bedbugs in an apartment, house, and even in a heavily infested room. When using any insecticide, it is important to consider that in an infected apartment building, even the most effective products will have a temporary effect. Therefore, in order to remove bedbugs, the best option would be to treat all apartments together.
Effective and proven drugs for bedbugs that can be used at home:
- Karbofos (liquid) is an effective remedy for bedbugs, has long proven itself, is affordable and easy to use. The solution of the required concentration is sprayed with a brush or spray on all surfaces, then washed off with water;
- Executioner (a liquid nerve agent) is used according to the Karbofos principle, but to treat a 1-room apartment you will need at least 20 bottles;
- Insecticide (spray) is a very effective, but toxic remedy for bedbugs, which can only be used in an empty room, and after treatment, carry out thorough cleaning and long-term ventilation;
- Combat against bedbugs (spray) is an easy-to-use, effective and safe product with the aroma of lemon and mint;
- Fufanon (ampoules and concentrate) is widely used by pest control services, is effective against house bugs and is easy to use;
- Get (microcapsule) is a new word in means of fighting parasites. A highly effective, odorless product that kills bedbugs very quickly;
- Mashenka (pencil) is an effective insecticidal chalk, an insurmountable obstacle to domestic bugs. Intensive treatment of places where insects accumulate leads to their poisoning and death;
- Pest control. If you want to destroy bedbugs forever, then calling an exterminator will give you an excellent and most reliable result. Professional equipment and modern insecticides, toxic to bedbugs and safe for humans, allow specialists to destroy insects quickly and for a long time. The best option is also considered to be the simultaneous treatment of all apartments in one entrance of an apartment building against bedbugs, since domestic bedbugs migrate quite easily from one home to another. Homeowners will only need to provide specialists with access to all corners of the rooms, move furniture away from the walls, clear the edges of carpets, and remove food, dishes and personal hygiene items. After the disinfestation procedure, the room should be thoroughly cleaned with a wet type and the house or apartment should be well ventilated.
People's attitude towards bedbugs
Most people talk about bedbugs exclusively as blood-sucking parasites of humans, despite the fact that only representatives of one low-species family (of many dozens of families and tens of thousands of species) have directly adapted to feeding on human blood. However, partly the opinion about bedbugs as pronounced bloodsuckers is justified by the fact that occasionally individual individuals of species that usually do not feed on human blood, but only suck the fluids of small animals, still attack humans. This happens not only in tropical countries, but also in central Russia. However, these cases are quite rare and are, apparently, a “mistake” of bedbugs in choosing a food item[6].
Bed bugs are agricultural pests
Among ground bugs, many can be sucking pests of agricultural crops. They deplete plants and reduce yields by feeding on the juice of their generative organs and seeds. Particularly common are the tortoiseshell bug (Eurygaster integriceps) and Aelia stink bugs, the wandering and bread horseflies (Notostira and Trigonotylus) - on cereals, the cruciferous bugs Eurydema, the alfalfa bug Adelphocoris lineolatus, the beet bugs Poeciloscytus, etc.
Beneficial bugs in agriculture
Predatory bugs, in particular bugs of the genus Orius and Nabis, destroy insects harmful to agriculture and forestry - caterpillars, aphids, beetle larvae, etc.
Bedbugs and human hygiene
- A bedbug disrupts normal sleep.
- Triatomine bugs can carry pathogens of dangerous infectious diseases, for example.
Where do bedbugs live?
Bedbugs are insects that are widespread throughout the world. Bedbugs live in Russia, Asian and European countries; their range also includes Africa, Australia and Oceania, South and North America. Some species even live in Greenland, Alaska and Chukotka (for example, the polar variety of bedbugs Nysius groenlandicus).
Bedbugs are absolutely unpretentious to their place of residence. They inhabit apartments and human houses with equal comfort, in nature they settle in bird nests, animal burrows and tree hollows, they take a liking to basements and wet cellars, they settle on the foliage of plants and even in the thickness of sand.
Photo credit: Surender Dalal
Morphology
Scanning electron microscope image of a bug of the species Cimex lectularius. Colors were added digitally, with parts of the mouthparts intended for piercing the skin highlighted in purple and red.
The bedbug has a strongly flattened body ranging from 3 to 8.4 mm in length, depending on blood saturation. Males are on average smaller than females. Color ranges from dirty yellow to dark brown. A proboscis extends from the anterior edge of the head, adapted for piercing tissue and sucking blood. The upper and lower jaws have the appearance of piercing, undivided bristles and form two channels: a wide one for receiving blood and a narrow one for secreting it into the injection site.
Thanks to the geometry and flexibility of the segmented body, the hungry bug is weakly vulnerable to mechanical methods of combating it. A well-fed bug becomes less mobile, its body acquires a more rounded shape and a color corresponding to blood (by the color of which - from scarlet to black - you can roughly determine when this individual last fed).
Let's recognize the enemy by sight
The bed bug has a round, flat body shape.
Sizes from 5 - 8 mm in length and up to 4 mm in width. Here I’ll immediately make a reservation that color and shape depend on the insect’s saturation with blood. A hungry bug has a lighter color and a rounded shape, unlike a well-fed one. It becomes dark brown, almost brown, and significantly elongates in length. In the process of evolution, nature has deprived these insects of wings, which makes them almost invulnerable to humans. Try to squash a hungry bed bug! It's not that easy! The parasite can press itself so tightly to the surface that you will need something very hard to deal with it. With well-fed bedbugs everything is much simpler. Having drunk blood, these vampires themselves often become victims of their nightly forays, leaving characteristic blood stains on the bed linen. Which indicates that there are bedbugs in the house.
Due to the fact that bed bugs do not have wings, they have clearly visible segments. Males and females are practically no different from each other, the only difference is the amount of blood consumed. Females drink more: a prerequisite for laying eggs is regular nutrition.
Bedbug eggs look like grains of rice and have a milky white hue. When the larva emerges from the egg, it resembles an adult bug, only smaller in size. It has an almost transparent body and only when it is full, a red spot appears in the middle of the abdomen - this is the larva’s stomach, filled with blood.
The maturation period from egg to adult bug takes about a month and a half. Becoming a mature individual, the larva goes through five stages of molting. After which the adult insect can reproduce itself.
Bedbugs have a number of external signs by which they can be distinguished from other insect pests:
- The difference from cockroaches is primarily in the absence of wings and in size. Cockroaches are larger than bedbugs, have a more elongated body and have two outgrowths on the back.
- It is very easy not to confuse bed bugs with ticks. The main difference between both is the number of legs. Bed bugs have 6, like all insects, and ticks have 8, like all arachnids.
- Ants are primarily distinguished by their slender, elongated bodies, something that bedbugs cannot boast of. Also, ants have a constriction in the middle of the body, but the bug does not.
Fleas and lice are quite different from bedbugs and it is almost impossible to confuse them, unless it is a bedbug larva. In general, fleas and lice are much smaller in size. It also needs to be said here that the lifestyles of both are significantly different from each other. So lice and fleas settle on the hairy parts of the body and spend the majority of their time there, including reproduction. And bedbugs prefer quiet, secluded places, making forays only at night in search of food.
Read more about the lifestyle of bed bugs in the following article.
