You can get a plentiful and high-quality onion harvest in various ways. Of course, it is not enough to simply plant a crop and wait until the harvest time passes. It is necessary to feed the plant in every possible way, choosing between homemade and store-bought preparations.
If you resort to the second option, then ammonia is considered effective. A solution prepared on its basis perfectly repels pests, especially onion flies, and also contributes to the production of beautiful greens and large bulbs.
Pest control
If a pest infestation is confirmed, immediate action must be taken. The set of measures against the pest includes the following methods:
- agrotechnical measures;
- use of chemicals;
- folk remedies.
You need to act quickly, using several methods at once, only then will the fight against the onion fly be crowned with success and the harvest will be saved.
Agrotechnical control measures
In the fight against onion fly, agrotechnical measures cannot be avoided. These include the following:
dig up the beds before planting (it is better to do this in the fall); plant onions on ridges; throughout the entire growing season, it is necessary to regularly weed the beds and remove plant debris from them; you need to periodically loosen the soil; mulch the beds with peat crumbs; pay special attention to sweet varieties of onions, as they attract insects; treatment of onion plantings with wood ash; planting onions next to carrots or tomatoes.
Wood ash
Experienced gardeners advise picking onion feathers as little as possible, as the smell attracts insects.
These measures will help both get rid of onion flies on onions and get a good harvest.
Application of insecticides
Insecticidal preparations for onion flies are used when other means are ineffective. Insecticides can be in the form of granules, powder, tablets or concentrates for solution. The preparations are sprayed on plants, watered on the soil or scattered on the garden bed. The greatest demand is:
- Aktara;
- Fitoverm;
- Fly eater;
- Zemlin.
When working with all chemicals, you must be careful, wear a mask and gloves, follow the dosage and frequency of treatments specified in the instructions. When choosing what exactly to treat plants against onion flies, you should give preference to the safest product, which does not accumulate in plant tissues and in the soil and quickly decomposes
The best choice is biological products; they can also be used to get rid of onion midges at home
When choosing what exactly to treat plants against onion flies, you should give preference to the safest product, which does not accumulate in plant tissues and in the soil and quickly decomposes. The best choice is biological products; they can also be used to get rid of onion midges at home.
How to fight onion fly with folk remedies?
Many gardeners prefer to get rid of onion midges using the most natural and safe means possible, so they choose folk recipes. The most popular methods of combating midges and larvae:
- salt solution (200 g of salt per 10 liters of water);
- solution of ammonia (per 10 liters of water, 3 tablespoons of substance);
- watering the beds with herbal infusions (wormwood, mint, valerian, you can use pine infusion);
- deep pink solution of potassium permanganate.
All these liquids are used to water the beds. In addition to these methods to get rid of pests, do the following:
- a mixture of salt and soda is poured under the bulbs;
- tobacco dust is poured into the aisles;
- You can pour kerosene, turpentine or tar between the beds;
- grated laundry soap is dissolved in water, and the beds are sprayed with the solution.
Planting parsley, celery, parsnips, and marigolds in the garden will also help repel the onion fly.
Chemical "blow"
Preparations that can be purchased at garden stores fight onion flies no worse than folk remedies. Unlike the latter, the so-called “chemistry” acts faster. There are many modern chemical drugs against onion flies:
- "Aktara"
- "Karate Zeon"
- "Fly-eater"
- "Medvetox"
- "Ant"
- "Zemlin"
- "Tobacco dust"
- "Tabazol".
The listed medications must be used according to the instructions. It is also important to follow safety rules when working with chemicals. Brief description of application:
Description and life cycle
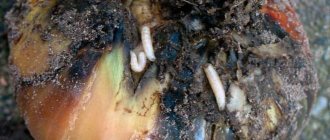
The onion fly is small in size and looks very similar to an ordinary house insect. The body of the pest reaches 6 mm, the color is most often gray with a slight faded green tint. Therefore, the pest is practically invisible on the plant. Eyes are red or burgundy.
The insect appears in the beds at the end of April, mid-May, depending on weather conditions. The female can lay up to 15 eggs at a time, from which larvae appear after 3-4 days. Externally, the larvae are white and small in size. The larvae feed on young onion shoots and can sometimes accumulate in large numbers in the bulbs. After 10-12 days they pupate and fall into the soil for several weeks. After this time, new adults appear and spread throughout the area.
