Treatment and prevention
The most elementary and well-known since ancient times method of treating a poisonous spider bite, supported by official medicine, is cauterization. The predator's venom is sensitive to heat and is destroyed when heated, losing its toxic properties. Therefore, immediately, within 2 minutes after the attack, the damaged area must be burned with a cigarette, match or other method. The spider does not have powerful jaws, the bite depth does not exceed 0.5 mm, so immediate cauterization has a strong effect. In any case, you should contact a medical facility as soon as possible.
As special measures, anti-caracourt serum is used, which is administered intramuscularly. The serum relieves the main symptoms of poisoning, and recovery time is reduced to 3-4 days.
The disadvantage of this product is its high cost. In the absence of a special substance, the following is administered intravenously:
- novocaine;
- calcium chloride;
- magnesium hydrogen sulfate.
- 33% ethyl alcohol;
- 2-3% solution of potassium permanganate.
The victim must be given water, rubbed with alcohol, and enemas are recommended. Universal remedies can be used as painkillers: Analgin, Diphenhydramine, Ketanol.
In cases of living in the territory inhabited by karakurts, it is necessary to be careful when cleaning residential premises, especially in adobe houses, and pay attention to the presence of cobwebs in personal areas. When going outdoors, you should follow certain rules:
do not spend the night in the open air in habitats of poisonous spiders; do not come into contact with the inside of the tents; examine the place where you spend the night or rest, paying attention to holes and natural depressions in the ground, rodent burrows, and if there are any, cover them with earth; use covering clothing and wear a hat; periodically, and without fail before going to bed, carefully inspect the tent, sleeping places, clothes, shoes and other property; use the canopy, tucking it under the sleeping place; dig around the tent, making a shallow ditch; do not take off your shoes; If you find a karakurt, do not touch it; if the spider is on your clothes, shake it off or knock it down with a click.
To prevent the death of domestic animals, the soil is treated with hexachlorane and other poisons.
Attention, TODAY only!
Among all the inhabitants of the earth, spiders have an unusual, even frightening appearance, and can live in various conditions: from deserts to tropical forests.
Nature has endowed spiders with a large number of legs, with which they move quickly, the ability to weave webs, and some of them are endowed with strong poison that can even kill a person. So today we will present the 10 most poisonous spiders living on our planet, and find out where the most poisonous spider in the world lives.
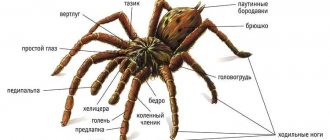
Description of the spider
Body structure
The body of side-walking spiders has two parts connected by a small tube:
The cephalothorax (prosoma) has the following features:
- divided into head and chest sections;
- on the head there are two pairs of limbs. Chelicerae are equipped with poisonous glands and a claw for their secretion. The pedipalps are formed from six segments; in males they are equipped with a mating apparatus;
- on the frontal part there are 8 eyes, 2 of which are main, the rest are additional;
- 4 pairs of limbs are attached to the cephalothorax behind the pedipalps. Side-walking spiders are able to move sideways due to the upward-turned front surfaces of the first two pairs of legs. With its movements it resembles a crab;
- The spider's leg consists of several sections: coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia calyx, pretarsus, tarsi with claw.
Abdomen (opisthosoma):
- oval shape;
- contains the spider's main internal organs;
- The genital opening is located below.
Nutrition
Side-walking spiders are predators; they are not afraid to attack even insects larger than themselves
. Spiders wait for their prey for a long time, camouflaging themselves with the terrain (flowers, soil, bark). Side-walking spiders are very mobile and when the long-awaited profit appears, they quickly grab it with their feet and inject their paralyzing venom into the body of the victim. Then, after some time, all the nutrients are sucked out of it, leaving only one shell.
Reproduction
Mating of sidewalk spiders occurs at the beginning of summer and consists of the following stages:
- Searching for a female by a male, attracting attention to himself. If the female has accepted the gentleman's advances, he climbs onto her back.
- The male moves to the female's genital opening and alternately inserts pedipalps containing seminal fluid into it.