General characteristics of a bed bug
The bedbug, also known as Cimex Lectularius, is a small insect that rarely exceeds 5-8 millimeters in length - although the female bedbug will be slightly smaller than the typical male. Its body is flattened, with small hairs on its surface. The abdomen is very segmented; if you look at pictures of a domestic bug and any other species of this insect, you can immediately see that the domestic variety has brighter and more distinct stripes on its body. In front of the body is a head, which ends in a proboscis. When saturated, the parasite increases in size and swells slightly.
The parasite feeds on blood, piercing the skin of a person or animal with a proboscis in those places where the blood vessels are closest to the surface.
Note! The “victim” of the parasite may not feel anything, because special saliva with analgesic components is secreted through one of the channels of the proboscis. .
Mouthparts and nutrition of bedbugs.
All representatives have a similar structure of the oral apparatus. The oral limbs form the alimentary canal, through which food is absorbed, and the salivary canal, through which saliva is injected. The maxillae and mandibles form a tuft running in the food canal and may have teeth or serrations at the ends. Solenophagous bugs. They apply the mouthparts to the host’s skin and anchor themselves with the jagged ends of the mandibles; moving the maxillae, they penetrate into the skin tissue and reach the blood vessel. Like lice, bedbugs depend partly for their nutrition on symbiotic bacteria. The bacteria are found in the intestinal epithelial cells of triatomine bugs; in cimicids, the bacteria are found in special two disc-shaped organs (mycetomes) in the abdomen on either side of the gonads. There is no evidence that these bacteria cause any harm to bedbugs. At the very least, mutualistic intestinal bacteria are necessary for the normal development of triatomine bugs - with artificial “disinfection” of bacteria, the bugs reach only the second or third stage of development and die.
Literature
- Vinokurov N. N., Kanyukova E. V., Golub V. B. Catalog of hemipteran insects (Heteroptera) of the Asian part of Russia. — Publisher: SIF “Nauka”, Novosibirsk, 2010, 320 p. ISBN 978-5-02-023318-8
- Vinokurov N. N., Kanyukova E. V. Hemipteran insects (Heteroptera) of Siberia. - Novosibirsk: Nauka SIF RAS, 1995. - 238 p.
- Harmful turtle. Collection, vol. 1-4, M. - L., 1947-60.
- Kanyukova E. V. Aquatic hemiptera insects (Heteroptera: Nepomorpha, Gerromopha) of the fauna of Russia and neighboring countries. — Publisher: “Dalnauka”, Vladivostok, 2006, 297 p. ISBN 5-8044-0645-0
- Kerzhner I. M. and Yachevsky T. L., Order Hemiptera (Heteroptera) - hemiptera, or bugs, in the book: Key to insects of the European part of the USSR, vol. 1, M. - L., 1964.
- Methods for collecting real hemipterans and studying local faunas, M. - L., 1957.
- True hemiptera of the European part of the USSR. Key and bibliography, M. - L., 1951
- Hemiptera, in the book: Animal World of the USSR, vol. 1-5, M. - L., 1936-58.
- Saulich A. Kh., Musolin D. L. Seasonal development of aquatic and semi-aquatic hemipteran insects (Heteroptera). - St. Petersburg University Publishing House, St. Petersburg, 2007, 205 p. ISBN 978-5-288-04332-1
- Animal Life, ed. L. A. Zenkevich, vol. 3. M., 1969.
- Bedbugs //: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional ones). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
Larvae or nymphs: which is correct?
Immature bed bugs can be called either larva or nymph. If we talk about entomology, the science that studies insects specifies that nymphs are larvae that, after emerging from the egg, have the same body structure as an adult. In other words, a nymph is a larva that is similar to an adult bedbug.
All insects can be divided into 2 groups:
- With complete transformation - nymphs are characterized by the presence of strong differences from adults in external factors - as an example, butterflies or beetles can serve, having larvae in the form of caterpillars or worms, that is, they are completely different from adult insects;
- With incomplete transformation - in this case there are no radical differences between individuals of different stages of development; among such insects are bedbugs, cockroaches, grasshoppers. Their larvae are nymphs, so in fact they can be called differently.
It is worth noting that the larva of an insect with an incomplete cycle of transformation, most often, has the same lifestyle as an adult. Their differences are only in body size, underdevelopment of the reproductive system and organs, as well as the lack of possibility of reproduction.
Bedbug nymphs are no exception here. They are able to live under the same conditions as adults and eat the same things. Therefore, we can conclude that already from birth, even when they are difficult to notice with the naked eye, they bite people and drink their blood. But their bite is not so painful in comparison with adults, but it is more correct to say this: if a lump or redness remains at the site of the bite, then the consequences will be less pronounced.
And also the bites from the larvae itch less. Some people do not feel the effects of the bites at all - instead of bumps, small reddish spots may remain on the skin. But in general, a bedbug larva is just as dangerous as an adult bedbug.
Types of flying bugs
About 40 thousand species of parasites that have wings have been recorded in the world. Some of the owners of wings either cannot fly due to the underdevelopment of this part of the body, or, over time and circumstances, lose this ability.
This subspecies includes the stick-shaped water strider, which after overwintering can no longer use its wings for their intended purpose. During the cold period, the flight muscles become deformed and dissolve. This is necessary in order to gain strength in the first days of hunting and mating after winter.
You can also observe the wings of the soldier bug. This is just a purely visual characteristic. In fact, we see the elytra, and with the help of them it is impossible to rise into the air.
Both the elytra and hind wings have shields or woodworts on their bodies. They do not fly often, so their wings are not as developed as those of many flying insects.
The bug, which is popularly called the “Harmful Turtle,” constantly uses its wings. It received this definition due to its ability to cause serious damage to agricultural crops. Moreover, several of these individuals spoil plants at once, flying from one crop to another.
Bedbugs that live in open areas can fly into apartments in the spring and summer. If warm weather persists into early fall, the likelihood of seeing the bug in question in your home increases.
The end of the season for these winged insects can be expected in November. At this time, they are intensively looking for overwintering places.
In our latitudes, flying bugs do not pose a danger to humans. But if you are planning to fly across the Pacific Ocean and visit tropical countries, be careful - the triatomine species lives there. These insects are dangerous because they transmit a terrible infection along with their feces. A person becomes infected with Chagas disease, for which there is no vaccine. More people die from the “deadly kiss” of the bloodsucker than from the bite of any other dangerous insect.
Bedbugs of the predatory species are also found in Russia, but are characterized by completely different behavior. They never attack themselves. And their bite does not have any consequences.
The most effective and useless methods against bedbugs
When pinning your hopes on certain methods of fighting bedbugs, you need to analyze how effective they will be. Chemicals work well in a neglected room that has not been renovated for a long time and has a lot of old furniture. There are also a lot of cracks, holes, torn wallpaper - possible hiding places for parasites. Traditional methods will be ineffective in this situation. You will have to use strong chemicals. Re-processing may be required.
In a room with a new, high-quality renovation, with a small infestation of bedbugs, it is quite possible to get by with aromatic oils from folk recipes. If bedbugs were accidentally brought in with things from a trip, it will be enough to wash things at high temperatures, wash the floors several times with the addition of essential oils, and spread dry grass around the apartment.
The use of kerosene, vinegar and other strong-smelling substances does not bring the desired result, and the smell from things remains for a long time. Turpentine cannot be removed from clothes; it is easier to throw them away. It is better not to use such methods against bedbugs.