Appearance and life cycle
The onion fly is an inconspicuous, small (about 7 mm) insect of ash-gray or yellow-gray color. The pest belongs to the order Diptera and is very similar to the common housefly. The wings are transparent and may have two or three longitudinal veins or without them. At the edges of the wings there is a fringe of thin long hairs.
The onion fly is a small insect (7 mm), very similar in appearance to an ordinary housefly
The female lays from 40 to 60 eggs during her life, and from 5 to 20 at a time. Their size is about 1 mm. The eggs are white and have an elongated oval shape. Embryonic development is promoted by high soil moisture (60–80%). After about a week, larvae up to 10 mm in size emerge from them, which immediately penetrate into the bulb. They are legless and white. The body tapers towards the head, which has black mouth hooks. Larvae born from the same clutch stick together and eat away a single cavity inside the bulb.
The fly lays from 5 to 20 eggs at a time, from which, after a week, larvae hatch, which eat the bulbs and feathers
After 15–20 days, the larvae leave the bulbs, crawl into the ground and pupate there, forming a false cocoon. After 2–3 weeks, young flies of the next generation emerge from the pupae. This usually happens in July. In total, two generations of onion fly develop during the season; in the southern regions, under favorable conditions, a third generation may appear. The pest overwinters in the soil of those areas where the larvae developed, at a depth of 5–20 cm in the form of false cocoons.
The onion fly overwinters in the soil at a depth of 5–20 cm in the form of a pupa (false cocoon)
What harm does the onion fly cause?
The period of appearance of the onion fly depends on climatic conditions and varies in different regions from late April to early June. The main landmark for the beginning of the mass emergence of the pest is the moment of flowering of dandelions, lilacs and cherries.
As soon as the cherry blossoms, the gardener must be on alert - the massive flight of the onion fly begins
Adult flies do not eat onions; they feed on pollen from flowering plants. Their harm lies in the fact that females actively lay eggs during the season in the soil, on protruding parts of the bulbs or between the leaves. Fly larvae cause direct harm. They attack onions of the first and second years of development. In seedlings, the larvae damage the feathers. In onions of the second year of growing season, they crawl through the axils of the leaves into the bulb or penetrate it from the bottom, suck out the juice and eat away the pulp, as a result of which the bulbs rot and the plants die.
Causes of defeat
The fight against onion flies that have already appeared can be quite difficult and not always successful. To carry out timely and correct preventive measures, it is necessary to know the reasons for the mass invasion of the pest on onion beds. Among them are:
- violation of crop rotation rules;
- incorrect placement of crops in the garden (poor choice of neighbors);
- late planting of onions;
- lack of deep autumn digging of the soil;
- use of infected and untreated seed material before planting.
Reasons for appearing in the garden
Onion flies will appear in a bed with onions that are planted in the same place as last year - there is a violation of the crop rotation order, which is the main reason for the appearance of the pest. If the soil under the onion beds has not been dug to a depth of 25 cm, then the pupae and eggs will not die, and in the spring young flies will emerge from them. You can also bring insect eggs into the garden with seed material, if you do not check its quality and do not treat the bulbs before planting them in the soil.
Fighting bulb fly
If it has been possible to confirm the connection between the painful state of the onion and the activity of the pest, you should immediately begin to fight the larvae. There are different approaches on how to deal with this scourge. Let's look at the simplest ones.
Simple remedies
The larvae die upon contact with products containing tar or ash. For example, you can take 1 tablespoon of tar, mix it with a spoon of liquid soap and dissolve it in 10 liters of water. The bulbs should be soaked in the resulting solution immediately before planting, and the plants should also be treated when signs of a pest appear. You can repeat the treatment only after two weeks, so as not to damage the onion.
Another means is based on the use of ash, which is obtained by burning wood or weeds. You need to take 200 grams of it, mix it with a teaspoon of tobacco dust and a spoonful of ground pepper. If the presence of pest larvae is suspected, the space between the rows of plantings is sprinkled with this composition. Compared to the previous method, this method can also be used as a preventive measure.
It is very simple to prepare such a remedy. Every year, a large number of weeds are collected in the garden, which, when burned, will produce good ash. You can use any dead wood or dried sunflowers. After burning, the ashes are collected and diluted in water, then the beds are watered with this mixture.
