Caterpillars are dangerous pests for agricultural land. Unlike the moth larva, which lives only a few days, the life cycle of the caterpillar larva is several months. During all this time, it eats a huge amount of vegetation and thereby harms the crop.
If you do not treat the plants with a special remedy for caterpillars in time, this insect will turn into a butterfly, and then lay eggs - and everything will start all over again. Therefore, gardeners and farmers strive to detect this pest as early as possible and neutralize it.
What anti-caterpillar remedies exist?
As a rule, special chemicals (insecticides) are used to control pests. They are applied to those plants where insects live. Based on their effect on the caterpillar body, insecticides are divided into contact, systemic and intestinal.
Scientists also identify another subtype of pest control agents – translaminar. These drugs penetrate the leaves, which the caterpillar then eats.
In addition, there are insect control products aimed only at a specific type of caterpillar, and there are those that fight all garden and garden pests. These are drugs with continuous and selective effects.
Chemicals are also classified according to the main active ingredient they contain. For example, those working on pyrethrins, avermictins and other substances.
If you are choosing a remedy for caterpillars, carefully study their instructions. After all, on each preparation it is indicated in detail at what phase of the plant this preparation can be used, in what area, against what types of insects, in what weather, and so on. This way you will reduce the burden on the environment, which is very important.
Fighting caterpillars in the garden and vegetable garden - how to treat plants
Adding an article to a new collection
The question of how to treat cabbage, roses, apple trees and other plants against caterpillars worries most gardeners. After all, these pests are not averse to eating not only green leaves. Caterpillars can even be found on pine and other conifers.
Almost all people love butterflies, but in our latitudes no one likes caterpillars. Meanwhile, there is a place in the world where caterpillars have earned honor and respect, and not at all for their culinary merits.
Many years ago, one Brazilian decided to move to Australia and took his favorite cactus with him - the prickly pear. The plant took root and began to reproduce, so actively that it soon took over vast areas and threatened agriculture and livestock farming. Felling, fire and chemicals could not cope with the invader. But the little butterfly succeeded. It was its caterpillars, brought from Argentina, that destroyed huge areas of prickly pear, restoring biological balance. And grateful Australians not only introduced strict quarantine on the import of plants, but also erected a monument to the little caterpillar.
But such stories, unfortunately, are very few. Most often, caterpillars damage the garden and vegetable garden, depriving us of our treasured harvest.
Contact drugs
Contact agents act on caterpillars very quickly. However, they can be used on just one part of the plant. At the same time, the effectiveness of the drug is significantly reduced if it rains: water reduces the concentration of the main active substance or simply washes it off the tree. Therefore, if it rains constantly in the summer, it is necessary to treat the plants with contact poison after each precipitation.
Intestinal poison
Intestinal agents enter the body of the caterpillar after it eats the leaf of the plant on which the drug was applied. There the poison begins to act and leads to death of the insect. Today, intestinal poison is the most effective against leaf-eating caterpillars.
System Tools
Systemic preparations are applied to flowers, trunks, leaves, and stems of plants and penetrate inside along with their juice. Due to this, massive destruction of caterpillars occurs. This method is quite effective, because its outcome is not affected by any external factors: when the poison is inside the plant, it will not be washed away by precipitation, will not be dried out by sunlight and will not be blown away by the wind.
Signs of defeat
Insect larvae are easier to control in the early stages of infestation. Regular inspection of currants for the appearance of butterflies, beetles and caterpillars on the leaves and shoots helps to notice pests in a timely manner. Warning symptoms include changes in the appearance of foliage, drying of buds and shoots, and the appearance of cobwebs. If you look closely, you can see clutches of eggs, which are usually found on the inside of currant leaves.
Signs of damage to currants by pest caterpillars:
- Leaves with through holes or completely gnawed down to the veins are the result of the activity of sawfly or moth caterpillars. Summer generations of larvae are particularly voracious.
- Damage by bud moth caterpillars is manifested by the presence of curled, limp leaves on currants with traces of black excrement.