It is important to constantly change anti-bed bug products because the parasites become accustomed to the substances and do not respond to them. Prevention of recurrence
Prevention of recurrence
Preventive measures will help protect the premises from the reappearance of parasites. As a preventive measure after removing bedbugs, you need to do the following:
- regularly carry out wet cleaning by adding a few drops of essential oils to the water;
- seal cracks in the apartment, glue baseboards and torn wallpaper;
- wash items at high temperature after traveling;
- iron bed linen with a hot iron on both sides, this way you can get rid of clutches of eggs;
- throw away cardboard packaging from furniture, parasites often live there.
Prevention will prevent parasite eggs from being transferred into the apartment, which will prevent re-infection.
Nutrition and reproduction
Hemiptera are found everywhere, their colonies are very extensive. However, bedbugs cannot boast of excessive fertility.
Most bedbugs lay their eggs in secluded places, but there are species that bear their offspring on themselves. The development of larvae takes place in 5 stages, the time of growth to an adult insect ranges from a couple of weeks to 2 years.
The larvae are very similar to adult bedbugs; they are distinguished by nuances of color, smaller size, shorter antennae, lack of spines and other characteristic features.
Most bugs are herbivorous, but there are predators, as well as individuals with a mixed type of diet. A significant portion of hemipterans are pests and cause great damage to agricultural crops.
Depending on the family, bugs destroy cereals (both spring and winter), cruciferous crops (cabbage, lettuce, rapeseed, mustard), and attack fruit trees.
Adult insects and larvae suck the juice from the leaves, after which they turn white, curl and fall, and the plant itself may die or stop bearing fruit.
Predatory bugs specialize in killing insects. Most families live in the wild, but some representatives prefer human habitations. There they hunt flies, midges and other insects.
A special place is occupied by bed bugs, which feed on the blood of humans and small animals (pika mice, bats, birds). Several species of this family live exclusively in human dwellings, others are found in bird nests, hollows and other shelters.
After biting, characteristic red dots remain on the skin, arranged in clusters or in the form of chains. Bedbug bites cause severe itching, pain, local swelling, and allergic reactions are possible.
rusfermer.net
Types of bedbugs
Bedbugs are divided into the following types:
- useful;
- harmful;
- harmless.
The soldier bug belongs to the last category. The insect wakes up in early spring. The peculiarities of these bugs lie in their numbers and bright colors. They feed on the sap of young vegetation, seeds and dead insects.
Another harmless bug is the alder bug. It lives on the leaves of birch or alder.
Beneficial bugs
Small ground bugs feed on eggs, larvae and small insects. These nutritional features are used in biological plant protection in greenhouses.
The bug Macrolophus nubilus is used against spider mites, aphids and whiteflies. This type is specially populated in greenhouses. During the breeding season of pests, bedbugs first eat insects of a given species, and then destroy others.
To control pests indoors, bugs from the genus Orius are used. The size of these small insects is only 2 mm. Orius breed equally well in wet and dry places. These bugs destroy thrips and spider mites, whiteflies and aphids.
Parasitic bugs
There are 2 types of bedbugs that parasitize people and animals, these include:
Types of bedbugs parasites.
- bed bug;
- kissing bug.
There are up to 100 types of bedding. The insect does not have wings, but has a good sense of smell, which helps to find blood vessels. If the pest has a choice between an adult and a child, it will bite the latter.
The kisser carries a mortal threat because it suffers from Chagas disease, which can only be cured at the initial stage.
The following species harm plants:
- the cabbage bug is an enemy of cruciferous plantings, sucking juice from the leaves;
- rapeseed - destroys radishes and radishes;
- light green shield bug - prefers berry juice and plant leaves, can feed on carrion;
- lined scale insect - loves the juice of parsley, dill and carrots;
- harmful bug - spoils wheat, barley, oats and corn;
- berry - lives on currant, raspberry, and gooseberry bushes.
The majority of bedbugs are herbivorous; pests include those that destroy agricultural crops.
Proven methods of struggle
The fight against bedbugs has its own characteristics. Firstly, bedbugs, unlike other household pests such as cockroaches and ants, have an organism that is resistant to many insecticides. Therefore, their use may give poor results. And secondly, the body of bedbugs has the ability to very quickly adapt to external environmental threats, that is, to those poisons that people use to combat insect pests.
However, bedbugs can and should, of course, be fought against.
It is important to choose the most suitable method for you. For best results, use proven control methods
For example, temperature methods, the purpose of which is to destroy bedbugs by exposing them to high or low temperatures. This includes freezing bedbugs, washing contaminated clothes in hot water, or treating bedbugs with boiling water.
The advantage of these methods is that they are absolutely harmless to humans and do not carry with them consequences that can ruin their health. But using low temperatures can cause pipes to burst, and high temperatures require expensive equipment, which not every disinfection service has.
The second method is the use of insecticides. They are used in aerosol form to completely destroy bedbugs in the area where they are located. This method is the most popular and versatile, since it is easy to use, does not require expensive equipment and allows you to fight bedbugs on your own. The disadvantage of this method is that some people are sensitive to the chemicals contained in insecticides.
Methods of repelling bedbugs using certain means are widely used in everyday life. For example, essential oils such as eucalyptus and rosemary, which have a very pleasant smell and at the same time are a good remedy for repelling bedbugs. For them, the smell of oils is quite strong and unpleasant. You can use various chemical liquids that smell less pleasant to humans, but are no less effective for preventing bedbugs, such as kerosene, ammonia and others.
hloptarakan.ru
Epidemiology and control.
One female is enough to form a new focus of invasion. Control of bed bugs - application of long-lasting insecticides to likely harborage areas. Shows resistance to some insecticides. A high level of home cleanliness helps.
Family Reduviidae (Predators).
Most reduviids are predators that feed on other insects and are called “killer bugs.” Many of them can, but usually do not, bite people. The bites are quite painful. Extraintestinal digestion. One subfamily, Triatominae, is of great medical importance because its species act as a vector for Trypanosoma cruzi. Unlike assassin bug bites, triatomine bug bites are virtually painless to the host, as would be expected for a species that needs to suck blood and remain undetected for several minutes. They are also called kissing bugs, as they often bite a sleeping person on the lips.
Morphology of predatory bugs.
Triatomine bugs are quite large, up to 34 mm in length. Usually have wings. The head is narrow, large eyes are located on the sides in the middle or far back on the head. Behind the eyes there may be two ocelli. May make a squeaking sound.
Biology of predatory bugs.
Different types of reduviids are characterized by different habitats - on the ground, trees, human habitation. Eggs ranging from several tens to thousands are laid in the usual habitats of adults. Embryonic development - 2-3 weeks. There are usually five nymphal stages. Triatomine bugs are not necessarily located near a food source. Blood sucking is necessary for egg production and normal development of the nymphal stages, but adults can lay eggs without feeding if the nymphal stages have been well fed. The entire development cycle lasts from one to two years.
Epidemiology and control.