Chemicals
There are also various chemicals available to control pests. However, it is worth saying that in home gardens it is better not to use them, since many substances are dangerous not only to the health of insects and their larvae, but also to people
Therefore, they should be used only if other methods are ineffective and with great caution.
The most common representative of such a remedy is a solution of ammonia. To prepare it, add 1-3 drops of iodine, potassium permanganate, 5 ml of boric acid and 15 ml of ammonia to one bucket of water. For each onion, one mug of the resulting product is required.
An important place among chemical methods of getting rid of pest larvae is the use of insecticides. These substances are sold in the form of powders or tablets that must be dissolved in water
This solution is sprayed on diseased crops. When using them, you should strictly follow the recommendations given in the instructions for use of the drug.
In any garden there are flowering plants, for the development of which pollination plays a vital role. Therefore, the destruction of beneficial insects will damage the entire garden.
Table: drugs against onion fly
| Name | Short description |
| Fly eater | Active ingredient: diazinon. Non-toxic to plants, does not accumulate in soil. The granules are buried in the soil when preparing the bed. They retain toxic properties for up to 60 days. |
| Creolin | The emulsion is used to prepare an aqueous solution for irrigation (2 tablespoons per bucket of water). Watering the beds: for the first time - when the length of the onion feathers has reached 8-10 cm, repeated treatment - after three weeks. |
| ExtraFlor | Biological product based on plant components (tobacco extract). Non-toxic, does not accumulate in plants and soil. The protection period is 15 days. |
| Aktara | Insecticide of enteric contact action of the third class of danger. Active ingredient: thiamethoxam. Resistant to rain and ultraviolet rays. Used twice per season. Dangerous for bees and animals. |
| Fitoverm | Insecticide of enteric contact action of the third class of danger. The active ingredient is aversectin S. It paralyzes the pest after it enters its stomach. It does not affect eggs, which means it must be sprayed systematically. Treatment with a solution (5 ml per 1 liter of liquid) during the growing season. Break - 14 days. |
Disadvantages of the method
The advantages of using ammonia are undeniable, but there are also disadvantages.
It is very important to observe the concentration of the solution and the frequency of watering. If you notice that the onion leaves have darkened and become glossy, stop fertilizing with nitrogen immediately.
Also, if the concentrations are not observed, you can cause a chemical burn to the plant or burn the root system.
To prevent chemical burns from ammonia on a plant, half an hour after treating the onion with an aqueous solution of ammonia, spray it with clean water.
Using ammonia water to fertilize onion beds
In most cases, ammonia water is watered in the fall to grow onions in the spring. Moreover, for the owner of the site, such soil fertilization can be associated with a number of difficulties. Firstly, it must be applied to a depth of at least 10 cm, so it is recommended to first dig up the area and then water it with ammonium hydroxide. Secondly, you can only use ammonia. Its ammonia concentration is 10%. At higher concentrations, the vapor of this substance already seriously harms the human body.
When fertilizing in spring, ammonia water for watering onions is used in diluted form. Before treating the area with it, you should prepare a suitable solution. For a bucket of water, the volume of which is 10 liters, take no more than 2 tbsp. l. 10% ammonia. In this proportion, water and ammonium hydroxide must be diluted and thoroughly mixed together.
It is necessary to water the bed as follows: per 2 meters of the bed there is 1 bucket of the resulting solution. After this procedure, it is necessary to water the bed again, but with clean water, as a result of which the solution will be absorbed deeper into the ground and act in full force.
Use of ammonium hydroxide against pests
You can also use this substance to protect onions or garlic from pests such as onion flies. Both onions and garlic suffer greatly from this insect. But not only the onion fly does not like ammonia, its vapors are also poisonous to many other pests.
Of course, the gardener himself should not inhale these fumes. You need to use a special mask that protects your eyes and respiratory tract from exposure to ammonia. With this treatment, a solution is used in a higher concentration than when fertilizing the beds.
The following solution is prepared for spraying. Dissolve 3 tbsp in a 10 liter bucket of lukewarm water. l. classic ammonia. Then the resulting solution is sprayed onto the beds so that the moisture covers not only the leaves, but also the soil. One 10 liter bucket of water goes to 3-5 m of the bed, depending on the planting density. Treatment must be carried out only in the evening so that the moisture has time to be absorbed into the soil and into the surface of the leaves, otherwise it will evaporate and the effect of spraying will be incomplete.