- Currant clusters with shriveled berries entangled in cobwebs indicate infection of the bush with moth larvae. When kneading damaged berries, caterpillars are discovered.
- Leaf roller infestation is manifested by the appearance of leaves twisted with the help of a web.
- Glassworm is a pest that is difficult to detect in the early stages of infection. Insect caterpillars penetrate the stems, feeding on their pith. On a cut of a damaged shoot, dark-colored wood is clearly visible.
- Leaf, flower and stem gall midges injure various parts of the currant bush. Swellings with yellow and purple spots appear on the leaves, the buds turn pale and dry out, scratches and areas of bark peeling appear on the bark of the shoots.
When the first symptoms of pest infestation appear, measures must be taken immediately. Timely treatment of currants reduces the damage caused to the bush.
Rating of industrially produced anti-caterpillar drugs
The purpose of any poison is to destroy the pest insect. Below is a rating of drugs that cope with this task best. You need to choose them depending on the type of plants being grown.
"Intavir"
“Intavir” is a contact-intestinal insecticide. Its active ingredient is cypermethrin. The poison is suitable for garden crops, as well as indoor trees and flowers. “Intavir” dissolves in water and is available in the form of powder and tablets. 1 tablet is enough for 10 liters of water.
It is necessary to treat garden and vegetable crops with this preparation only in dry and windless weather. In addition, you should not spray trees and other plantings with this poison near rivers and lakes. It is also not recommended to spray plants while they are flowering, otherwise the bees will eat the poison and die.
“Intavir” is used when the degree of damage to plants by caterpillars is high. In other cases, it is better to use more gentle methods.
“Tanrek”
The drug for caterpillars “Tanrek” is a contact-intestinal drug and belongs to neonicotinoids. It can be used to process apple trees and currant bushes, as well as tomatoes, bell peppers and potatoes.
The product itself is available in the form of bottles and ampoules. The solution is prepared at the rate of 3 ml of product per 10 liters of water for trees, or 1 ml per 10 liters of water for other plants. The drug must be used immediately after dilution, otherwise the poison will lose its properties.
“Tanrek” can be used near bodies of water, but during the flowering period of plants it cannot be used, as it is dangerous for bees.
“Fufanon”
This poison is created on the basis of organophosphorus compounds. Previously, “Fufafon” was used everywhere. However, WHO has banned the use of this drug on food crops.
The poison is produced in ampoules and vials. This is a contact-intestinal drug that affects all types of insects, even those that can camouflage themselves well. It is diluted at the rate of 5 ml per 6 liters of water. It can also be used as a fumigation agent.
“Fufanon” can be used to treat shrubs, peppers and tomatoes. You can also spray it on trees - pear, quince, cherry and apple trees.
“Karbofos”
“Karbofos” is the most effective drug that has a strong effect on all living things. Its main active ingredient is malathion. This product is available in the form of powder, granules, tablets and emulsion.
“Karbofos” is a contact preparation that can be used to treat many fruit trees and flowers. The concentration of the poison is calculated based on the area of treatment and the type of crop.
Remember that when working with this drug it is important to exercise extreme caution, as it is very toxic!
“Iskra-M”
This product is also organophosphorus, so it is used to treat gardens, orchards and even forests. The product contains potassium fertilizer, which has a positive effect on green spaces.
“Iskra-M” is produced in the form of ampoules and diluted at the rate of 5 ml per 1 liter of water. It is better to spray plants with poison in the early morning or evening.
“Golden spark”
This drug is complex and destroys caterpillars on almost all types of plants. Its distinctive feature is that it does not lose its properties even in dry and hot weather. Therefore, the poison can be used in hot regions with arid climates.
“Spark of Gold” is not addictive to insects, so it does not need to be alternated with other means. It is available in bottles and ampoules. The poison should be diluted at the rate of 1 ml per 5 liters of water. This is enough to spray 1 hectare of land.