It is likely that all species of triatomine bugs are suitable hosts for Trypanosoma cruzi, but it is clear that species differ in their susceptibility to trypanosoma and their ability to serve as vectors. The importance of a bug species depends on the degree of its connection with human habitation (synanthropy). The most common vector species: Pantostrongylus megistus (Brazil), Triatoma infestans (Argentina), T.sanguisuga, T.dimidiata, Rhodnius prolixus. Relative importance varies by area. These insects are nocturnal; during the day they hide in brushwood, cracks, and thatched or thatched roofs. Low quality buildings play an important epidemiological role. The number of triatomine bugs in a building increases with the number of people living in it, but the number of bedbugs can be reduced by reducing the number of places of refuge - improving the design of the home, or tidying up the immediate environment. An important factor is the reduction of other sources of food for bedbugs - dogs, birds, rats. Use long-lasting insecticides around potential refuge sites. Painting with compounds containing insecticides (especially in wooden buildings). The diet of bedbugs greatly influences their resistance to insecticides - starving nymphs were 200 times more resistant than well-fed ones.
Lifestyle
Bed bugs and their clutches
A parasitic lifestyle and feeding on blood is characteristic of both sexes of the imago, as well as the larval stage[2][3][4]. Leads a nocturnal lifestyle, and during the day hides in the cracks of walls, under wallpaper, in the grooves of furniture, books, clothes, beds, electronics, in dark and warm places, in the cages of birds and animals, however, in case of severe hunger, it can attack during the day[5] . Bedbugs don't have a nest like ants, but they tend to cluster in safe places near a food source. Such places can be visually identified by dark spots of insect excrement, along with which their eggs and larval skins can be found. Bedbugs take root equally well in almost any room, regardless of its sanitary condition. In the dark, bedbugs come out of their shelter and attack a person (suck blood on open areas of the body), usually at 3-8 o'clock in the morning. Bedbugs feed exclusively on blood[6].
The average lifespan of bedbugs is one year, the maximum is up to 14 months[7]. In the absence of food, bedbugs can enter a state similar to suspended animation, in which, at sufficiently low ambient temperatures, they remain viable for more than one year.[8] In unfavorable conditions, bedbugs are able to migrate between rooms through ventilation ducts, and in the summer - along the outer walls of houses[9]. An adult bug travels over 1 m in one minute[9], a nymph - up to 25 cm.
Bedbugs have a well-developed sense of smell and drink blood at all phases of development. To move to the next instar, the larva must drink a full portion of blood, only after which another moult can occur[7]. The first instar larva drinks about 1/3 mg of blood during one blood sucking; subsequent instars are correspondingly larger; an adult female drinks up to 7 mg[7]. Usually feeds regularly every 5-10 days, mainly on human blood, but can also attack domestic animals, birds, rats and mice. In rural areas, they often crawl from infected poultry houses into houses.
Bedbugs are able to survive in a limited temperature range. Adult bedbugs do not tolerate sudden drops or increases in ambient temperature. Like the larvae, at -17°C they live only for a day; at +45°C they die after 45 minutes.
How long can bedbugs live without bleeding?
In general, we can say that bedbugs live for a long time without food. One or two months of hunger strikes are practically harmless for them and do not even require falling into torpor or any inhibition of physiological processes.
If there is no food source near the blood-sucking bug for too long, then it can fall into a state similar to suspended animation, in which the biochemical processes in its body are greatly slowed down. An insect can spend up to a year in this kind of hibernation, remaining alive.
There are known cases where apartment residents wrapped bedbug-infested mattresses with plastic wrap in the hope that the parasites would have nothing to eat and would die without blood in a couple of months. However, even after keeping the mattress wrapped in film for six months, the bedbugs were still alive in it.
It is useful to consider the following nuances:
- adult bedbugs live longer without food than larvae;
- without receiving fresh blood, the female cannot lay another batch of eggs, so the reproduction of parasites practically stops;
- Without receiving blood, the larva is not able to molt, and its development slows down sharply.
Even if several dozen bedbugs live in a house, a person may not pay attention to their bites for a long time. Often, parasites bite only one person in the family, practically not touching the rest of the residents.
How do house bugs reproduce?
House bugs reproduce using so-called traumatic insemination. Females have a reproductive tract that ends in a functioning ovipositor, but males cannot use this physiological opening to deposit their sperm. Instead, the male literally penetrates the female's abdomen using his subcutaneous genital organ, which introduces seed into the female's body cavity.
An interesting fact is that some male bedbugs sometimes try to mate with other males and even pierce their stomachs. This happens because sexual attraction among this type of parasite is based primarily on the size of the insect - females are always larger. Therefore, young males may covet older ones who are larger than them. It is worth noting that those males who are sexually attacked practically do not resist and are very pliable, but they could. After all, they have special glands that produce aromatic substances - pheromones, which scare away other males.
After fertilization, sperm remains viable for a long time in the female’s body, in a special area called the spermatheca. Here, the male seed is able to be stored for a long period of time, as long as the female's body temperature is optimal, and this is always while she is alive.
The female lays eggs of domestic bugs until she depletes the sperm reserves in her spermatheca. After supplies run out, several sterile eggs may be laid, which quickly dry out and the larvae of house bugs do not hatch from them. And the female is again ready to fill her spermatheca.
Like males, females are capable of producing alarm pheromones to avoid multiple matings, but they do this extremely rarely and there are a couple of reasons for this:
- Firstly, the production of pheromones is an expensive process for the female body in terms of energy expenditure. And females must take care of it to maintain normal egg production.
- The second reason that scientists consider is the possibility of repeated mating, which ensures constant renewal of the seed in the spermatheca, which improves the gene pool of the offspring. But this hypothesis is still only theoretical.
Differences between bedbugs and other household pests
As we have already said, they are often confused with other insects. To prevent this from happening, we will tell you how they differ from other parasites.
- Most often they are confused with ticks. However, if you look closely, you will notice that the legs of bedbugs are noticeably shorter than those of ticks. Moreover, there are 6 of them, not 8.
- Bedbugs are distinguished from cockroaches by the absence of wings. In addition, cockroaches move much faster.
- Confusing bedbugs with fleas is also quite difficult. Firstly, these parasites are unable to jump like fleas. Secondly, bedbugs are much larger in size.
- Sometimes pest larvae are confused with ants - they are approximately the same color. But ants have a noticeable “waist.” It is by this feature that insects are most easily distinguished.
Recognizing bed bug bites (photo below) is also quite simple. They look like tracks of red dots at a distance of 2-3 cm. The most unpleasant thing about bloodsucker bites is that, by piercing the skin, they introduce poisonous saliva into the body. The consequences are terrible: the skin swells and turns red, itches and hurts.
Why are bedbugs dangerous for humans?
Bed bugs are true hematophages, meaning they feed exclusively on human blood and nothing else.
There are many opinions that at this moment they are capable of transmitting pathogens of dangerous infectious diseases to us along with their saliva, but to date there is no evidence of this.
Although, there is still some harm from them:
- Violation of moral, aesthetic, sanitary and hygienic standards of human habitation.
- Chronic disturbance of night sleep, since a person always remembers that somewhere nearby there are terrible bloodsuckers rustling. Additionally, although bedbug saliva contains painkillers, some bedbug bites can be quite sensitive.
- The saliva of parasites contains a large amount of allergic proteins for our immune system, so the bites are characterized by severe itching the next day. This is not very pleasant, in addition, scratching often occurs in these places with possible inflammatory processes, which in turn require systematic treatment.