- After a short break, the act of mating is repeated.
- The female attaches cocoons to the stems or leaves of plants, hiding them from predators.
Wolf spiders – Lycosidae
Wolf spiders are a family of araneomorph spiders that number 2,367 species. The body color is usually gray-brown. The body is covered with small short hairs. Some species reach more than 3 cm (leg span). The wolf spider lives almost everywhere except Antarctica. He prefers damp forests, meadows, hiding under fallen leaves, stones, and wood. They don't weave webs. These are earth spiders, so they live in a hole, which is only covered with cobwebs inside. If this is the private sector, you can easily stumble upon it in the basement. If there is a vegetable garden nearby, he can easily get into your cellar. Active at night. The wolf spider hunts insects or catches those who run near its burrow. This spider is a good jumper. He can jump on the victim, securing himself with a web. Mating occurs in the summer. After mating, the female lays eggs in a cocoon that she carries at the end of her abdomen. After 2-3 weeks, the spiderlings emerge from the cocoon and climb onto their mother’s abdomen. They sit like this until they learn to get their own food. The wolf spider is not dangerous to humans. Its bite is equivalent to a bee sting, which causes itching, swelling and redness, which goes away fairly quickly.
Predator's net
When hearing the word “spider,” a person immediately imagines an openwork web or dense snares. The spider weaves a web using a solidifying liquid substance found in the arachnoid glands located inside the abdomen. A sticky mass is released from arachnoid warts. The threads of the web woven by a spider are thin webs glued together from several different glands.
Spiders use webs:
- for catching prey;
- for creating a cocoon around the masonry;
- burrowing spiders line their dug-out dwellings with soft webs;
- In the autumn, young spiders use long threads from the web for migration.
What do spiders eat?
Spiders are quite original creatures that eat very interestingly. Some types of spiders may not eat for a long time - from a week to a month or even a year, but if they start, there will be little left. Interestingly, the weight of food that all spiders can eat during the year is several times greater than the weight of the entire population living on the planet today. How and what do spiders eat? Depending on the species and size, spiders forage and eat differently. Some spiders weave webs, thereby organizing clever traps that are very difficult for insects to notice. Digestive juice is injected into the caught prey, corroding it from the inside. After some time, the “hunter” draws the resulting “cocktail” into his stomach. Other spiders “spit” sticky saliva while hunting, thereby attracting prey to themselves.
a snail or an earthworm and eat them there quietly.
The queen spider hunts only at night, creating a sticky web bait for unwary moths
Noticing an insect next to the bait, the queen spinner quickly swings the thread with her paws, thereby attracting the attention of the prey. The moth happily hovers around such a bait, and having touched it, it immediately remains hanging on it.
As a result, the spider can calmly attract it to itself and enjoy its prey.
Large tropical tarantula spiders happily hunt small ones,
Haymaking spiders prefer cereal grains.
Lifestyle
Representatives of this species prefer to live in small groups of 20 individuals each. They live in fields and meadows, in forest areas, as well as in other places with dense vegetation. At the same time, they choose open areas that are well translucent and warmed by the sun's rays.
To build a web, these insects choose a large spreading plant or build it between several bushes. It takes a spider about an hour to make one trapping net, and the construction process itself always occurs at dusk. The central part of the web consists of a stabilimentum - a pair of clearly visible threads located opposite each other, which diverge from the middle.
The finished fishing net is very beautiful - it has small cells arranged in a zigzag pattern. And at its center there is always a wasp-like spider. The mistress sits on the underside of the web, spreading her long legs wide apart, and patiently waits for the next victim to fall into the trap.
Nutrition
The basis of the wasp spider's diet consists of insects, both orthoptera and others. Most often, the following networks fall into the placed networks:
- grasshoppers;
- flies;
- mosquitoes;
- butterflies;
- fillies;
The victim caught in the web begins to twitch, which attracts a hunter located nearby. The spider immediately approaches, plunges its jaws into the body of the prey and paralyzes the caught insect with poison. As soon as the prey freezes, the hunter deftly wraps it in a web, bites off the restraining threads and hides it in a secluded place.