“Iskra-bio”
Another name for the drug is “Akarin”. It can be used 2-3 days before harvest. The dosage is indicated on the poison packaging depending on the type of crop. The product itself is universal.
“Spark Double Effect”
This drug contains two active ingredients – cypermethrin and permethrin. Like all products with this name, it contains potassium to fertilize plants.
The poison is available in the form of tablets that must be dissolved in water. 1 tablet is for 10 liters of water.
Fipronil
Fipronil-based insecticides belong to the chemical class of phenylpyrazoles. Preparative forms - water-dispersible granules (80%), emulsion concentrate (4%), and also used in the composition of gels against crawling insects.
| Examples of drugs | Aria, Monarch, Regent, Taboo Super, Fumitox, gel, etc. |
| Purpose | Fipronil is effective against plant pests from the orders Orthoptera and Coleoptera, as well as soil-dwelling pests. Today this is one of the best for controlling the number of synanthropic insects - cockroaches, ants, etc. (for example, the drug "Regent VDG") Also used in veterinary medicine against fleas and ticks. |
| Peculiarities | a) Has high long-term insecticidal toxicity. b) High toxicity to bees - hazard class 1. c) In household disinsection, due to the high toxicity of the substance for warm-blooded animals, only bait stations and gels are allowed. |
Folk remedies for caterpillars
Of course, people began to grow fruit and berry crops and fight caterpillars much earlier than scientists invented chemical preparations for them. Therefore, people have found their own methods of pest control based on improvised means.
Today, folk remedies and chemicals can be combined together to achieve high efficiency. For example, soap or washing powder is added to many preparations when they are diluted to treat plants. This way the poison attaches more easily to the surface of the leaves and stems and does not flow down. In addition, caterpillars do not become addicted to folk remedies, so they can be used regularly.
Tobacco infusion
To treat plants against caterpillars, you can use both fresh tobacco leaves and crumbled industrial tobacco products. In order to dilute this product, you need to mix 1 kg of shag or fresh tobacco with 10 liters of boiling water. Next, the solution is infused for 24 hours, then filtered and diluted by half with water.
Chamomile from the pharmacy
A kilogram of chamomile should be diluted with 10 liters of water, boil the solution and leave for half a day. After this, the poison must be filtered, diluted with water in a ratio of 1:3, and then sprayed on the necessary plants.
Common yarrow herb
To prepare the solution, you need to take 800 g of yarrow herb and pour enough water into it so that it covers all the grass. Next, all this is boiled for 30 minutes and infused for 2 days.
Onion peel
A decoction of onion peels also shows a good effect. To prepare it, 200 g of purifications are diluted in 10 liters of warm water. Next, the mass is infused for 5 days, filtered and poured into a sprayer.
Tomato tops
Tomato greens are good protection against insect pests. To prepare a product based on tomato tops, 2 kg of these tops are finely chopped and poured with 10 liters of warm water. The product is infused for 4 hours and becomes ready for use.
Celandine
Celandine is simply dried and ground into powder. Then the necessary parts of the plants are powdered with this powder and scattered on the ground nearby.
Sagebrush
One kilogram of wormwood is poured with water so that it covers the entire part of it and this mass is boiled for 15 minutes. Next, the product is mixed in 10 liters of water and sprayed from a spray bottle. This poison is effective against leaf-eating insects.
Table soda
Dilute 2 tablespoons of soda in 10 liters of water and treat the desired plantings with the resulting solution. If it is expected to rain, you can simply sprinkle the cabbage with soda, because the rainwater will dissolve it.
Soap + birch tar
Birch resin is good at repelling caterpillars. In order to prepare a product based on it, you need to mix 4 tablespoons of tar with a third of a piece of grated soap. Next, the mass is mixed in a bucket of water and applied to the trees.
We identify a pest by appearance: how to understand the species
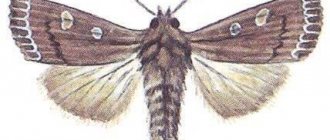
To choose the right drug or folk remedy against the caterpillar, you need to know the enemy by sight. There are a huge number of species of butterflies that lay eggs, and each caterpillar of its own species has characteristic features. For ease of understanding, we will conditionally divide pests by color.