If our readers still have questions about the areas indicated in this article, we will be happy to answer them in the comments.//www.youtube.com/embed/sHyVS-DiivM
Beneficial bugs
Zikrona blue is an assistant for humans against the Colorado potato beetle. A representative of heteroptera with a metallic green color and black legs. Originally from England, it hunts only during the day and does not see at night. It hunts the Colorado potato beetle and its eggs, eating up to 10 pieces a day. Zhukov. It also eats leaf beetle larvae and fleas.
Arma is predatory - the insect has a length of 10 -14 mm; in addition to the Colorado potato beetle, it feeds on caterpillars, silkworms, codling moths and various types of leaf beetles.
Perillus - Perillus bioculatus - in Canada, Mexico and the USA is the main entomophage (insect, predator that eats a certain type of pest) and regulator of the Colorado potato beetle population. Eats both adults and eggs of pests.
Conclusions from Tikhon: It is impossible to list all types of bedbugs; we are accustomed to seeing them as a threat and a problem. Among them there are parasites and pests, there are helpers and simply harmless specimens that please the eye.
If you have anything to add to this article, leave your thoughts in the comments below. Perhaps you can tell us something interesting. Happiness to you and your loved ones.
What types of house bugs are there?
Many sources, when describing domestic bedbugs, begin to list several species, compare them with each other, and so on.
In fact, next to humans, in the temperate zone of our country, only one species of these parasites is able to survive - Cimex lectularius.
Other species “specialize” primarily in other animals, for example, the bat has its own bugs - Cimex pipistrelli, and birds - Oeciacus Vicarius, which do not want to have anything in common with humans, despite the contrary assurances of some online primary sources.
As for tropical regions, the choice is somewhat wider. Here, another type of insect parasitizes in human dwellings - Cimex Hemipterus, which in appearance is not much different from “ours”, but it does no less harm.
Bedbug at multiple magnification
Destruction of bedbugs
Rooks and other birds, predatory beetles, ants and spiders destroy bedbugs. But the main enemy of bedbugs is a tiny insect, the telenomus egg-eater. Telenomus lays its eggs in the eggs of the turtle, thereby destroying the bug. Their larvae develop by feeding on the contents of the turtle bug egg. A female telenomus lays up to 100 eggs.
In recent years, to destroy the bug, crops in our country have been pollinated with special means and preparations - chlorophos dust, metaphos dust and other poisons.
After the destruction of the bugs 20 days before harvesting, pollination is stopped.
Ecology
Aquatic lifestyle
Bugs from the infraorder Gerromorpha share the surface of the water with beetles from the family Gyrinidae. In order to stay on the surface of the water, representatives of the suborder have various adaptations, including specially adapted paws, a non-wettable surface of the body, as well as other adaptations that allow them to exist in this environment [5]: 21.
Aquatic lifestyle
Bedbugs are the only insects other than beetles that have adapted to living in an aquatic environment at the adult stage of development (imago). Among them are water scorpions (Nepidae), Belostomatidae (both breathe directly from the atmosphere through a siphon), Notonectidae, Pleidae, Helotrephidae, Naucoridae (Hydradephaga) breathe with the help of bubbles on the ventrum of the abdomen, and with the help of the plastron - Naucoridae and almost all Aphelocheiridae[5] :21.
Life in intertidal zones
Some bugs from the infraorder Leptopodomorpha live only in the intertidal zone, the most specialized of which is the species Aepophilus bonnairei. Representatives of this species have underdeveloped wings, reduced eyes, are not capable of flight (outwardly they resemble bedbugs, Cimicidae) and are able to withstand prolonged immersion in sea water during high tide. Underwater they breathe through the plastron - a layer of air that remains on areas of the body surface covered with short bristles: 21.
Water bugs
This species is found in almost any body of water. A small insect with very long legs and chaotic movement on the surface of the water. No matter how much you try to catch him, it is unlikely to succeed. The water strider is nimble, fast and sharp.
She manages to change direction much faster than you can follow her with your eyes. The special structure of the legs, on which there are many bristles and a fatty layer covering them, gives the water strider bug speed and lightness. It glides briskly and attacks small insects that have fallen into the water. It feeds on animal remains, small fish, mollusks, tadpoles, etc.
The water scorpion vaguely resembles a land arthropod. The bug also has front legs very similar to claws and a stinger on its abdomen, like a regular scorpion. Its element is shallow water, the insect is not able to swim. And for food it prefers small insects, frogs and tadpoles.
Features of the structure of the bug
Next, we will answer the following questions: are bedbugs insects or not, what order do bedbugs belong to, do they jump or crawl, do bedbugs have wings?
The order of hemipteran bugs got their name from the special structure of their front wings. They are heterogeneous, most of them are covered with hard chitin, while the apical part is softer, with clearly defined veins. The hind wings are transparent. There are short-winged and long-winged individuals, and one species can include both options.
Do bedbugs fly or not? Some bedbugs have wing lengths that vary depending on sex. Long-winged individuals can fly, while short-winged individuals are unable to do so. The detachment also includes representatives who have completely lost their wings. Prominent representatives of this category are bed bugs, which are absolutely not adapted to flight.
How do bedbugs move? The appearance is complemented by three pairs of legs, the length of which depends on the species. Many herbivorous individuals have strong, well-developed limbs that allow them to move quickly.
The size of bedbugs varies depending on the species. The smallest ones have a body length of no more than 1 mm, the largest ones can reach 10 cm.
The body is flattened, rounded or slightly angular, the wings are folded on the back and are almost invisible. Occasionally, rod-shaped or spherical forms are found.
The color can be dark or bright; protective coloring is practically never found.
Predatory bugs are the brightest colored, their wings can have a shiny metallic green, deep red, orange, bluish tint, and there are also variegated forms. Bed bugs are painted in deep dark tones of brown and brown.
What do bedbugs smell like? The noticeable coloring is combined with the characteristic smell of secretion, which is secreted by the mammary glands of bedbugs, located behind the first pair of legs. Entomologists believe that the fragrant secretion serves not only to repel predators, but also to attract the opposite sex, playing the role of pheromones.
The smell of bedbugs is very unpleasant for humans and animals; cimicic acid is responsible for its intensity. The mammary glands that secrete secretions are well developed in parasitic bugs. Many predatory species, as well as water bugs, lack scent glands.
Folk remedies
A reliable way is to get rid of pests using high temperature. It is necessary to treat bedbug nests using a steam generator. An ordinary household hair dryer will not work - it will not be able to maintain a high temperature for a long time. Insect nests and possible places of their stay are processed.
Folk recipes suggest using products with a pungent odor, for example, kerosene, vinegar, turpentine. When diluted, these substances are used to lubricate baseboards, bed legs, and furniture parts. But the pungent smell will be unpleasant for humans and pets, and they will have to leave the apartment for a while.
You can use aromatic oils and herbs with a more pleasant aroma for humans. Essential oils of tea tree, eucalyptus, and orange are not liked by bedbugs. Among the plants they do not like tansy and wormwood. But it should be remembered that parasites do not die from odors, but only leave the room. There is a risk that they will return after some time.
What do bed bugs look like?
As a rule, the appearance of bedbugs in an apartment is spontaneous, unpredictable and a complete surprise to the owners. No one could imagine that bedbugs could appear in their apartment, so the appearance of the first itchy bites is attributed to either mosquitoes or fleas if there are pets in the apartment. Very often, people receive information about the presence of bedbugs in an apartment from the words of dermatologists or allergists, whom they had to contact due to the increasing number of itchy pimples, reminiscent of allergic manifestations. And it turns out that this is not an allergy at all, but the most common bedbugs.