After some time, the poison, which contains digestive enzymes, softens the victim’s body, after which the spider begins to eat.
Reproduction
The female becomes sexually mature immediately after molting. She sheds her old chitinous cover and allows the male to fertilize her, after which she eats him.
A female spider with a color like a wasp lays eggs about a month after mating. She weaves several cocoons from the web and places approximately 400 eggs in each. She hangs all the cocoons near her fishing net and soon dies.
Future offspring spend the entire winter in a dense, warm cocoon. With the arrival of warmth, the young emerge from the eggs and spend some time in close proximity to the cocoon. During this period, many spiderlings die and there is only one reason for this - overpopulation of the territory, due to which there is not enough food for everyone. Thus, some packs die due to hunger, others are eaten by their own brothers.
The survivors leave their homes around August. In windy weather, they scatter around the surrounding area using their web. In the fall, the young reach sexual maturity.
How to get rid of house spiders
The first step is to remove those insects
, which serve as food for spiders, which is why first of all it is necessary to destroy cockroaches, bedbugs, flies and other unpleasant insects.
You can fight cobwebs with an ordinary broom. However, if there are a large number of arthropods
, this may indicate the presence of masonry, which can be removed using household chemicals - these creatures do not tolerate strong aromas. If possible, surfaces regularly inhabited by arthropods can be painted.
Also, if spiders begin to appear frequently, you can place containers with flavored liquids around the room. Thus, arthropods cannot tolerate the aromas of chestnut, citrus, mint, and eucalyptus. The number of spiders will sharply decrease, and after some time the unpleasant neighbors will leave your home.
However, if the spiders managed
breed, you will have to purchase special chemicals aimed at destroying them. First of all, these are products based on pyrethroids.
An excellent preventive measure would be to keep the room clean and regularly remove dust and dirt, especially in hard-to-reach places. It is not for nothing that spiders are considered indicators of cleanliness: in those rooms where a lot of them have accumulated, the conditions are far from complete sanitation.
There are more than 40 thousand species of spiders in the world. They are distributed in almost all corners of our planet. Green spider is a generalized informal name for spiders with a characteristic color. What are they? Let's find out more about this.
Reasons for appearance
The main habitat of insects is gardens, forests, orchards and trees. They build nests on plants and weave webs there.
The main reason why house spiders appear in residential areas is an abundance of suitable food. Adults are voracious, so they settle wherever there is a sufficient number of flies, cockroaches, mosquitoes and beetles.
Another factor that provokes the dispersal of creatures is suitable living conditions in terms of temperature and humidity.
Spiders love darkness, coolness and high humidity. In an apartment or house, insects settle behind radiators, on the back walls of furniture, and in the bathroom. Frequent destruction of the web forces predators to change their habitat.
More often, small animals can be seen in houses with damp foundations. Spiders do well in damp and dark rooms.
Creatures enter a person’s home through windows, doors, or the basement. People can bring an unwanted guest on clothes or with food (vegetables, fruits). If the home does not have conditions suitable for the insect, then it is unlikely to stay long.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter. We will definitely fix it, and you will get + to karma
“>
Green spider: photos, varieties
Contrary to popular belief, “eight-legged” animals are not insects. They are considered distant relatives of crabs and are grouped into a separate class of arachnids. They are distributed everywhere, even in water. Spiders do not live only in areas that are covered with ice all year round.
They have very different colors, depending on the environment. This helps to camouflage when hunting. In their arsenal there are yellow, white, brown, black and other colors. The green spider is a typical inhabitant of grass and thickets. It blends perfectly into the background and becomes invisible to prey and enemies.
The largest subspecies of jumping spiders is green. They hunt during the day and move by jumping. You can meet horses in the tropics of New Guinea and Western Australia. One of the species of garden orb-weavers, as well as some crab spiders, have a similar color. The latter move sideways, which is why they are called “side walkers.”
Steps
Recognizing Poisonous Spiders
Determine if it's crawling on your arm.