Another method of treating beds from pests is watering with the same soil solution, followed by loosening. This procedure is carried out only in the evenings, and after it the beds are not immediately filled with clean water.
If ammonia is contained in the upper layers of the soil, it will become unsuitable for pests. But such treatment can be carried out no more often than once a week and only if insects are suspected.
Preventive spraying is carried out no more than once every 2 weeks. This is done in June and July. It is during these months that onion pest activity peaks.
Security Recommendations
The use of any fertilizer requires compliance with safety measures. Ammonia is a volatile gas and inhalation or contact with skin can lead to serious consequences. To prevent dangerous conditions, the following precautions should be observed:
- Before carrying out the treatment, you should wear glasses and an apron.
- The hair is covered with a headdress.
- A respirator (or gas mask) is advisable.
- The presence of other family members during the procedure should be excluded.
Fertilizing garlic and onions with ammonia: instructions
We figured out how useful it is for and, now let's figure out how to use it
How to dilute ammonia for garlic
In order to protect the crop from pests
, and sprayed with an ammonia solution, but diluted in certain proportions along with.
To prepare the composition
for spraying, grate 100 g of 72% laundry soap or any other soap, but without fragrances, on a fine grater. Pour a liter of hot water over it and stir until dissolved. The resulting solution is slowly poured into a bucket of water, stirring until the soap is completely dissolved. Now you can pour 25% product into this mixture in a volume of 50 ml. That's the whole process explaining how to dilute ammonia.
The resulting mixture should be used immediately by spraying the plants. The procedure is carried out every few days. Subsequently, after such spraying, the green part of the plants must be washed well before use.
The product is also used for fertilizer.
In this case, the dosages differ slightly depending on the purpose of the solution. So, if plants show acute signs of nitrogen starvation, pour a tablespoon of 25% product into a liter of water. This is the maximum dosage that, in principle, can be used to feed plants with ammonia.
If the leaves of the plant are not thin, rich green and even, the product can be used as a preventive measure.
To do this, it is diluted in an amount of 30 ml (2 tablespoons) per bucket of water.
Important! It is advisable to spray at sunset or in cloudy weather so that the sun does not burn the leaves after treatment.
Fertilizing onions with ammonia
The question of how to dilute ammonia is solved a little differently. But even in this case, everything depends on the purpose of using the solution. To combat a pest such as, dilute 5 ml of the product in a bucket of water and water the soil around the plant with this solution. The pungent odor that spreads will repel the insect.
Dilute 10 ml of the product in a bucket of water and water the plants with it. For a secretive proboscis, you will need 25 ml per ten liters of water. Plants are treated at the beginning of summer once a week.
Fertilizing with ammonia is carried out with a solution in the ratio of a teaspoon per liter of water. This will provide thick and juicy greens.
If you need to get large root crops,
The beds are watered with a solution prepared in the following proportions: a tablespoon of ammonia per bucket of water. This watering is done once a week, which significantly increases the crop yield.
Important! Watering with ammonia for this purpose can be done no more than once every seven days. But you need to start with solutions of low concentration, gradually increasing the dose to the recommended one.. It should be remembered that this liquid is a rather caustic substance, which, if it comes into contact with the skin, especially mucous membranes, can cause a severe burning sensation
Therefore, it should always be stored out of the reach of children and animals. In case of sudden inhalation of its vapors, a reflex cessation of breathing may occur, and if swallowed, a burn of the esophagus and mouth may occur.
It should be remembered that this liquid is a rather caustic substance, which, if it comes into contact with the skin, especially mucous membranes, can cause a severe burning sensation. Therefore, it should always be stored out of the reach of children and animals. In case of sudden inhalation of its vapors, a reflex cessation of breathing may occur, and if swallowed, a burn of the esophagus and mouth may occur.
If you plan to use ammonia, you must follow safety precautions and use personal protective equipment - a mask, gloves.
It is advisable to prepare the solution in the fresh air, or at least in well-ventilated areas. If you suffer from hypertension, it is better to avoid using this remedy as it may increase your blood pressure. Make sure that the substance is not mixed with chlorine-containing products.
As you can see, ammonia also helps to cope with nitrogen starvation of vegetable crops and ensure a large harvest
It is only important to take precautions when preparing the solution and use it in the right proportions
Was this article helpful? Not really
Useful tips
There are some nuances when growing onions and processing them with ammonia. Here they are:
- If onions are grown for feathers, they must be processed. In addition to ammonia solution, an aqueous solution with dry mustard is used.