For this reason, it is very important to know what house bugs look like in order to independently determine whether they are infested, because allergists do not go door to door. . Common signs of adult bed bugs:
Common signs of adult bed bugs:
- The insects are approximately the size of an apple seed - 5-7 mm long.
- Long, flat, oval body shape, brown in color if the bug ate several hours ago. If not, the color may be lighter.
- The parasite's entire body is divided into a head with short antennae and a segmented abdomen, which can take the shape of a ball after a heavy feeding.
- Places where bedbugs are infested are characterized by an unpleasant, moldy, sweetish odor, which is associated with a secretion produced by glands on the underside of the bedbugs’ body. Mixed in here is the smell of bedbug feces, which eat nothing but blood, which, as you know, contains a large amount of organic substances.
Young individuals of bedbugs, which are called nymphs, look similar to their adult relatives, but there are still differences:
- smaller in size, body translucent or whitish-yellow in color,
- If the nymph has not recently taken a portion of blood, it may not be visible to the naked eye at all due to its color and size.
There are a few things you should know about parasite eggs:
- tiny formations, about the size of a pinhead,
- pearly white color,
- at one of the poles they have a brown dot if they are more than five days old.
Differences between bedbugs and other insects in the house
Males feed on blood, although in some insect species only females feed on blood to be able to reproduce.
Bed bugs are often confused by name with bed dust mites. Dust mites are very small and cannot bite through human skin; they live in pillows and other parts of furniture. They feed on microscopic particles of skin that fall off our bodies. It is unlikely that you will be able to see a dust mite with the naked eye, but it still causes harm: a person can develop an allergy from its waste products, which is confirmed by tests, and this is what is written in the diagnosis “dust mite allergy.”
Dust mite under a microscope
Unlike ants, bedbugs do not build nests and do not form colonies; they prefer to randomly accumulate near a food source, usually near the place where a warm-blooded living creature spends the night. Ants do not feed on human blood, but can only bite in defense.
Unlike fleas, bedbugs are larger in size and cannot jump. Traces of their vital activity are easier to detect than to understand that there are fleas in the apartment. Scars from flea bites most often appear on the legs, in contrast to marks from bedbugs, which can also cover the upper body.
Nutrition
The mouthparts are piercing-sucking type. There are predators, parasites (particularly hematophagous) and herbivorous species. Species with mixed nutrition are not uncommon. There is cannibalism.
Herbivory
Phytophagy is characteristic of most species of bedbugs and appeared at least twice during evolution from predatory ancestral forms [5]: 20.
Predation
It is found among most families, but completely specialized families of predators are predator bugs (Reduviidae) and hunter bugs (Nabidae), also swimmers (Naucoridae) and Belostomatidae. Lygaeidae feed on seeds or dead invertebrate organisms, but predation has been noted in the subfamily Geocorinae. Asopinae from the herbivorous group Pentatomidae feed on butterfly caterpillars[5]:21.
Hematophagous
Blood feeding occurs among bedbugs Cimicidae, Triatominae (many of which are carriers of Chagas disease), Cleradini (Lygaeidae), Polyctenidae (ectoparasites of bats)[5]:21.
Commensalism and inquilinism
Among the bugs there are inquilines and commensals. Species of some families live in associations with ants and anthills; such species are found in the families: ground shield insects, laceworts, Enicocephalidae, Anthocoridae, Lygaeidae. Most of these species do not prey on ants[5]:21.
All species of the family Termitaphididae live in obligate association with termites[5]:21.
There are also representatives living in the networks of spiders or other insects. Representatives of the subfamily Plokiophilinae (Plokiophilidae), the genus Ranzovius (horseflies), the genus Arachnocoris (hunting bugs) and the family of predators live in spider webs, where they feed on insects that are caught in the spider's trap. Representatives of another subfamily, Embiophilinae from the family Plokiophilidae, inhabit embial networks, where they feed on eggs, weak and dead embials:21.
How do bedbugs bite?
The bedbug's mouth is of a piercing-sucking type, looks like a segmented proboscis on the head and is adapted for sucking liquids. There are 2 channels in the bug's proboscis: one is designed to suck in blood, the second is for introducing an anesthetic into the bite.
How a bed bug bites.
The length of the proboscis is only 0.7 mm, so the parasite searches for an area of skin where blood vessels are located close to each other. For 1 bite, the insect absorbs about 1-1.5 μl of blood. After receiving the dose, the bug crawls 2-4 cm to bite again. In a young individual, the bite takes 2-3 minutes, in an adult – 15 minutes.
The bug leaves 3-5 bites on the body and during this time takes up to 7 µl of blood. This portion is enough for an insect for a week. However, it all depends on the number of parasites in the room. If the area is densely populated by these parasites, then in the morning there may be up to 500 bites on the body.
Consequences of bites
The bite has the following symptoms:
- swelling around the bite;
- severe itching;
- inflammation;
- red spots located close to each other.
A dangerous consequence of this insect bite is an allergy. There were even cases when the victim experienced anaphylactic shock. In addition, allergic reactions can cause the following consequences:
- erosion of the skin;
- severe swelling in the bite area;
- spasms in the bronchi;
- hyperemia;
- urge to feel sick;
- fainting.
In most cases, a bedbug bite is no more dangerous than a mosquito bite. These insects do not carry infections that are dangerous to humans.
Sometimes a skin rash appears. At the same time, bugs crawling on the bed can cause psychological disorders. A person is afraid to sleep, which causes his health to deteriorate, his performance to decrease, and his nervousness to increase.
In some cases, bites do not heal for a long time and begin to fester. This may be a sign that the wound has become infected when scratched.
How to treat
There is no universal remedy for bedbug bites, because the reaction of each person is unpredictable. In the best case, redness and swelling disappear within 10 hours. If an allergy occurs, it takes several days to heal. Most often, a blister appears at the site of the bite, which bursts and disappears.
Used for allergies after bed bug bites.
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms, ice and anti-itch ointment are used. Appropriate medications are taken for allergies. You can use Fenistil gel or Rescuer. Before applying the ointment, you need to disinfect the bite site.
Ways to fight
If you find signs of bedbugs in your bed, you should immediately begin fighting them. The question of how to get rid of bedbugs in a mattress arises for everyone who has encountered such a problem. In this situation, you can use the services of a pest control service and order professional treatment of the apartment, or carry out the pestering yourself, using chemicals or folk remedies.
- If the mattress is heavily infested with bedbugs, it is better to get rid of it. Since baiting a mass accumulation of insects requires very high costs. To prevent parasites from spreading throughout the house, the mattress is wrapped in plastic and taken outside in this form.
- If the mattress is slightly contaminated, the bed linen is removed, which must be washed and heat treated. Do the same with the mattress cover (if there is one).
- Using a vacuum cleaner, eggs laid by bedbugs are removed from the mattress.
- If the sofa or bed has armrests, it is better to unscrew them. This way it will be possible to more thoroughly treat the favorite habitats of bloodsuckers.
- In the winter season, when it is frosty outside, the freezing method will help rid the mattress of bedbugs (the air temperature should not be higher than -17 degrees).
- You can also treat a mattress against bedbugs using a steam generator (high temperature is also detrimental to insects).