When it comes to spider identification, the first thing to rule out is the brown recluse spider. It is the most dangerous spider in the United States and is most common in the Southeast and Midwest. A brown recluse bite can cause an infection, which may require medical attention. Here's how to tell if the spider you find is a brown recluse:
Do your research to find out the type of spider.
Memorize or write down the spider's appearance, and if you have time, look at the World Spider Catalog, the Online Journal of Arachnology, and other expert-compiled online sources to find the spider you're looking for and compare it with pictures of other species.
WikiHow also has useful articles about spiders. More information can be found in the articles “How to identify a garden spider”, “How to identify a barn spider”, “How to identify a redback spider”, “How to recognize a tarantula spider”.
Poisonous spiders in Russia are not such a rare phenomenon. A meeting with them can end in quite a lot of trouble, including a hospital bed and even death. The latter happens rarely and only in the case of untimely or incorrectly provided assistance.
Here, neither specialists nor ordinary people have any disagreements and there cannot be any. Karakurt is the only one of all the representatives of arthropods living in the vast expanses of our country whose bite can be fatal.
Appearance
Only females reaching a size of 15-20 mm are dangerous to humans. They have two distinctive signs that prevent karakurts from being confused with other representatives of arthropods. There are exactly 13 bright spots or dots on the upper side of the black abdomen. Naturally, there is no time to count them, but the very combination of black with bright spots should serve as a signal of danger. On the underside of the abdomen there is one equally bright spot in the shape of an hourglass.
Habitats
Karakurts are thermophilic. They live in the Southern Urals, the Caucasus and the Black Sea regions. However, recently the habitat of this spider has expanded to more northern regions of Russia, right up to the Moscow region. This is explained by global warming, but more optimistic scientists are confident that this only happens in very hot years, and not always.
Consequences of a bite
Karakurt, which has a very strong poison, unlike other spiders, is very aggressive and bites not only for the purpose of self-defense
He can attack purposefully, so you should not only tease him, but also approach him with great caution. The bite itself is very painful, and after 10-15 minutes the pain spreads throughout the person’s body and becomes almost unbearable
If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, which consists of administering a special serum, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, rapid heartbeat, fever, headache and dizziness, tremor, profuse sweating, and a feeling of heaviness in the chest may develop.
Main families in the country
The territory of our country includes a variety of climatic zones and natural conditions in which many representatives of arachnids exist. Spiders in Russia impress with their features and amazing life, they frighten with their appearance and help people. Many of them are rare and are listed in the Red Book.
Wolves
The Latin name - Licisidae, is a representative of a vast species, numbering more than two thousand species. It has a gray, brown or brown color, an average body size of 3 cm, and has a “standard” structure. The wolf spider has no blood; it is replaced by hemolymph, a nutritious fluid that circulates in the body. In case of injury, the hemolymph flowing from the wound acquires a blue tint.
Licisidae is a dangerous predator and an assistant to amateur gardeners in the fight against harmful insects. Its diet consists of flies, midges and insect larvae. Representatives of this species are very cunning; in the event of a threat that they cannot cope with, they prefer to pretend to be dead. The spider falls belly up and lies in this position until the threat passes. They are semi-venomous spiders whose bite does not cause harm to health.
Hunters
Latin name: Heteropoda, family Sparassidae. You definitely can’t call a hunter’s spider a standard one. It has an amygdala-shaped body, 2 to 4 cm long, and very long legs, the length of which can exceed the length of the body up to four times. The longest legs are the front ones. Color varies from mustard to red-brown. The hunter is active at night and hides in dry branches, hollows and tree bark during the day. The maximum lifespan is three years, during which time Heteropoda is able to molt up to 12-15 times. The molting period is easily determined visually: the paws become very dark.
Funnel
The Latin name is Agelenidae, there are more than 1000 species. The funnel spider got its name because of its special web, which it weaves in the shape of a funnel or pipe. It serves as a reliable shelter and trap for other insects. Every three to four weeks the spider changes its location and builds a new labyrinth. An adult male grows up to 2 cm, females are slightly larger. The color is mainly brown or black. Agelenidae live in grass. They can be easily distinguished from other species by their characteristic, swaying mode of movement. Spider venom is harmless to humans.