- Some gardeners use special adhesives to keep the ammonia solution on the onion feathers. When using cat and dog flea shampoos as adhesives, you should remember that such onion feathers are not suitable for food.
- If the onion tops turn dark green, this indicates an oversaturation of ammonia. In this case, such feeding onions is not needed, and processing should be stopped.
How to get rid of onion fly?
It’s not difficult to decide what onion fly is, how to fight it, the main thing is to take care of everything on time. It is not at all necessary to buy very expensive products - there are many methods that will help cope with the scourge. It is much easier to prevent the appearance of a pest, so you should listen to the advice of experienced gardeners.
Remedies for controlling onion flies in the garden:
If you plant onions and garlic near carrots, rosemary and tomatoes, the onion fly will not touch them. Spraying
You can sprinkle with decoctions of mint, valerian or pine needles; it is important to water, feed and loosen the soil on time. Disinfect the soil before planting onions. Solutions or copper sulfate are suitable. Treat with folk remedies or chemicals.
What does an onion fly look like?
To better understand what kind of creature the onion fly is and how to fight it, you need to know how this pest “works.” Individuals from the same clutch stay in a group and eat away the pulp in the bulb, leaving a void. After a couple of weeks, the larvae burrow into the ground and turn into pupae, from which a new generation of onion flies soon emerges.
Characteristic features:
- gray-yellow color;
- length – 7-8 mm;
- on the wings there is a fringe of bristles and stripes.
Flies do not directly cause harm; their larvae do this. Large individuals are dangerous because they lay a lot of them. They hatch from eggs on days 3-5, and mature in about 8 days. Pests fly out at the end of April - beginning of May, and immediately begin to actively care for the offspring; eggs are laid on bulbous beds or dried plant scales. Over the course of her entire life, one female can lay 40-60 eggs.
Distinctive features of onion fly eggs:
- White color;
- length up to 1 mm;
- longitudinal stripe along the egg.
What does an onion look like if it is affected by an onion fly:
- onions grow slowly;
- green feathers turn yellow;
- there is a smell of rot;
- the bulbs become soft;
- cavities with larvae form inside and on the roots of the plant.
General characteristics
The onion fly is a small, ash-gray insect. It is widespread in all climatic zones suitable for growing onion crops. It cannot be found only in deserts, as well as in permafrost areas.
In one season, the onion fly can produce one or two generations of offspring, and in the southern regions - three or even four. Such fecundity leads to the fact that the pest can completely ruin the seasonal harvest of onions and garlic.
Therefore, it is important to carry out preventive actions to exclude the appearance of the parasite and begin to fight it immediately after the first signs of plant infection appear:
- yellowing and falling of feathers;
- the formation of putrefactive plaque on the feathers and the top of the bulb;
- the appearance of an unpleasant smell of rot in onion beds.
This is an insect with complete metamorphosis. Its development includes the phases of egg, larva, pupa and imago (adult). The onion fly overwinters in the larval or pupa phase in the ground. The flight of adult individuals begins with the onset of stable warm weather, approximately at the end of April - at the beginning of May.
The adult is attracted by the smell of onion crops, to which she flies to lay eggs (they are white and oblong in shape). The adult locates them in beds directly next to plants or in green shoots.
The larvae hatch in about a week and immediately burrow into the ground. They begin to bite into the bulb, making large cavities in it. Onion fly larvae are the most dangerous for garden crops because they tend to stick together and attack the plant together. The bulb begins to fade, its scales become soft, and in the future it can no longer be used for food.
Other folk remedies
| Remedy 1. Salt solution To get rid of onion flies, you can spill the plants with a saline solution:
| |
| Remedy 2. Tobacco dust To combat onion flies, you can use a solution of tobacco dust and laundry soap.
| |
| Remedy 3. Ammonia Another effective way to get rid of onion flies is to treat onions with ammonia:
| |
| Remedy 4. Dandelion tincture Another remedy that will help in the fight against onion flies is dandelion tincture:
| |
| Remedy 5. Wood ash You can treat onions against flies using a mixture of wood ash, tobacco and black pepper:
| |
| Remedy 6. Potassium permanganate solution A saturated solution of potassium permanganate is an excellent remedy against onion flies and their larvae:
|
In the arsenal of folk remedies for onion flies, ammonia takes an honorable first place! Experienced gardeners and vegetable gardeners advise: as soon as you notice signs that an onion fly has “ruined” in the garden bed, the onion should be watered at the root with water with the addition of ammonia. The proportions are:
for 10 liters of water 2-3 tablespoons of ammonia.