- Many people use kerosene to kill parasites. It is mixed with water in a ratio of 2:1, after which laundry soap is added to the resulting mixture and mixed thoroughly. It is better to treat surfaces and hard-to-reach places with the resulting solution using a spray bottle. After a week, the treatment process should be repeated.
- You can also get rid of bloodsuckers using turpentine, phenol and salicylic acid. They are taken in a ratio of 40:20:3, respectively. Processing is carried out in a similar way.
- If there is no result when using the methods described above, you should use effective chemicals to treat the bed and mattress. In this case, it is necessary to pay attention to the composition of the product, since bedbugs quickly develop immunity to many insecticides. The degree of contamination, presence of odor and level of toxicity should also be taken into account. The products that are most in demand among consumers are Get, Executioner, Fufanon or Cucaracha. They have a long residual period of action, which allows you to count even on the death of larvae that hatch after treatment.
- After treatment with insecticidal preparations, the mattress is re-cleaned with a vacuum cleaner to remove dead insects.
- If a crib is infested with pests, it is recommended to replace the mattress and wash the wooden parts with hot water. After this, the structure must be treated with an antiparasitic agent. It is important that it is as safe as possible for the child’s health and does not have a specific odor. An example of this is Pyrethrum powder. If the bed is treated with a highly toxic drug, the child will be isolated from the room for several days.
Anyone can find a bedbug in their bed. In such situations, it is important not to get lost and not leave the situation to chance, but to urgently take countermeasures. Only timely treatment will give quick and effective results and help get rid of bedbugs.
Bedbugs - description
Bedbugs (lat. Heteroptera) are a suborder of arthropod insects, which belongs to the subclass winged, infraclass neoptera, order hemiptera (lat. Hemiptera). The bug is found in all countries of the world. Due to the diversity of species, the body shape and size of bedbugs are very variable: some varieties of bedbugs are very small and have a length of less than 1 mm, representatives of the largest species grow up to 10-15 cm. Females are usually larger than males.
The largest bugs in the world are giant water bugs (lat. Belostomatidae), which live in the tropics and grow up to 15 cm in length. Giants are able to eat even small salamanders, but do not pose any danger to humans.
The body shape of most species of bedbugs is adapted to their habitat conditions and can be varied:
- The flattest are parasitic types of bedbugs, acquiring a more rounded shape only after being saturated with blood.
- Representatives of the family of earthen bugs (lat. Cydnidae), as well as desert species of bugs, have spherical bodies, which, in combination with digging limbs, makes life easier for insects in the thickness of the sand.
- Certain species of bedbugs have a rod-shaped body, for example, the South American rod-shaped predator (lat. Ghilianella filiventris),
- Some bugs resemble turtles and are called harmful turtles.
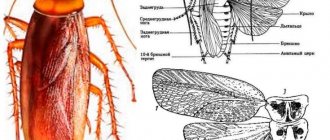
The bug is a hemiptera insect, which received its name due to the morphology of the fore wings, transformed into elytra, the main part of which is a hard chitinous shell with a membranous apical part.
The presence of front wings (elytra) and hind wings depends on the type of bug:
- Some bugs have elytra and developed wings , with the help of which they are able to travel long distances through the air (for example, long-winged female pine bedbugs);
- In other species, the elytra are shortened and the wings are absent , which is why the insects cannot fly (for example, these are the short-winged females of the pine bark bug);
- Still others have developed elytra, but no wings (for example, male pine bedbugs);
- The fourth ones elytra and wings , as, for example, in bed bugs, so they do not fly.
All bugs have 3 pairs of limbs, developed to varying degrees and used for movement, swimming and holding prey. In most bedbugs, on the metathorax, between the second and third pairs of limbs, there are open ducts of odorous glands that secrete a characteristic and unpleasant “bedbug” smell that scares off enemies and plays the role of pheromones during the mating season. Bedbugs that live in water, as well as predatory individuals, often do not have scent glands, or these glands are poorly developed.
The organs of touch are well-developed sensory antennae; some species have excellent vision.
The coloring of bedbugs comes in two types: protective or “combat”, frankly demonstrative. All parasites, as well as vulnerable species of bedbugs in which the odorous glands are reduced or poorly developed, have a protective protective coloration. Contrastingly colored bugs, with bright colors in combinations of red, black, blue, green and white, are usually herbivorous species with virtually no natural enemies.
- Weasel
- Whale shark
- 34 facts about raccoons
- Maned wolf
- Nettle
- Elk
A common feature of bedbugs is the piercing-sucking type of mouthparts. It is represented by an elongated lower lip, forming a long proboscis, inside of which there is a deep groove with modified jaws, transformed into spiny, thin and long bristles. The proboscis is divided into 2 channels: the upper and wider one is used to absorb food, the lower one is used to secrete saliva. The top of the proboscis is covered with the upper lip. The specific structure of the mouth allows the bug to easily pierce the skin of humans and animals, as well as green parts of plants, sucking blood and cell sap. In herbivorous bugs, the proboscis is thin and long; in a calm state, it is tucked under the body and hidden in a groove located on the head and chest. Predatory bugs have a short, thick and strong proboscis, beak-shaped and curved in the form of an arc.
Linen bug bites
The bites of these pests do not go unnoticed. As a rule, in the morning a whole chain of marks appears on a person’s body, since in one night a bug is capable of sucking as much blood as it weighs.
Main signs of bites:
- the appearance of red spots in the form of pimples, mainly on accessible areas of the body;
- characteristic itching;
- bites appear in the form of a chain;
- At the peak of the bite there is a puncture point in the skin.
These parasites are not distinguished by their selectivity. Both children and adults of any gender can come under attack. But due to their thin skin and special smell, children and women are more likely to become victims.
In an infected room, up to three hundred bites can appear on the torso of an adult per night.
Bite areas may itch and hurt. Many people initially confuse bites with a normal allergic reaction, however, antihistamines do not alleviate the symptoms.
After some time, an allergic reaction may appear and the bite sites begin to swell and swell, while the initial unpleasant symptoms also do not go away. It is still not entirely clear whether bedbugs carry infections; it is believed that they do not, and they do not transmit diseases such as HIV, typhoid fever and hepatitis B.
External data and characteristics of the parasite
The linen bug differs from midges and other species of its own kind by its inability to fly. Born to crawl and suck the blood of living things, it has a clearly segmented abdomen. If you look closely, it seems as if his entire miniature body is tied with shiny belts and divided into striped segments.
- Head. Has the shape of a triangle. Below there is a long proboscis, which is essentially jaws fused together. True, all this can be seen only under a microscope. The proboscis is sharp enough to pierce human skin. But it cannot pierce the skin of cattle or dogs of large and medium breeds.
- Length. The body length of a hungry insect does not exceed 3 mm. However, as it becomes saturated, the body stretches and lengthens. After gorging themselves, bed bugs reach more impressive sizes - up to 8 mm.
- Form. When hungry, bed bugs look like a flattened cake. But the insect, which has managed to feed on the blood of its victim, noticeably rounds, stretches, turning into a tiny barrel.
- Color. The shell is brown or red-brown with a brown tint. And here, too, everything depends on the satiety of the creature. A hungry bug is lighter than its well-fed counterparts, but after a meal it also takes on a deep dark shade.