Black
There are few species of black caterpillars that attack apple trees. The most notable and noticeable is the gypsy moth caterpillar . This is a large, hairy caterpillar about 7 cm long. The body is black with red dots and yellow longitudinal stripes. She eats foliage, flowers and ovaries.
Small black caterpillars with yellow longitudinal stripes on the body and white short hairs are the caterpillars of the hawthorn butterfly . They often weave webs. Damage to foliage is also typical - they eat only the flesh of the leaf, without affecting the veins.
Gray
Of the gray caterpillars, the most common raider on the apple tree is the ringed silkworm caterpillar . She has a bluish-gray body with narrow longitudinal stripes on her back - white in the center, then orange and black. The body is covered with short orange fluff. The activity of these pests is mainly nocturnal; during the day they sleep in spider cocoons.
Greens
Small, bright green moth caterpillars have thin white longitudinal stripes on their backs. They feed on leaves, flowers and ovaries, forming a sticky web as a waste product, which they use to twist the leaves.
Small dense green caterpillars, darker near the head section - these are leaf rollers . They also feed on all parts of the plant and roll the leaves into a tube before pupating. They easily damage young leaf buds and therefore require quick destruction.
White
White or yellowish-white, with black dots all over their bodies, dense caterpillars of the corrosive woodworm live in thin branches and bark of trees. Its presence can be determined by the large entrance on the bark and long corridors, inside of which the pests themselves can sometimes be found. They are dangerous because they are practically invisible to the eye.
Yellow
Yellow apple moth form nesting colonies. They reproduce several times per season. These are small yellowish worms that use a web to weave a nest of leaves.
Codling moth caterpillar
Codling moths are one of the most dangerous pests. They live in the soil and in the bark of a tree, and closer to fruiting they make their way inside the fruit and eat the pulp and seeds. They look like dense small caterpillars with an orange head, a dark head end and a light, almost white tail.
Apple glass caterpillar
Very small, up to 2 cm long, white worms with a bright red orange head. Only apple crops are affected. They live under the upper layer of the bark, making passages in it. The branches damaged by them quickly die, and black voids are found inside such branches.
We select the poison against caterpillars correctly
Before you start fighting caterpillars, you must first select the right drug for treatment. Modern agricultural enterprises are trying to create a poison that would be suitable for any conditions and crops. However, some products are designed exclusively for certain plants, terrain and weather conditions.
For open ground
All modern means can be used both in open ground and in greenhouses. But it is better to use products that do not depend in any way on weather conditions.
For garden crops
The drug for caterpillars on fruit trees is selected depending on the type of insect. However, the product can only be applied to trees by spraying. You also need to take into account the toxicity class of the drug so that bees are not harmed during processing.
For closed ground
For greenhouses and hotbeds, those preparations that quickly evaporate or are washed away by precipitation in open areas are suitable. However, it must be remembered that the space is closed and the concentration of dangerous chemical vapors will be higher.
For prevention
To avoid the invasion of insect pests, you need to do preventive treatment in a timely manner. This is best done before the season starts and after it ends. In this case, not only visible places are sprayed with poison, but also hard-to-reach places where caterpillar larvae can overwinter.
For prevention, it is better to use traditional methods. After all, they do not harm the environment and humans themselves.
Processing times
When treating trees for caterpillars, it is necessary to take into account the life stages of insects and the drugs used. Not all chemically active substances act on the eggs and larvae of pest butterflies. Some drugs have a contact-intestinal mechanism of action, so they work exclusively through the oral apparatus.
Before sap flow begins
In the spring, even before the start of sap flow, apple trees are inspected for cobweb formations and entrance holes in the bark. All cobwebs, ovipositions and cocoons are removed and burned. Treatment for treatment or prevention is carried out before the leaf buds open. For prevention, the soil around the tree trunk is additionally treated with copper sulfate of 3% concentration.