Horses
The Latin name is Salticidae, there are about 6000 species. They are quite fluffy representatives of arachnids. Males and females differ in color: the main color of the female is gray or orange, the male is black. Each individual has a characteristic pattern in the form of spots and stripes. The jumping spider is an active daytime hunter. He does not wait, but acts: when he sees potential prey, he jumps and grabs it. The web is used to construct protective nests for eggs and as insurance during a jump. Because of its ability to jump, it is called a jumper and a grasshopper. This species is absolutely harmless and does not even bite on contact.
Cibeids
The Latin name is Argeroneta aquatica - silver spider. The only species of spider that can live underwater. Their peculiarity is the construction of underwater houses - tents, the dome of which they fill with air. Special hairs on the body allow you to form an air sphere and carry it with you under water. Among the representatives of this species of arachnids, equality reigns: females do not eat males. Silverfish overwinter under thick ice, in their houses or empty shells.
Diggers
The Latin name is Atypus affinis, a family of digger spiders. It grows up to 2 mm, has a dark, “earthy” color. The mole rat got its name because of the characteristic feature of the same name. The spider breaks a hole in the ground, up to 40 cm long, covers it with cobwebs, bringing the weaving out. Thus, a tube of web is obtained, the end of which is sealed, and the spider itself is inside and awaits the victim. If the hunt is successful, the web tube breaks through and the victim is carried inside. Afterwards the hole is “patched”, and the spider again takes a wait-and-see position.
Black widows
Latin name - Latrodectus mactans - black widow. The name of this species has become a household name due to the characteristic behavior of the females. The spider lives its entire life in the same web, which it impregnates with pheromones to attract suitors. Partners do not keep you waiting. The very first male to enter the territory of a dangerous female begins to “punch” her web to remove the smell of pheromones in order to avoid competition.
If the black widow does not like the groom or is hungry at the time of the meeting, the female immediately eats the potential partner. If contact is established, then the moment of eating is postponed only until mating. The body diameter of females is 1 cm, males are half as large. The legs of a dangerous spider are five times longer than the body. The color is black, glossy, and there is a “mark” in the form of a red spot on the abdomen.
They live mainly in the south. For example, in the Astrakhan region or Krasnodar region.
The black widow is considered one of the most dangerous spiders in the world. Aggressive females helped the species earn this reputation. In case of the slightest provocation and aggression, a lightning attack and a poisonous bite follows. Black widow venom contains a powerful neurotoxin. It causes respiratory arrest, severe joint and muscle pain, and cramps. Scientists have found that the concentration of neurotoxin in black widow venom is 15 times higher than that of a rattlesnake.
If you are bitten, you should immediately go to the hospital. The issue of providing timely assistance is a matter of life and death.
Steatodes
Latin name: Steatoda grossa. The spider is characterized by sexual differences: females reach 1-1.2 mm in length, while males are half as much. The color is dark brown and black. There are oval spots on the chest, pink-red in females and white in males.
Steatodes' favorite habitats are forests and bushes; they often coexist with villagers. Their love for “tree” shelters pushes them to be close to people. The crevices of wooden private houses and fences provide excellent shelter, and garden plots are the best place for hunting.
The web of the steatode is distinguished by its horizontal arrangement and large size, which reaches 1.5 meters. A spider bite is not fatal, but can be very harmful: it causes fever and temporary paralysis. Spiders are not aggressive, but you shouldn’t irritate them too much.
Knitting spiders
Latin name: Tetragratha. Individuals are predominantly gray in color, with a brown stripe on the abdomen, and differ from their counterparts in their elongated body structure, similar to that of an ant. The knitter's thin body carries long legs that can be folded in half. The body length of an adult female varies from 7 to 12 mm, of a male – 6-8 mm. The length of the limbs exceeds the length of the body three times.
The habitat is the area near water bodies and the sea coast. The knitter's web is directed vertically and is aimed at catching flying insects: flies, mosquitoes and midges. Representatives of this genus are absolutely harmless to humans. There are known cases of mass invasion of the species, as a result of which coastal and agricultural areas were covered with webs.