The parasite's proboscis has two separate valves. One is designed to absorb blood, and the second is to introduce an analgesic, a substance that relieves pain, into a hole made in the skin, allowing the insect to strike the victim as unnoticed as possible.
Features of life
The life cycle of a bed bug is quite monotonous and lasts on average 12 months. Particularly tenacious representatives of the species live for a year and three months.
- Pairing. A female may have only one mating process in her life. The male “transplants” his seed into the chosen one in a traumatic way. In fact, he pierces her abdomen with his genitals to share genetic material. The female periodically lays eggs if she considers the surrounding conditions favorable for “children.” On average, she lays up to five hundred eggs during her life.
- Transformation of an egg into a nymph. After a week or two, the egg turns into a nymph, that is, into a larva. The next transformation will occur only when the nymph drinks a full portion of human blood. Compare: the female drinks 7 ml of “food” in one sitting, and the nymph drinks no more than 0.3 mg.
- Incubation period. Depending on conditions, the transformation of an egg into a mature individual takes from a month to 100 days.
- Period of suspended animation. Bed bugs feed on human blood. Sometimes - the blood of bats and domestic animals (those whose skin can be bitten through). If an insect remains hungry for a long time, it goes into hibernation - suspended animation. Bed bugs can live without food for up to a year. But as soon as food begins to loom on the horizon, they immediately awaken from sleep and begin to act instantly.
At a temperature of 50 °C, bed bugs die. And instantly. These creatures are more resistant to frost than to heat. For an egg to die, the air temperature in its habitat must remain at –30 °C for at least two to three days.
Differences from other insects
Due to ignorance, the bedbug can easily be confused with other insects. For example, with ants, which nymphs (parasite larvae) look like, or with fleas. Four main differences will help you get to the bottom of the truth.
- Lack of wings. If an insect has wings, it is most likely a cockroach. Or, alternatively, any other insect that has entered the house from the street.
- Inability to jump. A miniature bug that dashingly jumps from object to object is a flea. A real laundry parasite can neither jump nor fly. In his arsenal of talents there is only prosaic crawling.
- No constrictions in the abdominal area. If the insect you find has such a constriction, then it is an ant.
- The presence of six legs. Flat, round, small bugs with eight legs are mites. They are extremely dangerous, but they do not settle in human habitation and do not form nests in sofas.
Bedbugs are often confused with cockroach larvae. However, the latter have a characteristic difference - a double tail (a bifurcation in the lower part of the abdomen). Biting parasites have nothing like this.
Bedbug lifestyle
The bug leads a parasitic nocturnal lifestyle; both females and males with larvae feed on blood. The main time for an attack on a sleeping person or pet is 3-8 am. During the day, these insects hide in the mattress, under the wallpaper, behind the baseboards, in books, in clothes and beds. During the day they come out into the light extremely rarely, only in case of severe hunger. They are able to move from one room to another through ventilation systems, as well as along walls both inside and outside the apartment. The speed at which an adult bedbug travels one meter is 1 minute. Bedbugs have a well-developed sense of smell, which helps them find victims and places of shelter. For example, they can smell the clothes you wear most often, such as a dressing gown, and hide in it. An adult can drink up to 7 mg of blood at a time, and a larva can drink less than 1 mg. Parasites feed approximately once a week. If a person is not nearby, they can bite cats, dogs, rodents and even birds.
How do you know if there are bedbugs in your apartment?
First of all, the appearance of bed bugs is indicated by the symptoms of bites. You can see what they look like in the photo above. Flat scars or swollen red bumps appear on the affected area, the occurrence of which is accompanied by severe itching. Moreover, bites, as a rule, appear every night.
You can also try to examine the bedbugs in the sleeping area or conduct a complete inspection of the room. If there are minor bloody spots on the seams of the mattress, sheets, near sockets or baseboards, we can say with confidence that these marks were left by a bed bug.
In order to finally verify or refute your assumption, you should perform the following steps:
Bedbug exoskeletons appear during their molting period. They can usually be found in the places they use for shelter. If your home already has an impressive infestation of bed bugs, evidence of this fact will be their numerous skins and even carcasses. Moreover, in this case, a specific almond-shaped smell usually appears in the room. The mattress must be checked. For these purposes, it is better to use a bright flashlight, which will make it very difficult not to notice the remains of parasites.
Particular attention should be paid to the seams and tufts of the mattress. But the most effective way to finally understand whether there are bedbugs in your home is to use double-sided adhesive tape
It should be placed near the edges of the mattress, on springs and glued to the floor near the bed
After a week, you will get the result and determine whether there is actually a reason for concern.
Interesting Facts
- The house bug can carry infections such as smallpox, typhoid fever and hepatitis. An adult bedbug is the size of a grain of rice, and its eggs pass through the eye of a needle.
- The diet of a domestic bug contains only human or animal blood. A well-fed young bug can live without food for four days, and an adult for up to one and a half years.
- A bug can smell human sweat ten meters away.
- For a long time, in Europe and Russia, places where bedbugs accumulated were scalded with boiling water.
- In Africa, North America and Thailand, the water bug "belostoma", called the "fish killer", can reach 10 cm in length. Among the Thais, it is considered an exquisite delicacy.
Video
Signs of the presence of bedbugs
It is not always possible to see bedbugs due to their small size. Insects go hunting only in the morning, when their future victim is in the deepest sleep.
The following symptoms will help you understand that there are bed bugs:
- waste products - the presence of black crumbs (excrement) resembling ground pepper, as well as dry chitinous covers shed during the molting process, indicate the presence of pests; they can often be found in the seams of the mattress;
- if the mattress is saturated with a specific smell reminiscent of sour raspberries;
- blood stains on the bed left after bed bug bites;
- bites on open areas of the skin - they can appear in different places, pests especially often attack children's skin, since it is more delicate;
- yellow spots on the sheet indicate that bedbugs have settled in the bed.
How dangerous are shield bugs and how do they get into an apartment? ⛔
These bugs do not bite people. They can get into people's houses by accident, for example, in the spring, when they just crawl out of their shelters and fly into windows. Much less often, representatives of this family appear in houses on purpose.
They behave this way for various reasons, for example, if the places where stink bugs previously lived are no longer possible due to fire and widespread fire spread or flooding.
If they are near a person's home, they can enter there. Sometimes insects find house plants and begin to feed on them.
Shield bugs enter the apartment primarily through windows
What do bedbugs eat?
The diet of bedbugs depends on their species and lifestyle. So, for bed bugs it is exclusively human blood. They need it not only as a food product, but also for development and reproduction. Sucking of blood from a person occurs mainly during sleep, when the human body does not move. The bug finds its victim by the smell of carbon dioxide released during exhalation, as well as by the sweat glands. In this case, preference is given to women and children.
Having bitten through the skin, the bug injects a special painkiller, and the victim does not feel anything for ten minutes. During this time, the parasite manages to calmly drink blood and crawl away to a secluded place. In one go, a bug can drink twice its weight in blood. It is believed that its female is capable of drinking up to 10 ml at a time.
Other bugs can feed on plant juices and small insects, like soldier bugs or forest bugs. The order of bugs also includes water striders, which, in addition to small insects, can feed on fish fry. Firebugs also help cleanse nature of carrion. The bug, called the pest bug, feeds on the juices of winter wheat inputs. It can cause significant damage to grain crops.