You can start treating with ammonia in the spring, at the very beginning of the flight of the onion fly (usually mid-May, coinciding with the beginning of dandelion flowering). You need to water 3 times, with an interval of 10 days.
By the way!
Ammonia is also useful because it reduces the acidity of the soil and improves its structure. It is known that onions and garlic do not grow well in acidic soils. In this case, ammonia will also come in handy.
- Washing powder. Scoop up 1 handful of the cheapest powder and drop it into 10 liters of water. First, thoroughly pour water or treat after rain. Scoop up the soap solution with a ladle and pour the onion under the root. (advice from the video channel “Garden Head”).
- Sawdust or peat are mixed with creolin (20:1) and mulch the soil around the onions and garlic. This will scare away the pest.
- Dandelion infusion for prevention. Recipe: 350 g of finely chopped dandelion leaves are placed in 10 liters of water and infused for a week. You can water the onions with dandelion infusion every 2 weeks. And the first treatment should be carried out in the spring, before the fly begins to fly.
Prevention
A saturated solution of potassium permanganate is used to water the beds prepared for planting onions, regardless of whether onion fly larvae and cocoons are found in the soil or not. In order to avoid the spread of the pest, the time for planting onions is chosen when the onion fly has not yet begun to fly. Onions are not afraid of return frosts and will calmly tolerate a short-term drop in temperature to -3-5°C.
The bulbs must be prepared for planting: they are treated either with chemical protection agents, or in a strong saline solution, or in potassium permanganate, or soaked in hot water. Before processing, it is necessary to inspect the bulbs and discard any damaged specimens. It is better to burn heads with traces of pest bites or signs of disease.
When choosing land for onion beds, you need to choose an area where onions have not been grown for the previous four years. Near the beds with onions, it is necessary to plant pest-repellent plants. Plots of soil for onion beds are dug up in the fall, after the onset of cold weather, so that layers of soil with larvae appear on the surface and freeze in the cold.
Ammonia for indoor flowers
Having transplanted indoor plants into a nutrient substrate, the supply of nutrients is enough for a maximum of 2 months. Beneficial substances are absorbed by plants, and some of them are washed out of the pot through drainage holes when watering. A lack of nitrogen in indoor flowers causes the leaves to lose their rich green color, young leaves turn yellow and die, and plants lose their ability to flower. Plants cannot resist diseases and pests. Indoor flowers lack nutrition and most of all they need nitrogen. If the plant does not enter a period of rest, then it requires constant feeding during growth and flowering.
A simple and effective way to save plants is to water them with a solution of ammonia, providing them with the necessary amount of nitrogen. To do this, make a solution in the following proportions (to choose from depending on the required volume of liquid):
- for 10 liters of water – 5 tbsp. l. ammonia, or
- for 5 liters of water – 1.5-2 tbsp. l. ammonia solution, or
- for 1 liter of water – 1 teaspoon or 1 dessert spoon.
Stir the working solution well and water the plant. How much water to pour depends on the volume of the pot and the age of the plant, but no more than 25 ml for a small plant and no more than 200 ml for a larger plant.
Houseplants also suffer from aphids, which are most likely carried in garden soil. To combat aphids and midges, apply a solution: add 3 tbsp to 2 liters of water. l. ammonia. Carry out treatments once every 7-10 days until the problem disappears. To treat the soil against fruit flies, treat with a solution of 1 tbsp. l of the drug per 1 l of water.
And one more important point. Before planting the plant in a new pot, do not forget to disinfect it with a hot solution of ammonia. To do this, rub 100 g of laundry soap, dissolve the shavings in 5 liters of hot water and add 60 ml of 10% ammonia solution. Stir the solution thoroughly, wash the pots with it and rinse well under running water.
In conclusion, I want to say that ammonia is not a panacea. This is just one of the options for solving some problem in the garden or vegetable garden. Still, ammonia is a toxic substance and it can be harmful if consumed in excess. Whenever possible, choose alternative methods of feeding plants and controlling pests. And I highly recommend watching this video.