Read also: New Year's festive table recipes
Orb weavers
Latin name – Araneidae. One of the largest families of arachnids, includes more than 3,000 species. The size of an adult spider reaches 8 mm, it is brown in color and has a striped pattern on its abdomen. Orb weavers are distinguished by a rounded abdomen and dark color at the end of the legs. Despite its small size, the hardworking orb weaver is capable of weaving a web with a diameter of up to two meters. The most famous representative of the species is the cross spider. The bite of such a spider causes only pain, similar to a bee sting.
Heiracanthium
One of the most poisonous spiders in Russia. The green poisonous spider is found in the middle zone of the country, living among green foliage and grass. It appears accidentally on the territory of a residential building, penetrates through open windows and doors, and is carried on clothes after visiting a forest or meadow.
Heiracanthium
Photos and description of the appearance can be seen below. The size of females reaches 15 mm, males – 10 mm. Body color is uneven. Spider with a green abdomen and orange cephalothorax. Our area is inhabited by yellow and brown cheiracantiums. The forelimbs are somewhat longer, reminiscent of crab claws. Powerful jaws and tentacles are clearly visible.
A predator with a green back skillfully hides in the grass, waiting for its prey. It feeds on insects and small spiders. When it sees a victim, it freezes for a few seconds, then rushes to attack. He immediately bites, immobilizes, and after a few minutes starts eating.
The venom of a large green spider is dangerous for insects, beetles, and rodents. In humans, a bite causes a local allergic reaction - redness, burning, pain, swelling.
In people prone to allergies, with weak immune systems, and small children, an attack by a predator ends in a deterioration in their well-being. Nausea, vomiting, headache, weakness, increased blood pressure, and difficulty breathing appear. Symptoms develop within 20 minutes and require the help of specialists. There have been no recorded cases of death from a Cheiracanthium bite.
Not every person can relate to a spider completely without emotion; most often, the fear of such an insect turns into a real phobia that cannot be overcome without psychological help.
Often, spiders can be found at home, for example, green spiders often appear in the house, usually coming from the street. Who is a green spider?
This representative of arachnids is a quite common species, and its size is rarely more than ten millimeters. However, this representative of arachnids, the green spider, can terrify anyone, especially if a person suffers from arachnophobia.
In principle, if we talk about the green spider, which most often lives in forests and which can be found exclusively on various green leaves, then it will not pose any particular danger.
You should not be afraid when you see a green spider at home; most likely, it simply wandered into a human building by mistake, since these representatives of arachnids prefer to live exclusively in forests or groves, in addition, not every climate will be acceptable for this type of spider.
In domestic conditions, the green spider will not survive because it will not be able to get food for itself. When a green spider occurs at home, you should maintain composure and simply kick it out of your home.
Micromat greenish
The green spider in Russia is found in Siberia and the Far East. Widespread in Europe. Its lifestyle resembles that of a wolf. The small green spider does not form hunting nets, lives in burrows, and prefers live hunting. The main diet is insects. Hunts during the day, sitting in the green grass.
- The size of females is 15 mm, males - 12 mm.
- The body color is green, almost light green. There are red and yellow stripes on the abdomen and cephalothorax of the male.
- The cubs are the same color, but before molting they darken and turn brown.
Where does the wasp spider (Argiope Brünnich) live?
The wasp spider is a fairly numerous species. It is widespread in the countries of North Africa, Asia Minor and Central Asia, India, China, Korea, Japan and the USA. It is also a common arachnid in Central and Southern Europe, Kazakhstan, Crimea and the Caucasus. In Russia, the spider wasp was noticed in several regions: Chelyabinsk, Saratov, Ulyanovsk, Tambov, Oryol, Lipetsk, Penza and Bryansk. Probably due to the increase in average annual air temperature, Argiope Brünnich also began to be noticed in the Tula, Ryazan regions and in the Moscow region. According to the latest data, the black and yellow wasp spider began to appear in the Kaluga region, as well as in the Novgorod region on the territory belonging to the Rdeisky Nature Reserve.