Before flowering
When the leaf buds have hatched, but flowering has not yet begun, the second stage of processing comes. It will destroy populations of caterpillars that feed on young ovaries, buds and parts of flowers. Organophosphorus preparations (Karbofos, Fufanon) are most often used.
During flowering
During the active generative period, it is not recommended to treat apple trees, as there is a risk of harming pollinating insects. At this time, it is better to pay attention to the mechanical collection of pests, if any. If there is a need for processing, it is better to give preference not to chemicals, but to folk remedies.
After flowering
After flowering and at the moment the ovary begins to form, treatment with insecticidal preparations is allowed. Most often, this is the last opportunity to protect the apple tree from attack by moths. Later treatment will have no effect, since the caterpillars will move into the ripening fruits.
During fruiting
During fruiting, treatment with chemically active substances is excluded, or it is carried out no later than 3 weeks before harvest. At this time, mechanical collection of caterpillars and damaged parts of the plant is used, and folk remedies are also used.
After fruiting
Prevention measures. Leaf litter from under the trees is removed and burned, as are fallen fruits, since they can carry pests that have fallen asleep until the next season. The soil around the tree trunk is carefully dug up and treated with copper sulfate. At the same time, sanitary pruning of the branches is carried out, carefully examining the sections for passages in the bark and wood. All cracks and wounds are carefully treated with garden varnish.
FYTOSPORIN
Place No. 9: FYTOSPORIN is a new generation microbiological preparation. It would be correct to say that the drug is not an insecticide. Its basis is a spore culture, whose metabolic products (produces fungicidal oligopeptides) suppress the proliferation of pathogens of fungal and bacterial plant diseases. It is a systemic drug that can spread throughout the vascular system of plants. The drug is effective against fungal and bacterial diseases on any crops. It copes well with late blight, powdery mildew, dry and wet rot of tubers and many other diseases. The advantages of the drug are that it is compatible with many chemical pesticides (Aktara, Fitoverm) and the ability to use it at any time at any stage of plant development. The manufacturer guarantees the safety of the crop even on the day of treatment with phytosporin. The drug is not phytotoxic and harmless to beneficial insects.
However, there is a drawback: Bacillus subtilis (any of its strains) die in bright sunlight, so treatments should be done in the evening or in cloudy weather. Also, do not forget that the drug is bacterial, so you should wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly. More information about the drug
BITOXIBACILLIN
Place No. 6: BITOXIBACILLIN / BICOL is an easy-to-use and safe insectoacaricide that belongs to the group of biological products. Its basis is the spore of Bacillus thuringiensis var., a pathogenic bacteria for a wide range of pests. Mainly used for the Colorado potato beetle . The main advantage is harmlessness and safety for consumers of agricultural products, low toxicity for bees, no phytotoxicity or negative impact on the environment has been identified, a long period of protective action - at least 20 days, guaranteed protection against 2-3 generations of pests. Without restrictions, we can use it in organic farming, because does not affect the activity of other biological products. There are also disadvantages in application. This is a long waiting period for a protective effect (insect pests begin to die on 2-3 days, and the complete death of active individuals occurs only within 10-14 days). Also, not compatible with fertilizers and chemical pesticides. Almost does not penetrate plant tissues, and therefore requires frequent repeated treatments. Toxic to some beneficial soil microorganisms.
More information about the drug "Bitoxibacillin"
RESPECT
Place No. 2: RESPECT is an effective insecto-fungicide. This remedy can overcome rhizoctonia and the invasion of Colorado potato beetles , as well as soil pests. The effect of the drug lasts up to 50 days. The suspension form is convenient for work, since the spraying of the drug is easy and fairly quick. Potato tubers are processed on the day of planting. It is required to measure using a Respect measuring cup at the rate of 10 ml of the drug per 10 kg of prepared tubers. Add water to the preparation at the rate of 100 ml per 10 ml. Mix and pour the solution into the sprayer. Safe for humans and bees. More information about the drug