I wish you good harvests!
Precautionary measures
This useful product can become hazardous to health if you do not follow the safety rules when using it:
- it is necessary to work with ammonia using rubber gloves;
- Avoid contact of the solution with the skin; to do this, wear closed clothing before working with it;
- to avoid inhaling ammonia fumes, wear a mask;
- Do not mix the solution with active substances such as chlorine;
- do not use for people with hypervascular dystonia;
- Store ammonia in a carefully closed container, out of the reach of children.
How does salt affect onion flies?
First, let's figure out what an onion fly is. This is an insect that is very easy to confuse with an ordinary fly. But onion multiplies very quickly and causes great harm to the plant. You can recognize it by its external signs:
- the size of an adult does not exceed 7 cm;
- color ash-gray or yellow-gray;
- two transparent wings, on which there are several longitudinal veins, the edges of the wings are covered with fringe.
The onion fly overwinters deep underground, where it lays its offspring. Under favorable climatic conditions, an adult can make 2–3 clutches per season, each of which will contain about 15–20 eggs. In soil with a high moisture coefficient, from 60% to 80%, the fly's offspring develop very quickly. After just 10 days, the eggs can hatch into larvae. These are worms that begin to eat the root system of plants. And after 20 days, young individuals themselves are able to lay offspring.
From this we can conclude that if you do not start fighting the onion fly in time, its population will increase with each passing day. And this will lead to the complete destruction of the crop, that is, the entire harvest is at risk.
There is one proven folk remedy that helps get rid of onion flies, and this is table salt. How do you understand that a plant needs to be treated with a saline solution? You need to carefully examine it from April to June. It is during this period that insect activity is most noticeable. If the onion is affected by a parasitic insect, the plant changes:
- the mouth and cultural development slow down;
- the green feathers and arrows of the plant wither, turn yellow and dry out before the allotted time;
- an unpleasant smell of rot appears;
- the bulb itself becomes soft and begins to rot;
- a lot of white larvae and worms form inside the bulb;
- Larvae accumulate at the root of the plant.
All this indicates that the plant is suffering from an onion fly attack. And as soon as you notice that the plant is showing at least one of the above signs, you need to immediately start fighting.
Why can a saline solution help in pest control? Everything is very simple. The fact is that salt, even in small concentrations, changes the structure and properties of the soil. The soil in which it is present is called saline, and the amount of moisture in it decreases. In such soil, the onion fly cannot survive and lay offspring.
Preventive measures
To prevent the occurrence of the pest, it is necessary to take appropriate measures in a timely manner.
Digging
Digging up the land will help get rid of the pest. Most often, insect pupae are stored in the soil; when digging in the autumn, the soil is disinfected with the help of frost.
Important. The onion fly reproduces quickly. She can lay eggs up to three times during the season.
Boarding time
Choose the right time to plant onions. All varieties of vegetables must be planted in the soil as early as possible, after it has warmed up to the required degree. Onions tolerate low temperatures well, and light frosts will be an additional method of pest control. Autumn is the right time to prepare the site for sowing, so it is necessary to remove all old leaves that may contain larvae.
High-quality planting material
The material for planting onions must be selected very carefully. You should not purchase onions from unverified places. The planting material may contain pest eggs, which, once in the soil, will begin to develop and after a few weeks will appear as a swarm of onion flies. Before planting, it is necessary to treat the seeds with a manganese solution.
Selecting a location
When planting onions, you need to pay great attention to the location of the site. The bed should be in a ventilated place with sufficient sunlight. Also, the crop planting site should not be in places with high humidity, which can lead to the appearance of diseases and pests.
Crop rotation rules
To reduce the risk of pest occurrence, it is necessary to follow the basic rules of crop rotation; onions should not be planted in one area for several years; it is necessary to regularly change crop planting sites.
Also, onions are not planted in places where crops that had the same pests as onions previously grew.
Neighborhood with carrots
Proximity to carrots can protect onions from fly infection. Carrots repel the pest and do not affect the development and yield of onions. It is recommended to alternate onion beds with carrot beds.
Proper watering
Onions need to be watered as the soil dries out; excessive moisture can provoke the formation of rot on the bulbs. Weakened plants are susceptible to pest attacks.
In order to properly water the plant, it is necessary to use watering cans to distribute the liquid evenly, and moistening is carried out until the end of June, after which it stops.