The wasp spider's favorite habitats are located in areas exposed to the sun: fields, lawns, along roadsides, forest clearings and forest edges. The black-and-yellow striped wasp spider places its hunting nets on various low vegetation, giving particular preference to xerophilous plants growing in particularly dry areas of the area.
A unique feature of all orb weavers, including the wasp spider, is their ability to move considerable distances thanks to their web threads, picked up by rising air currents. This manner of settlement has led to the fact that some southern populations often end up in northern territories.
Types of house spiders
Spiders are predators by nature. They live all over the world except Antarctica. Insects feed on other arthropods or smaller animals.
Of all the species of spiders (more than 42 thousand) only a few are able to survive in a human home.
It is difficult to notice the presence of arthropods, since they prefer to settle in secluded corners of the apartment: behind furniture, under window sills, on the ceiling. You can recognize the type of insect by its distinctive external features and the features of its web.
Haymaker
The haymaker is also called a window spider or centipede. The body size of the animal does not exceed 1 cm. House spiders differ from other types of arthropods by the presence of long legs.
The color of the insect varies from red to brown. The belly of the harvestman is slightly darker than the back. The individual weaves its web chaotically and often settles in attics, in the corners of rooms, and on windows.
During the day, the insect can be seen on the wall with its legs spread out to the sides - this is how the animal basks in the sun. The individual attacks people only if there is a threat to his life. The bite of a harvestman is not dangerous to humans, since this type of insect is not poisonous.
Female centipedes lay eggs in the fall or summer. They weave cocoons for eggs from their own web. Larvae emerge from eggs after 2-3 weeks. The larvae resemble the adult harvestman, but are lighter in color.
The pigtail lives up to 12 months.
Black house spider
The insect's usual habitat is trees. An animal can get to a person with a flow of wind through open doors and vents. Animals enter the living space by moving along the walls.
Female black house spiders are larger than males: they grow up to 3 cm (including splayed legs).
In rooms, insects hide in corners, behind furniture. In appearance, the web resembles complex, random patterns. Animals feed on other small insects: moths, cockroaches, beetles, butterflies.
Black spiders cannot actively reproduce outside their own free will. Their activity fades with the onset of winter. Wet cleaning will help you get rid of the problem in your apartment.
Hobo Spider
The house spider reveals its presence only by its web. He does not appear in bright areas of the apartment, but prefers dark corners.
Arthropods enter from the street accidentally: through open windows and doors. Hobo spiders have a brown body color and powerful long legs. There are dark stripes on the insect's legs.
Females of the species are always larger and more agile than males. The average lifespan of hobo spiders is 2 years, but in captivity they live much less.
Females are able to reproduce only in nature (once a year). In the apartment, the reproduction of arthropods stops.
Jumper
In total, there are 6 thousand species of jumping spiders. They got their name from their ability to jump. Unlike their relatives, individuals have good eyesight and catch prey not only with the help of a web.
The color of the insect has a varied range. The house spider has a flattened abdomen, a raised cephalothorax and massive legs. Animals live in trees and bushes. It gets into the house by chance, just like other spiders.
Jumpers are the few species of arthropods that do not spin webs. They hunt during the day.
Female racehorses lay eggs in large numbers. To do this, they weave a special cocoon. The adult guards its nest until the larvae are born.
White house spider
One of the most dangerous spiders living in Russia is white. House spiders live in the south of the country and are otherwise called karakurts. The insect is able to enter people's homes in the summer.
Video
Tarantula spiders for beginners. WHICH SPIDER TO GET FIRST.
Notes
- ↑Seifulina R.R., Kartsev V.M. Spiders of central Russia: Atlas-determinant. - M.: Fiton, 2011. - P. 423. - 1000 copies. — ISBN 978-5-93457-348-6.
- ↑Platnick, Norman I. Fam. Sparassidae (undefined). The World Spider Catalog, Version 12.5. New York, NY, USA: American Museum of Natural History (December 10, 2011). doi:10.5531/db.iz.0001. Retrieved April 22, 2012. Archived December 18, 2012.
- ↑A. Holl{amp}amp; W. Rüdiger. Micromatabilin, a new biliverdin conjugate in the spider, Micromata rosea [sic] (Sparassidae) (English) // Journal of Comparative Physiology B: Biochemical, Systemic, and Environmental Physiology: journal. - 1975. - Vol. 98, no. 2. - P. 189-191. — DOI:10.1007/BF00706130.
- ↑GS Oxford {amp}amp; R. G. Gillespie. Evolution and ecology of spider coloration (undefined) // Annual Review of Entomology. - 1998. - T. 43, No. 1. - P. 619-643. — DOI:10.1146/annurev.ento.43.1.619. - PMID 15012400.
- ↑Hänggi, Ambros; Stöckli, Edi; Nentwig, Wolfgang, 1995. Lebensräume Mitteleuropäischer Spinnen. Miscellanea Faunistica Helvetiae – Center suisse de cartographie de la faune, Neuchatel. ISBN 2-88414-008-5
Green lynx spider Peucetia viridans
The lynx spider gets its name because it pounces on its prey like a cat. These skilled hunters can leap distances up to 40 times their body length and often leap upward to catch flying insects. But there is an exception - the American green lynx spider. This is a patient predator that prefers to watch for prey among the grass.
The green lynx spider is found in the southern states, northern California, Central America and Venezuela. In North America, this is the largest representative of the family: the female’s body size can reach 22 mm (males are smaller and slimmer, only 12 cm long). At the end of the season, the green lynx spider tends to change its color to a paler, yellow color, which is associated with degradation of pigments. But it is known that pregnant females can change their color within 16 days to match their background. Spiders living in California are not grass-green, but yellow in color. This allows them to hide in the buckwheat fields in which they have settled there. These diurnal spiders sometimes make sounds similar to the hiss of a cobra. Adult spiders can be recognized by numerous large spines on their legs, as well as by sharp, sudden movements. They feed on a wide variety of insects: wasps and bees (they make up up to 40% of prey), dipterans (15%), beetles, etc. These spiders rarely bite humans and their venom is of low toxicity. They are very fast and have excellent vision.
In September, the female green lynx spider constructs 1 to 5 egg cocoons, each containing 25 to 600 orange eggs. The female fiercely defends her offspring, and after 2 weeks the eggs hatch into tiny spiderlings. Before they become adults, they must molt as many as 8 times.
In nature, spiders are very common; there are many thousands of species. They prefer to live in warm climates. Often these arthropods move into a person’s home as an uninvited guest or pet. What types of these creatures can most often be found in the house?
The most popular representatives
Represented by a large number of representatives. Each spider is endowed with certain capabilities and is perfectly adapted to life in its region. Due to the fact that climate change has been observed over the past decade, the geography of arthropod habitats is changing. Species that previously occupied only certain regions migrate and colonize new territories.
Jumping spider
The jumping spider is found throughout Russia and is considered one of the best helpers for gardeners. Its advantage is the inability to bite through the human body. You can keep such a spider on your site to combat garden pests. It is enough to catch several individuals and plant them in a garden bed or under a tree. The horse will not be confused - it will immediately begin to spin a web and settle in a new place.
Pisaurid
They live in Siberia and the Far East. This species is predominantly characterized by gift-giving during the courtship period. The male, when preparing to meet his beloved, carefully packs the caught flies or midges into a cobweb cocoon. This offering reduces the chance of being eaten and increases the chance of mating.
Crosses
Crossweeds are one of the most common species of the orb weaver family. They live throughout the Russian Federation, make a great contribution to the fight against harmful insects and easily adapt to a new place of residence.
Recluse spider
A tiny spider, no more than 8 mm in size, with a leg span of up to 2 cm. A distinctive feature of the cross spider is its wide legs and a striped, elongated body, with a characteristic cross-shaped pattern. Color varies from brown to dark brown.
The hermit spider weaves its web randomly, as necessary. It is formed by careless and chaotic movements during the weaving process. The hermit's bite is not fatal. But its poison contains substances that strongly break down the skin, which threatens tissue necrosis (death).